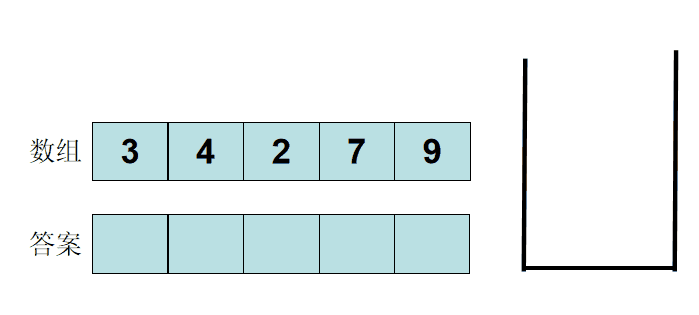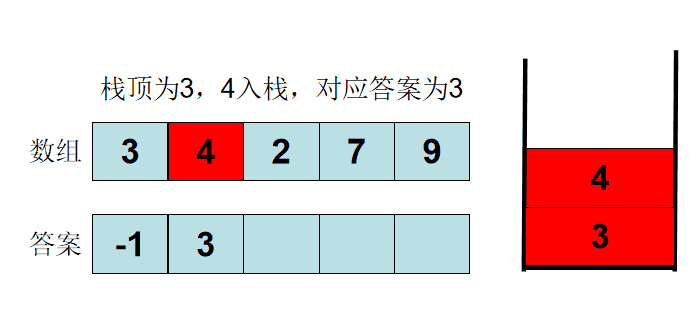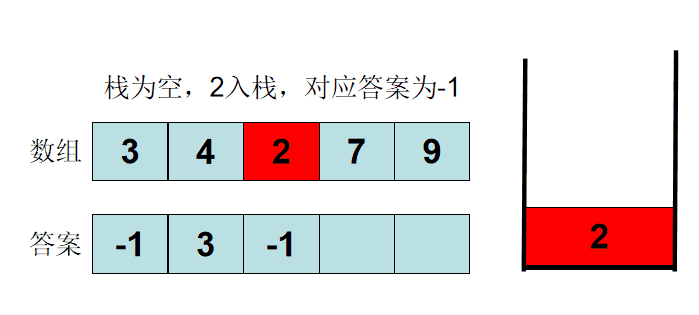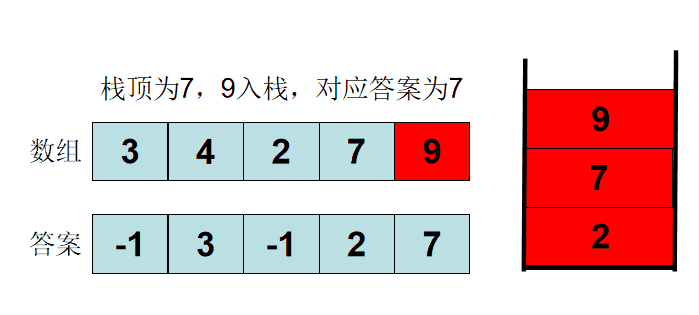
单调栈基本概念及实现

方案1:对于每一个数,遍历其左右位置,时间复杂度为O(N^2)
方案2:单调栈,每个元素入栈一次出栈一次,时间复杂度为O(N)
(一)数组中没有重复值
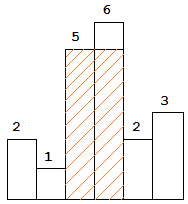
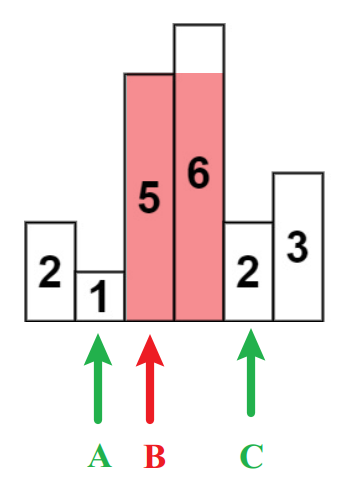
示例:[3, 4, 2, 6, 1, 7, 0]
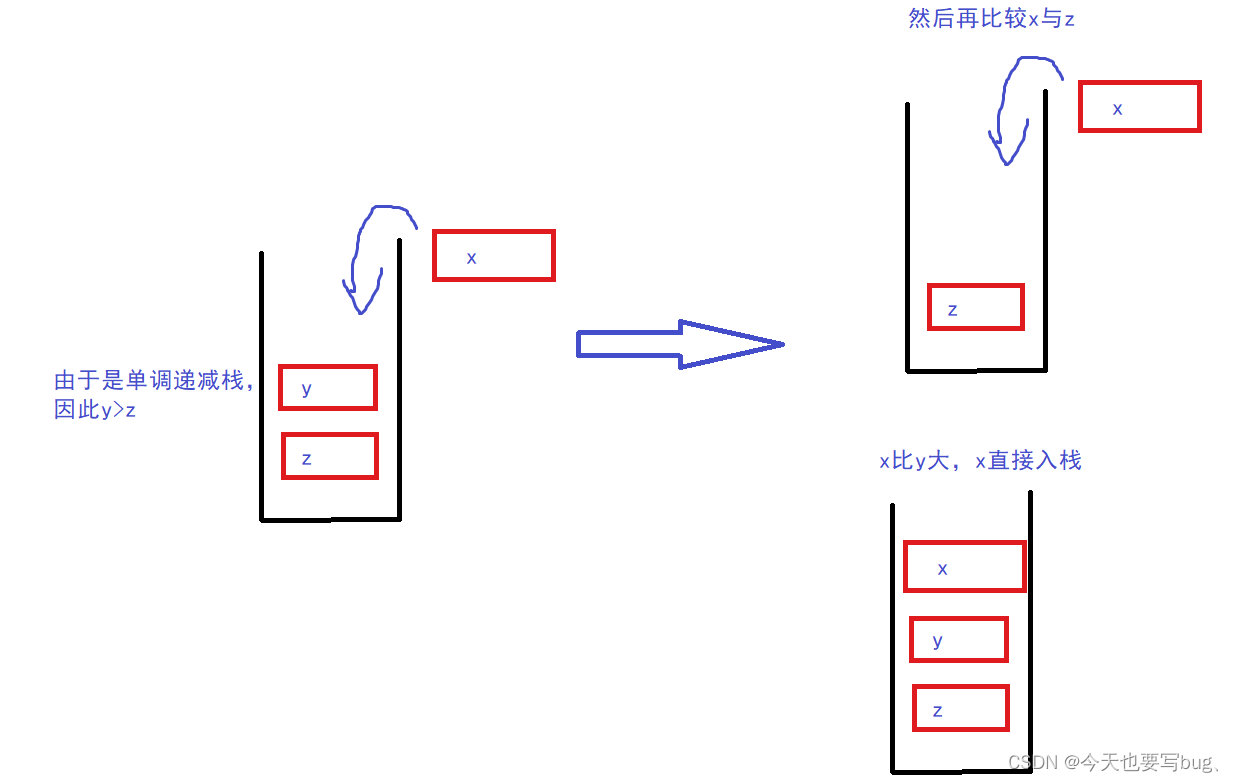
- 准备一个单调栈,栈中记录索引,对应值从栈底到栈顶,由小到大排列。
- 准备一个二维数组,记录每个位置左边离它最近且比它小的数和右边离它最近且比它小的数
- 当前元素准备入栈时,如果栈顶元素大于当前入栈元素需要弹出栈顶元素直到栈顶元素小于入栈元素,维持栈的单调性
- 每当有元素弹栈时,需要记录相关信息,使它弹栈的元素是其右边离它最近且比它小的元素,弹栈之后栈底元素是其左边最近且比它小的元素
- 当所有元素入栈之后,若栈不为空,依次弹栈,由于是主动弹栈,所以不存在右边最近且小的元素。
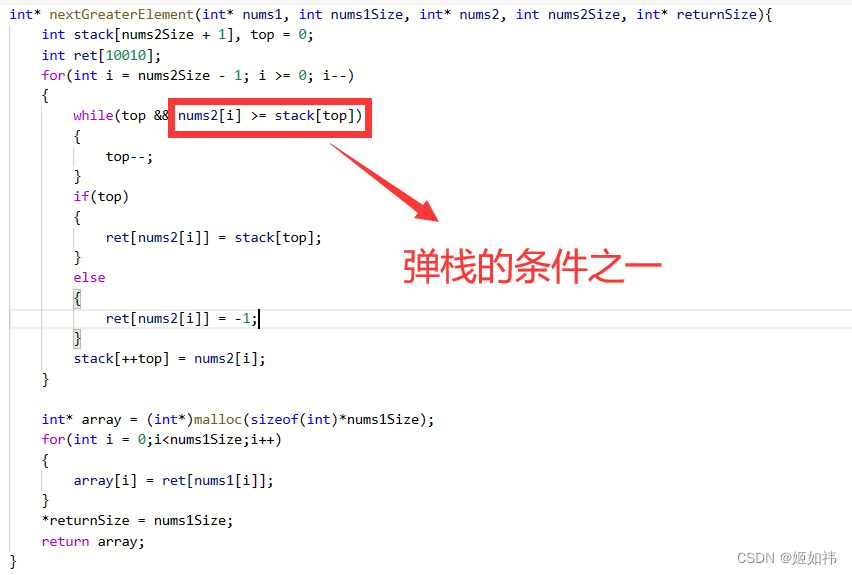
//数组中没有重复元素public static int[][] getNearLessNoRepeat(int[] arr) {int[][] ret = new int[arr.length][2];Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {while(!stack.isEmpty() && arr[stack.peek()] > arr[i]){//弹栈并记录相关信息int index = stack.pop();ret[index][1] = i;//记录右边离index最近且小的元素ret[index][0] = stack.isEmpty() ? -1 : stack.peek();//记录左边离index最近且小的元素}stack.push(i);}while(!stack.isEmpty()){int index = stack.pop();ret[index][1] = -1;//没有右边最近且小的元素ret[index][0] = stack.isEmpty() ? -1 : stack.peek();}return ret;}
(二)数组中有重复值
- 准备一个单调栈,栈中记录索引(List),对应值从栈底到栈顶,由小到大排列。
- 准备一个二维数组,记录每个位置左边离它最近且比它小的数和右边离它最近且比它小的数
- 当前元素准备入栈时,如果栈顶元素大于当前入栈元素需要弹出栈顶元素直到栈顶元素小于入栈元素,维持栈的单调性
