文章目录
- 单调栈的概念
- 单调栈的应用
- CD101 单调栈结构(无重复值)
- CD188 单调栈结构(有重复值)
- 496. 下一个更大元素 I
- 739. 每日温度
- 1856. 子数组最小乘积的最大值
- 84. 柱状图中最大的矩形
- 85. 最大矩形
- 1504. 统计全 1 子矩形
- 907. 子数组的最小值之和
- 1307 · 验证二叉搜索树中的前序序列
- 1008. 前序遍历构造二叉搜索树
- 剑指 Offer 33. 二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
单调栈的概念
单调栈是一种特殊的栈,顾名思义就是栈里面存放的数据都是有序的,所以可以分为单调递增栈和单调递减栈两种。
- 单调递增栈:单调递增栈就是从栈底到栈顶数据是从大到小,也就是大的值在下面,小的值在上面。
- 单调递减栈:单调递减栈就是从栈底到栈顶数据是从小到大,也就是小的值在下面,大的值在上面。
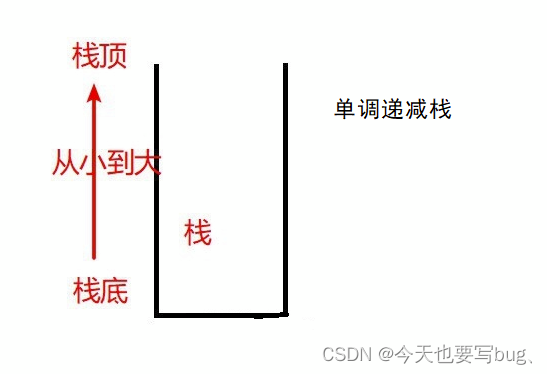
以单调递增栈为例,其伪代码为:
stack<int> st;
//此处一般需要给数组最后添加结束标志符,具体下面例题会有详细讲解
for (遍历这个数组)
{while (栈不为空 && 栈顶元素小于当前元素){栈顶元素出栈;更新结果;}当前数据入栈;
}
//到这里栈里的数据从栈底到栈顶都是从大到小,需要把它们弹出并进行处理
while (栈不为空)
{栈顶元素出栈;更新结果;
}
单调栈的应用
CD101 单调栈结构(无重复值)
CD101 单调栈结构
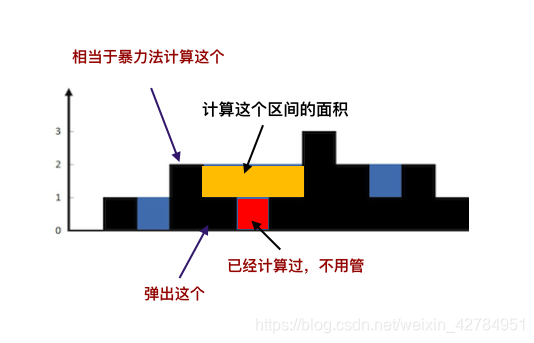
这个题要求我们找出数组中每个数左边和右边第一个比它小的数的下标,我们维护一个单调递减栈,当入栈的数据x比栈顶的数据y小时,弹出栈顶的数据y,y右边比它小的数据就是x,左边比它小的数据就是y下面压着的数z;如果x比y大,则y不弹出,x入栈。
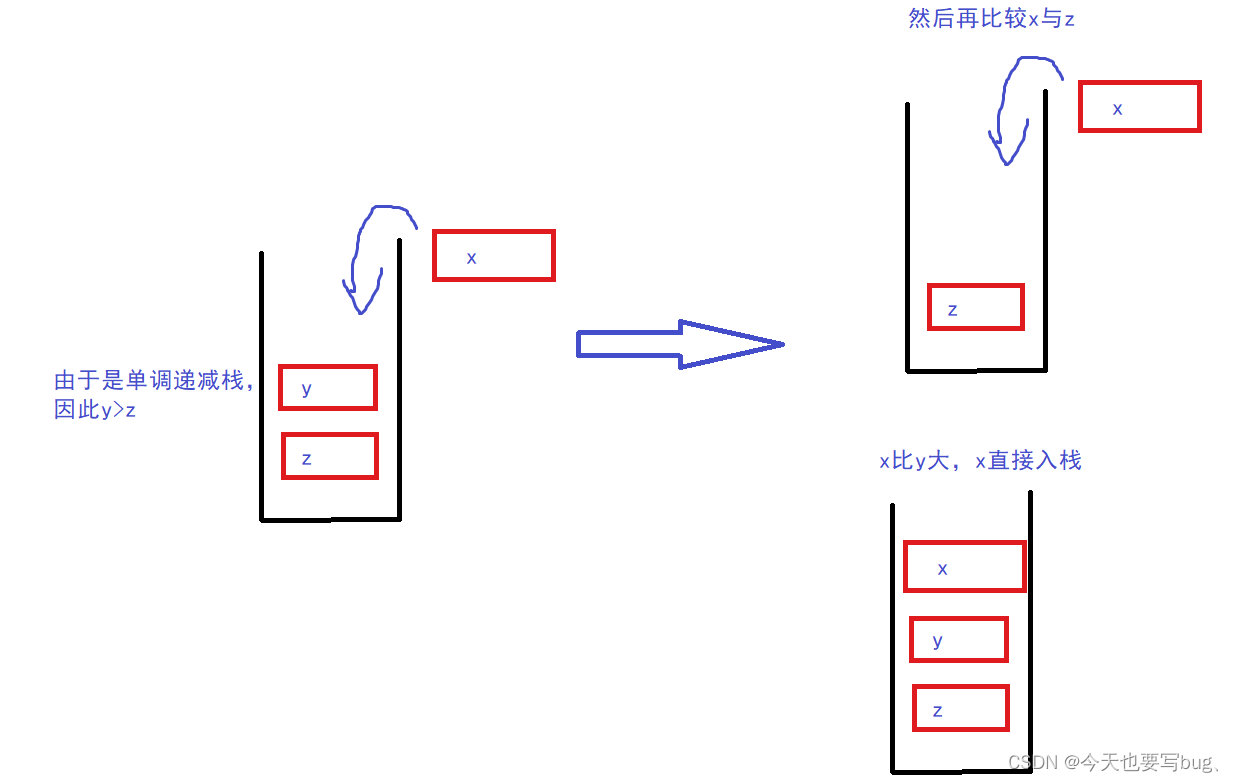
因此代码如下:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include<list>
using namespace std;
//数组当中没有重复的值
vector<vector<int>> getNearLessNoRepeat(const vector<int>& arr)
{//res用来记录左边和右边比栈顶元素小的数的下标vector<vector<int>>res(arr.size(), vector<int>(2));stack<int> st;for (int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++){//栈不为空并且arr[i]比栈顶的数小,说明arr[i]是右边第一个比栈顶数小的数while (!st.empty() && arr[st.top()] > arr[i]){//左边弹出数的下标int pop_index = st.top();st.pop();//更新结果//如果栈为空,则弹出数的左边小的数下标为-1,否则为栈顶的下标int left_index = st.empty() ? -1 : st.top();res[pop_index][0] = left_index;res[pop_index][1] = i;}st.push(i);}//栈不为空,此时栈里面所有的数,它们右边都没有比他们小的数//左边比他们小的数就是下一个栈顶的数while (!st.empty()){//弹出栈顶数的下标int pop_index = st.top();st.pop();//如果栈为空,则弹出数的左边小的数下标为-1,否则为栈顶的下标int left_index = st.empty()? -1 : st.top();res[pop_index][0] = left_index;res[pop_index][1] = -1;}return res;
}
int main()
{int n=0;cin>>n;vector<int>arr(n,0);for(int i=0;i<n;i++){cin>>arr[i];}vector<vector<int>>ans = getNearLessNoRepeat(arr);for (int i = 0; i < ans.size(); i++){//使用printf会比cout效率更高一些printf("%d %d\n",ans[i][0],ans[i][1]);//cout << ans[i][0] << " " << ans[i][1] << endl;}
