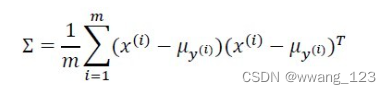布谷鸟搜索(Cuckoo Search,缩写 CS),也叫杜鹃搜索,是由剑桥大学杨新社(音译自:Xin-She Yang)教授和S.戴布(S.Deb)于2009年提出的一种新兴启发算法。
1.定义
CS算法是通过模拟某些种属布谷鸟的寄生育雏(BroodParasitism),来有效地求解最优化问题的算法。同时,CS也采用相关的Levy飞行搜索机制。
2.算法
(1)使用布谷鸟搜索算法的三个理想规则
a.每只布谷鸟一次只下一个蛋,然后把蛋放进随机选择的鸟巢里;(Each cuckoo lays one egg at a time, and dumps it in a randomly chosen nest)
b.在随机选择的鸟巢中,最好的鸟巢将被保留到下一代;(The best nests with high-quality eggs will be carried over to the next generations)
c.可用的寄主巢的数量是固定的,而且布谷鸟产卵的概率是由寄主鸟发现的。在这种情况下,宿主鸟要么扔掉蛋,要么干脆放弃鸟巢,建造一个全新的鸟巢。(The number of available host nests is fixed, and the egg laid by a cuckoo is discovered by the host bird with a probability . In this case, the host bird can either get rid of the egg, or simply abandon the nest and build a completely new nest)
从实现的角度来看,我们可以使用以下简单的表示法,即巢穴中的每个蛋代表一个解决方案,而每个布谷鸟只能产一个蛋(因此代表一个解决方案),目的是使用新的和潜在更好的解决方案(布谷鸟)来替换巢穴中不太好的解决方案。显然,该算法可以扩展到更复杂的情况,即每个嵌套有多个表示一组解的蛋。在目前的介绍中,我们将使用最简单的方法,即每个巢只有一个蛋。在这种情况下,蛋、巢或布谷鸟之间没有区别,因为每个巢对应一个蛋,也代表一只布谷鸟。
(2)算法相关参数
该算法采用局部随机游走和全局探索性随机游走的平衡组合,由切换参数控制。
局部随机游走可以写成:
![]()
(1)
其中,和
是通过随机置换随机选择的两个解,
是Heaviside函数,
是从均匀分布中提取的随机数,
是步长。⊗是一种新的运算符(点乘)。
另一方面,全局探索性随机游走是通过Levy飞行实现的:
![]()
而,
![]()
其中 ,这里是步长比例因子,它应该与感兴趣问题的规模相关。在大多数情况下,我们可以使用α=O(L/10),L是感兴趣问题的特征量表,而在某些情况下,α=O(L/100)可以更有效,避免飞得太远。上述方程本质上是随机行动的随机方程。一般来说,随机游走是一个马尔可夫链,其下一个状态/位置仅取决于当前位置(上述等式中的第一项)和转移概率(第二项)。
附:Levy Flight的简单代码实现
>> clc;
clear;
x = [0,0];
y = [0,0];
beta = 3/2;
alpha_u = (gamma(1+beta)*sin(pi*beta/2)/(gamma(((1+beta)/2)*beta*2^((beta-1)/2))))^(1/beta);
alpha_v = 1;
for i=1:1000 u=normrnd(0,alpha_u,1);v=normrnd(0,alpha_v,1);s = u/(abs(v))^(1/beta);x(:,1) = x(:,2);x(:,2) = x(:,1)+1*s;u=normrnd(0,alpha_u,1);v=normrnd(0,alpha_v,1);s = u/(abs(v))^(1/beta);y(:,1) = y(:,2);y(:,2) = y(:,1)+1*s;plot(x,y);hold on;
end
axis square;
3.特点
a.满足全局收敛性;
b.布谷鸟搜索有两种搜索能力:局部搜索和全局搜索,由切换/发现概率控制。局部搜索非常密集,大约占搜索时间的1/4,而全局搜索大约占总搜索时间的3/4。这使得搜索空间可以在全局范围内得到更有效的探索,从而以更高的概率找到全局最优性。
4.算法步骤
步骤1:设置鸟巢的个数为n,搜索空间的维数为d,初始化鸟巢的位置,并找出最优鸟巢的位置
,
和最优解
;
步骤2:循环体
(1)保留上代最优鸟巢的位置,
为整数,并利用(1)式更新其他鸟巢的位置;
(2)利用Levy Flight得到一组新的鸟巢的位置;
(3)与上一组产生的鸟巢位置进行对比,用适应值较好的鸟巢位置替换适应值较差的鸟巢位置,从而得到一组较优的鸟巢位置
;
(4)通过位置更新后,用随机数与宿主鸟发现外来鸟蛋的概率是
(
一般设置为0.25)进行对比,若
,则对
的位置进行随机改变。保留
中发现概率较小的鸟蛋的位置,并随机改变发现概率较大的鸟巢的位置,得到一组新的鸟巢的位置,与
中鸟巢的位置进行对,用测试值较好的鸟巢位置代替测试值较差的鸟巢位置,得到一组较优的鸟巢位置
;
步骤3:找出步骤2中最后得到的中的最优鸟巢位置
和最优值
,若达到迭代条件(规定的迭代次数或要求的精度)则输出全局最优值
和全局最优位置
,反之,返回步骤2继续迭代更新。

附.布谷鸟算法Java实现(别人写的)
package com.gxx.matrix;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random;/*** 布谷鸟算法* 原理是,使用多个 散列函数,通过计算放到 表 中,当其中一个散列函数计算到的对应位置为空,则放入,* 当都不为空就进行一层层替换,达到一定次数后还是插入不了,则进行扩容,或者重新散列*/
public class Cuckoo {private String [] array ;//表private static final int DEFAULTSIZE = 7;private int size ;private int reHash =0;private int tryCount = 33;List<HashAlgorithm> hashAlgorithmList = new ArrayList<HashAlgorithm>();{//初始2个散列函数。hashAlgorithmList.add(new HashAlgorithm(17));hashAlgorithmList.add(new HashAlgorithm(23));}void remove(String key){if (key == null) {return;}for (HashAlgorithm hashAlgorithm : hashAlgorithmList) {//遍历算法集合 计算index值,int hashCode = hashAlgorithm.hashCode(key);int index = getIndex(hashCode);if (array[index]!