AQS核心数据结构
AQS内部主要维护了一个FIFO(先进先出)的双向链表。
AQS数据结构原理
AQS内部维护的双向链表中的各个节点分别指向直接的前驱节点和直接的后续节点。所以,在AQS内部维护的双向链表可以从其中的任意一个节点遍历前驱结点和后继结点。
链表中的每个节点都是对线程的封装,在并发场景下,如果某个线程竞争锁失败,就会被封装成一个Node节点加入AQS队列的末尾。当获取到锁的线程释放锁后,会从AQS队列中唤醒一个被阻塞的线程。同时,在AQS中维护了一个使用volatile修饰的变量state来标识相应的状态。AQS内部的数据结构如下图:
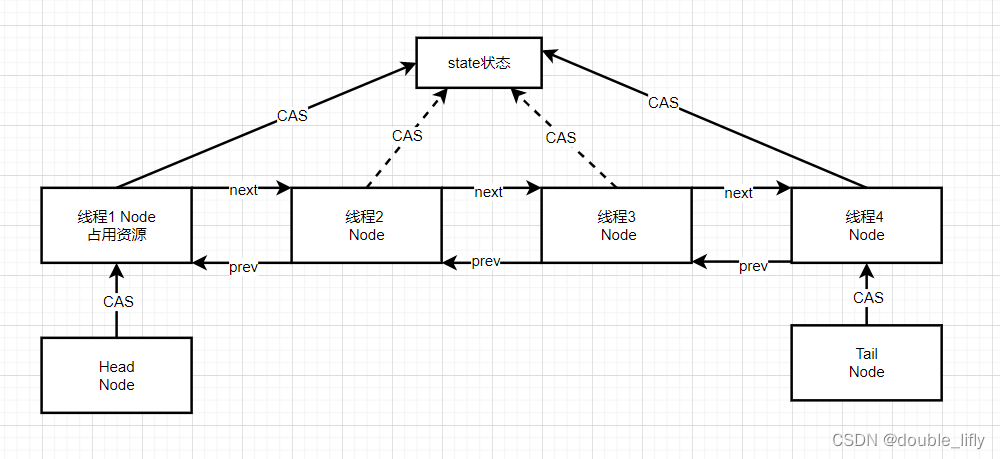 从上图可以看出,在AQS内部的双向链表中,每个节点都是对一个现成的封装。同时,存在一个头结点指针指向链表的头部,存在一个尾结点指向链表的尾部。头结点指针和尾指针会通过CAS操作改变链表节点的指向。
从上图可以看出,在AQS内部的双向链表中,每个节点都是对一个现成的封装。同时,存在一个头结点指针指向链表的头部,存在一个尾结点指向链表的尾部。头结点指针和尾指针会通过CAS操作改变链表节点的指向。
另外,头结点指针指向的节点封装的线程会占用资源,同时会通过CAS的方式更新AQS中的state变量。链表中其他节点的线程未竞争到资源,不会通过CAS操作更新state资源。
AQS内部队列模式
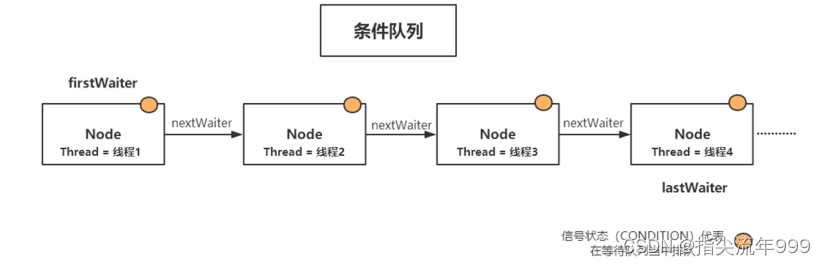
从本质上讲,AQS内部实现了两个队列,一个是同步队列,另一个是条件队列。同步队列的结构如下:

在同步队列中,如果当前线程获取资源失败,就会通过addWaiter()方法将当前线程放入队列的尾部,并且保持自旋的状态,不判断自己所在的节点是否是队列的头结点。如果自己所在的节点是头结点,那么此时不断判断尝试获取资源,如果获取资源成功,则通过acquire()方法退出同步队列。
AQS同步条件队列的结构如下图:
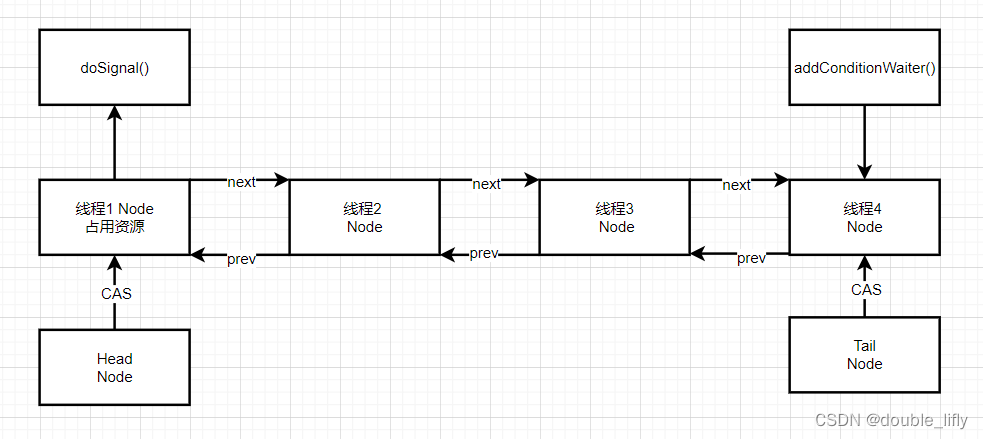
AQS中的条件队列就是为Lock锁实现的一个基础同步器,只有在使用了Condition时才会存在条件队列,并且一个线程可能存在多个条件队列。
AQS底层锁的支持
AQS底层支持独占锁和共享锁两种模式。其中,独占锁同一时刻只能被一个线程占用,例如,基于AQS实现的ReentrantLock锁。共享锁则在同一时刻可以被多个线程占用,例如,基于AQS实现的CountDownLatch和Semaphore等。基于AQS实现的ReadWriteLock则同时实现了独占锁和共享锁两种模式。
核心状态位
在AQS中维护了一个volatile修饰的核心状态标识state,用于标识锁的状态,如下所示:
private volatile int state
state标量使用volatile修饰,所以能够保证可见性,所以能够保证可见性,当任意改变了state变量的值后,其他线程能够立刻读取到state变量的最新值。
AQS针对state变量提供了getState()方法来读取state变量的值,提供了setState()方法来设置state变量的值。由于setState()方法无法保证原子性,所以,AQS中又提供了compareAndSetState()方法保证修改state变量的原子性。AQS中提供了getState(),setState()和compareAndSetState()方法如下:
/*** Returns the current value of synchronization state.* This operation has memory semantics of a {@code volatile} read.* @return current state value*/protected final int getState() {return state;}/*** Sets the value of synchronization state.* This operation has memory semantics of a {@code volatile} write.* @param newState the new state value*/protected final void setState(int newState) {state = newState;}/*** Atomically sets synchronization state to the given updated* value if the current state value equals the expected value.* This operation has memory semantics of a {@code volatile} read* and write.** @param expect the expected value* @param update the new value* @return {@code true} if successful. False return indicates that the actual* value was not equal to the expected value.*/protected final boolean compareAndSetState(int expect, int update) {return U.compareAndSetInt(this, STATE, expect, update);}
核心节点类
AQS实现的独占锁和共享锁模式都是在其静态内部类Node中定义的。静态内部类Node的源码如下(java17版本的Node与1.8的不太一样,17版本的是abstract static final class Node{}):
static final class Node {/** Marker to indicate a node is waiting in shared mode */static final Node SHARED = new Node();/** Marker to indicate a node is waiting in exclusive mode */static final Node EXCLUSIVE = null;/** waitStatus value to indicate thread has cancelled */static final int CANCELLED = 1;/** waitStatus value to indicate successor's thread needs unparking */static final int SIGNAL = -1;/** waitStatus value to indicate thread is waiting on condition */static final int CONDITION = -2;/*** waitStatus value to indicate the next acquireShared should* unconditionally propagate*/static final int PROPAGATE = -3;/*** Status field, taking on only the values:* SIGNAL: The successor of this node is (or will soon be)* blocked (via park), so the current node must* unpark its successor when it releases or* cancels. To avoid races, acquire methods must* first indicate they need a signal,* then retry the atomic acquire, and then,* on failure, block.