布谷鸟算法
- 一、布谷鸟算法背景知识
- 二、布谷鸟算法思想简介
- 三、布谷鸟算法流程
- 四、布谷鸟算法的Python实现
- 五、布谷鸟算法matlab实现
一、布谷鸟算法背景知识
2009年,Xin-She Yang 与Suash Deb在《Cuckoo Search via Levy Flights》一文中提出了布谷鸟算法(简称CS)。假设每只布谷鸟一次只产一枚卵 ,并且宿主鸟发现外来鸟蛋后,就舍弃该鸟窝,另寻他地建造新的鸟窝 ,那么可以认为 :鸟窝=卵蛋=解,卵蛋是否能够成功被宿主鸟孵化并茁长成长是衡量解好坏的唯一标准 。布谷鸟寻找鸟窝下蛋的过程就是在D维空间中寻找解的过程 ,而鸟窝的好坏象征着解的好坏。
二、布谷鸟算法思想简介
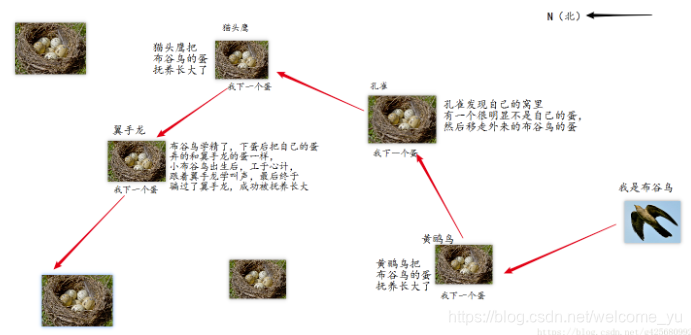
如图所示,布谷鸟下蛋之后会把蛋扔到其他鸟的鸟窝,为了不被宿主鸟发现,它会扔掉宿主鸟一个蛋,并且把蛋装扮成与宿主鸟的蛋外观相似,被宿主鸟发现之后会被移走,没有被宿主鸟发现则会被宿主鸟养育长大,一段时间后,布谷鸟下蛋了,小布谷鸟出生,会移走宿主鸟的一只蛋,继续按照上面的方式进行。
它的大致过程整理下:

更新位置方式:
更新位置的方式会关系到最后算法的收敛速度,在上述的算法步骤中,我们在第3步和第4步都需要更新点的位置。通过随机行走(random walk)的方式更新点的位置,随机生成一个方向和长度,叠加到原有点上就成了新的点,但是需要指出的是,这个随机生成的方向和长度都是有讲究的,有研究发现通过莱维飞行(Levy Flight)的方式能比较有效地去寻找全局最优解而不至于陷入局部最优解中,并且它和布谷鸟算法配合达到了相当不错的效果,接下来就是解答什么是莱维飞行了。
莱维飞行
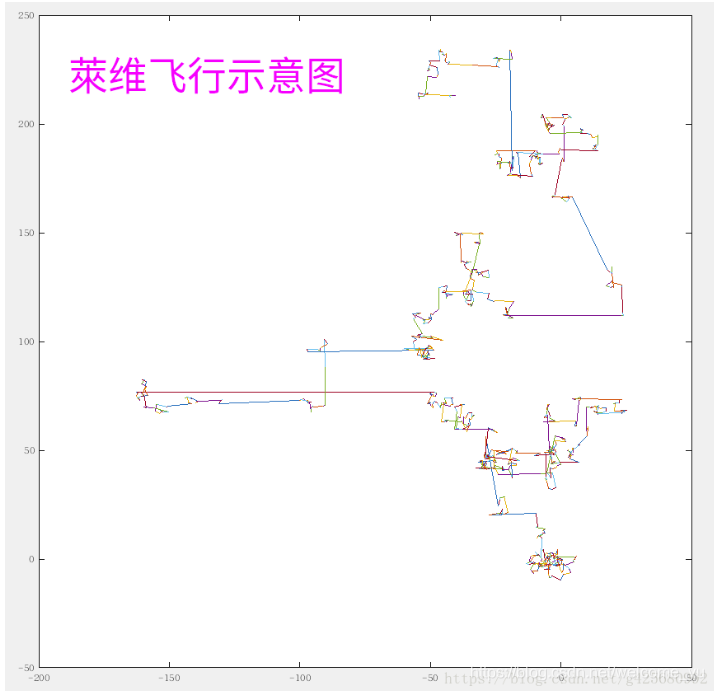
莱维飞行是由较长时间的短步长和较短时间的长步长组成。
点大多数时间只有小距离移动,偶尔会有大距离移动的情况。这和自然界中大多数动物觅食方式类似。
找到一块区域后细致的查找猎物,如果没找到,就换一片区域。
那么如何实现这种移动方式呢?
