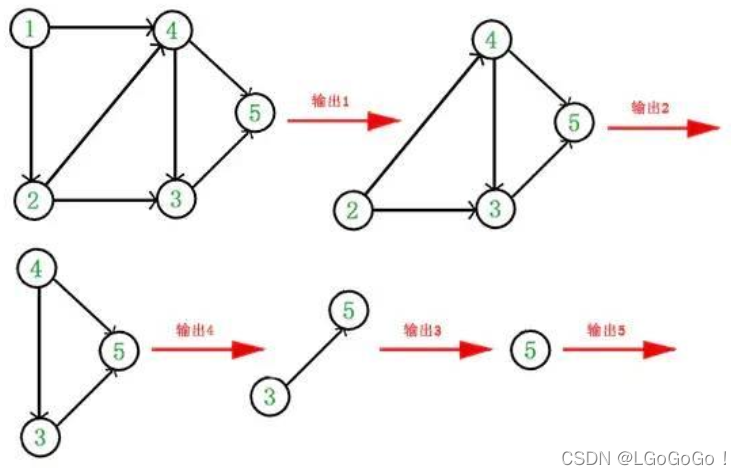
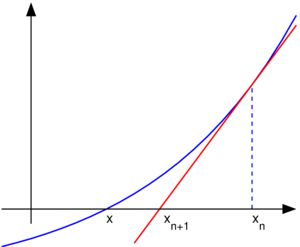
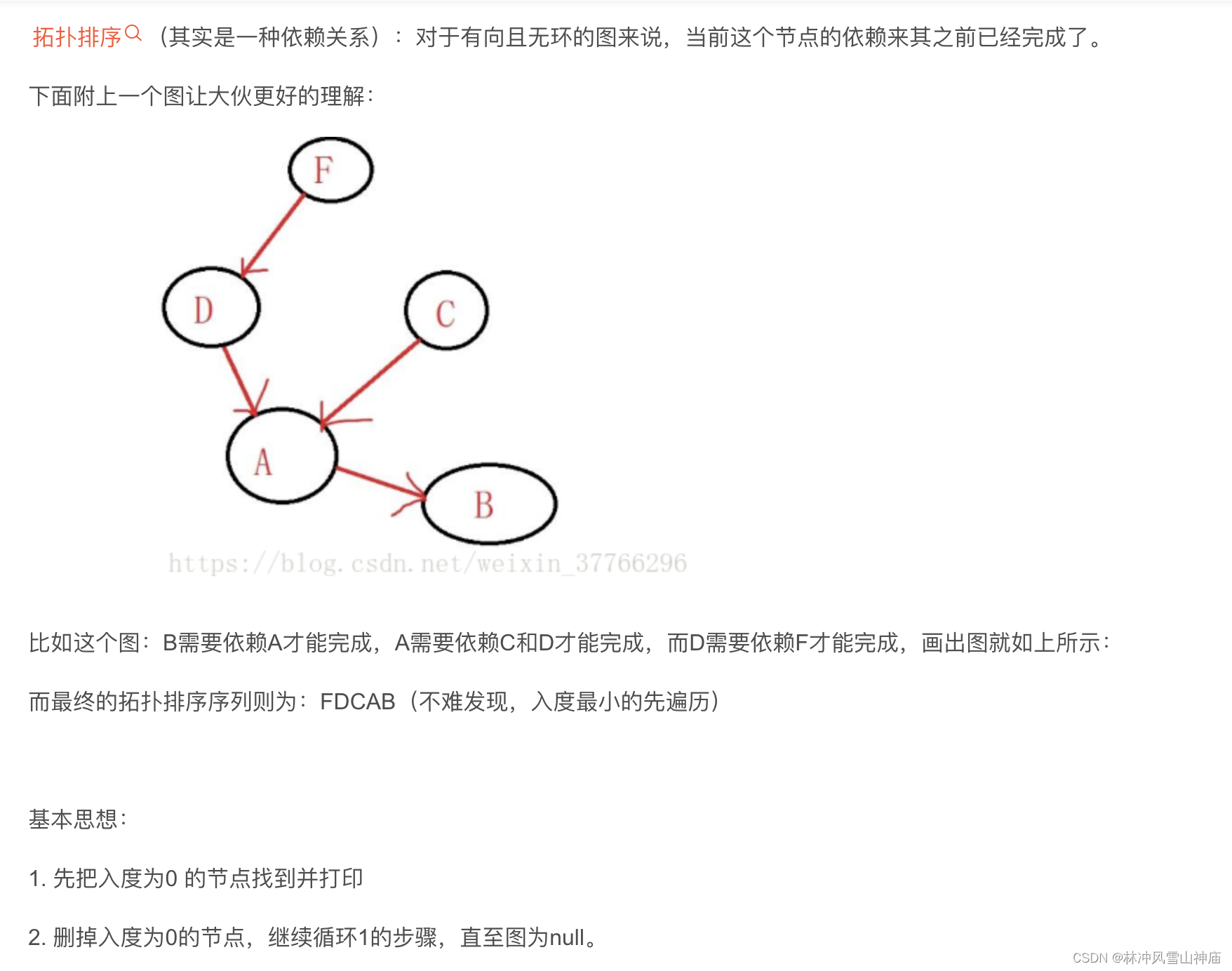
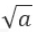拓扑排序原理
拓扑排序算法分析(通俗易懂)_hongjie_lin-CSDN博客_拓扑排序算法
207 课程表

bfs和dfs都可以。先来看一下bfs。
思路是:入度法,入度为0的时候,表示这门课程没有先修课程了,可以学习这门课程了。
1.存储每个课程的入度值
2.存储每个课程的入度节点
为什么?
#存储节点的先修课程,key是先修课程,value是这个先修课程的下一个节点。
edges=collections.defaultdict(list)。
答:因为是遍历到当前入度为0的课程时,他对应的下一个课程的入度可以减去1.如下图所示。

注意:会有节点没出现在列表里,但是也是存在的。

class Solution:from collections import dequedef canFinish(self, numCourses: int, prerequisites: List[List[int]]) -> bool:#入度法:当前节点没有先修课程。最后每个节点的先修可能为0,则说明可以完成。#存储节点的先修课程,key是先修课程,value是这个先修课程的下一个节点。edges=collections.defaultdict(list)#存储当前每个节点的入度indegree=[0]*numCourses#遍历赋予初始值for cur,pre in prerequisites:edges[pre].append(cur)indegree[cur]+=1#找到当前入度为0的节点# queen=collections.deque([u for u in range(numCourses) if indegree[u] == 0])queen=deque()# for u in indegreefor u in range(numCourses):if indegree[u]==0:queen.append(u)visited = 0while queen:visited +=1pre=queen.popleft()for cur in edges[pre]:indegree[cur]-=1if indegree[cur]==0:queen.append(cur)return visited==numCourses851 喧闹和富有
题解:
力扣![]() https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/loud-and-rich/solution/tong-ge-lai-shua-ti-la-yi-ti-liang-jie-t-gses/
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/loud-and-rich/solution/tong-ge-lai-shua-ti-la-yi-ti-liang-jie-t-gses/


class Solution(object):from collections import dequedef loudAndRich(self, richer, quiet):""":type richer: List[List[int]]:type quiet: List[int]:rtype: List[int]"""#存储节点,key是富有的人,value是这个富人指向的下一个穷人edges=collections.defaultdict(list)#入度表indegree=[0]*len(quiet)#赋予初始值for info in richer:edges[info[0]].append(info[1])indegree[info[1]]+=1#ans赋予初始值ans=[i for i in range(len(quiet))]#找到入度为0的节点queen=deque()for