布谷鸟搜索算法(Cuckoo Search,CS)
布谷鸟算法的启发当然来自于布谷鸟,因为布谷鸟这种鸟很有意思,生出来的孩子自己不养,直接被扔到其他鸟的鸟巢中去了,但有时候,这些布谷鸟蛋会被被寄宿的那些鸟妈妈发现,然后就被抛弃,有时候,这些宿主会直接放弃整个鸟巢寻找新住处。然而道高一尺魔高一丈,有些品种的布谷鸟生下来的布谷鸟蛋的颜色能和去寄宿的鸟的鸟蛋颜色很相似,并且布谷鸟的破壳时间往往比那些宿主的鸟蛋早,这样,一旦小布谷鸟破壳,它就会将一些鸟蛋扔出鸟巢去以求获得更多的食物,并且,小布谷鸟能模拟宿主鸟孩子的叫声来骗取更多的食物!简单来说,就是如何更高效地去骗吃骗喝。
流程图如下图所示。

程序如下:
import numpy as np
import scipy.special as sc_special
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #matplotlib的pyplot模块一般是最常用的,可以方便用户快速绘制二位图表
from matplotlib import cm #matplotlib是python最著名的绘图库
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D #3D绘图
"""Cuckoo search function---------------------------------------------------Input parameters:n: 巢的数量m: 维数fit_func: 适用度函数lower_boundary: 下边界upper_boundary: 上边界iter_num: 迭代次数 (默认: 100)pa: 被宿主发现蛋的概率 (default: 0.25)beta:与问题规模相关的步长比例因子 (note: 1 < beta < 2) (default: 1.5)step_size: 与问题规模相关的步长比例因子 (default: 0.1)Output:最佳解决方案及值
"""#绘制图像
def plot_3d(ax):x = np.arange(-3, 3, 0.1) #在指定的间隔内返回均匀间隔的数字y = np.arange(-3, 3, 0.1)x,y = np.meshgrid(x, y)z = 3*(1-x)**2*np.e**(-x**2-(y+1)**2) - 10*(x/5-x**3-y**5)*np.e**(-x**2-y**2) - (np.e**(-(x+1)**2-y**2))/3ax.plot_surface(x,y,z,rstride=1,cstride=1,cmap=cm.coolwarm)# rstride:行之间的跨度 cstride:列之间的跨度,cmap是颜色映射表ax.set_zlim(-10,10) ##坐标系的下边界和上边界ax.set_xlabel('x')ax.set_ylabel('y')ax.set_zlabel('z')plt.pause(3) #延时plt.show() #显示def fit_func(nest):x, y = nestreturn 3*(1-x)**2*np.e**(-x**2-(y+1)**2) - 10*(x/5-x**3-y**5)*np.e**(-x**2-y**2) - (np.e**(-(x+1)**2-y**2))/3#计算适应度
def calc_fitness(fit_func, nests):n, m = nests.shapefitness = np.empty(n)for each_nest in range(n):fitness[each_nest] = fit_func(nests[each_nest])return fitness#主要过程
def cuckoo_search(n, m, fit_func, lower_boundary, upper_boundary, iter_num = 100,pa = 0.25, beta = 1.5, step_size = 0.1):# 得到最初蛋的位置nests = generate_nests(n, m, lower_boundary, upper_boundary)fitness = calc_fitness(fit_func, nests)# 得到最好的巢的位置并更新best_nest_index = np.argmax(fitness)best_fitness = fitness[best_nest_index]best_nest = nests[best_nest_index].copy()for _ in range(iter_num):nests = update_nests(fit_func, lower_boundary, upper_boundary, nests, best_nest, fitness, step_size)nests = abandon_nests(nests, lower_boundary, upper_boundary, pa)fitness = calc_fitness(fit_func, nests)x=np.empty((n, 1))y=np.empty((n, 1))z=np.empty((n, 1))for i in range(20):x[i],y[i]=nests[i]z=3*(1-x)**2*np.e**(-x**2-(y+1)**2) - 10*(x/5-x**3-y**5)*np.e**(-x**2-y**2) - (np.e**(-(x+1)**2-y**2))/3if 'sca' in locals():sca.remove()sca = ax.scatter(x, y, z, c='black', marker='o');plt.show();plt.pause(0.1) #ax.scatter特征值散点图max_nest_index = np.argmax(fitness)max_fitness = fitness[max_nest_index]max_nest = nests[max_nest_index]if (max_fitness > best_fitness):best_nest = max_nest.copy()best_fitness = max_fitnessreturn (best_nest, best_fitness)#生成巢穴位置
