转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/cheney23reg/archive/2010/08/08/1795067.html
http://wiki.multimedia.cx/index.php?title=PCM
PCM数据格式
PCM(Pulse Code Modulation)也被称为 脉码编码调制。PCM中的声音数据没有被压缩,如果是单声道的文件,采样数据按时间的先后顺序依次存入。(它的基本组织单位是BYTE(8bit)或WORD(16bit))
一般情况下,一帧PCM是由2048次采样组成的( 参考 http://discussion.forum.nokia.com/forum/showthread.php?129458-请问PCM格式的音频流,每次读入或输出的块的大小是必须固定为4096B么&s=e79e9dd1707157281e3725a163844c49 )。
如果是双声道的文件,采样数据按时间先后顺序交叉地存入。如图所示:
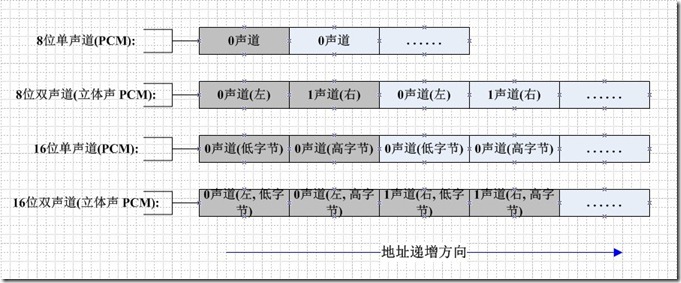
PCM的每个样本值包含在一个整数i中,i的长度为容纳指定样本长度所需的最小字节数。
首先存储低有效字节,表示样本幅度的位放在i的高有效位上,剩下的位置为0,这样8位和16位的PCM波形样本的数据格式如下所示。
样本大小 数据格式 最小值 最大值
8位PCM unsigned int 0 225
16位PCM int -32767 32767
PCM Parameters
PCM audio is coded using a combination of various parameters.
Resolution/Sample Size
This parameter specifies the amount of data used to represent each discrete amplitude sample. The most common values are 8 bits (1 byte), which gives a range of 256 amplitude steps, or 16 bits (2 bytes), which gives a range of 65536 amplitude steps. Other sizes, such as 12, 20, and 24 bits, are occasionally seen. Some king-sized formats even opt for 32 and 64 bits per sample.
Byte Order
When more than one byte is used to represent a PCM sample, the byte order (big endian vs. little endian) must be known. Due to the widespread use of little-endian Intel CPUs, little-endian PCM tends to be the most common byte orientation.
Sign
It is not enough to know that a PCM sample is, for example, 8 bits wide. Whether the sample is signed or unsigned is needed to understand the range. If the sample is unsigned, the sample range is 0..255 with a centerpoint of 128. If the sample is signed, the sample range is -128..127 with a centerpoint of 0. If a PCM type is signed, the sign encoding is almost always 2's complement. In very rare cases, signed PCM audio is represented as a series of sign/magnitude coded numbers.
Channels And Interleaving
If the PCM type is monaural, each sample will belong to that one channel. If there is more than one channel, the channels will almost always be interleaved: Left sample, right sample, left, right, etc., in the case of stereo interleaved data. In some rare cases, usually when optimized for special playback hardware, chunks of audio destined for different channels will not be interleaved.
Frequency And Sample Rate
This parameter measures how many samples/channel are played each second. Frequency is measured in samples/second (Hz). Common frequency values include 8000, 11025, 16000, 22050, 32000, 44100, and 48000 Hz.
Integer Or Floating Point
Most PCM formats encode samples using integers. However, some applications which demand higher precision will store and process PCM samples using floating point numbers.
Floating-point PCM samples (32- or 64-bit in size) are zero-centred and varies in the interval [-1.0, 1.0], thus signed values.
PCM Types
Linear PCM
The most common PCM type.
Logarithmic PCM
Rather than representing sample amplitudes on a linear scale as linear PCM coding does, logarithmic PCM coding plots the amplitudes on a logarithmic scale. Log PCM is more often used in telephony and communications applications than in entertainment multimedia applications.
There are two major variants of log PCM: mu-law (u-law) and A-law. Mu-law coding uses the format number 0x07 in Microsoft multimedia files (WAV/AVI/ASF) and the fourcc 'ulaw' in Apple Quicktime files. A-law coding uses the format number 0x06 is Microsoft multimedia files and the fourcc 'alaw' in Apple Quicktime files.
Every byte of a log PCM data chunk maps to a signed 16-bit linear PCM sample. [TODO: Add either the conversion tables or conversion formulas]
Differential PCM
Values are encoded as differences between the current and the previous value. This reduces the number of bits required per audio sample by about 25% compared to PCM.
Adaptive DPCM
The size of the quantization step is varied to allow further reduction of the required bandwidth for a given signal-to-noise ratio.
Platform-Specific PCM Identifiers And Characteristics
This section describes how different computing platforms store PCM audio data and any format identifiers they use.
DOS/Windows
The first widely available, PC audio card that could play back PCM audio was the Creative Labs' Sound Blaster. This drove the audio format for a lot of early audio-capable DOS applications and games. The original Sound Blaster could only play mono, unsigned 8-bit PCM data. Later Sound Blaster cards were capable of playing back 16-bit audio data. However, while these cards still played unsigned 8-bit PCM data, 16-bit data needed be signed.