i in range(len(quiet)):if indegree[i]==0:queen.append(i)while queen:pre=queen.popleft()for cur in edges[pre]:if quiet[ans[pre]]<quiet[ans[cur]]:ans[cur]=ans[pre]indegree[cur]-=1if indegree[cur]==0:queen.append(cur)return ansclass Solution {public int[] loudAndRich(int[][] richer, int[] quiet) {// 拓扑排序:取入度为0的先入队,减少它下游节点的入度,如果为0了也入队,直到队列中没有元素为止int n = quiet.length;// 先整理入度表和邻接表int[] inDegree = new int[n];List<Integer>[] g = new List[n];for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {g[i] = new ArrayList<>();}for (int[] r : richer) {inDegree[r[1]]++;g[r[0]].add(r[1]);}// 初始化ans各位为自己// 题目说的是:在所有拥有的钱肯定不少于 person x 的人中,person y 是最安静的人// 注意这里的不少于,说明可以是自己int[] ans = new int[n];for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {ans[i] = i;}// 拓扑排序开始Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {if (inDegree[i] == 0) {queue.offer(i);}}while (!queue.isEmpty()) {int p = queue.poll();// q是p的下游,也就是p比q有钱for (int q : g[p]) {// 如果p的安静值比q小,更新p的安静值对应的那个人// 注意这里p的安静值,并不是原始的quiet数组中的quiet[p]// 而是已经更新后的安静值,所以,应该取quiet[ans[p]]// 这里没有改变原来数组的内容,而是通过ans[p]间接引用的,细细品一下// 想像一下上图中的3的安静值被更新成了5的1if (quiet[ans[p]] < quiet[ans[q]]) {ans[q] = ans[p];}if (--inDegree[q] == 0) {queue.offer(q);}}}return ans;}
}作者:tong-zhu
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/loud-and-rich/solution/tong-ge-lai-shua-ti-la-yi-ti-liang-jie-t-gses/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
310 最小高度树
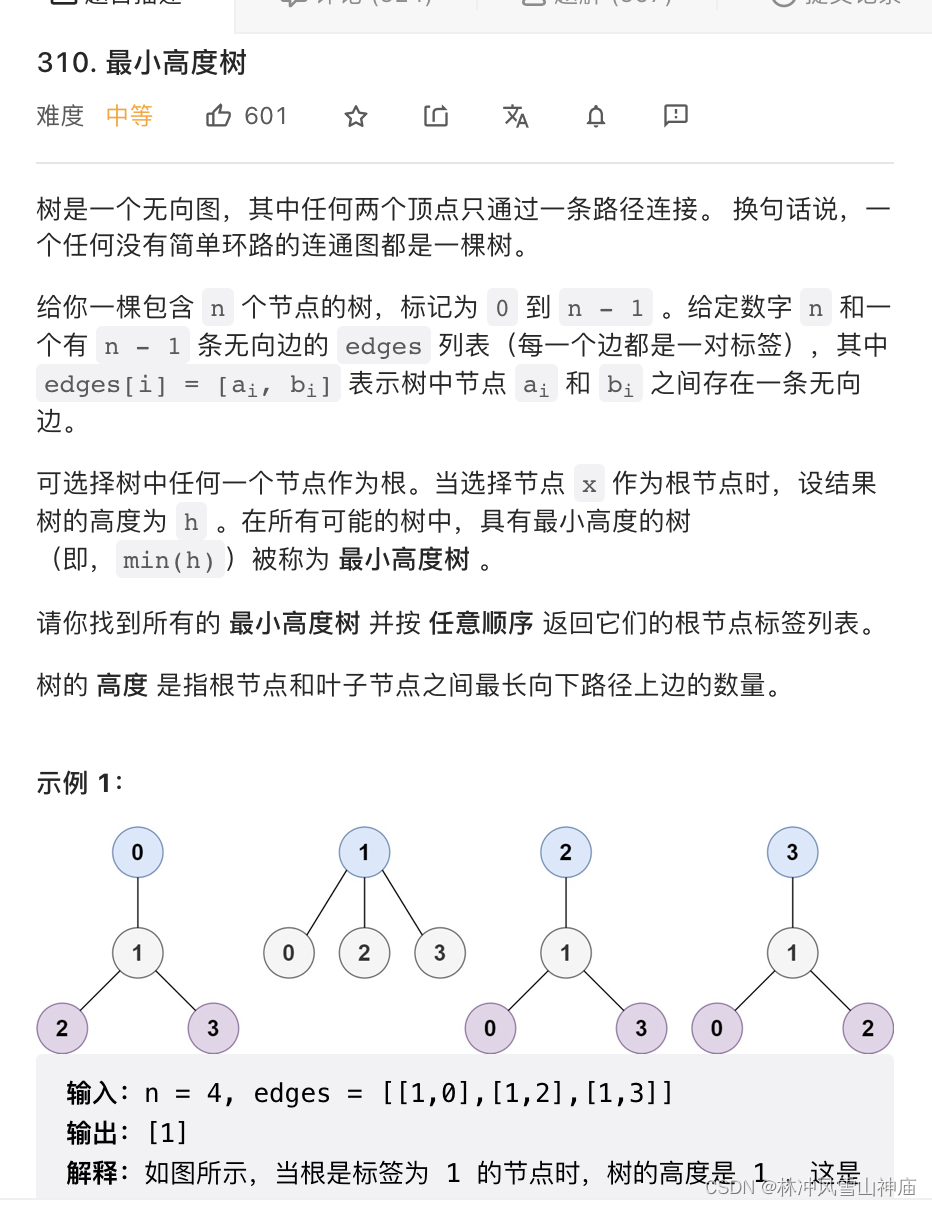
力扣
力扣
暴力超时
class Solution:def findMinHeightTrees(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:if not edges:return [0]import collectionsgraph = collections.defaultdict(list)for i in range(len(edges)):graph[edges[i][0]].append(edges[i][1])graph[edges[i][1]].append(edges[i][0])def bfs(root):deq = collections.deque()d = 0deq.append((root, d))visited = set()visited.add(root)while deq:node, d = deq.popleft()next_nodes = graph[node]for next_node in next_nodes:if next_node not in visited:deq.append((next_node, d + 1))visited.add(next_node)# 都遍历完了之后,记录dreturn dres = float("inf")res_list = []res_list_root = []for root in graph.keys():cur_height = bfs(root)res_list.append(cur_height)res_list_root.append(root)res = min(res, cur_height)ans = []for i in range(len(res_list)):if res_list[i] == res:ans.append(res_list_root[i])return ans
利用入度



class Solution:def findMinHeightTrees(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:res = []if n==1:res.append(0)return resdegree = [0]*n #记录每个点的度map = defaultdict(list) #存储邻居节点# 初始化每个节点的度和邻居for edge in edges:degree[edge[0]]+=1degree[edge[1]]+=1map[edge[0]].append(edge[1])map[edge[1]].append(edge[0])# 记录度为1的叶子节点queue = deque()for i in range(n):if degree[i]==1:queue.append(i)#每次遍历叶子节点,每一轮将叶子节点从树上删除后将新的叶子节点入队进行下一轮遍历while len(queue)>0:res = []size = len(queue)# 遍历叶子节点for i in range(size):cur = queue.pop()res.append(cur)neighbors = map[cur]for neighbor in neighbors:# 将叶子节点的邻居节点的度减一,若是新的叶子节点,则入队degree[neighbor]-=1if degree[neighbor]==1:queue.appendleft(neighbor)# 返回最后一轮的叶子节点,就是最小高度树的根节点return res269 火星词典

class Solution:def alienOrder(self, words: List[str]) -> str:# 将词典中字符串的字符两两对比,只有第一个不同的字符才是正确的排序,如ert和wrf,只能推断出e的优先级高于w,剩余字符的优先级不能推断。将字符串的优先级构建为图,然后进行拓扑排序。如果图中无环,则将拓扑排序输出,否则顺序是非法的。# 每个字母代表图的一个顶点; 邻接表表示有向图. graph = {}indegree = {}# 初始化graph 和 入度表. 注意这个初始化是要对每个出现的字符都进行初始化for word in words:for char in word:if char not in graph:graph[char] = []indegree[char] = 0# 两两单词中的每个字母进行比较,确定图的方向. for i in range(len(words) - 1):j = 0while j < len(words[i]) and j < len(words[i + 1]):if words[i][j] != words[i + 1][j]:# 当前的两个字母按这门新语言的字母顺序进行了排序, 所以优先级高 -> 优先级低。 加入graph。graph[words[i][j]].append(words[i + 1][j])# 为什么这里需要break?