}
CD188 单调栈结构(有重复值)
CD188 单调栈结构(进阶)
这个题和上个题类似,主要在于多了重复值,我们可以将重复值的下标都放到一个链表中,更新时直接更新链表中所有的下标。
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include<list>
using namespace std;
//数组当中有重复的值
vector<vector<int>> getNearLess(const vector<int>& arr)
{vector<vector<int>>res(arr.size(), vector<int>(2));//栈中存放链表,因为要把重复的的下标放到链表中stack<list<int>> st;for (int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++){//栈不为空并且arr[i]比栈顶的数小,说明arr[i]是右边第一个比栈顶数小的数while (!st.empty() && arr[st.top().back()] > arr[i]){list<int> pop_index_list = st.top();st.pop();int left_index = st.empty() ? -1 : st.top().back();for (auto& pop_index : pop_index_list){res[pop_index][0] = left_index;res[pop_index][1] = i;}}//栈不为空,并且arr[i]和栈顶的数相等,则插到栈顶链表后面if (!st.empty()&&arr[st.top().back()] == arr[i]){st.top().push_back(i);}//栈为空,或者当前元素比栈顶链表中的元素大//则将i构成链表放到栈中else{st.push(list<int>{i});}}//此时栈中所有的数,数组右边都没有比他们小的数,//左边则是它们压着的链表最后一个节点的下标while (!st.empty()){list<int> pop_index_list = st.top();st.pop();int left_index = st.empty() ? -1 : st.top().back();for (auto& pop_index : pop_index_list){res[pop_index][0] = left_index;res[pop_index][1] = -1;}}return res;
}
int main()
{int n=0;cin>>n;vector<int>arr(n,0);for(int i=0;i<n;i++){cin>>arr[i];}vector<vector<int>>ans = getNearLess(arr);for (int i = 0; i < ans.size(); i++){printf("%d %d\n",ans[i][0],ans[i][1]);//cout << ans[i][0] << " " << ans[i][1] << endl;}
}
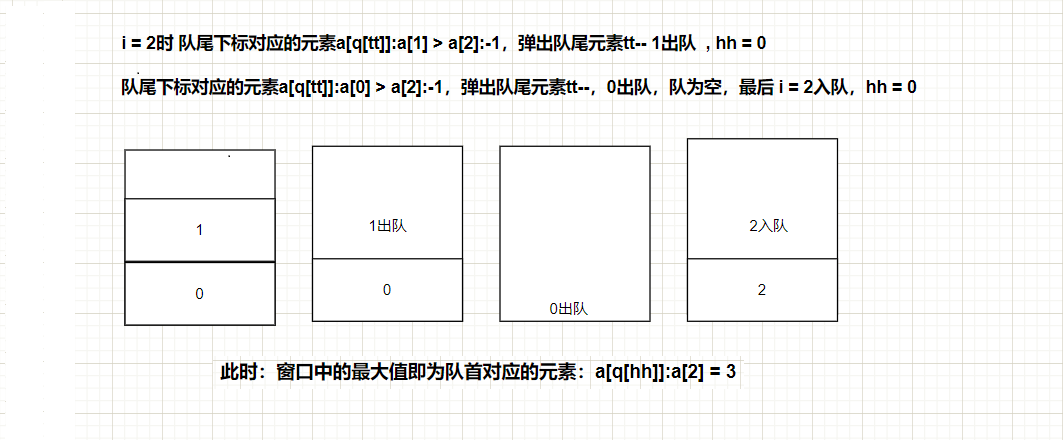
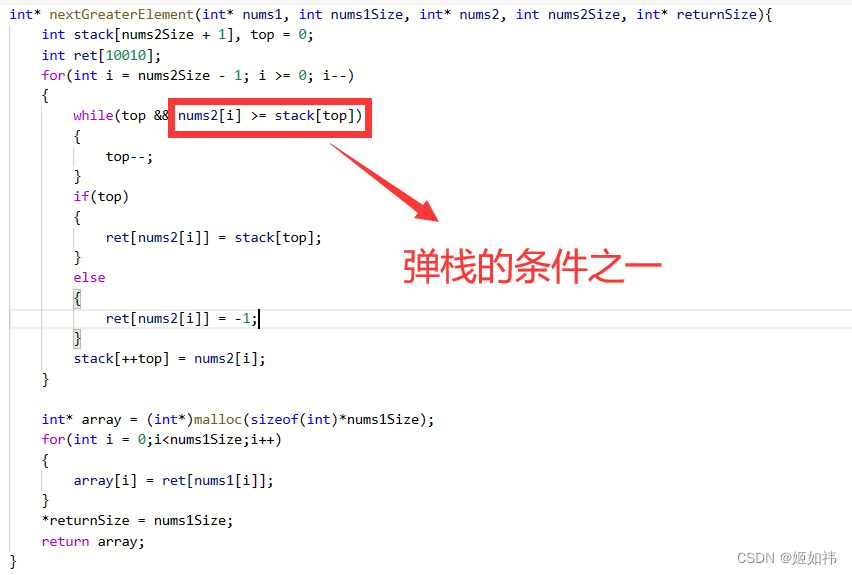
496. 下一个更大元素 I
下一个更大元素 I
class Solution {
public:vector<int> nextGreaterElement(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {vector<int>res(nums1.size());map<int,int>m;stack<int>stk;for(int i=0;i<nums2.size();i++){while(!stk.empty()&&nums2[i]>stk.top()){m[stk.top()]=nums2[i];stk.pop();}stk.push(nums2[i]);}while(!stk.empty()){m[stk.top()]=-1;stk.pop(); }for(int i=0;i<nums1.size();i++){res[i]=m[nums1[i]];}return res;}
