1、【什么是生产者与消费者模型呢?】
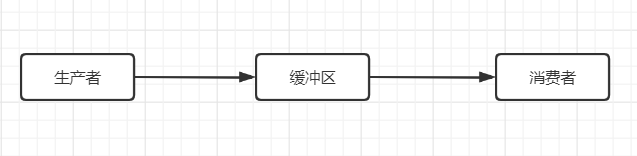
一种重要的模型,基于等待/通知机制。生产者/消费者模型描述的是有一块缓冲区作为仓库,生产者可将产品放入仓库,消费者可以从仓库中取出产品,生产者/消费者模型关注的是以下几个点:
1、生产者与消费者不能同时进行工作,形成的是互斥关系;
2、生产者与生产者之间不能同时生产,处于互斥关系;
3、消费者与消费者之间不能同时工作,处于互斥关系;
4、当缓冲区之内的资源满时,生产者不能生产;
5、当缓冲区之内的资源空时,消费者不能消费;
6、消费者消费的速度不能超过生产者;
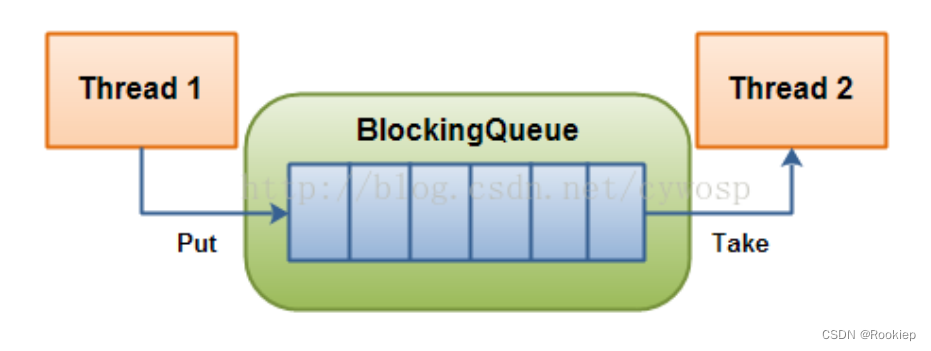
形象图显示:

2、【生产者与消费者之间的关系】
基于消费者与生产者模型的概念;在形成了三种关系 、两个对象、一种机制; 我们称之为是321原则
、、、三种关系指的是:
生产者与消费者关系、生产者与生产者关系、消费者与消费者的关系(三种关系都是互斥关系);
、、、两个对象指的是:
生产者对象、消费者对象
、、、一种机制指的是:
互斥机制
3、【实现单生产者与单消费者模型】
基于单链表实现:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<pthread.h>
#include<stdlib.h>//mutex设置锁,来实现生产者与消费者的互斥关系
pthread_mutex_t lock = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
//cond设置条件变量
pthread_cond_t cond = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;//定义一个 链表
typedef struct Node
{int _val;struct Node * _next;
}Node_t,*Node_p,**Node_pp;Node_p head = NULL;
/链表的实现/
Node_p allocNode(int val)
{Node_p ret = (Node_p)malloc(sizeof(Node_t));ret->_val = val;ret->_next = NULL;return ret;
}void freeNode(Node_p del)
{free(del);
}
int initList(Node_pp _head)
{*_head = allocNode(0);if(*_head == NULL)return 0;return -1;
}void PushNode(Node_p _head,int val)
{Node_p node = allocNode(val);node->_next = _head->_next;_head->_next = node;
}
int Empty(Node_p _head)
{return (_head->_next==NULL)?0:-1;
}
int PopNode(Node_p _head,int * val)
{if(Empty(_head) == 0){return -1;}Node_p del = _head->_next;_head->_next = del->_next;*val = del->_val;freeNode(del);del = NULL;return 0;
}
void PrintList(Node_p _head)
{Node_p tmp = _head->_next;while(tmp){printf("%d ",tmp->_val);tmp=tmp->_next;}printf("\n");
}void DestroyList(Node_pp _head)
{while(Empty(*_head) < 0){int tmp;PopNode(*_head,&tmp);}freeNode(*_head);*_head = NULL;
}
//
//生产者者 插入数据
void * producter(void * arg)
{while(1){pthread_mutex_lock(&lock);int val = rand()%1024;PushNode(head,val);printf("producter push done: %d \n",val);sleep(1);//生产者 插入数据,此时唤醒消费者消费pthread_cond_signal(&cond);pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock);} return NULL;
}
//消费者弹出数据
void * consumer(void * arg)
{while(1){pthread_mutex_lock(&lock);if(Empty(head)==0){ //要是当前的链表为空printf("consumer check\n");//消费者使用 条件变量 挂起pthread_cond_wait(&cond,&lock);}else{int val;PopNode(head,&val);printf("producter pop done: %d \n",val);}//sleep(1);pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock);}
}
int main()
{/*initList(&head);int count = 0 ;while(count++ <10){//int val = rand()%1024;PushNode(head,count);PrintList(head);sleep(1);}count = 0 ;while(count ++ < 7){int val ;PopNode(head,&val);PrintList(head);sleep(1);}DestroyList(&head);*/initList(&head);pthread_t c,p;pthread_create(&c,NULL,consumer,NULL);pthread_create(&p,NULL,producter,NULL);pthread_join(c,NULL);pthread_join(p,NULL); DestroyList(&head);pthread_mutex_destroy(&lock);pthread_cond_destroy(&cond);return 0 ;
}#include<stdio.h>
#include<pthread.h>
#include<semaphore.h>//使用信号量实现环形队列
int databuf[64];
sem_t semblank;//信号量 格子数
sem_t semdata;//信号量 数据数量void * consumer(void *arg)