=null && array[index].equals(key)) {array[index] = null;size--;}}}void insert(String key){while(true){for (int i = 0; i < tryCount; i++) {for (HashAlgorithm hashAlgorithm : hashAlgorithmList) {//遍历算法集合 计算index值,int hashCode = hashAlgorithm.hashCode(key);int index = getIndex(hashCode);if (array[index] == null ) {array[index] = key;//当表中索引无值,将元素放到表中size++;return;}}//执行到这说明 算法集合计算的index全部有值 进行替换操作int hashAlgorithmListIndex = new Random().nextInt(hashAlgorithmList.size());//随机选取一个函数int hashCode = hashAlgorithmList.get(hashAlgorithmListIndex).hashCode(key);int index = getIndex(hashCode);String oldKey = array[index];//原本表中这个索引对应的值array[index] = key;//把要插入的值 放到当前索引上key = oldKey; //现在就是要插入原来替换掉的值}if (++reHash >1 || size>=array.length) {//说明要进行扩容操作了expandArray();reHash =0;}else {computeHash();//重新计算hash值}}}/*** 更新 hash函数 重新计算*/private void computeHash() {hashAlgorithmList.clear();//清空原有的函数int one = new Random().nextInt(100);int two = new Random().nextInt(100);two = one == two ? two*2 : two;//只是两个不一样的值hashAlgorithmList.add(new HashAlgorithm(one));hashAlgorithmList.add(new HashAlgorithm(two));rehash(array.length);}private void expandArray() {rehash(nextPrime(array.length*2));}/*** 重新计算所有的 hash 同时放到表中* @param length*/private void rehash(int length) {String [] oldArray = array;array = new String[length];size = 0 ;for (String string : oldArray) {if (string != null) {insert(string);}}}public static void main(String[] args) {Cuckoo cuckoo = new Cuckoo();for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {cuckoo.insert("a"+new Random().nextInt(1000));}for (String string : cuckoo.array) {System.out.println(string);}}//素数计算public static Integer nextPrime(Integer begin) {int i;int j;for (i = begin;; i++) {boolean flag = true;for (j = 2; j <= i / 2; j++) {if (i % j == 0) {flag = false;break;} else if (i % j != 0) {continue;} else {break;}}if (flag) {return i;}}}/*** 是否包含当前元素* @param key* @return*/Boolean cotains(String key){for (HashAlgorithm hashAlgorithm : hashAlgorithmList) {int hashCode = hashAlgorithm.hashCode(key);int index = getIndex(hashCode);if (array[index] !=null ) {return true;}}return false;}/*** 获取hash值对应的表中索引* @param hashCode* @return*/int getIndex(int hashCode){int index = hashCode % array.length;index = index < 0 ? index + array.length : index;return index;}public Cuckoo() {this(DEFAULTSIZE);}public Cuckoo(int size) {array = new String[size];}public int getSize() {return size;}//定义散列函数集合class HashAlgorithm{private int initNumber;public HashAlgorithm(int initNumber) {super();this.initNumber = initNumber;}public int hashCode(String key){return (initNumber +key).hashCode();//传递进来的固定值 +key 模拟两个不同的 hashcode}}
}5.应用
a.Walton等人改进的布谷鸟搜索已被证明对解决网格搜索等非线性问题非常有效;
b.Vazquez使用布谷鸟搜索来训练尖峰神经网络模型;
c.Chifu等人使用布谷鸟搜索优化语义web服务组合过程;
d.Kumar和Chakarverty使用布谷鸟搜索实现了可靠嵌入式系统的优化设计;
e.Kaveh和Bakhshpoori使用CS成功设计了钢框架;
f.Yildiz使用CS在铣削操作中选择最佳的机器参数,结果得到了增强;
g.Zheng和Zhou则提供了一种使用高斯过程的布谷鸟搜索
h.Tein和Ramli提出了一种离散布谷鸟搜索算法来解决护士排班问题;
i.布谷鸟搜索也被用于生成软件测试和测试数据生成的独立路径;
j.布谷鸟搜索与基于量子的方法相结合的一种变体已经被开发出来,以有效地解决背包问题。