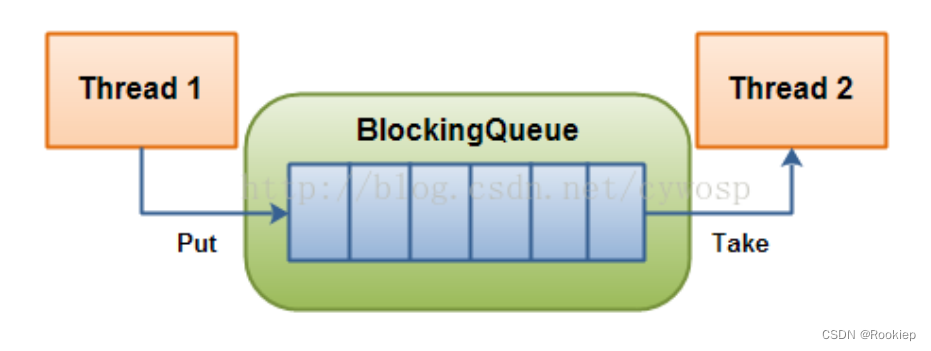
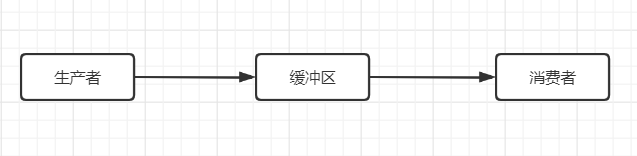
生产者消费者模型主要结构如下,是一个典型的线程同步的案例。下面就来使用java做几种线程同步的方式来实现以下该模型

确保一个生产者消费者模型的稳定运行的前提有以下几个
- 生成者应该具备持续生成的能力
- 消费者应该具备持续消费的能力
- 生产者的生成和消费消费有一定的阀值,如生成总量到100需要停止生产,通知消费;消费到0的时候停止消费开始生产;
- wait,notify方案
- ReentrantLock的实现
- 阻塞队列的实现
wait,notify方案
wait,notify方案 主要是通过,使用对象的wait方法和notify方法来实现线程的切换执行。其中我们可以看到对象的wait和notify或者notifyAll方法都是调用native的对应的方法来处理,追溯到最后也还是控制cpu进行不同的时间片的切换
下面这个例子比较简单,模拟一个生产速度大于消费速度的这样一个案例,在生产到阀值的时候停止生产通知消费者进行消费(wait)。消费者在消费到一定阀值的时候停止消费通知生产者进行生产(notifyall)
public class TestWaitNotifyConsumerAndProducer {/*当前生成数量*/static int currentNum = 0;/*最大生成数量*/static int MAX_NUM = 10;/*最小消费数量*/static int MIN_NUM = 0;/*wait和notify控制对象*/private static final String lock = "lock";public static void main(String args[]) {//创建一个生产者new Thread(new Producer()).start();//创建两个消费者new Thread(new Consumer()).start();new Thread(new Consumer()).start();}static class Producer implements Runnable {public void product() {while (true) {try {Thread.sleep(10);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}synchronized (lock) {currentNum++;System.out.println("Producer now product num:" + currentNum);lock.notifyAll();if (currentNum == MAX_NUM) {try {lock.wait();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}}@Overridepublic void run() {product();}}static class Consumer implements Runnable {public void consume() {while (true) {try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}synchronized (lock) {if (currentNum == MIN_NUM) {lock.notifyAll();continue;}System.out.println(new StringBuilder(Thread.currentThread().getName()).append(" Consumer now consumption num:").append(currentNum));currentNum--;}}}@Overridepublic void run() {consume();}}
}
ReentrantLock的实现
ReentrantLock 也是java.util.concurrent中显示锁的一种,允许同一个线程重复进入一段执行代码(递归),并且反复lock加锁。重复加锁相当于计数器累加,因此当一个线程想释放这个锁的时候就需要有对应的unlock执行。
如下这段代码依然是我们开篇讲到的生成和消费的模型,只是换了一种实现;这里特别注意的是可重入锁或者递归锁需要成对的出现lock和unlock否则执行Condition的await 或者signal的时候就可能如下抛出
java.lang.IllegalMonitorStateException
public class TestReentrantLockConsumerAndProducer {/*当前生成数量*/static int currentNum = 0;/*最大生成数量*/static int MAX_NUM = 10;/*最小消费数量*/static int MIN_NUM = 0;//创建一个锁对象private static Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();//缓冲区已空的变量private static final Condition emptyCondition = lock.newCondition();//缓冲区已满的变量private static final Condition fullCondition = lock.newCondition();public static void main(String args[]) {//创建一个生产者new Thread(new Producer()).start();//创建两个消费者new Thread(new Consumer()).start();new Thread(new Consumer()).start();}static class Producer implements Runnable {public void product() {while (true) {try {Thread.sleep(10);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}lock.lock();currentNum++;System.out.println("Producer now product num:" + currentNum);if (currentNum == MAX_NUM) {emptyCondition.signal();try {fullCondition.await();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}lock.unlock();}}@Overridepublic void run() {product();}}static class Consumer implements Runnable {public void consume() {while (true) {try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}lock.lock();if (currentNum == MIN_NUM) {fullCondition.signal();try {emptyCondition.await();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}continue;}System.out.println(new StringBuilder(Thread.currentThread().getName()).append(" Consumer now consumption num:").append(currentNum));currentNum--;lock.unlock();}}@Overridepublic void run() {consume();}}