- 如果栈顶元素等于当前入栈元素,将当前元素索引添加到栈顶索引集合的尾部(使用ArrayList)
- 每当有元素弹栈时,需要记录相关信息,使它弹栈的元素是其右边离它最近且比它小的元素,弹栈之后栈底元素是其左边最近且比它小的元素
- 当所有元素入栈之后,若栈不为空,依次弹栈,由于是主动弹栈,所以不存在右边最近且小的元素。
//数组中有重复值public static int[][] getNearLess(int[] arr) {int[][] res = new int[arr.length][2];Stack<List<Integer>> stack = new Stack<>();for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {while(!stack.isEmpty() && arr[stack.peek().get(0)] > arr[i]){List<Integer> list = stack.pop();//左边最近且小的元素为栈顶集合最后一个索引Integer left = stack.isEmpty() ? -1 : stack.peek().get(stack.peek().size()-1);for (Integer integer : list) {res[integer][0] = left;res[integer][1] = i;}}//判断当前栈顶值是否等于待入栈元素的值if(!stack.isEmpty() && arr[stack.peek().get(0)] == arr[i]){stack.peek().add(i);}else {ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add(i);stack.push(list);}}while(!stack.isEmpty()){List<Integer> pop = stack.pop();Integer left = stack.isEmpty() ? -1 : stack.peek().get(stack.peek().size()-1);for (Integer integer : pop) {res[integer][0] = left;res[integer][1] = -1;}}return res;}
题目一:子数组的累加和*子数组的最小值

解法一:暴力解法
//暴力解法,时间复杂O(N^3)public static int method(int[] arr){int ans = Integer.MIN_VALUE;//找出所有子数组for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {for (int j = i; j < arr.length; j++) {//遍历所有子数组,计算累加和同时找出最小值int min = arr[i];int sum = 0;for(int k = i; k <= j; k++){min = Math.min(arr[k],min);sum += arr[k];}ans = Math.max(ans, min * sum);}}return ans;}
