和前面的系列不同,布谷鸟这里没有现成的Python的包,使用我们需要自己写各种源码模块进行组合,达到布谷鸟搜索算法(CS)的功能。
这里的CS算法是面向过程的编程,都是自定义函数,不涉及类与对象。还是很简单的,知道原理的话可以看得懂的。
布谷鸟代码
# cuckoo_search via levy flight for global optimization
import numpy as np
import scipy.special as sc_special
import random
import timetime_start = time.time() # 记录开始时间
#a=[]
#生成莱维飞行的步长
def levy_flight(n, m, beta):"""This function implements Levy's flight.---------------------------------------------------Input parameters:n: Number of steps m: Number of dimensionsbeta: Power law index (note: 1 < beta < 2)Output:'n' levy steps in 'm' dimension"""sigma_u = (sc_special.gamma(1+beta)*np.sin(np.pi*beta/2)/(sc_special.gamma((1+beta)/2)*beta*(2**((beta-1)/2))))**(1/beta)sigma_v = 1u = np.random.normal(0, sigma_u, (n, m))v = np.random.normal(0, sigma_v, (n, m))steps = u/((np.abs(v))**(1/beta))return steps#计算每个鸟巢的适应值(即函数值)
def calc_fitness(fit_func, nests):"""calculate each nest's fitness---------------------------------------------------Input parameters:fit_func: User defined fitness evaluative functionnests: Nests' locationsOutput:Every nest's fitness"""n, m = nests.shapefitness = np.empty(n)for each_nest in range(n):fitness[each_nest] = fit_func(nests[each_nest])return fitness#产生鸟巢的位置
def generate_nests(n, m, lower_boundary, upper_boundary):"""Generate the nests' locations---------------------------------------------------Input parameters:n: Number of nestsm: Number of dimensionslower_boundary: Lower bounary (example: lower_boundary = (-2, -2, -2))upper_boundary: Upper boundary (example: upper_boundary = (2, 2, 2))Output:generated nests' locations"""lower_boundary = np.array(lower_boundary)upper_boundary = np.array(upper_boundary)nests = np.empty((n, m))for each_nest in range(n):nests[each_nest] = lower_boundary + np.array([np.random.rand() for _ in range(m)]) * (upper_boundary - lower_boundary)return nests#更新鸟巢的位置
def update_nests(fit_func, lower_boundary, upper_boundary, nests, best_nest, fitness, step_coefficient):"""This function is to get new nests' locations and use new better one to replace the old nest---------------------------------------------------Input parameters:fit_func: User defined fitness evaluative functionlower_boundary: Lower bounary (example: lower_boundary = (-2, -2, -2))upper_boundary: Upper boundary (example: upper_boundary = (2, 2, 2))nests: Old nests' locations best_nest: Nest with best fitnessfitness: Every nest's fitnessstep_coefficient: Step size scaling factor related to the problem's scale (default: 0.1)Output:Updated nests' locations"""lower_boundary = np.array(lower_boundary)upper_boundary = np.array(upper_boundary)n, m = nests.shape# generate steps using levy flightsteps = levy_flight(n, m, 1.5)new_nests = nests.copy()for each_nest in range(n):# coefficient 0.01 is to avoid levy flights becoming too aggresive# and (nest[each_nest] - best_nest) could let the best nest be remainedstep_size = step_coefficient * steps[each_nest] * (nests[each_nest] - best_nest)step_direction = np.random.rand(m)new_nests[each_nest] += step_size * step_direction# apply boundary condtionsnew_nests[each_nest][new_nests[each_nest] < lower_boundary] = lower_boundary[new_nests[each_nest] < lower_boundary]new_nests[each_nest][new_nests[each_nest] > upper_boundary] = upper_boundary[new_nests[each_nest] > upper_boundary]new_fitness = calc_fitness(fit_func, new_nests)nests[new_fitness > fitness] = new_nests[new_fitness > fitness]return nests#按照一定概率抛弃鸟蛋,换巢(局部搜索)
