什么是生产者消费者模型
生产者 - 消费者模型( Producer-consumer problem) 是一个非常经典的多线程并发协作的模型,在分布式系统里非常常见。
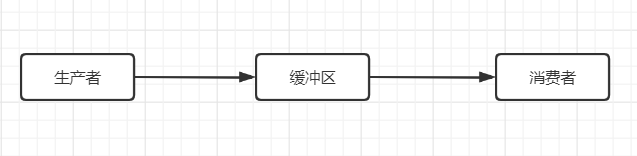
这个模型由两类线程和一个缓冲区组成来组成
- 生产者线程:生产数据,并把数据放在这个队列里面
- 缓冲区:存放生产者的数据的地方
- 消费者线程:从队列里面取数据,消费数据
运行流程
- 生产者和消费者在同一时间段内共用同一个存储空间
- 生产者往存储空间中添加产品
- 消费者从存储空间中取走产品
- 当存储空间为空时,消费者阻塞,当存储空间满时,生产者阻塞。
为什么要用生产者消费者模型
在多线程世界里,生产者就是生产数据的线程,消费者就是消费数据的线程。在多线程开发当中
- 如果生产者处理速度很快,而消费者处理速度很慢,那么生产者就必须等待消费者处理完,才能继续生产数据。
- 如果消费者的处理能力大于生产者,那么消费者就必须等待生产者。为了解决这个问题于是引入了生产者和消费者模式。
实现方式
wait()和notify()方法的实现
-
wait方法:执行该方法的对象释放同步锁,JVM把该线程存放到等待池中,等待其他线程唤醒
-
notify方法:唤醒在等待池中的等待的任意一个线程,把线程转移到锁池中
-
notifyAll方法:唤醒在等待池中等待的所有线程,把线程转移到锁池中
public class WaitTest {private static int count = 0;private static final int buffCount = 10;private static String lock = "lock";class Producer implements Runnable {@Overridepublic void run() {for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}synchronized (lock) {while (count == buffCount) {try {lock.wait();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}count++;System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-生产者生产,数量为:" + count);lock.notifyAll();}}}}class Consumer implements Runnable {@Overridepublic void run() {for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}synchronized (lock) {while (count == 0) {try {lock.wait();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}count--;System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-消费者消费,数量为:"+ count);lock.notifyAll();}}}}public static void main(String[] args) {WaitTest waitTest = new WaitTest();new Thread(waitTest.new Producer()).start();new Thread(waitTest.new Consumer()).start();new Thread(waitTest.new Producer()).start();new Thread(waitTest.new Consumer()).start();new Thread(waitTest.new Producer()).start();new Thread(waitTest.new Consumer()).start();}}使用ReentrantLock实现
juc并发包中的 Lock 框架是锁的一个抽象,通过对lock的lock()方法和unlock()方法实现了对锁的显示控制,而synchronize()则是对锁的隐性控制。
可重入锁,也叫做递归锁,指的是同一线程的外层函数获得锁之后 ,内层递归函数仍然有获取该锁的代码,但不受影响
简单来说,该锁维护这一个与获取锁相关的计数器,如果拥有锁的某个线程再次得到锁,那么获取计数器就加1,函数调用结束计数器就减1,然后锁需要被释放两次才能获得真正释放。
已经获取锁的线程进入其他需要相同锁的同步代码块不会被阻塞。
public class LockTest {private static int count = 0;private static final int buffCount = 10;private static Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();//创建两个条件变量,一个为缓冲区非满,一个为缓冲区非空private final Condition notFull = lock.newCondition();private final Condition notEmpty = lock.newCondition();class Producer implements Runnable {@Overridepublic void run() {for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}lock.lock();try {while (count == buffCount) {try {notFull.await();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}count++;System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-生产者生产,数量为:" + count);notEmpty.signal();} finally {lock.unlock();}}}}class Consumer implements Runnable {@Overridepublic void run() {for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}lock.lock();try {while (count == 0) {try {notEmpty.await();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}count--;System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-消费者消费,数量为:"+ count);notFull.signal();} finally {lock.unlock();}}}}public static void main(String[] args) {LockTest lockTest = new LockTest();new Thread(lockTest.new Producer()).start();new Thread(lockTest.new Consumer()).start();new Thread(lockTest.new Producer()).start();new Thread(lockTest.new Consumer()).start();new Thread(lockTest.new Producer()).start();new Thread(lockTest.new Consumer()).start();}
}
使用阻塞队列BlockingQueue实现
BlockingQueue即阻塞队列,拥有队列先进先出的特性,在某些情况下对阻塞队列的访问可能会造成阻塞。被阻塞的情况主要有如下两种:
- 当队列满了的时候进行入队列操作
- 当队列空了的时候进行出队列操作
阻塞队列是线程安全的,因为:
- 当一个线程对已经满了的阻塞队列进行入队操作时会阻塞,除非有另外一个线程进行了出队操作,
- 当一个线程对一个空的阻塞队列进行出队操作时也会阻塞,除非有另外一个线程进行了入队操作。