解法二:单调栈
思路:
- 分别找出以i位置的值作为最小值的所有子数组
- 在保证i位置的值作为最小值的前提下,使子数组的累加和最大:找到i左边最近且比它小的索引left,找到i右边最近且比它小的索引right
- (left…i…right)开区间内的累加和最大
- 虽然数组中有重复值,但是栈中可以不用存放列表。如果当前栈顶元素等于待入栈元素,直接弹出相同元素。实际上弹出相同元素时,我们并没有找到其右边最近且小的元素,计算的结果是错误的。但我们并不严格要求每个位置都计算正确,因为相同元素之间实际上是联通的,我们并不会错过正确的结果。
- 每次弹出元素后,就计算累加和*最小值
因为要计算累加和,所以要预处理前缀和数组
假设原数组arr[3, 2, 1, 2, 4, 5]
预处理前缀和数组为 pre[3, 5, 6, 8, 12, 17], pre[i]代表原数组0-i的累加和
(i-j)累加和 = (0-j)累加和 - (0-i-1)累加和
public static int method1(int[] arr){//预处理前缀和数组int[] sum = new int[arr.length];sum[0] = arr[0];for(int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++){sum[i] = sum[i-1] + arr[i];}Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();int ret = Integer.MIN_VALUE;for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {while(!stack.isEmpty() && arr[stack.peek()] >= arr[i]){Integer pop = stack.pop();//以pop位置的值作为最小值int right = i;//右边最近且小int left = stack.isEmpty() ? -1 : stack.peek();//左边最近且小int total = left == -1 ? sum[right-1] : sum[right-1] - sum[left];ret = Math.max(ret, arr[pop] * total);}stack.push(i);}while(!stack.isEmpty()){Integer pop = stack.pop();int left = stack.isEmpty() ? -1 : stack.peek();int total = left == -1 ? sum[pop] : sum[pop] - sum[left];ret = Math.max(ret, total * arr[pop]);}return ret;}
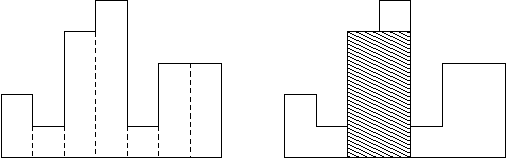
题目二:直方图的最大长方形面积