{int step = 0;while(1){if(sem_wait(&semdata) <0){printf("consumer check!\n");}else{int data = databuf[step];step++;step %= 64; printf("consumer done :%d \n",data);sem_post(&semblank);}usleep(500000);}return NULL;
}
void * producter(void *arg)
{int step = 0 ;while(1){ if(sem_wait(&semblank)< 0 ){printf("producter check! \n");}else{int data= rand()%1234;databuf[step] = data;step++;step %= 64;printf("producter done :%d \n",data);sem_post(&semdata);}usleep(1);}return NULL;
}
int main()
{//初始化两个信号值 格子数是 64 ,数据量为 0sem_init(&semblank,0,64);sem_init(&semdata,0,0);pthread_t c,p;pthread_create(&c,NULL,consumer,NULL);pthread_create(&p,NULL,producter,NULL);pthread_join(c,NULL);pthread_join(p,NULL);sem_destroy(&semblank);sem_destroy(&semdata); return 0;
}4、【实现多生产者与消费者模型】
在这有两个生产者与两个消费者
#include<stdio.h>
#include<pthread.h>
#include<semaphore.h>
//实现多生产者 、多消费者
//使用信号量实现环形队列
int databuf[64];
sem_t semblank;//信号量 格子数
sem_t semdata;//信号量 数据数量//生产者与生产者是 互斥关系;
//消费者与消费者是 互斥关系;
//互斥锁
pthread_mutex_t conlock =PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
pthread_mutex_t prolock =PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
int stepc = 0 ;//consumer step ;
int stepp = 0 ;//productor step ;void * consumer1(void *arg)
{while(1){pthread_mutex_lock(&conlock);if(sem_wait(&semdata) <0){printf("consumer1 check!\n");}else{int data = databuf[stepc];stepc++;stepc %= 64; printf("consumer1 done :%d \n",data);sem_post(&semblank);}usleep(500000);pthread_mutex_unlock(&conlock);}return NULL;
}
void * consumer2(void *arg)
{while(1){pthread_mutex_lock(&conlock);if(sem_wait(&semdata) <0){printf("consumer2 check!\n");}else{int data = databuf[stepc];stepc++;stepc %= 64; printf("consumer2 done :%d \n",data);sem_post(&semblank);}sleep(1);pthread_mutex_unlock(&conlock);}return NULL;
}void * producter1(void *arg)
{while(1){ pthread_mutex_lock(&prolock);if(sem_wait(&semblank)< 0 ){printf("producter1 check! \n");}else{int data= rand()%1234;databuf[stepp] = data;stepp++;stepp %= 64;printf("producter1 done :%d \n",data);sem_post(&semdata);}sleep(1);pthread_mutex_unlock(&prolock);}return NULL;
}
void * producter2(void *arg)
{while(1){ pthread_mutex_lock(&prolock);if(sem_wait(&semblank)< 0 ){printf("producter2 check! \n");}else{int data= rand()%1234;databuf[stepp] = data;stepp++;stepp %= 64;printf("producter2 done :%d \n",data);sem_post(&semdata);}sleep(1);pthread_mutex_unlock(&prolock); }return NULL;
}
int main()
{//初始化两个信号值 格子数是 64 ,数据量为 0sem_init(&semblank,0,64);sem_init(&semdata,0,0);pthread_t c1,p1,c2,p2;pthread_create(&c1,NULL,consumer1,NULL);pthread_create(&p1,NULL,producter1,NULL);pthread_create(&c2,NULL,consumer2,NULL);pthread_create(&p2,NULL,producter2,NULL);pthread_join(c1,NULL);pthread_join(p1,NULL);pthread_join(c2,NULL);pthread_join(p2,NULL);sem_destroy(&semblank);sem_destroy(&semdata); pthread_mutex_destroy(&conlock);pthread_mutex_destroy(&prolock);return 0;
}5、【实现进程之间的单生产者与单消费者模型】
进程之间实现生产者与消费者模型:在这里要使用到进程通信;
在这里我是使用的是 共享内存 来实现进程之间的通信的,但是,共享内存不提供任何的同步与互斥机制,所以我还是用到 信号量 来实现互斥机制
实现 共享内存 与 信号量
#ifndef _COMM_H_
#define _COMM_h_#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/ipc.h>
#include<sys/shm.h>
#include<sys/sem.h>#define PATHNAME "."
