树
- 一,树的定义
- 二,树的基本术语
- 三,二叉树的定义
- 四,二叉树的性质和存储结构
- 五,关于二叉树的算法
一,树的定义
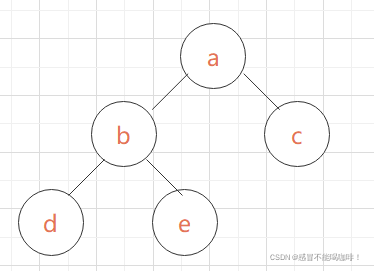
树是n(n>=0)个结点的有限集合。
若n=0,称为空树。
若n>0,则它满足如下两个条件;①有且仅有一个特定的称为根(root)的结点。②其余结点可分为m(m>=0)个互不相交的有限集合T1,T2….
其中每一个集合本身又是一棵树,并称为根的子树。
二,树的基本术语

| ①孩子与双亲: | 结点的子树的根称为该结点的孩子,该结点称为孩子的双亲。 |
|---|---|
| ②根结点: | 非空树中无前驱结点的结点。 |
| ③结点的度: | 结点拥有的子树的数目。 |
| ④树的度: | 树内各结点的度的最大值。 |
| ⑤树的深度: | 树中结点的最大层次。 |
| ⑥堂兄弟: | 双亲在同一层的结点。 |
| ⑦叶子: | 度等于0的结点。 |
| ⑧有序树: | 树中结点的各子树从左至右有次序。(最左边的为第一个孩子) |
| ⑨无序树: | 树中结点的各子树无次序。 |
| ⑩森林: | 森林是m(m>=0)棵互不相交的树的集合。 |
(①把根结点删除,树就变成了森林。②一棵树可以看做是一个特殊的森林。③给森林的各子树加上一个双亲结点,森林就变成了树)。
树一定是森林,森林不一定是树。
三,二叉树的定义
二叉树是n(n>=0)个结点的有限集合,它或者是空集(n=0)或者是由一
个根结点及两棵互不相交的分别称作这个根的左子树和右子树的二叉树组成。
特点: ①每个结点最多有两个孩子(二叉树中不存在度大于2的结点)。②子树有左右之分,其次序不能颠倒。③二叉树可以是空集合,根可以有空的左子树或空的右子树。
二叉树不是树的特殊情况,它们是两个概念。

二叉树结点的子树要区分左子树和右子树,即使只有一棵子树也要进行区分,说明它是左子树,还是右子树。树当结点只有一个孩子时,就无须区分它是左还是右的次序。这是二叉树与树的最主要的差别。
(也就是说二叉树的每个结点位置或者说次序都是固定的,可以是空,但是不能说它没有位置,而树的结点位置是相对于别的结点来说的,没有别的结点时,它就无所谓左右了)。
四,二叉树的性质和存储结构

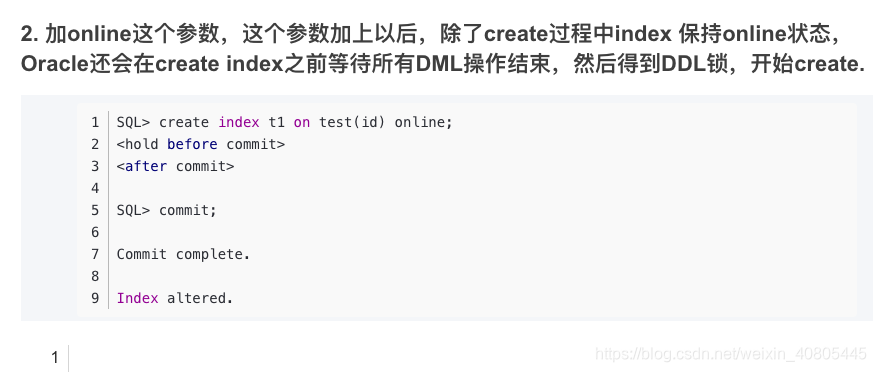
性质1:在二叉树的第i层上最多有 2^(i-1)个结点(i>=1)。
性质2:深度为k的二叉树最多有 2^k-1个结点(k>=1)。深度为k时至少有k个结点。
性质3:对任何一棵二叉树T,如果其叶子数为 m,度为2的结点数为 p,则m=p+1。 总边数为n-1或者为2p+m。
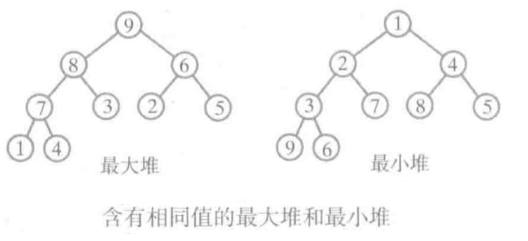
两种特殊形式的二叉树:

满二叉树:一棵深度为k且有2^k-1个结点的二叉树称为满二叉树。
特点:①每一层上的结点数都是最结点数(每一层都满)。②对满二叉树的结点位置进行编号,从根结点开始,自上而下,自左而右,每一结点位置都有元素。
满二叉树在同样深度的二叉树中结点个数最多。
满二叉树在同样深度的二叉树中叶子结点个数最多。
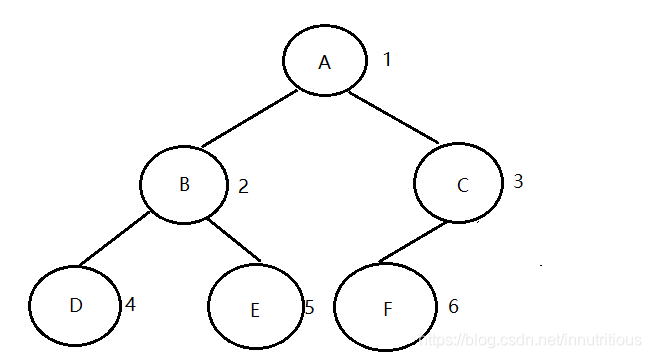
完全二叉树:深度为k的具有n个结点的二叉树,当且仅当其每一个结点都与深度为k的满二叉树中编号为1~n的结点一一对应时,称之为完全二叉树。
特点:①叶子只可能分布在层次最大的两层上。②对任一结点,如果其右子树的最大层次为i,则其左子树的最大层次为i或i+1。性质:①具有n个结点的完全二叉树的深度为【〖log〗_2^n】+1(【x】表示不大于x的最大整数)。 ②如果对一棵有n个结点的完全二叉树按层序编号,则对于任一结点i,有:1,如果i=1,则结点i是二叉树的根,无双亲;如果i>1,则其双亲结点为【i/2】。2,如果2i>n,则结点为叶子结点,无左孩子;否则,其左孩子是结点2i。3,如果2i+1>n,则结点i无右孩子;否则,其右孩子时结点2i+1。
满二叉树一定是完全二叉树。
在满二叉树中,从最后一个结点开始,连续去掉任意个结点,即是一棵完全二叉树。在n个结点的二叉链表中,有n+1个空指针域。
五,关于二叉树的算法
一,遍历算法:
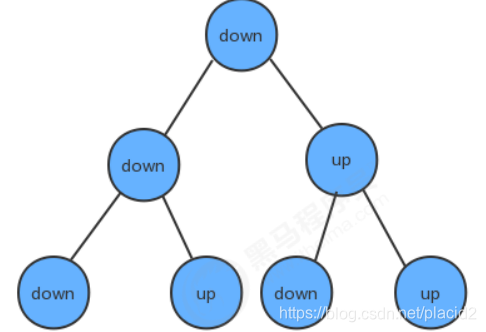
若规定先左后右,则只有前三种情况:
DLR——先序遍历
LDR——中序遍历
LRD——后序遍历
举个栗子:
Problem Description
已知二叉树的一个按先序遍历输入的字符序列,如abc,de,g,f, (其中,表示空结点)。请建立二叉树并按先序,中序和后序的方式遍历该二叉树。
Input
连续输入多组数据,每组数据输入一个长度小于50个字符的字符串。
Output
每组输入数据对应输出2行:
第1行输出先序遍历序列;
第2行输出中序遍历序列。
第3行输出后序遍历序列。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node//二叉树的数据结构
{char ch;struct node *lchild,*rchild;
};
char s[100];
int key;
struct node *CreatTree()//建立二叉树