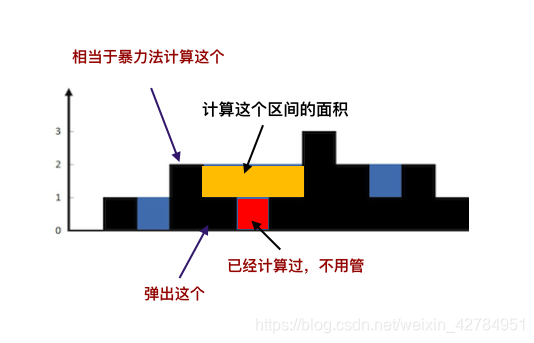
思路分析:计算以i位置的值为高的长方形的最大面积
自己手动实现栈,效率更高
class Solution {public int largestRectangleArea(int[] heights) {int ans = Integer.MIN_VALUE;int top = -1;//栈顶指针指向当前栈顶元素int[] stack = new int[heights.length];for(int i = 0; i < heights.length; i++){//栈顶元素与当前待入栈元素相等时直接弹出,相同元素具有连通性while(top != -1 && heights[stack[top]] >= heights[i]){int pop = stack[top--];//以当前弹出元素为高int right = i;int left = top == -1 ? -1 : stack[top];int area = left == -1 ? (heights[pop]* right) : (heights[pop] * (right-1-left));ans = Math.max(ans, area);}stack[++top] = i;}while(top != -1){int pop = stack[top--];int right = -1;int left = top == -1 ? -1 : stack[top];int area = left == -1 ? heights[pop] * heights.length : heights[pop] * (heights.length - 1 - left);ans = Math.max(ans, area);}return ans;}
}
题目三:最大矩形

思路分析:
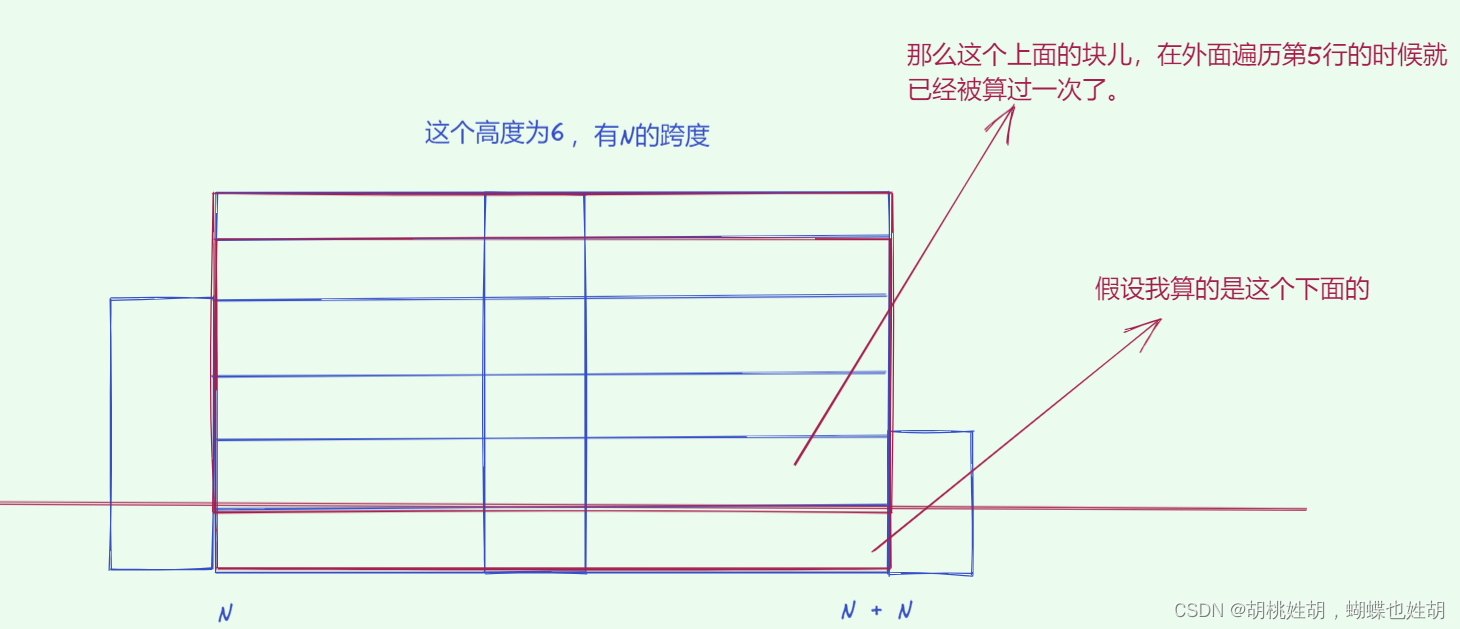
- 把二维矩阵每一行当作直方图,计算每一个位置的高
- 每一行作地基,计算对应直方图数组中最大矩形
- 直方图的高取决于1的个数
class Solution {public int maximalRectangle(char[][] matrix) {int[] arr = new int[matrix[0].length];int ans = Integer.MIN_VALUE;int[] stack = new int[arr.length];int top = -1;for(int i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++){for(int j = 0; j < matrix[0].length; j++){if(matrix[i][j] == '0'){arr[j] = 0;}else{arr[j] += 1;}while(top != -1 && arr[stack[top]] >= arr[j]){int pop = stack[top--];int right = j;int left = top == -1 ? -1 : stack[top];int total = left == -1 ? (arr[pop] * right) : (arr[pop] * (right-1-left));ans = Math.max(ans, total);}stack[++top] = j;}while(top != -1){int pop = stack[top--];int right = -1;int left = top == -1 ? -1 : stack[top];int total = left == -1 ? (arr[pop] * arr.length) : (arr[pop] * (arr.length-1-left));ans = Math.max(ans ,total);}}return ans;}
}
题目四:统计全1子矩阵
思路分析:
- 每一行作地基,计算直方图中子矩阵的数量
- 计算以i位置的值为高的子矩阵的数量

class Solution {public int numSubmat(int[][] mat) {int ans = 0;int arr[] = new int[mat[0].length];//直方图数组int top = -1;int[] stack = new int[arr.length];for(int i = 0; i < mat.length; i++){for(int j = 0; j < mat[0].length; j++){if(mat[i][j] == 0){arr[j] = 0;}else{arr[j] += 1;}while(top!=-1 && arr[stack[top]] >= arr[j]){int pop = stack[top--];int right = j;int left = top == -1 ? -1 : stack[top];int low = left == -1 ? arr[right] + 1 : Math.max(arr[left],arr[right])+1;int high = arr[pop];int n = left == -1 ? right : (right - 1 -left);ans += (high-low+1)*(n+1)*n/2;}stack[++top] = j;}while(top!=-1){int pop = stack[top--];int right = -1;int left = top == -1 ? -1 : stack[top];int high = arr[pop];int low = left == -1 ? 1 : arr[left]+1;int n = left == -1 ? arr.length : arr.length-1-left;ans += (high-low+1)*n*(n+1)/2;}}return ans;}
}
题目五:返回所有子数组中最小值的累加和(Leetcode907)

分析思路:
寻找以i位置的值作为最小值的所有子数组个数,由于数组中有重复元素,所以要考虑去重。
去重方案一:
- 寻找i左边最近“小于等于”arr[i]的数的位置 left
- 寻找i右边最近“严格小于”arr[i]的数的位置 right
- 子数组个数:(i-left) * (right-i)
- 元素入栈时,如果栈顶元素大于当前待入栈元素,则弹出栈顶元素直到栈顶元素小于等于待入栈元素
去重方案二:
5. 寻找i左边最近“严格小于”arr[i]的数的位置left
6. 寻找i右边最近“小于等于”arr[i]的数的位置right
7. 子数组个数: (i-left)*(right-i)
8. 元素入栈时,如果栈顶元素大于等于当前待入栈元素,则弹出栈顶元素直到栈顶元素严格小于当前待入栈元素
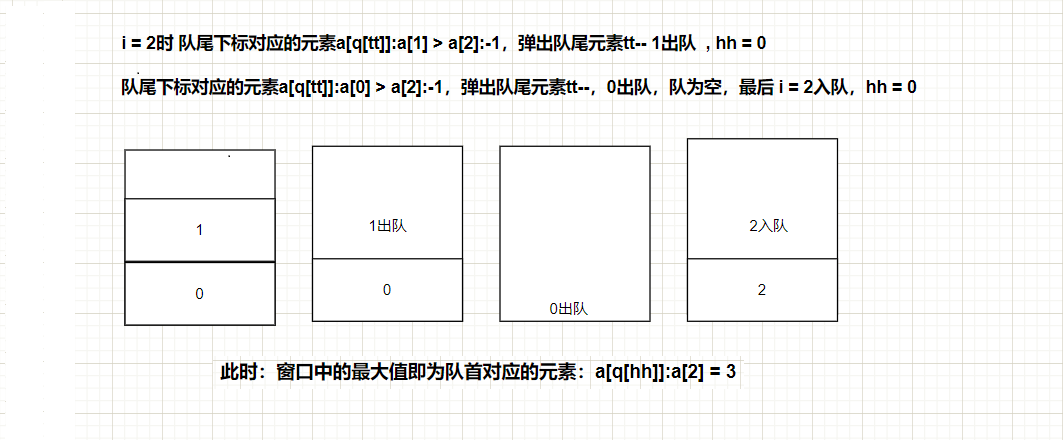
class Solution {public int sumSubarrayMins(int[] arr) {int[] stack = new int[arr.length];int top = -1;long sum = 0;for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++){while(top != -1 && arr[stack[top]] > arr[i]){int pop = stack[top--];int right = i;//右边严格小于int left = top ==-1 ? -1 : stack[top];//左边小于等于sum += (long)arr[pop] * (long)(left == -1 ? (pop+1) * (right-pop) : (pop - left)*(right-pop));sum = sum % (1000000000+7);}stack[++top] = i;}while(top != -1){int pop = stack[top--];int right = -1;int left = top == -1 ? -1 : stack[top];sum += (long)arr[pop] *(long)(left == -1 ? (pop + 1)*(arr.length-pop) : (pop-left)*(arr.length-pop));sum = sum % (1000000000+7);}return (int)sum%(1000000000+7);}
}


![[数据结构]单调栈](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/20201023000803873.jpg?x-oss-process=image)



![[数据结构]——单调栈](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/20190409164140937.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L2x1Y2t5NTI1Mjk=,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)