当前的两个字母不同,字母顺序也不同;所以单词在字典中的排序顺序只和这两个字母有关,而和后面的无关。因此我们需要看下一个单词对比而不是当前单词的字母对比。breakj += 1# 填充入度表for nexts in graph.values():for next_char in nexts:indegree[next_char] += 1# 把入度为0的点装进queue里queue = collections.deque()for key in indegree.keys():if indegree[key] == 0:queue.append(key)res = []while queue:pre = queue.popleft()res.append(pre)# 删除了pre节点,那么这个pre所对应的next,全部的入度都要-1. 然后顺带检查next的入度是否为0, 如果为0的话那么要把next加入queue. for next in graph[pre]:indegree[next] -= 1if indegree[next] == 0:queue.append(next)is_bad_dag = False# 判断有向图是否有环: 出队元素个数不等于图顶点个数,说明有环if len(res) != len(graph):is_bad_dag = True# abc 排在 ab前面,也属于非法输入。这种情况,a-> a b->b 不可能,c -> "" 也不可能for i in range(len(words) - 1):if len(words[i]) > len(words[i + 1]) and words[i][:len(words[i + 1])] == words[i + 1]:is_bad_dag = Truebreakreturn "" if is_bad_dag else "".join(res)
class Solution:def alienOrder(self, words: List[str]) -> str:import collections# 存储节点的先修课程,key是先修课程,value是这个先修课程的下一个节点。graph = collections.defaultdict(list)# 存储当前每个节点的入度indegree = collections.defaultdict(int)# 初始化入度表. 因为入度为0的节点在下面遍历不到# 初始化graph,为了后面判断图是否有环for word in words:for char in word:if char not in graph:graph[char] = []indegree[char] = 0# 先建图,当前char,当前char的下一个char,# 两两单词中的每个字母进行比较,确定图的方向.for i in range(len(words)-1):j = 0while j < len(words[i]) and j < len(words[i + 1]):if words[i][j] != words[i + 1][j]:# 当前的两个字母按这门新语言的字母顺序进行了排序, 所以优先级高 -> 优先级低。 加入graph。graph[words[i][j]].append(words[i + 1][j])# 入度加一indegree[words[i + 1][j]] += 1# 为什么这里需要break?当前的两个字母不同,字母顺序也不同;所以单词在字典中的排序顺序只和这两个字母有关,而和后面的无关。因此我们需要看下一个单词对比而不是当前单词的字母对比。breakj += 1# 把入度为0的点装进queue里queue = collections.deque()for key in indegree.keys():if indegree[key] == 0:queue.append(key)res = []while queue:pre = queue.popleft()res.append(pre)# 删除了pre节点,那么这个pre所对应的next,全部的入度都要-1. 