};
739. 每日温度
739. 每日温度
class Solution {
public:vector<int> dailyTemperatures(vector<int>& temperatures) {int size=temperatures.size();vector<int>res(size,0);stack<int>st;for(int i=0;i<size;i++){while(!st.empty()&&temperatures[i]>temperatures[st.top()]){int left=st.top();st.pop();res[left]=i-left;}st.push(i);}return res;}
};
1856. 子数组最小乘积的最大值
1856. 子数组最小乘积的最大值
这是一个前缀和+单调栈的题,我们用单调递减栈,假设当前入栈的值为x,栈顶元素y比x小,此时x的下标-1与y所压的元素的下标所在区间就是以y为最小值的子数组,使用前缀和计算该子数组的和,然后用y相乘。
class Solution {
public:int maxSumMinProduct(vector<int>& nums) {int size=nums.size();//sums保存前缀和vector<long long> sums(size,0);sums[0]=nums[0];for(int i=1;i<size;i++){sums[i]=sums[i-1]+nums[i];}long long res=INT_MIN;//st为单调栈,存数组下标,当nums[i]比栈顶的元素下标对应的值小时,出栈stack<int> st;for(int i=0;i<size;i++){while(!st.empty()&&nums[st.top()]>=nums[i]){long long num=nums[st.top()];st.pop();long long left_sum=st.empty()?sums[i-1]:sums[i-1]-sums[st.top()];res=max(res,num*left_sum);}st.push(i);}//此时栈中所有的数,它们右边都没有比其小的数,因为如果有,它们就会在上一步出栈//因此子数组的范围就是size-1~st.top()while(!st.empty()){long long num=nums[st.top()];st.pop();long long left_sum=st.empty()?sums[size-1]:sums[size-1]-sums[st.top()];res=max(res,num*left_sum);}return (int)(res%1000000007);}};
84. 柱状图中最大的矩形
84. 柱状图中最大的矩形
这个题和上个题类似,上个题是求一段子数组区间和。这个题也是求一段区间下标的差。
class Solution {
public:int largestRectangleArea(vector<int>& heights) {if(heights.size()==1){return heights[0];}int size=heights.size();int res=INT_MIN;//st为单调栈,存数组下标,当nums[i]比栈顶的元素下标对应的值小时,出栈stack<int> st;for(int i=0;i<size;i++){while(!st.empty()&&heights[st.top()]>=heights[i]){int num=heights[st.top()];st.pop();int left_sum=st.empty()?i:i-1-st.top();res=max(res,num*left_sum);}st.push(i);}while(!st.empty()){int num=heights[st.top()];st.pop();int left_sum=st.empty()?size:size-1-st.top();res=max(res,num*left_sum);}return res;}
};
85. 最大矩形
85. 最大矩形
通过枚举子矩阵以第0行为地基的情况,其只包含1的最大矩形的面积,然后枚举以第1行为地基的情况,重复上述的过程,即可算出只包含1的最大矩形的面积。算面积的方式就是上一道题。