}阻塞队列的实现
阻塞队列的实现本质上也还是基于可重入锁,只是进行了进一步的封装,有一个队列的数据结构
这里我们用到了一个数据结构LinkedBlockingDeque的双向队列的结构,当然我们使用任何一个阻塞队列都可以。这里主要用到阻塞队列超过最大容量的时候,自动阻塞等待;
这里使用了几个关键的方法peek,put,peekLast,take 这里大概看看相关源码。 这里源码我们不做过多解读,大概可以看到阻塞队列的内部实现也是依赖于可重入锁ReentrantLock,然后根据put和take的操作,动态的管理锁的获取和释放。
/** Maximum number of items in the deque */private final int capacity;/** Main lock guarding all access */final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();/** Condition for waiting takes */private final Condition notEmpty = lock.newCondition();/** Condition for waiting puts */private final Condition notFull = lock.newCondition();public E peekFirst() {final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;lock.lock();try {return (first == null) ? null : first.item;} finally {lock.unlock();}}public E peekLast() {final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;lock.lock();try {return (last == null) ? null : last.item;} finally {lock.unlock();}}//take元素的时候执行,可见如果当队列内容为空的时候阻塞public E takeFirst() throws InterruptedException {final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;lock.lock();try {E x;while ( (x = unlinkFirst()) == null)notEmpty.await();return x;} finally {lock.unlock();}}/*** Removes and returns first element, or null if empty.* 具体删除操作,当操作删除完成以后执行notFull.signal();释放notFull的阻塞*/private E unlinkFirst() {// assert lock.isHeldByCurrentThread();Node<E> f = first;if (f == null)return null;Node<E> n = f.next;E item = f.item;f.item = null;f.next = f; // help GCfirst = n;if (n == null)last = null;elsen.prev = null;--count;notFull.signal();return item;}/*** Links node as last element, or returns false if full.* 当执行成功添加时,释放notEmpty的信号*/private boolean linkLast(Node<E> node) {// assert lock.isHeldByCurrentThread();if (count >= capacity)return false;Node<E> l = last;node.prev = l;last = node;if (first == null)first = node;elsel.next = node;++count;notEmpty.signal();return true;}
public class TestBlockQueueConsumerAndProducer {/*最大生成数量*/static int MAX_NUM = 10;private static LinkedBlockingDeque mBlockQueue = new LinkedBlockingDeque<Integer>(MAX_NUM);public static void main(String args[]) {//创建一个生产者new Thread(new Producer()).start();//创建两个消费者new Thread(new Consumer()).start();//创建两个消费者new Thread(new Consumer()).start();}static class Producer implements Runnable {public void product() {while (true) {if (mBlockQueue.peek() == null) {try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {try {mBlockQueue.put(i);System.out.println("Producer now product num:" + i);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}}@Overridepublic void run() {product();}}static class Consumer implements Runnable {public void consume() {while (true) {try {Thread.sleep(500);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}Integer mLast = (Integer) mBlockQueue.peekLast();if (mLast != null && mLast == MAX_NUM) {try {int num = (Integer) mBlockQueue.take();System.out.println(new StringBuilder(Thread.currentThread().getName()).append(" Consumer now consumption num:").append(num));} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}@Overridepublic void run() {consume();}}
}