* CANCELLED: This node is cancelled due to timeout or interrupt.* Nodes never leave this state. In particular,* a thread with cancelled node never again blocks.* CONDITION: This node is currently on a condition queue.* It will not be used as a sync queue node* until transferred, at which time the status* will be set to 0. (Use of this value here has* nothing to do with the other uses of the* field, but simplifies mechanics.)* PROPAGATE: A releaseShared should be propagated to other* nodes. This is set (for head node only) in* doReleaseShared to ensure propagation* continues, even if other operations have* since intervened.* 0: None of the above** The values are arranged numerically to simplify use.* Non-negative values mean that a node doesn't need to* signal. So, most code doesn't need to check for particular* values, just for sign.** The field is initialized to 0 for normal sync nodes, and* CONDITION for condition nodes. It is modified using CAS* (or when possible, unconditional volatile writes).*/volatile int waitStatus;/*** Link to predecessor node that current node/thread relies on* for checking waitStatus. Assigned during enqueuing, and nulled* out (for sake of GC) only upon dequeuing. Also, upon* cancellation of a predecessor, we short-circuit while* finding a non-cancelled one, which will always exist* because the head node is never cancelled: A node becomes* head only as a result of successful acquire. A* cancelled thread never succeeds in acquiring, and a thread only* cancels itself, not any other node.*/volatile Node prev;/*** Link to the successor node that the current node/thread* unparks upon release. Assigned during enqueuing, adjusted* when bypassing cancelled predecessors, and nulled out (for* sake of GC) when dequeued. The enq operation does not* assign next field of a predecessor until after attachment,* so seeing a null next field does not necessarily mean that* node is at end of queue. However, if a next field appears* to be null, we can scan prev's from the tail to* double-check. The next field of cancelled nodes is set to* point to the node itself instead of null, to make life* easier for isOnSyncQueue.*/volatile Node next;/*** The thread that enqueued this node. Initialized on* construction and nulled out after use.*/volatile Thread thread;/*** Link to next node waiting on condition, or the special* value SHARED. Because condition queues are accessed only* when holding in exclusive mode, we just need a simple* linked queue to hold nodes while they are waiting on* conditions. They are then transferred to the queue to* re-acquire. And because conditions can only be exclusive,* we save a field by using special value to indicate shared* mode.*/Node nextWaiter;/*** Returns true if node is waiting in shared mode.