我的前一篇文章介绍了对于分配问题的Kuhn-Munkre算法,该算法其实可以看作是邻接矩阵形式的匈牙利算法,如果更抽象地看这个算法,它可以看成是一个二分图匹配算法的变体算法,具体的说,是二分图最大权重匹配算法。我打算也把二分图最大权重匹配算法也介绍下,不过最大权重匹配算法又是基于最大匹配算法设计的,所以这篇文章先介绍二分图的最大匹配算法
二分图最大匹配问题
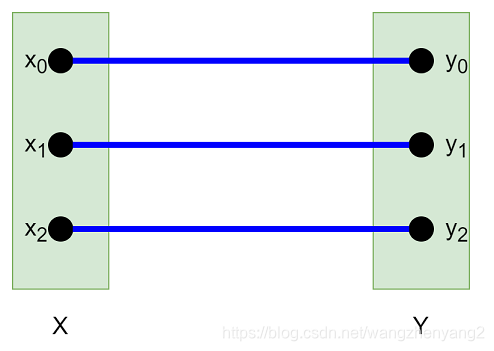
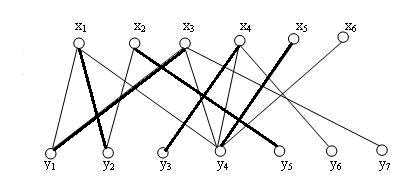
分配问题从图论的角度看其实是一个二分图(Bipartite Graph),就是说图中有两个点集,在各自的点集内的点互相没有连接,两个点集间的点可以连接,每个点存在多个允许的连接,如下图所示:

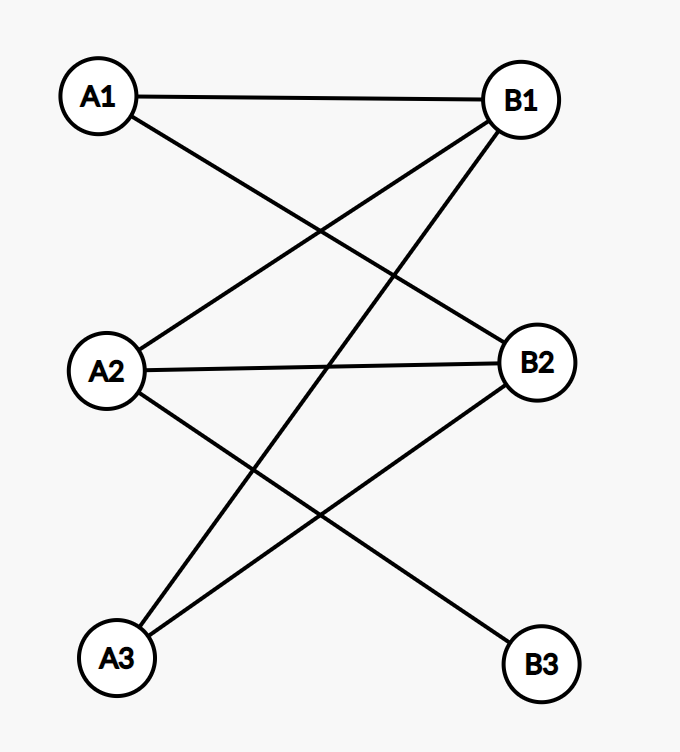
如果我们对二分图中的每个点,都确定最多只有一条连接,那么称之为该二分图的一个匹配,例如:

如果每个点都有一条线确定,即匹配的线数正好等于单个点集点数 n n n,那么称之为完美匹配,如下图:

对应于现实问题,我们当然希望尽量达到完美匹配,但是因为点的可选连线情况可能导致无论如何也达不到完美匹配,所以自然而然产生了最大匹配问题(Max-Bipartite Matching),最大可以找到多少条匹配线
用数学语言描述:
- 图 G = ( V , E ) G=(V,E) G=(V,E)是一个二分图, n = ∣ V ∣ n=|V| n=∣V∣, m = ∣ E ∣ m=|E| m=∣E∣, δ ( v ) , v ∈ V \delta(v), v\in V δ(v),v∈V表示一端连接到点 v v v的所有边, x e ∈ { 0 , 1 } x_e\in \{0,1\} xe∈{0,1}表示边 e e e是否被选中,则有最大匹配问题:
m a x ∑ e ∈ E x e s . t . ∑ e ∈ δ ( v ) ≤ 1 , ∀ v ∈ V x e ∈ { 0 , 1 } , ∀ e ∈ E \begin{aligned} max\quad& \sum_{e\in E} x_e\\ s.t.\quad& \sum_{e\in \delta(v)}\leq 1,\forall v \in V \\ & x_e\in \{0,1\},\forall e \in E \\ \end{aligned} maxs.t.e∈E∑xee∈δ(v)∑≤1,∀v∈Vxe∈{0,1},∀e∈E
算法主流程
在介绍算法前,先定义一些专用的算法术语,这些术语是算法的必备要素
- 自由顶点(free vertex):就是指当前匹配结果下没有任何连线的点
- 交替路径(alternating path): 由匹配边和非匹配边交替构成的一条路径,例如下面的图,加重的边表示已经在当前匹配中确定的边,细线表示还没确定的边