class Solution {
public:int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {int res=INT_MIN;int row=matrix.size();int col=matrix[0].size();vector<int>temp(col,0);//地基for(int i=0;i<row;i++){//当地基为0时,该矩形的高为0for(int j=0;j<col;j++){if(matrix[i][j]=='0'){temp[j]=0;}else{temp[j]+=1;}}//求出以i为地基的最大矩形的面积int temp_res=largestRectangleArea(temp);res=max(res,temp_res);}return res;}int largestRectangleArea(vector<int>& heights) {if(heights.size()==1){return heights[0];}int size=heights.size();int res=INT_MIN;//st为单调栈,存数组下标,当nums[i]比栈顶的元素下标对应的值小时,出栈stack<int> st;for(int i=0;i<size;i++){while(!st.empty()&&heights[st.top()]>=heights[i]){int num=heights[st.top()];st.pop();int left_sum=st.empty()?i:i-1-st.top();res=max(res,num*left_sum);}st.push(i);}while(!st.empty()){int num=heights[st.top()];st.pop();int left_sum=st.empty()?size:size-1-st.top();res=max(res,num*left_sum);}return res;}
};
1504. 统计全 1 子矩形
1504. 统计全 1 子矩形
这个题与上个题类似,区别在于上个题只让求最大的子矩阵,而这个题让求的是子矩阵的个数。
我们还是采用“地基”的思路,根据数学公式,我们可以推出当只有一行全1且其宽度为n时,其子矩阵的个数为(n+1)*n/2,然后我们只需要算出该列左右最小的数的下标,然后就能求出以该列为高的子矩阵的高度,然后用高度乘该列的个数,就是该矩形的子矩阵的个数。
class Solution {
public:int numSubmat(vector<vector<int>>& mat) {int row=mat.size();int col=mat[0].size();int res=0;vector<int>temp(col,0);for(int i=0;i<row;i++){for(int j=0;j<col;j++){if(mat[i][j]==0){temp[j]=0;}else{temp[j]+=1;}}res+=proecss(temp);}return res;}int proecss(vector<int>& heights) {if(heights.size()==1){return heights[0];}int size=heights.size();int res=0;//st为单调栈,存数组下标,当nums[i]比栈顶的元素下标对应的值小时,出栈stack<int> st;for(int i=0;i<size;i++){while(!st.empty()&&heights[st.top()]>=heights[i]){//cur为当前的下标,其左右两边比它小的数的下标为i和st.top()int cur=st.top();st.pop();//为了防止heights[cur]=heights[i],要进行筛选//两列高度相等,后面的列进行计算if(heights[cur]>heights[i]){//left为左边小的数的下标int left=st.empty()?-1:st.top();//n为宽度,left为最左边小的数下标//i为右边小的数的下标int n=i-left-1;//计算高度,down为左右两边最小值较大的一个//heights[cur]-down即为矩形的高度int down=max(left==-1?0:heights[left],heights[i]);res+=(heights[cur]-down)*num(n);}}st.push(i);}while(!st.empty()){int cur=st.top();st.pop();int left=st.empty()?-1:st.top();int n=size-left-1;int down=left==-1?0:heights[left];res+=(heights[cur]-down)*num(n);}return res;}//如果矩阵只有一列,且矩阵的高度为n,那它有num(n)个子矩阵int num(int n){return ((n*(1+n))>>1);}