*/final boolean isShared() {return nextWaiter == SHARED;}/*** Returns previous node, or throws NullPointerException if null.* Use when predecessor cannot be null. The null check could* be elided, but is present to help the VM.** @return the predecessor of this node*/final Node predecessor() throws NullPointerException {Node p = prev;if (p == null)throw new NullPointerException();elsereturn p;}Node() { // Used to establish initial head or SHARED marker}Node(Thread thread, Node mode) { // Used by addWaiterthis.nextWaiter = mode;this.thread = thread;}Node(Thread thread, int waitStatus) { // Used by Conditionthis.waitStatus = waitStatus;this.thread = thread;}}
通过上述代码可以看出,静态内部类Node是一个双向链表,链表中的每个节点都存在一个指向前驱节点的指针prev和一个指向直接后继节点的指针next,每个节点中都保存了当前的状态waitStatus和当前线程thread。并且在Node类中通过SHARED和EXCLUSIVE将其定义成共享锁和独占锁,如下所示:
/** Marker to indicate a node is waiting in shared mode *///标识当前节点为共享模式static final Node SHARED = new Node();/** Marker to indicate a node is waiting in exclusive mode *///标识当前节点为独占模式static final Node EXCLUSIVE = null;
在Node类中定义了4个常量
/** waitStatus value to indicate thread has cancelled */static final int CANCELLED = 1;/** waitStatus value to indicate successor's thread needs unparking */static final int SIGNAL = -1;/** waitStatus value to indicate thread is waiting on condition */static final int CONDITION = -2;/*** waitStatus value to indicate the next acquireShared should* unconditionally propagate*/static final int PROPAGATE = -3;
- CANCELLED :表示当前节点中的线程已被取消
- SIGNAL :表示后继节点中的线程处于等待状态,需要被唤醒
- CONDITION :表示当前节点中的线程在等待某个条件,也就是当前节点处于condition队列中。
- PROPAGATE :表示在当前场景下能够执行后续的acquireShared操作
另外,在Node类中存在一个volatile修饰的成员变量waitStatus,如下所示:
volatile int waitStatus;
waitStatus的取值就是上面的4个常量值,在默认情况下,waitStatus的取值为0,表示当前节点在sync队列中,等待获取锁。
独占锁模式
在AQS中,独占锁模式比较常用,使用范围也比较广泛,它的一个典型实现就是reentrantLock。独占锁的加锁和解锁都是通过互斥实现的。
独占模式加锁流程
在AQS中,独占模式中加锁的核心入口就是acquire()方法,如下所示
/*** Acquires in exclusive mode, ignoring interrupts. Implemented* by invoking at least once {@link #tryAcquire},* returning on success. Otherwise the thread is queued, possibly* repeatedly blocking and unblocking, invoking {@link* #tryAcquire} until success. This method can be used* to implement method {@link Lock#lock}.** @param arg the acquire argument. This value is conveyed to* {@link #tryAcquire} but is otherwise uninterpreted and* can represent anything you like.*/public final void acquire(long arg) {if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))selfInterrupt();}
当某个线程调用acquire()方法获取独占锁时,在acquire()方法中会首先调用tryAcquire()方法尝试获取锁资源,tryAcquire()方法在AQS中没有具体的实现,只是简单的抛出了UnsupportedOperationException异常,具体的逻辑由AQS的子类实现,如下所示:
/*** Attempts to acquire in exclusive mode. This method should query* if the state of the object permits it to be acquired in the* exclusive mode, and if so to acquire it.** <p>This method is always invoked by the thread performing* acquire. If this method reports failure, the acquire method* may queue the thread, if it is not already queued, until it is* signalled by a release from some other thread. This can be used* to implement method {@link Lock#tryLock()}.** <p>The default* implementation throws {@link UnsupportedOperationException}.