{struct node *T;if (s[key]==','){T=NULL;key++;}else{T=(struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));T->ch=s[key++];T->lchild=CreatTree();T->rchild=CreatTree();}return T;
}
void PreOrderTraverse(struct node *T)//先序遍历二叉树
{if (T){printf("%c",T->ch);PreOrderTraverse(T->lchild);PreOrderTraverse(T->rchild);}
}
void InOrderTraverse(struct node *T)//中序遍历二叉树
{if (T){InOrderTraverse(T->lchild);printf("%c",T->ch);InOrderTraverse(T->rchild);}
}
void PostOrderTraverse(struct node *T)//后序遍历二叉树
{if (T){PostOrderTraverse(T->lchild);PostOrderTraverse(T->rchild);printf("%c",T->ch);}
}
int main()
{while (~scanf("%s",s)){key=0;struct node *T;T=CreatTree();PreOrderTraverse(T);printf("\n");InOrderTraverse(T);printf("\n");PostOrderTraverse(T);printf("\n");}return 0;
}层序遍历:对于一棵二叉树,从根结点开始,按从上到下,从左到右的顺序访问每一个结点,每个结点仅仅访问一次。
举个栗子:
Problem Description
已知一个按先序输入的字符序列,如abd,eg,cf,(其中,表示空结点)。请建立二叉树并求二叉树的层次遍历序列。
Input
输入数据有多行,第一行是一个整数t (t<1000),代表有t行测试数据。每行是 一个长度小于50个字符的字符串。
Output
输出二叉树的层次遍历序列。
示例输入
2
abd,eg,cf,
xnl,i,u,
示例输出
abcdefg
xnuli
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node
{char data;struct node *lchild,*rchild;
};
int i;
char s[100];
struct node *creatTree()
{i++;struct node *p;if (s[i]==','){p=NULL;}else{p=(struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));p->data=s[i];p->lchild=creatTree();p->rchild=creatTree();}return p;
}
void levelTraversal(struct node *p)//用队列实现
{struct node *q[100];q[0]=p;int head=0,tail=1;while (head<tail){if (q[head]!=NULL){printf("%c",q[head]->data);q[tail++]=q[head]->lchild;q[tail++]=q[head]->rchild;}head++;}
}
int main()
{int t;scanf("%d",&t);while (t--){struct node *p;scanf("%s",s);i=-1;p=creatTree();levelTraversal(p);printf("\n");}return 0;
}二,其他算法
复制二叉树:
举个栗子:
Problem Description
已知一个按先序输入的字符序列,如abd,eg,cf,(其中,表示,表示空结点),请复制这棵二叉树并输出。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node
{char data;struct node *lchild,*rchild;
};
int i;
char s[100];
struct node *creatTree()
{i++;struct node *p;if (s[i]==','){p=NULL;}else{p=(struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));p->data=s[i];p->lchild=creatTree();p->rchild=creatTree();}return p;
}
struct node *copy(struct node *p)//复制二叉树
{struct node *q;if (p==NULL){q=NULL;}else{q=(struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));q->data=p->data;q->lchild=copy(p->lchild);q->rchild=copy(p->rchild);}return q;