def generate_nests(n, m, lower_boundary, upper_boundary):lower_boundary = np.array(lower_boundary) #转成矩阵形式upper_boundary = np.array(upper_boundary)nests = np.empty((n, m)) #生成n行m列的数组for each_nest in range(n):nests[each_nest] = lower_boundary + np.array([np.random.rand() for _ in range(m)]) * (upper_boundary - lower_boundary) #生成在[-3,3]范围内的下x,y的n个样本,即20*2的矩阵return nests#获取新的巢穴位置并用好的替换掉旧的不好的
def update_nests(fit_func, lower_boundary, upper_boundary, nests, best_nest, fitness, step_coefficient):lower_boundary = np.array(lower_boundary)upper_boundary = np.array(upper_boundary)n, m = nests.shape# 使用莱维飞行产生步长steps = levy_flight(n, m, 1.5)new_nests = nests.copy()for each_nest in range(n):# coefficient 0.01 is to avoid levy flights becoming too aggresive# and (nest[each_nest] - best_nest) could let the best nest be remainedstep_size = step_coefficient * steps[each_nest] * (nests[each_nest] - best_nest)step_direction = np.random.rand(m)new_nests[each_nest] += step_size * step_direction# apply boundary condtionsnew_nests[each_nest][new_nests[each_nest] < lower_boundary] = lower_boundary[new_nests[each_nest] < lower_boundary]new_nests[each_nest][new_nests[each_nest] > upper_boundary] = upper_boundary[new_nests[each_nest] > upper_boundary]new_fitness = calc_fitness(fit_func, new_nests)nests[new_fitness > fitness] = new_nests[new_fitness > fitness]return nests#卵被丢弃寻找新巢
def abandon_nests(nests, lower_boundary, upper_boundary, pa):lower_boundary = np.array(lower_boundary)upper_boundary = np.array(upper_boundary)n, m = nests.shapefor each_nest in range(n):if (np.random.rand() < pa):step_size = np.random.rand() * (nests[np.random.randint(0, n)] - nests[np.random.randint(0, n)])nests[each_nest] += step_size# apply boundary condtionsnests[each_nest][nests[each_nest] < lower_boundary] = lower_boundary[nests[each_nest] < lower_boundary]nests[each_nest][nests[each_nest] > upper_boundary] = upper_boundary[nests[each_nest] > upper_boundary]return nests#计算莱维飞行
def levy_flight(n, m, beta):sigma_u = (sc_special.gamma(1+beta)*np.sin(np.pi*beta/2)/(sc_special.gamma((1+beta)/2)*beta*(2**((beta-1)/2))))**(1/beta)sigma_v = 1u = np.random.normal(0, sigma_u, (n, m))v = np.random.normal(0, sigma_v, (n, m))steps = u/((np.abs(v))**(1/beta)) #steps为20*2的矩阵return steps#主函数
if __name__=='__main__':fig = plt.figure() #绘制背景图ax = Axes3D(fig)plt.ion()#将画图模式改为交互模式,程序遇到plt.show不会暂停,而是继续执行plot_3d(ax)best_nest, best_fitness = cuckoo_search(25, 2, fit_func, [-3, -3], [3, 3], step_size = 0.4)print('最大值为:%.5f, 在(%.5f, %.5f)处取到!'%(best_fitness, best_nest[0], best_nest[1]))plt.ioff() #将画图交互模式关闭plot_3d(ax)
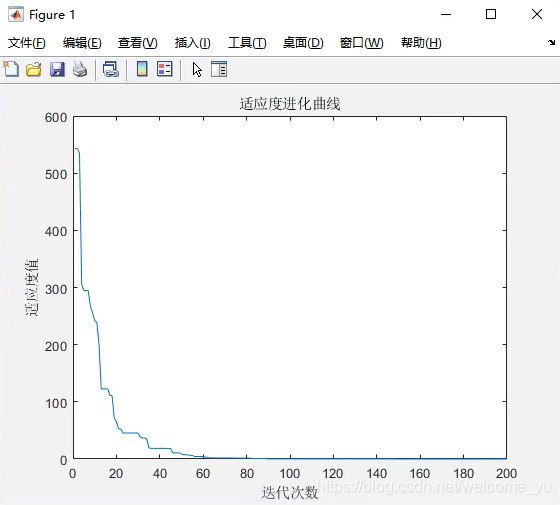
运行后图像及结果如图所示