然后顺带检查next的入度是否为0, 如果为0的话那么要把next加入queue.for next in graph[pre]:indegree[next] -= 1if indegree[next] == 0:queue.append(next)# abc 排在 ab前面,也属于非法输入。这种情况,a-> a b->b 不可能,c -> "" 也不可能is_bad_dag = False# 判断有向图是否有环: 出队元素个数不等于图顶点个数,说明有环if len(res) != len(graph):is_bad_dag = Truefor i in range(len(words) - 1):if len(words[i]) > len(words[i + 1]) and words[i][:len(words[i + 1])] == words[i + 1]:is_bad_dag = Truebreakif is_bad_dag:return ""return "".join(res)6163. 给定条件下构造矩阵

class Solution(object):def buildMatrix(self, k, rowConditions, colConditions):""":type k: int:type rowConditions: List[List[int]]:type colConditions: List[List[int]]:rtype: List[List[int]]"""import collectionsgraph_row = collections.defaultdict(list)indegree_row = [0] * k# 遍历赋予初始值for abovei, belowi in rowConditions:graph_row[abovei-1].append(belowi-1)indegree_row[belowi-1] += 1graph_col = collections.defaultdict(list)indegree_col = [0] * k# 遍历赋予初始值for lefti, righti in colConditions:graph_col[lefti-1].append(righti-1)indegree_col[righti-1] += 1print(indegree_row,indegree_col)from collections import dequequeen1 = deque()for i in range(len(indegree_row)):if indegree_row[i] == 0:queen1.append(i)row = []while queen1:pre = queen1.popleft()row.append(pre)for cur in graph_row[pre]:indegree_row[cur] -= 1if indegree_row[cur] == 0:queen1.append(cur)queen2 = deque()for i in range(len(indegree_col)):if indegree_col[i] == 0:queen2.append(i)col = []while queen2:pre = queen2.popleft()col.append(pre)for cur in graph_col[pre]:indegree_col[cur] -= 1if indegree_col[cur] == 0:queen2.append(cur)print(row)print(col)# 不满足条件if len(row) != k or len(col) != k:return []# 确定每个数值放置的位置进行赋值row_ind = {row[i]: i for i in range(k)}col_ind = {col[i]: i for i in range(k)}res = [[0] * k for _ in range(k)]for i in range(k):res[row_ind[i]][col_ind[i]] = i+1return res