}
void PreOrderTraverse(struct node *h)
{if (h){printf("%c",h->data);PreOrderTraverse(h->lchild);PreOrderTraverse(h->rchild);}
}
int main()
{scanf("%s",s);struct node *p,*q;i=-1;p=creatTree();q=copy(p);PreOrderTraverse(p);//输出原二叉树printf("\n");PreOrderTraverse(q);//输出复制后的二叉树printf("\n");return 0;
}求二叉树的深度:
举个栗子:
Problem Description
已知一个按先序输入的字符序列,如abd,eg,cf,(其中,表示,表示空结点),求这棵树的深度。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node
{char data;struct node *lchild,*rchild;
};
int i;
char s[100];
struct node *creatTree()
{i++;struct node *p;if (s[i]==','){p=NULL;}else{p=(struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));p->data=s[i];p->lchild=creatTree();p->rchild=creatTree();}return p;
}
int depth(struct node *h)//求二叉树的深度
{int n,m;if (h==NULL){return 0;}else{m=depth(h->lchild);n=depth(h->rchild);if (m>n){return (m+1);}else return (n+1);}
}
int main()
{scanf("%s",s);struct node *p;i=-1;p=creatTree();printf("%d\n",depth(p));return 0;
}求二叉树的结点总数:
举个栗子:
Problem Description
已知一个按先序输入的字符序列,如abd,eg,cf,(其中,表示,表示空结点),求这棵树的结点总数。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node
{char data;struct node *lchild,*rchild;
};
int i;
char s[100];
struct node *creatTree()
{i++;struct node *p;if (s[i]==','){p=NULL;}else{p=(struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));p->data=s[i];p->lchild=creatTree();p->rchild=creatTree();}return p;
}
int score(struct node *h)//求结点总数
{if (h==NULL){return 0;}else{return score(h->lchild)+score(h->rchild)+1;}
}
int main()
{scanf("%s",s);struct node *p;i=-1;p=creatTree();printf("%d\n",score(p));return 0;
}求叶子结点总数:
举个栗子:
Problem Description
已知一个按先序输入的字符序列,如abd,eg,cf,(其中,表示,表示空结点),求这棵树的叶子结点总数。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node
{char data;struct node *lchild,*rchild;
};
int i;
char s[100];
struct node *creatTree()
{i++;struct node *p;if (s[i]==','){p=NULL;}else{p=(struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));p->data=s[i];p->lchild=creatTree();p->rchild=creatTree();}return p;
}
int deaf(struct node *h)//求叶子结点总数
{if (h==NULL){return 0;}if (h->lchild==NULL&&h->rchild==NULL){return 1;}else{return deaf(h->lchild)+deaf(h->rchild);}
}
int main()
{scanf("%s",s);struct node *p;i=-1;p=creatTree();printf("%d\n",deaf(p));return 0;
}未完待续…