** @param arg the acquire argument. This value is always the one* passed to an acquire method, or is the value saved on entry* to a condition wait. The value is otherwise uninterpreted* and can represent anything you like.* @return {@code true} if successful. Upon success, this object has* been acquired.* @throws IllegalMonitorStateException if acquiring would place this* synchronizer in an illegal state. This exception must be* thrown in a consistent fashion for synchronization to work* correctly.* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if exclusive mode is not supported*/protected boolean tryAcquire(long arg) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}当tryAcquire()方法返回false时,首先会调用addWaiter()方法将当前线程封装成独占式模式的节点,添加到AQS的队列尾部。addWaiter()方法的源码如下:
/*** Creates and enqueues node for current thread and given mode.** @param mode Node.EXCLUSIVE for exclusive, Node.SHARED for shared* @return the new node*/private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);// Try the fast path of enq; backup to full enq on failureNode pred = tail;if (pred != null) {node.prev = pred;if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) {pred.next = node;return node;}}enq(node);return node;}
在addWaiter()方法中,当前线程会被封装成独占模式的Node节点,Node节点被尝试放入队列尾部,如果放入成功,则通过CAS操作修改Node节点与前驱节点的指向关系。如果Node节点放入队列尾部失败或者CAS操作失败,则调用end()方法处理Node节点。
/*** Inserts node into queue, initializing if necessary. See picture above.* @param node the node to insert* @return node's predecessor*/private Node enq(final Node node) {for (;;) {Node t = tail;if (t == null) { // Must initializeif (compareAndSetHead(new Node()))tail = head;} else {node.prev = t;if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) {t.next = node;return t;}}}}
在end()方法中,Node节点通过CAS自旋的方式被添加到队列尾部,直到添加成功为止。具体的实现方式是判断队列是否为空,如果队列为空,则创建一个空节点作为head节点,然后将tail指向head节点。在下次自旋时,就会满足队列不为空的条件,通过CAS方式将Node节点放入队列尾部。
此刻,回到acquire()方法,当通过调用addWaiter()成功将当前线程封装成独占模式的Node节点放入队列后,会调用acquireQueued()方法在等待队列中排队。acquireQueued()方法的源码如下:
/*** Acquires in exclusive uninterruptible mode for thread already in* queue. Used by condition wait methods as well as acquire.** @param node the node* @param arg the acquire argument* @return {@code true} if interrupted while waiting*/final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, long arg) {boolean failed = true;try {boolean interrupted = false;for (;;) {final Node p = node.predecessor();if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {setHead(node);p.next = null; // help GCfailed = false;return interrupted;}if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&parkAndCheckInterrupt())interrupted = true;}} finally {if (failed)cancelAcquire(node);}}
在acquireQueued()方法中,首先定义一个failed变量来标识获取资源是否失败,默认值为true,表示获取资源失败。然后,定义一个表示当前线程是否被中断过的标识interrupted,默认值为false,表示没有被中断过。
最后,进入一个自旋逻辑,获取当前Node节点的前驱节点,如果当前Node节点的前驱节点是head节点,便是当前Node节点可以尝试获取资源。如果当前节点获取资源成功,则将head节点指向Node节点。也就是说,head节点指向的Node节点就是获取到资源的节点或者为null。
在setHead()方法中,当前节点的prev指针会被设置为null,随后,当前Node节点的前驱节点的next指针被设置为null,表示head节点出队列,整个操作成功后会返回等待过程是否被中断过的标识。
如果当前节点的前驱节点不是head,则调用shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire()方法判断当前线程是否可以进入waitting状态。如果可以进入阻塞状态,则进入阻塞状态直接调用LockSupport的unpark()方法唤醒当前线程。
shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire()方法的源码如下:
/*** Checks and updates status for a node that failed to acquire.* Returns true if thread should block. This is the main signal* control in all acquire loops. Requires that pred == node.prev.** @param pred node's predecessor holding status* @param node the node* @return {@code true} if thread should block*/private static boolean shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(Node pred, Node node) {int ws = pred.waitStatus;if (ws == Node.SIGNAL)/** This node has already set status asking a release* to signal it, so it can safely park.*/return true;if (ws > 0) {/** Predecessor was cancelled. Skip over predecessors and* indicate retry.*/do {node.prev = pred = pred.prev;} while (pred.waitStatus > 0);pred.next = node;} else {/** waitStatus must be 0 or PROPAGATE. Indicate that we* need a signal, but don't park yet. Caller will need to* retry to make sure it cannot acquire before parking.*/compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL);}return false;}
在shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire()方法中,先获取当前节点的前驱节点的状态,如果前驱结点的状态为SIGNAL(-1),则直接返回true。如果前驱结点的状态大于0,则当前节点一直向前移动,直到找到一个waitStatus状态小于或等于0的节点,排在这个节点的后面。
在acquireQueued()方法中,如果shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire()方法返回true,则调用parkAndCheckInterrupt()方法阻塞当前线程。parkAndCheckInterrupt()方法的源码如下:
/*** Convenience method to park and then check if interrupted** @return {@code true} if interrupted*/private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() {LockSupport.park(this);return Thread.interrupted();}
在parkAndCheckInterrupt()方法中,通过LockSupport的park()方法阻塞线程。至此,在独占模式下,整个加锁流程分析完毕。
独占模式解锁流程
在独占锁模式中,释放锁的核心入口是release()方法,如下所示:
/*** Releases in exclusive mode. Implemented by unblocking one or* more threads if {@link #tryRelease} returns true.* This method can be used to implement method {@link Lock#unlock}.** @param arg the release argument. This value is conveyed to* {@link #tryRelease} but is otherwise uninterpreted and* can represent anything you like.* @return the value returned from {@link #tryRelease}*/public final boolean release(long arg) {if (tryRelease(arg)) {Node h = head;if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)unparkSuccessor(h);return true;}return false;}
在relase()方法中,会先调用tryRelease()方法尝试释放锁,tryRelease()方法在AQS中同样没有具体的实现逻辑,只是简单的抛出了UnsupportedOperationException异常,具体的逻辑由AQS的子类实现,如下所示:
/*** Attempts to set the state to reflect a release in exclusive* mode.** <p>This method is always invoked by the thread performing release.** <p>The default implementation throws* {@link UnsupportedOperationException}.** @param arg the release argument. This value is always the one* passed to a release method, or the current state value upon* entry to a condition wait. The value is otherwise* uninterpreted and can represent anything you like.* @return {@code true} if this object is now in a fully released* state, so that any waiting threads may attempt to acquire;* and {@code false} otherwise.* @throws IllegalMonitorStateException if releasing would place this* synchronizer in an illegal state. This exception must be* thrown in a consistent fashion for synchronization to work* correctly.* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if exclusive mode is not supported*/protected boolean tryRelease(long arg) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}