};
907. 子数组的最小值之和
907. 子数组的最小值之和述
这个题要求所有子数组中最小值的和。我们可以用单调栈求出一个数x(下标为a)左边和右边第一个比它小的数的下标(下标为b和c),然后用就能求出以x为子数组的个数((a-b)*(c-a)),这些子数组中最小的数都是x,所以再乘上x。
最后枚举所有的数即可。
当相邻的数相等时,我们用左边的数来结算子区间个数,比如6 6 6三个数,最左边的6的区间个数为3(左区间为1,右区间为3),中间的为2,右边为1(它本身)。
class Solution {
public:int sumSubarrayMins(vector<int>& arr) {//left[i]=x:arr[i]左边,离arr[i]最近,<=arr[i]的位置在xvector<int>left=leftNearLessEqual2(arr);//left[i]=x:arr[i]右边,离arr[i]最近,<arr[i]的位置在xvector<int>right=rightNearLessEqual2(arr);long res=0;for(int i=0;i<arr.size();i++){long start=i-left[i];long end=right[i]-i;res+=start*end*arr[i];res%=1000000007;}return (int)res;}vector<int> leftNearLessEqual2(vector<int>&arr){int n=arr.size();vector<int>left(n,0);stack<int>st;for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--){while(!st.empty()&&arr[i]<=arr[st.top()]){left[st.top()]=i;st.pop();}st.push(i);}while(!st.empty()){left[st.top()]=-1;st.pop();}return left;}vector<int> rightNearLessEqual2(vector<int>&arr){int n=arr.size();vector<int>right(n,0);stack<int>st;for(int i=0;i<n;i++){while(!st.empty()&&arr[i]<arr[st.top()]){right[st.top()]=i;st.pop();}st.push(i);}while(!st.empty()){right[st.top()]=n;st.pop();}return right;}
};
1307 · 验证二叉搜索树中的前序序列
1307 · 验证二叉搜索树中的前序序列
前序遍历是按照左右根的顺序来的,因此前面的几个数是递减的(因为要一路遍历左子树),当出现递增时,说明此时遍历到了右子树。假设这个递增的数为x,但是我们不能确定x是哪一个父节点的左子树,因此我们需要一个单调栈来记录这一路减小的根节点,然后用栈顶的数与x比较,小于则弹出,并且记录最后弹出的栈,最后弹出的数就是x的父节点。将x压栈。
此后的数一定会比x的父节点大,如果比它小,则不符合前序遍历的规则。
后面的数不断重复上面的过程。
class Solution {
public:/*** @param preorder: List[int]* @return: return a boolean*/bool verifyPreorder(vector<int> &preorder) {// write your code herestack<int>minStack;int lastRoot=INT_MIN;for(int i=0;i<preorder.size();i++){if(preorder[i]<lastRoot){return false;}while(!minStack.empty()&&preorder[i]>minStack.top()){lastRoot=minStack.top();minStack.pop();}minStack.push(preorder[i]);}return true;}