#define PROJ_ID 0x0666//实现信号量 与共享内存的函数声明int creatshm(int size);
int getshm(int size);
void * attshm(int shmid);
int dttshm(void *addr);
int destroyshm(int shmid);union semun {int val; /* Value for SETVAL */struct semid_ds *buf; /* Buffer for IPC_STAT, IPC_SET */unsigned short *array; /* Array for GETALL, SETALL */struct seminfo *__buf; /* Buffer for IPC_INFO (Linux-specific) */
};int creatSem(int nsems);
int getSem(int nsems);
int destroySem(int semid);
int initSem(int semid,int which,int value);
int P(int semid,int which);
int V(int semid,int which);#endif#include"comm.h"//Sem
static int commSem(int flag,int nsems)
{key_t key = ftok(PATHNAME,PROJ_ID);if(key < 0){perror("ftok");return -1;}int semid = semget(key,nsems,flag);if(semid < 0 ){perror("semget");return -2;}return semid;
}
//创建的信号量
int creatSem(int nsems)
{return commSem(IPC_CREAT|IPC_EXCL|0666,nsems);
}
//得到已创建的信号量
int getSem(int nsems)
{return commSem(IPC_CREAT,nsems);
}
//销毁信号量集
int destroySem(int semid)
{if(semctl(semid,0,IPC_RMID) < 0 ){perror("semctl");return -1;}return 0;}
//信号量集的初始化
int initSem(int semid ,int which,int value)
{union semun _semun;_semun.val = value;if(semctl(semid,which,SETVAL,_semun) < 0 ){perror("semctl");return -1;}return 0;
}
int Semop(int semid,int which,int op)
{struct sembuf _sembuf;_sembuf.sem_num = which;_sembuf.sem_op = op;_sembuf.sem_flg = 0;return semop(semid,&_sembuf,1);
}int P(int semid,int which)
{if(Semop(semid,which ,-1) ==0 )return 0;perror("P_sem");return -1;
}int V(int semid,int which)
{if(Semop(semid,which ,1) == 0 )return 0;perror("V_sem");return -1;
}//shm
static int commshm(int flag,int size)
{key_t key=ftok(PATHNAME,PROJ_ID);if(key < 0){perror("ftok");return -1;}int shmid = shmget(key,size,flag);if(shmid<0){perror("shmget");}return shmid;
}
//创建共享内存
int creatshm(int size)
{return commshm(IPC_CREAT|IPC_EXCL|0666,size);}
//得到共享内存
int getshm(int size)
{return commshm(IPC_CREAT,size);}
//销毁共享内存
int destroyshm(int shmid)
{if(shmctl(shmid,IPC_RMID,NULL) < 0 ){perror("shmctl");return -1;}return 0;
}
//搭接到共享内存
void * attshm(int shmid)
{void * shmaddr = shmat(shmid,NULL,0);return shmaddr;}
//断开连接
int dttshm(void *addr)
{return shmdt(addr);
}
实现生产者函数
#include"comm.h"//conducter put data
int main()
{// creat shmint shmid = creatshm(4096);int *addr= (int *)attshm(shmid);int step = 0;// creat semint semid = creatSem(2);//consumer sem blank 64initSem(semid,0,64);//server sem data 0;initSem(semid,1,0);;while(1){P(semid,0);int data = rand()%1234;addr[step] = data;++step;step %= 64;printf("conducter done : %d! \n",data);sleep(1);V(semid,1);}dttch(addr);destroySem(semid);destroyshm(shmid);return 0;} 实现消费者
#include"comm.h"//consumer get data
int main()
{// get shmint shmid = getshm(4096);int *addr= (int *)attshm(shmid);// get semint semid = getSem(2);int step = 0 ;while(1){P(semid,1);int data = addr[step] ;++step;step %= 64;printf("consumer done : %d! \n",data);sleep(1);V(semid,0);}dttch(addr);return 0;}