在release()方法中,如果tryRelease()方法返回true,则会先获取head节点,当head节点不为空,并且head节点的waitStatus状态不为0时,会调用unparkSuccessor()方法,并将head节点传入方法中。unparkSuccessor()方法的远吗如下:
/*** Wakes up node's successor, if one exists.** @param node the node*/private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) {/** If status is negative (i.e., possibly needing signal) try* to clear in anticipation of signalling. It is OK if this* fails or if status is changed by waiting thread.*/int ws = node.waitStatus;if (ws < 0)compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0);/** Thread to unpark is held in successor, which is normally* just the next node. But if cancelled or apparently null,* traverse backwards from tail to find the actual* non-cancelled successor.*/Node s = node.next;if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) {s = null;for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev)if (t.waitStatus <= 0)s = t;}if (s != null)LockSupport.unpark(s.thread);}
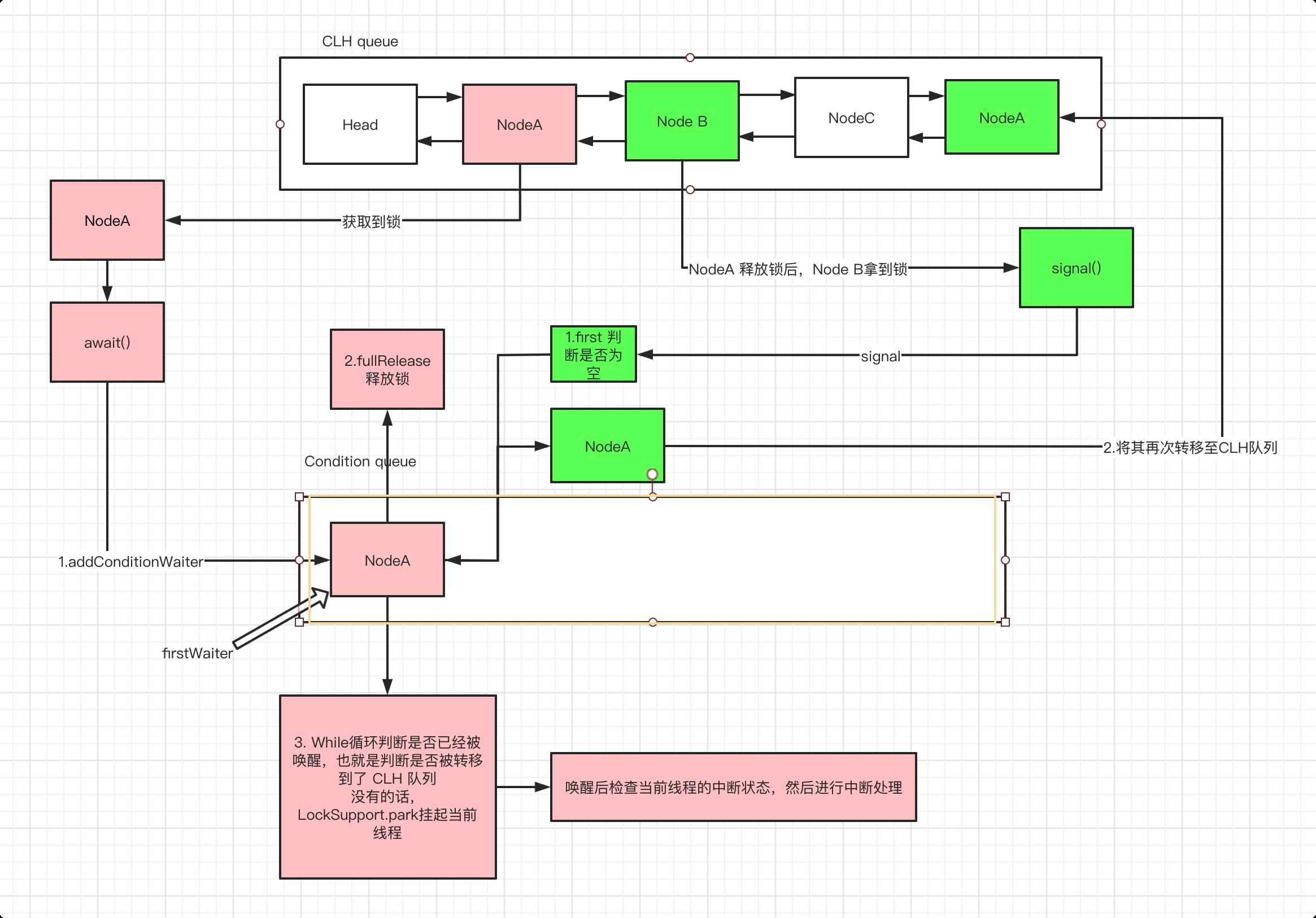
unparkSuccessor()方法的主要逻辑是唤醒队列中最前面的线程。这里需要结合acquireQueued()方法理解,当线程被唤醒后,会进入acquireQueued()方法中的if(p==head && tryAcquier(arg))逻辑判断,当条件成立是,被唤醒的线程会将自己所在的节点设置为head,表示已经获取到资源,此时,acquire()方法也执行完毕了。
共享锁模式
在AQS中,共享锁模式下的加锁和释放锁操作和独占锁不同,接下来,就简单介绍下AQS共享锁模式下的加锁和释放锁的流程。
共享模式下加锁流程
在AQS中,共享模式下的加锁操作核心入口方法是acquireShared(),如下所示:
/*** Acquires in shared mode, ignoring interrupts. Implemented by* first invoking at least once {@link #tryAcquireShared},* returning on success. Otherwise the thread is queued, possibly* repeatedly blocking and unblocking, invoking {@link* #tryAcquireShared} until success.** @param arg the acquire argument. This value is conveyed to* {@link #tryAcquireShared} but is otherwise uninterpreted* and can represent anything you like.*/public final void acquireShared(long arg) {if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0)doAcquireShared(arg);}在acquireShared()方法中,会先调用tryAcquireShared()方法尝试获取共享资源,tryAcquireShared()方法在AQS中并没有具体的实现逻辑,只是简单的抛出UnsupportedOperationException异常,具体的逻辑由AQS的子类实现,如下所示:
/*** Attempts to acquire in shared mode. This method should query if* the state of the object permits it to be acquired in the shared* mode, and if so to acquire it.** <p>This method is always invoked by the thread performing* acquire. If this method reports failure, the acquire method* may queue the thread, if it is not already queued, until it is* signalled by a release from some other thread.** <p>The default implementation throws {@link* UnsupportedOperationException}.** @param arg the acquire argument. This value is always the one* passed to an acquire method, or is the value saved on entry* to a condition wait. The value is otherwise uninterpreted* and can represent anything you like.