Likely owing to the DOS/Intel little endian architecture, 16-bit PCM for the Sound Blaster also needs to be little endian.
Further, the original Sound Blaster was somewhat limited in the frequencies that it could support. The digital to analog conversion hardware (DAC) had to be programmed with a byte value (frequency divisor) that was processed through the following formula to yield the final playback frequency:
frequency = 1000000 / (256 - frequency_divisor)
A common divisor is 211 which yields an integer frequency of 22222 Hz, a common rate in the days of the Sound Blaster. Note that while very low frequencies (all the way down to 3921 Hz) were supported, frequencies above 45454 Hz were not.
Microsoft WAV/AVI/ASF Identifiers
Microsoft multimedia file formats such as WAV, AVI, and ASF all share the WAVEFORMATEX data structure. The structure defines, among other properties, a 16-bit little endian audio identifier. The following audio identifiers correspond to various PCM formats:
- 0x0001 denotes linear PCM
- 0x0006 denotes A-law logarithmic PCM
- 0x0007 denotes mu-law logarithmic PCM
Apple Macintosh
Native sample rates of early Apple Macintosh audio hardware included 11127 Hz and 22254 Hz. These sample rates are commonly seen in early QuickTime files.
Apple QuickTime Identifiers
Audio information in QuickTime files is stored along with an stsd atom that contains a FOURCC to indicate the format type. Apple QuickTime accomodates a number of different PCM formats:
- 'raw ' (need space character, ASCII 0x20, to round out FOURCC) denotes unsigned, linear PCM. 16-bit data is stored in little endian format.
- 'twos' denotes signed (i.e. twos-complement) linear PCM. 16-bit data is stored in big endian format.
- 'sowt' ('twos' spelled backwards) also denotes signed linear PCM. However, 16-bit data is stored in little endian format.
- 'in24' denotes 24-bit, big endian, linear PCM.
- 'in32' denotes 32-bit, big endian, linear PCM.
- 'fl32' denotes 32-bit floating point PCM. (Presumably IEEE 32-bit; byte order?)
- 'fl64' denotes 64-bit floating point PCM. (Presumably IEEE 64-bit; byte order?)
- 'alaw' denotes A-law logarithmic PCM.
- 'ulaw' denotes mu-law logarithmic PCM.
Red Book CD Audio
The "Red Book" defines the format of a standard audio compact disc (CD). The audio data on a standard CD consists of 16-bit linear PCM samples stored in little endian format, replayed at 44100 Hz (hence the standard term "CD-quality audio"), with left-right stereo interleaving.
Sega CD
Games made for the Sega CD, an add-on for the Sega Genesis game console, all seem to use sign-magnitude coding to store PCM information. It is a good guess that the Sega CD unit has custom hardware to play this format natively.
Sega Saturn
Games made for the Sega Saturn video game console generally seem to store PCM data as signed, 8-bit data or signed, big endian, 16-bit data. The curious property of the PCM, however, is the stereo handling. Generally, multimedia files on Sega Saturn games (most often stored using the Sega FILM format) would store a block of left channel information followed by a block of right channel information rather than interleaving left and right samples. This is likely due to custom multi-channel audio hardware in which individual channels are assigned pan positions. For playing stereo data, one channel is assigned extreme left and another is assigned extreme right. The correct samples are sent to their respective channels. Interleaved data would require deinterleaving before playback.
DVD PCM
Standard Video-DVDs can contain 16-bit, 20-bit and 24-bit signed, linear PCM (often called LPCM) streams. A stream can consist of up to 8 channels as long as the maximum bandwidth of 6.144 mbit/sec for any LPCM audio stream is not exceeded. Two samplerates are supported: 48kHz and 96kHz.
- technical info: [1]
24-Bit PCM
24-bit linear PCM is stored in blocks. Each block is divided into two parts. The first part contains the most significant two bytes of each channel for two samples in big endian order:
< --- sample 1 --- > < --- sample 2 --- >T0 M0 T1 M1 ... Tx Mx T0 M0 T1 M1 ... Tx Mx
The second part contains all least significant bytes of each channel for the two samples in the same order:
< sample 1 > < sample 2 >B0 B1 ... Bx B0 B1 ... Bx
The complete block looks like this:
< --- sample 1 --- > < --- sample 2 --- > < sample 1 > < sample 2 >T0 M0 T1 M1 ... Tx Mx T0 M0 T1 M1 ... Tx Mx B0 B1 ... Bx B0 B1 ... Bx
- T = top byte = bits 23..16
- M = middle byte = bits 15..8
- B = bottom byte = bits 7..0

20-Bit PCM
The 20-bit packing is similar to the 24-bit packing. The only difference is that 2 channels use the nibbles of one byte as their least significant bits.
- stereo 20-bit example:
< s1 > < s2 > < s1 > < s2 > <s1> <s2>T0 M0 T1 M1 T0 M0 T1 M1 L01 L01
The 4 high bits of L01 (higher nibble) being the least significant bits of channel 0 and the 4 lower bits (lower nibble) being the least significant bits of channel 1.
byte = 2^7 2^6 2^5 2^4 2^3 2^2 2^1 2^0L01 = B0 B0 B0 B0 B1 B1 B1 B1 (bitwise)
There are always 2 samples coded to not need to pad anything with 0s.
16-bit PCM
With this coding the block consists only of the first part described above.






![[数据结构]单调栈](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/20201023000803873.jpg?x-oss-process=image)