- 增广路径(augmenting path):属于交替路径,不过它的首末顶点都是自由顶点,即开头和最后的两条边必须是非匹配边,如下图所示

我们观察一下增广路径,它是一条匹配边接一条非匹配的构造,并且首末两条边都是未确定的,如果我们把这个路径"翻转"一下,把匹配边变成非匹配,非匹配变为匹配,那么可以发现,这条路径上的匹配数会多出1:

这就给了我们启发,只要我们能在当前匹配的二分图中找到一条增广路径,那么就能扩充1数量的匹配;从数学理论上看也确实如此,最大匹配算法的理论前提就是:
- 对于一个二分图,一个匹配 M M M是最大的,当且仅当图 G G G在 M M M的基础上找不到任何增广路径
自然地,我们就得到了算法的主流程:
- 初始化匹配 M M M, M = ∅ M=\empty M=∅
- 在当前匹配的基础上,在图 G G G中搜索增广路径 P P P
- 如果存在 P P P,对增广路径进行翻转更新匹配 M M M,回到步骤2
- 输出 M M M
搜索增广路径
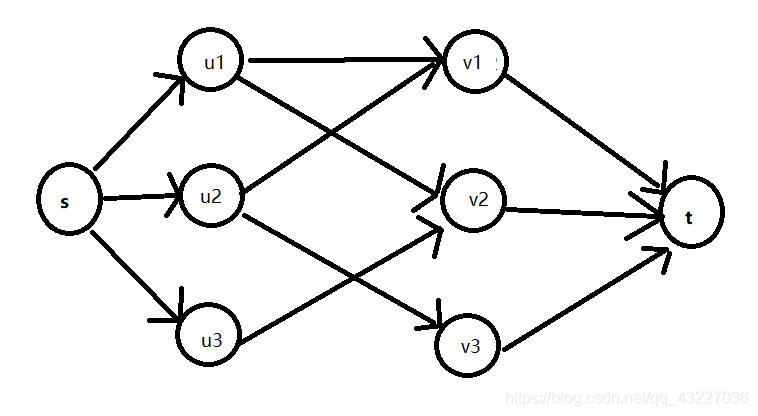
但是怎么搜索增广路径还是需要一个专门的子算法来处理;搜索过程一定是从一个自由顶点开始,到一个自由顶点结束,并且匹配边与非匹配边交替进行;这里介绍一种把匹配图转化成有向图的深度优先路径搜索算法:新增一个首节点 s s s和一个末结点 t t t,对于当前二分图中未确定的边,我们将其方向置为 X X X到 Y Y Y,对于匹配边,将方向置为 Y Y Y到 X X X;对于 X X X中未匹配的点,我们添加从 s s s到该点的边;对于 Y Y Y中未匹配的点,我们添加从该点到 t t t的边;这样二分图变成了一个有向图,我们采用深度优先遍历搜索从 s s s到 t t t的最短路径,如果能搜索到一条路径,那么去掉首末结点后就是一条增广路径
举个例子,当前二分图的匹配如下图所示:

将其转化成一个有向图:

然后我们就可以搜索到一条最短路径 s → x 0 → y 0 → x 1 → y 1 → t s\rightarrow x_0 \rightarrow y_0 \rightarrow x_1 \rightarrow y_1 \rightarrow t s→x0→y0→x1→y1→t,去掉 s s s和 t t t,就是一条增广路径
代码实现
我写了一段python代码来实现上述的算法过程。定义了MaxMatchAlgorithm类,它只需要一个边矩阵作为输入,矩阵的行列分别表示二分图的 X X X和 Y Y Y,矩阵的每个元素表示该边是否可选;maxMatch实现了算法的主流程,getAugmentingPath方法用于搜索增广路径,invert方法则用于翻转增广路径
import numpy as npclass MaxMatchAlgorithm:def __init__(self, edges):'''edges : Matrix with num_x X num_y size'''self.num_x=edges.shape[0]self.num_y=edges.shape[1]self.edges=edgesdef maxMatch(self):matches=[]iter=1while True:print("######## iteration "+str(iter)+" ##############")print("...")print("...")iter+=1augPath=self.getAugmentingPath(matches)if len(augPath)==0:breakmatches=self.invert(augPath,matches) return matchesdef invert(self, augPath, matches):for i in range(len(augPath)):if i%2==0:if augPath[i][2]:matches.append((augPath[i][0],augPath[i][1]))else:matches.append((augPath[i][1],augPath[i][0]))else:removeIndex=-1for index in range(len(matches)):if (matches[index][0]==augPath[i][0] and matches[index][1]==augPath[i][1]) or (matches[index][0]==augPath[i][1] and matches[index][1]==augPath[i][0]):removeIndex=indexbreakmatches.pop(removeIndex)return matchesdef getAugmentingPath(self,matches):#directMatrix[i,j]=1 : x_i -> y_jtotalVertexN=self.num_x+self.num_y+2directMatrix=np.zeros((totalVertexN,totalVertexN))for i in range(0,totalVertexN-1):for j in range(0,totalVertexN):if i==0 and j>=1 and j<=self.num_x:directMatrix[i,j]=1continueif j==totalVertexN-1 and i>self.num_x:directMatrix[i,j]=1continueif i==j or i==0 or j==0 or j==totalVertexN-1:continueiIsX=FalsejIsX=Falseif i>0 and i<=self.num_x:iIsX=Trueelif i>self.num_x and i<=totalVertexN-2:iIsX=Falseif j>0 and j<=self.num_x:jIsX=Trueelif j>self.num_x and j<=totalVertexN-2:jIsX=Falseif iIsX and jIsX==False:directMatrix[i,j]=self.edges[i-1,j-1-self.num_x]for (x,y) in matches:directMatrix[x+1,y+1+self.num_x]=0directMatrix[y+1+self.num_x,x+1]=1for j in range(1, self.num_x+1):isMatched=Falsefor k in range(self.num_x, totalVertexN-1):if directMatrix[k][j]==1:isMatched=Truebreakif isMatched:directMatrix[0][j]=0for i in range(self.num_x, totalVertexN-1):isMatched=Falsefor k in range(1, self.num_x+1):if directMatrix[i][k]==1:isMatched=Truebreakif isMatched:directMatrix[i][totalVertexN-1]=0shortestRoute=self.findRoute(directMatrix,[0],[])augmentingPath=[]for i in range(1,len(shortestRoute)-2):vertexIndex_A=shortestRoute[i]actualIndex_A=0vertexIsX_A=Falseif vertexIndex_A>=1 and vertexIndex_A<=self.num_x:actualIndex_A=vertexIndex_A-1vertexIsX_A=Trueelse:actualIndex_A=vertexIndex_A-1-self.num_xvertexIndex_B=shortestRoute[i+1]actualIndex_B=0vertexIsX_B=Falseif vertexIndex_B>=1 and vertexIndex_B<=self.num_x:actualIndex_B=vertexIndex_B-1vertexIsX_B=Trueelse:actualIndex_B=vertexIndex_B-1-self.num_xaugmentingPath.append((actualIndex_A,actualIndex_B,vertexIsX_A))return augmentingPathdef findRoute(self, directMatrix, currentRoute, currentShortestRoute):if currentRoute[-1]==directMatrix.shape[0]-1:if len(currentShortestRoute)==0 or len(currentShortestRoute)>len(currentRoute):currentShortestRoute=currentRoute.copy()return currentShortestRoutefor i in range(0,directMatrix.shape[0]):if directMatrix[currentRoute[-1],i]==1:nextRoute=currentRoute.copy()nextRoute.append(i)route=self.findRoute(directMatrix, nextRoute,currentShortestRoute)if len(currentShortestRoute)==0 or len(currentShortestRoute)>len(route):currentShortestRoute=route.copy()return currentShortestRoute
用下面的代码测试,输入数据就是上面的例子:
import numpy as np
from MaxMatchAlgorithm import MaxMatchAlgorithm edges=np.array([[1,0,1],[1,1,1],[0,0,1]
])maxMatchAlgorithm=MaxMatchAlgorithm(edges)
print(maxMatchAlgorithm.maxMatch())
结果

对应图上就是