假设我们是捕猎者出去捕猎,刚开始会随机选个方向,接着确定要走多远。
Levy分布要求大概率落在值比较小的位置,小概率落在值比较大的位置,刚好满足这种均匀分布。
局部随机行走:
计算公式为:
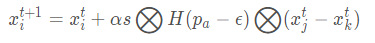

它只适用于局部,容易陷入局部最优解,优点是比较稳定。相对于莱维飞行,它最大程度利用已有点的位置信息,新产生的点便是这些已有点的“折中”。
三、布谷鸟算法流程
伪代码:

四、布谷鸟算法的Python实现
布谷鸟算法提出者之一的Xin-She Yang教授试了多组参数,发现种群规模在15到40,布谷鸟蛋被发现的概率 pa 取0.25时,对于大多数优化问题已足够,并且结果和分析也表明收敛速度在一定程度上对所使用的参数不敏感。这意味着对于任何问题都不需要进行仔细地调整。至于迭代次数,我在实验中发现100次的迭代次数已能很好地找到最优解,但迭代次数往往取决你问题的规模.
import numpy as np
import scipy.special as sc_specialversion = '1.0.0'def cuckoo_search(n, m, fit_func, lower_boundary, upper_boundary, iter_num = 100,pa = 0.25, beta = 1.5, step_size = 0.1):"""Cuckoo search function---------------------------------------------------Input parameters:n: Number of nestsm: Number of dimensionsfit_func: User defined fitness evaluative functionlower_boundary: Lower bounary (example: lower_boundary = (-2, -2, -2))upper_boundary: Upper boundary (example: upper_boundary = (2, 2, 2))iter_num: Number of iterations (default: 100) pa: Possibility that hosts find cuckoos' eggs (default: 0.25)beta: Power law index (note: 1 < beta < 2) (default: 1.5)step_size: Step size scaling factor related to the problem's scale (default: 0.1)Output:The best solution and its value"""# get initial nests' locations nests = generate_nests(n, m, lower_boundary, upper_boundary)fitness = calc_fitness(fit_func, nests)# get the best nest and record itbest_nest_index = np.argmax(fitness)best_fitness = fitness[best_nest_index]best_nest = nests[best_nest_index].copy()for _ in range(iter_num):nests = update_nests(fit_func, lower_boundary, upper_boundary, nests, best_nest, fitness, step_size)nests = abandon_nests(nests, lower_boundary, upper_boundary, pa)fitness = calc_fitness(fit_func, nests)max_nest_index = np.argmax(fitness)max_fitness = fitness[max_nest_index]max_nest = nests[max_nest_index]if (max_fitness > best_fitness):best_nest = max_nest.copy()best_fitness = max_fitnessreturn (best_nest, best_fitness)def generate_nests(n, m, lower_boundary, upper_boundary):"""Generate the nests' locations---------------------------------------------------Input parameters:n: Number of nestsm: Number of dimensionslower_boundary: Lower bounary (example: lower_boundary = (-2, -2, -2))upper_boundary: Upper boundary (example: upper_boundary = (2, 2, 2))Output:generated nests' locations"""lower_boundary = np.array(lower_boundary)upper_boundary = np.array(upper_boundary)nests = np.empty((n, m))for each_nest in range(n):nests[each_nest] = lower_boundary + np.array([np.random.rand() for _ in range(m)]) * (upper_boundary - lower_boundary)return nestsdef update_nests(fit_func, lower_boundary, upper_boundary, nests, best_nest, fitness, step_coefficient):"""This function is to get new nests' locations and use new better one to replace the old nest---------------------------------------------------Input parameters:fit_func: User defined fitness evaluative functionlower_boundary: Lower bounary (example: lower_boundary = (-2, -2, -2))upper_boundary: Upper boundary (example: upper_boundary = (2, 2, 2))nests: Old nests' locations best_nest: Nest with best fitnessfitness: Every nest's fitnessstep_coefficient: Step size scaling factor related to the problem's scale (default: 0.1)Output:Updated nests' locations"""lower_boundary = np.array(lower_boundary)upper_boundary = np.array(upper_boundary)n, m = nests.shape# generate steps using levy flightsteps = levy_flight(n, m, 1.5)new_nests = nests.copy()for each_nest in range(n):# coefficient 0.01 is to avoid levy flights becoming too aggresive# and (nest[each_nest] - best_nest) could let the best nest be remainedstep_size = step_coefficient * steps[each_nest] * (nests[each_nest] - best_nest)step_direction = np.random.rand(m)new_nests[each_nest] += step_size * step_direction# apply boundary condtionsnew_nests[each_nest][new_nests[each_nest] < lower_boundary] = lower_boundary[new_nests[each_nest] < lower_boundary]new_nests[each_nest][new_nests[each_nest] > upper_boundary] = upper_boundary[new_nests[each_nest] > upper_boundary]new_fitness = calc_fitness(fit_func, new_nests)nests[new_fitness > fitness] = new_nests[new_fitness > fitness]return nestsdef abandon_nests(nests, lower_boundary, upper_boundary, pa):"""Some cuckoos' eggs are found by hosts, and are abandoned.So cuckoos need to find new nests.---------------------------------------------------Input parameters:nests: Current nests' locationslower_boundary: Lower bounary (example: lower_boundary = (-2, -2, -2))upper_boundary: Upper boundary (example: upper_boundary = (2, 2, 2))pa: Possibility that hosts find cuckoos' eggsOutput:Updated nests' locations"""lower_boundary = np.array(lower_boundary)upper_boundary = np.array(upper_boundary)n, m = nests.shapefor each_nest in range(n):if (np.random.rand() < pa):step_size = np.random.rand() * (nests[np.random.randint(0, n)] - nests[np.random.randint(0, n)])nests[each_nest] += step_size# apply boundary condtionsnests[each_nest][nests[each_nest] < lower_boundary] = lower_boundary[nests[each_nest] < lower_boundary]nests[each_nest][nests[each_nest] > upper_boundary] = upper_boundary[nests[each_nest] > upper_boundary]return nestsdef levy_flight(n, m, beta):"""This function implements Levy's flight.