def abandon_nests(nests, lower_boundary, upper_boundary, pa):"""Some cuckoos' eggs are found by hosts, and are abandoned.So cuckoos need to find new nests.---------------------------------------------------Input parameters:nests: Current nests' locationslower_boundary: Lower bounary (example: lower_boundary = (-2, -2, -2))upper_boundary: Upper boundary (example: upper_boundary = (2, 2, 2))pa: Possibility that hosts find cuckoos' eggsOutput:Updated nests' locations"""lower_boundary = np.array(lower_boundary)upper_boundary = np.array(upper_boundary)n, m = nests.shapefor each_nest in range(n):if (np.random.rand() < pa):step_size = np.random.rand() * (nests[np.random.randint(0, n)] - nests[np.random.randint(0, n)])nests[each_nest] += step_size# apply boundary condtionsnests[each_nest][nests[each_nest] < lower_boundary] = lower_boundary[nests[each_nest] < lower_boundary]nests[each_nest][nests[each_nest] > upper_boundary] = upper_boundary[nests[each_nest] > upper_boundary]return nests#算法迭代
def cuckoo_search(n, m, fit_func, lower_boundary, upper_boundary, iter_num = 1000,pa = 0.25, beta = 1.5, step_size = 0.01):"""Cuckoo search function---------------------------------------------------Input parameters:n: Number of nestsm: Number of dimensionsfit_func: User defined fitness evaluative functionlower_boundary: Lower bounary (example: lower_boundary = (-2, -2, -2))upper_boundary: Upper boundary (example: upper_boundary = (2, 2, 2))iter_num: Number of iterations (default: 100) pa: Possibility that hosts find cuckoos' eggs (default: 0.25)beta: Power law index (note: 1 < beta < 2) (default: 1.5)step_size: Step size scaling factor related to the problem's scale (default: 0.1)Output:The best solution and its value"""# get initial nests' locations nests = generate_nests(n, m, lower_boundary, upper_boundary)fitness = calc_fitness(fit_func, nests)# get the best nest and record itbest_nest_index = np.argmin(fitness)best_fitness = fitness[best_nest_index]best_nest = nests[best_nest_index].copy()for _ in range(iter_num):nests = update_nests(fit_func, lower_boundary, upper_boundary, nests, best_nest, fitness, step_size)nests = abandon_nests(nests, lower_boundary, upper_boundary, pa)fitness = calc_fitness(fit_func, nests)min_nest_index = np.argmin(fitness)min_fitness = fitness[min_nest_index]min_nest = nests[min_nest_index]a.append(min_fitness)if (min_fitness < best_fitness):best_nest = min_nest.copy()best_fitness = min_fitnessreturn (best_nest, best_fitness)上述代码都是拆分为一个个小函数。最后的cuckoo_search是总体的搜索迭代的函数。
对布谷鸟算法的搜索能力,我们采用 Goldstein-Price函数进行测试。Goldstein-Price函数是二元八次多项式,是一个常见的用来进行算法测试的函数,可以用算法找它的局部最小值。该函数理论在x=0,y=-1处取得最小值3,该函数的公式如下:
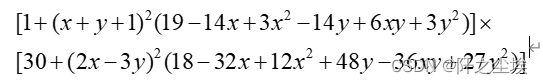
进行定义和计算
if __name__=='__main__':def fit_func(nest):x= nest #return 3*(1-x)**2*np.e**(-x**2-(y+1)**2) - 10*(x/5-x**3-y**5)*np.e**(-x**2-y**2) - (np.e**(-(x+1)**2-y**2))/3return (1+pow((1+x[0]+x[1]),2)*(19-14*x[0]+3*x[0]*x[0]-14*x[1]+6*x[0]*x[1]+3*x[1]*x[1]))*(30+pow((2*x[0]-3*x[1]),2)*(18-32*x[0]+12*x[0]*x[0]+48*x[1]-36*x[0]*x[1]+27*x[1]*x[1]))best_nest, best_fitness = cuckoo_search(100, 2, fit_func, [-3, -3], [3, 3],iter_num = 1000, step_size = 0.1)time_end = time.time() # 记录结束时间time_sum = time_end - time_start # 计算的时间差为程序的执行时间,单位为秒/sprint(time_sum)print('最小值为:%.5f, 在(%.5f, %.5f)处取到!'%(best_fitness, best_nest[0], best_nest[1]))
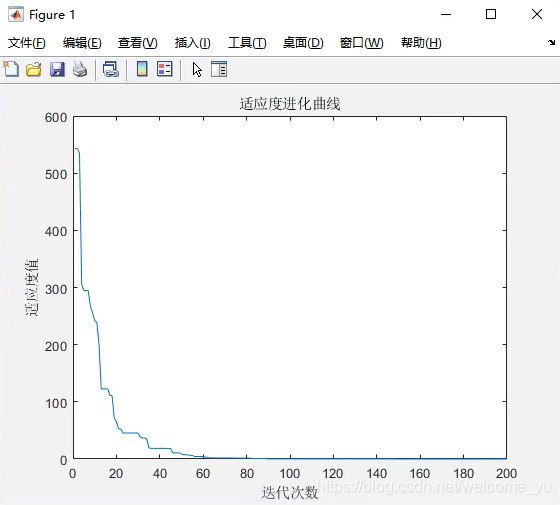
可以看到迭代1000次用时4s,还是很快的。和理论的最小值3很接近,x1和x2的值和真实值也还比较接近。
想复用这段代码到别的问题只需要改最后的这个fit_func()就行,返回你要评价的指标,布谷鸟会自动找最小值,并且告诉你参数为多少时取到。