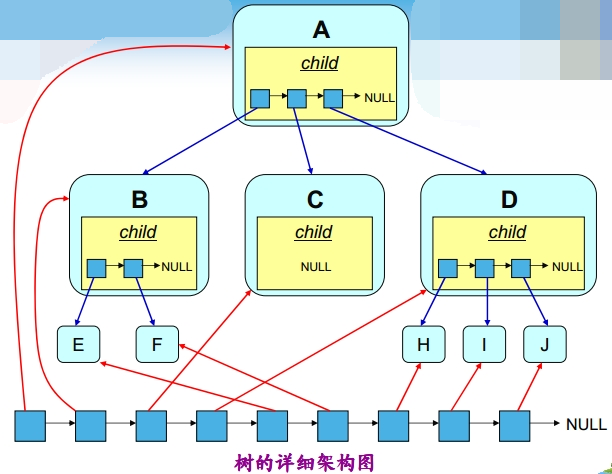
二叉搜索树
- 一:二叉搜索树概念
- 二: 二叉搜索树实现
- 节点的定义
- 二叉搜索树实现
- 三:二叉搜索树的应用
- 四:二叉树有关面试题
- ps
很多小伙伴为了刷题发愁
今天为大家推荐一款刷题神奇哦:刷题面试神器牛客
各大互联网大厂面试真题。从基础到入阶乃至原理刨析类面试题 应有尽有,赶快来装备自己吧!助你面试稳操胜券,solo全场面试官
一:二叉搜索树概念
二叉搜索树又称二叉排序树,它或者是一棵空树,或者是具有以下性质的二叉树:
- 若它的左子树不为空,则左子树上所有节点的值都小于根节点的值
- 若它的右子树不为空,则右子树上所有节点的值都大于根节点的值
它的左右子树也分别为二叉搜索树 - 例:

int a [] = {5,3,4,1,7,8,2,6,0,9};
二: 二叉搜索树实现
节点的定义
template <class K> //模板
class TreeNode
{
public:TreeNode<K>* _left;TreeNode<K>* _right;K _key;TreeNode(const K & key):_left(nullptr),_right(nullptr),_key(key){}
};
二叉搜索树实现
- 代码:
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;template <class K>
class TreeNode
{
public:TreeNode<K>* _left;TreeNode<K>* _right;K _key;TreeNode(const K & key):_left(nullptr),_right(nullptr),_key(key){}
};template <class K>
class BSTree
{typedef TreeNode<K> Node;
private:Node* _FindR(Node* root, const K& key){if (root == nullptr)return nullptr;if (root->_key > key){return _FindR(_root->_left, key);}else if (root->_key < key){return _FindR(_root->_right, key);}else{return _root;}}bool _insertR(Node*& root, const K& key) //递归版本,注意传引用{ if (root == nullptr){root = new Node(key);return true;}if (root->_key > key){return _FindR(_root->_left, key);}else if (root->_key < key){return _FindR(_root->_right, key);}else{return false;}}bool _EraseR(Node*& root, const K& key){if (root == nullptr){return false;}if (root->_key > key){return _EraseR(_root->_left, key);}else if (root->_key < key){return _EraseR(_root->_right, key);}else //找到了{if (root->_left == nullptr) //假如左子树为空,直接等于右子树{Node* tem = root;root = root->_right;delete tem;}else if (root->_right == nullptr)//假如右子树为空,root直接等于左子树{Node* tem = root;root = root->_left;delete tem;}else //左右子树都不为空时,1.先找到右边最小值 2.再保留最小值 3.递归去删除最小值 4.将最小值赋值给root{Node* right = root->_right;while (right->_left){right = right->_left;}K temkey = right->_key;_EraseR(right,right->_key);root->_key = temkey;}return true;}}void _Destroy(Node* root) //后序销毁{if (root == nullptr)return;_Destroy(root->_left);_Destroy(root->_right);delete root;}Node* _BSTree(const Node*& root) //深拷贝一个树{if (root == nullptr)return nullptr;Node* cur = new Node(root->_key);cur->_left = _BSTree(root->_left);cur->_right = _BSTree(root->_right);return cur;}
public:BSTree():_root(nullptr){}~BSTree(){_Destroy(_root);}BSTree(const BSTree<K>& a){_root=_BSTree(a._root);}BSTree<K>& a operator=(const BSTree<K> a){swap(_root, a._root);return *this;}bool insertR(const K& key) //递归版本{return _insertR(_root,key);}Node* FindR(const K& key){return _FindR(_root, key);}bool EraseR(const K& key){return _EraseR(_root,key);}bool insert(const K& key) //插入一个值{if (_root == nullptr) //为空时,直接构造一个{_root = new Node(key);return true;}else //不为空时,利用搜索数的特性找到该插入的位置{Node* cur = _root;Node* parent = _root;while (cur){if (cur->_key > key){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else if (cur->_key < key){parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else{return false; //搜索二叉树不允许有重复的数}}//循环走完,已经找到了cur = new Node(key);if (parent->_key > key){parent->_left = cur;}else{parent->_right = cur;}return true;}}Node* Find(const K& key){Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (cur->_key > key){cur = cur->_left;}else if (cur->_key < key){cur = cur->_right;}elsereturn cur;}return nullptr;}bool Erase(const K& key){Node* parent = nullptr;Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (cur->_key > key){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else if (cur->_key < key){parent = cur;cur = cur->_right; }else // 找到了{if (cur->_left == nullptr){if (cur == _root)_root = cur->_right;else{if (parent->_left == cur){parent->_left = cur->_right;}else{parent->_right = cur->_right;}}delete cur;}else if (cur->_right == nullptr){if (cur == _root){_root = cur->_left;}else{if (parent->_left == cur){parent->_left = cur->_left;}else{parent->_right = cur->_left;}}delete cur;}else{Node* right = cur->_right;while (right->_left){right = right->_left;}K temkey = right->_key;Erase(right->_key);cur->_key = temkey;}return true;}}return false;}void PrintIoder(){Print(_root);cout << endl;}void Print(Node* root){if (root == nullptr)return;Print(root->_left);cout << root->_key << " ";Print(root->_right);}
private:Node* _root;
};
三:二叉搜索树的应用
- K模型:
K模型即只有key作为关键码,结构中只需要存储Key即可,关键码即为需要搜索到的值。
- 比如:给一个单词word,判断该单词是否拼写正确,具体方式如下:
以单词集合中的每个单词作为key,构建一棵二叉搜索树 在二叉搜索树中检索该单词是否存在,存在则拼写正确,不存在则拼写错误。
- KV模型:
每一个关键码key,都有与之对应的值Value,即<Key, Value>的键值对。
- 比如:
- 英汉词典就是英文与中文的对应关系,通过英文可以快速找到与其对应的中文,英
文单词与其对应的中文<word, chinese>就构成一种键值对; - 统计单词次数,统计成功后,给定
单词就可快速找到其出现的次数,单词与其出现次数就是<word, count>就构成一种键值对。
四:二叉树有关面试题
二叉树常见oj题
ps
想和博主一样刷优质面试和算法题嘛,快来刷题面试神器牛客吧,期待与你在牛客相见