};
1008. 前序遍历构造二叉搜索树
1008. 前序遍历构造二叉搜索树
根左右的遍历顺序可以让根节点x很快地找到左子树节点y,右子树节点z是x右边第一个比x大的节点,所以我们可以用单调栈记录这个下标,然后就能够构建二叉树了。
class Solution {
public:TreeNode* bstFromPreorder(vector<int>& preorder) {int size=preorder.size();vector<int>right_first_big(size,-1);stack<int>big_stack;for(int i=0;i<size;i++){while(!big_stack.empty()&&preorder[i]>preorder[big_stack.top()]){right_first_big[big_stack.top()]=i;big_stack.pop();}big_stack.push(i);}return process(preorder,0,size-1,right_first_big);}TreeNode* process(vector<int>& preorder,int left,int right,vector<int>& right_first_big){if(left>right){return nullptr;}TreeNode* root=new TreeNode(preorder[left]);//如果右边第一个比root大的数的下标为-1,则说明root节点没有右子树int right_index=right_first_big[left]==-1?right+1:right_first_big[left];root->left=process(preorder,left+1,right_index-1,right_first_big);root->right=process(preorder,right_index,right,right_first_big);return root;}
};
剑指 Offer 33. 二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
剑指 Offer 33. 二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
后序遍历遵从左右根的原则,如果倒过来,就是根右左,根右是一个递增序列,这和上面的“验证二叉搜索树中的前序序列”解法相同。
class Solution {
public:bool verifyPostorder(vector<int>& postorder) {stack<int>big_stack;int last_root=INT_MAX;for(int i=postorder.size()-1;i>=0;i--){if(postorder[i]>last_root){return false;}while(!big_stack.empty()&&postorder[i]<big_stack.top()){last_root=big_stack.top();big_stack.pop();}big_stack.push(postorder[i]);}return true;}
};



![[数据结构]——单调栈](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/20190409164140937.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L2x1Y2t5NTI1Mjk=,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)


![[rtsp @ 0x55ba1dae9200] UDP timeout, retrying with TCP的解决办法](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/322d3e5647fd4654984f30d921431578.png)