* @return a negative value on failure; zero if acquisition in shared* mode succeeded but no subsequent shared-mode acquire can* succeed; and a positive value if acquisition in shared* mode succeeded and subsequent shared-mode acquires might* also succeed, in which case a subsequent waiting thread* must check availability. (Support for three different* return values enables this method to be used in contexts* where acquires only sometimes act exclusively.) Upon* success, this object has been acquired.* @throws IllegalMonitorStateException if acquiring would place this* synchronizer in an illegal state. This exception must be* thrown in a consistent fashion for synchronization to work* correctly.* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if shared mode is not supported*/protected long tryAcquireShared(long arg) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}
tryAcquireShared()方法的返回值存在如下几种情况。
- 返回负数:表示获取资源失败
- 返回0:表示获取资源成功,但是没有剩余资源
- 返回正数:表示获取资源成功,还有剩余资源
当tryAcquireShared()方法获取资源失败时,在acquireShared()方法中会调用doAcquireShared()方法。doAcquireShared()方法的源码如下:
/*** Acquires in shared uninterruptible mode.* @param arg the acquire argument*/private void doAcquireShared(long arg) {final Node node = addWaiter(Node.SHARED);boolean failed = true;try {boolean interrupted = false;for (;;) {final Node p = node.predecessor();if (p == head) {long r = tryAcquireShared(arg);if (r >= 0) {setHeadAndPropagate(node, r);p.next = null; // help GCif (interrupted)selfInterrupt();failed = false;return;}}if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&parkAndCheckInterrupt())interrupted = true;}} finally {if (failed)cancelAcquire(node);}}
doAcquireShared()方法的主要逻辑就是将当前线程放入队列的尾部并阻塞,直到有其他线程释放资源并唤醒当前线程,当前线程在获取到指定量的资源后返回。
在doAcquireShared()方法中,如果当前节点的前驱节点是head节点,则尝试获取资源;如果获取资源成功,则调用setHeadAndPropagate()方法将head指向当前节点;同时如果还有剩余资源,则继续唤醒队列中后面的线程。setHeadAndPropagate()方法的源码如下:
/*** Sets head of queue, and checks if successor may be waiting* in shared mode, if so propagating if either propagate > 0 or* PROPAGATE status was set.** @param node the node* @param propagate the return value from a tryAcquireShared*/private void setHeadAndPropagate(Node node, long propagate) {Node h = head; // Record old head for check belowsetHead(node);/** Try to signal next queued node if:* Propagation was indicated by caller,* or was recorded (as h.waitStatus either before* or after setHead) by a previous operation* (note: this uses sign-check of waitStatus because* PROPAGATE status may transition to SIGNAL.)* and* The next node is waiting in shared mode,* or we don't know, because it appears null** The conservatism in both of these checks may cause* unnecessary wake-ups, but only when there are multiple* racing acquires/releases, so most need signals now or soon* anyway.*/if (propagate > 0 || h == null || h.waitStatus < 0 ||(h = head) == null || h.waitStatus < 0) {Node s = node.next;if (s == null || s.isShared())doReleaseShared();}}
在setHeadAndPropagate()方法中,首先将head节点赋值给临时节点h,并将head指向当前节点,如果资源还有剩余,则继续唤醒队列中后面的线程。
共享模式释放资源流程
在共享模式下,释放锁的核心入口方法是releaseShared(),如下所示