public class BlockingQueueTest {private static int count = 0;private final BlockingQueue blockingQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue(10);class Producer implements Runnable {@Overridepublic void run() {for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}try {blockingQueue.put(1);count++;System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-生产者生产,数量为:" + count);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}class Consumer implements Runnable {@Overridepublic void run() {for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}try {blockingQueue.take();count--;System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-消费者消费,数量为:"+ count);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}public static void main(String[] args) {BlockingQueueTest blockingQueueTest = new BlockingQueueTest();new Thread(blockingQueueTest.new Producer()).start();new Thread(blockingQueueTest.new Consumer()).start();new Thread(blockingQueueTest.new Producer()).start();new Thread(blockingQueueTest.new Consumer()).start();new Thread(blockingQueueTest.new Producer()).start();new Thread(blockingQueueTest.new Consumer()).start();}
}
信号量Semaphore的实现
Semaphore(信号量)是用来控制同时访问特定资源的线程数量,它通过协调各个线程,以保证合理的使用公共资源,在操作系统中是一个非常重要的问题,用来解决哲学家就餐问题。
Java中的Semaphore维护了一个许可集,一开始先设定这个许可集的数量,可以使用acquire()方法获得一个许可,当许可不足时会被阻塞,release()添加一个许可。
在下列代码中,还加入了另外一个mutex信号量,维护生产者消费者之间的同步关系,保证生产者和消费者之间的交替进行
public class SemaphoreTest {private static int count = 0;//创建三个信号量private final Semaphore notFull = new Semaphore(10);private final Semaphore notEmpty = new Semaphore(0);private final Semaphore mutex = new Semaphore(1);class Producer implements Runnable {@Overridepublic void run() {for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}try {notFull.acquire();//获取许可mutex.acquire();count++;System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-生产者生产,数量为:" + count);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}finally {mutex.release();//释放notEmpty.release();}}}}class Consumer implements Runnable {@Overridepublic void run() {for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}try {notEmpty.acquire();mutex.acquire();count--;System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-消费者消费,数量为:"+ count);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {mutex.release();notFull.release();}}}}public static void main(String[] args) {SemaphoreTest semaphoreTest = new SemaphoreTest();new Thread(semaphoreTest.new Producer()).start();new Thread(semaphoreTest.new Consumer()).start();new Thread(semaphoreTest.new Producer()).start();new Thread(semaphoreTest.new Consumer()).start();new Thread(semaphoreTest.new Producer()).start();new Thread(semaphoreTest.new Consumer()).start();}
}
管道输入输出流实现
在java的io包下,PipedOutputStream和PipedInputStream分别是管道输出流和管道输入流。
它们的作用是让多线程可以通过管道进行线程间的通讯。在使用管道通信时,必须将PipedOutputStream和PipedInputStream配套使用。
- 先创建一个管道输入流和管道输出流,然后将输入流和输出流进行连接,
- 用生产者线程往管道输出流中写入数据,消费者在管道输入流中读取数据,
- 这样就可以实现了不同线程间的相互通讯,
- 但是这种方式在生产者和生产者、消费者和消费者之间不能保证同步,也就是说在一个生产者和一个消费者的情况下是可以生产者和消费者之间交替运行的,多个生成者和多个消费者者之间则不行
public class PipedTest {private final PipedInputStream pis = new PipedInputStream();private final PipedOutputStream pos = new PipedOutputStream();{try {pis.connect(pos);} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}class Producer implements Runnable {@Overridepublic void run() {try {while(true) {Thread.sleep(1000);int num = (int) (Math.random() * 255);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "生产者生产了一个数字,该数字为: " + num);pos.write(num);pos.flush();}} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {try {pos.close();pis.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}class Consumer implements Runnable {@Overridepublic void run() {try {while(true) {Thread.sleep(1000);int num = pis.read();System.out.println("消费者消费了一个数字,该数字为:" + num);}} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {try {pos.close();pis.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}public static void main(String[] args) {PipedTest pipedTest = new PipedTest();new Thread(pipedTest.new Producer()).start();new Thread(pipedTest.new Consumer()).start();}
}