---------------------------------------------------Input parameters:n: Number of steps m: Number of dimensionsbeta: Power law index (note: 1 < beta < 2)Output:'n' levy steps in 'm' dimension"""sigma_u = (sc_special.gamma(1+beta)*np.sin(np.pi*beta/2)/(sc_special.gamma((1+beta)/2)*beta*(2**((beta-1)/2))))**(1/beta)sigma_v = 1u = np.random.normal(0, sigma_u, (n, m))v = np.random.normal(0, sigma_v, (n, m))steps = u/((np.abs(v))**(1/beta))return stepsdef calc_fitness(fit_func, nests):"""calculate each nest's fitness---------------------------------------------------Input parameters:fit_func: User defined fitness evaluative functionnests: Nests' locationsOutput:Every nest's fitness"""n, m = nests.shapefitness = np.empty(n)for each_nest in range(n):fitness[each_nest] = fit_func(nests[each_nest])return fitnessif __name__=='__main__':def fit_func(nest):x, y = nest return 3*(1-x)**2*np.e**(-x**2-(y+1)**2) - 10*(x/5-x**3-y**5)*np.e**(-x**2-y**2) - (np.e**(-(x+1)**2-y**2))/3best_nest, best_fitness = cuckoo_search(25, 2, fit_func, [-3, -3], [3, 3], step_size = 0.4)print('最大值为:%.5f, 在(%.5f, %.5f)处取到!'%(best_fitness, best_nest[0], best_nest[1]))
python运行结果显示:
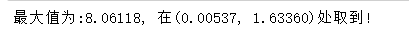
代码链接:
Python源码:
https://github.com/SJ2050SJ/Optimization_Algorithms
五、布谷鸟算法matlab实现
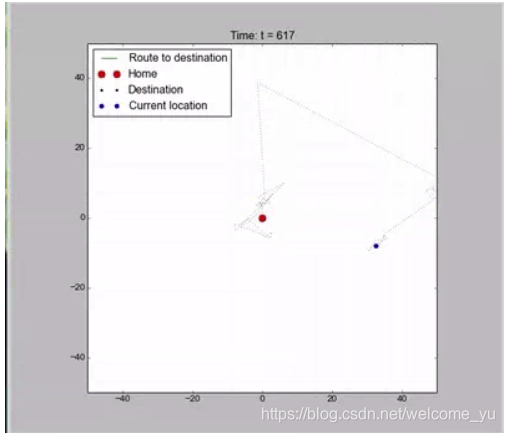
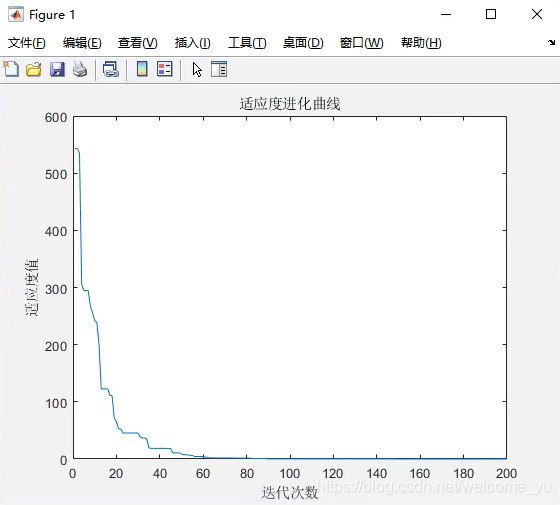
matlab运行结果显示:
代码链接:
matlab源码:
链接1:https://download.csdn.net/download/welcome_yu/14023295
链接2:https://download.csdn.net/download/g425680992/10517545
链接3:https://betterbench.blog.csdn.net/article/details/107285451?utm_medium=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task-blog-BlogCommendFromBaidu-2.control&depth_1-utm_source=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task-blog-BlogCommendFromBaidu-2.control
参考:
Xin-She Yang. 《Nature Inspired Optimization Algorithm.2nd》
布谷鸟算法学习1https://blog.csdn.net/sj2050/article/details/98496868?utm_medium=distribute.pc_relevant_download.none-task-blog-baidujs-2.nonecase&depth_1-utm_source=distribute.pc_relevant_download.none-task-blog-baidujs-2.nonecase
布谷鸟算法学习2 https://betterbench.blog.csdn.net/article/details/107285451?utm_medium=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task-blog-BlogCommendFromBaidu-2.control&depth_1-utm_source=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task-blog-BlogCommendFromBaidu-2.control
布谷鸟算法学习3 https://blog.csdn.net/zyqblog/article/details/80905019