/*** Releases in shared mode. Implemented by unblocking one or more* threads if {@link #tryReleaseShared} returns true.** @param arg the release argument. This value is conveyed to* {@link #tryReleaseShared} but is otherwise uninterpreted* and can represent anything you like.* @return the value returned from {@link #tryReleaseShared}*/public final boolean releaseShared(long arg) {if (tryReleaseShared(arg)) {doReleaseShared();return true;}return fal
在releaseShared()方法中,会先调用tryReleaseShared()方法尝试释放资源,tryReleaseShared()方法在AQS中并没有具体的逻辑实现,只是简单的抛出了UnsupportedOperationException异常,具体的逻辑仍然交给由AQS的子类实现,如下所示:
/*** Attempts to set the state to reflect a release in shared mode.** <p>This method is always invoked by the thread performing release.** <p>The default implementation throws* {@link UnsupportedOperationException}.** @param arg the release argument. This value is always the one* passed to a release method, or the current state value upon* entry to a condition wait. The value is otherwise* uninterpreted and can represent anything you like.* @return {@code true} if this release of shared mode may permit a* waiting acquire (shared or exclusive) to succeed; and* {@code false} otherwise* @throws IllegalMonitorStateException if releasing would place this* synchronizer in an illegal state. This exception must be* thrown in a consistent fashion for synchronization to work* correctly.* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if shared mode is not supported*/protected boolean tryReleaseShared(long arg) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}
在releaseShared()方法中,调用tryReleaseShared()方法尝试释放资源成功,会继续唤醒队列中后面的线程。
doReleaseShared()方法主要用来唤醒队列中后面的线程,doReleaseShared()方法的源码如下:
/*** Release action for shared mode -- signals successor and ensures* propagation. (Note: For exclusive mode, release just amounts* to calling unparkSuccessor of head if it needs signal.)*/private void doReleaseShared() {/** Ensure that a release propagates, even if there are other* in-progress acquires/releases. This proceeds in the usual* way of trying to unparkSuccessor of head if it needs* signal. But if it does not, status is set to PROPAGATE to* ensure that upon release, propagation continues.* Additionally, we must loop in case a new node is added* while we are doing this. Also, unlike other uses of* unparkSuccessor, we need to know if CAS to reset status* fails, if so rechecking.*/for (;;) {Node h = head;if (h != null && h != tail) {int ws = h.waitStatus;if (ws == Node.SIGNAL) {if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, Node.SIGNAL, 0))continue; // loop to recheck casesunparkSuccessor(h);}else if (ws == 0 &&!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, 0, Node.PROPAGATE))continue; // loop on failed CAS}if (h == head) // loop if head changedbreak;}}在doReleaseShared()方法中,通过自旋的方式获取头结点,当头结点不为空,且队列不为空时,判断头结点的waitStatus状态是否为SINNAL(-1)。当满足条件时,会通过CAS将头节点的waitStatus状态设置为0,如果CAS操作设置失败,则继续自旋。如果CAS操作设置成,则唤醒队列中的后继结点。
如果头结点的waitStatus状态值为0,并且在通过CAS操作将头结点的waitStatus状态设置为PROPAGATE(-3)时失败,则继续自旋逻辑。
如果在自旋的过程中发现没有后继结点了,则退出自旋逻辑。









![[变分法介绍]优美的旋轮线:最速下降线问题,通过费马光学原理的初等证明](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/20200621210611999.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3dlaXhpbl80MzcwMDczMg==,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70#pic_center)