背景知识:
Vector of Locally Aggregated Descriptors(VLAD)image retrieval.
【CC】是广泛使用的图像提取方式,本文是在在这个提取器上做改进;具体是啥下面有介绍
weakly supervised ranking loss
【CC】本文的另外一个创新点是弱监督的LOSS设计,后面有介绍
Place recongnition as an instance retrieval task:the query image location is estimated using the locations of the most visually similar images querying a large geotagged database;image is represented using local invariant features such as SIFT. the locations of top ranked images are used as suggestions for the location of the query
【CC】位置识别可以看成一个实例提取任务:给定一个查询图片,其位置通过已存储图片库中最相近的图片进行估计,图片库是经过几何标注的。肯定不能存储原图,一般是经过局部不变性过滤器进行了特征提取的,比如SIFT.
Representation compressed and effificiently indexed. image database augmented by 3D structure enables recovery of accurate camera pose.
【CC】经过提取后的特征肯定要压缩,并且能够高效索引(即,最好能够找一种排序算法). 图片库是经过3D增强的,能够从库中的特征还原camera的3D位姿
what is the appropriate representation of a place that is rich enough to distinguish similarly
【CC】位置识别问题本质是如何设计一个算子或者NN 表达一个PLACE能够提供足够的信息用来度量相似性
解题思路:
First, what is a good CNN architecture for place recognition?
【CC】设计一个NN的网络做特征提取用来做位置识别
inspired by the Vector of Locally Aggregated Descriptors (VLAD) representation, develop a convolutional neural network architecture aggregates mid-level (conv5) convolutional features extracted from the entire image into a compact single vector representation,resulting aggregated representation compressed PCA
【CC】整体的思路是对VLAD的改进. 引入卷积层(可以看到后面用来两种经典卷积网络VGG16/AlexNet做改造),加入一个COVN5的block,然后使用PCA进行压缩
Second, how to gather suffificient amount of annotated data?
【CC】如何搞到足够标签数据
we know the two panoramas are captured at approximately similar positions based on their (noisy) GPS but we don’t know which parts of the panoramas depict the same parts of the scene
【CC】全局场景数据会有噪声,只知道两幅图片位置相近,但不知道那部分特征是公共的
Third, how can we train the developed architecture tailored for the place recognition task
【CC】看看后面的rank loss函数设计就知道,只需要简单进行图片分类
a function f as the “image representation extractor”, given an image Ii it produces a fixed size vector f(Ii). the representations for the entire database {Ii}. Visual search finding the nearest database image to the query, exactly or through approximate nearest
neighbour search, by sorting images based on the Euclidean distance d(q, Ii) between f(q) and f(Ii).
【CC】形式化表述, f是一个提取器:输入图片Ii输出固定长度向量. 给定图片从库中找到“距离”最近的图片,距离定义为待查询的图片特征向量f(q)跟候选图片特征向量f(Ii)的欧式距离
The representation is parametrized with a set of parameters θ referring to it as fθ(I). Euclidean distance dθ(Ii, Ij ) = || fθ(Ii) − fθ(Ij)||
【CC】更进一步,参数为 θ的NN网络记作fθ(I).对应的欧式距离如上式子
设计要求
Most image retrieval pipelines are based on (i)extracting local descriptors, then (ii) pooled in an orderless manner.
【CC】传统特征提取的流水线:先提取本地特征,然后无序的池化(类似ORB+词袋模型)
Robustness to lighting and viewpoint changes is provided by the descriptors
【CC】对光照/视角变化的鲁棒性要靠提取器本身性能
(i), we crop the CNN at the last convolutional layer and view it as a dense descriptor extractor.
(ii) we design a new pooling layer that pools extracted descriptors into a fixed image representation and its parameters are learnable
【CC】先裁剪NN网络的最后一层作为提取器,使用新设计的池化层输出固定长度的向量
传统VLAD
Formally, given N D-dimensional local image descriptors {xi} as input, and K cluster centres (“visual words”) {ck} as VLAD parameters, the output VLAD image representation V is K×D-dimensional.
【CC】输入N个D维特征,有K个中心点(参数),VLAD输出K*D的阵
The (j, k) element of V is computed as follows:
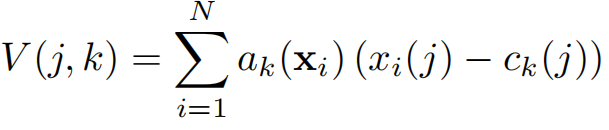
where xi(j) and ck(j) are the j-th dimensions of the i-th descriptor and k-th cluster centre, respectively. ak(xi) denotes the membership of the descriptor xi to k-th visual word, i.e. it is 1 if cluster ck is the closest cluster to descriptor xi and 0 otherwise
【CC】输出V计算式如上,xi(j)第i个特征的第j维, ck(j)第k个中心点的第j维;ak(xi)一个指示函数:第i个特征xi靠近第k个中心点就表征1, 否则0;V(j,k)就像一个xi关于ck的“协方差阵”(实际上是关于中心点距离的阵)
Intuitively, each D-dimensional column k of V records the sum of residuals (xi −ck) of descriptors which are assigned to cluster ck
【CC】V阵的K列就是xi关于ck的残差和
The matrix V is then L2-normalized column-wise, converted into a vector, and finally L2-normalized in its entirety .
【CC】先对V阵所有列进行L2正则化,得到一个向量,然后对整个向量L2正则化;
【总结】上面所有就是vlad的计算,得到了一个固定长度的向量,下面对VLAD进行改造
形式化改进
to mimic VLAD in a CNN framework ,the layer’s operation is differentiable. The source of discontinuities in VLAD is the hard assignment ak(xi), we replace it with soft assignment
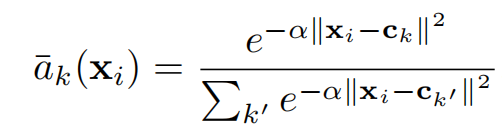
which assigns the weight of descriptor xi to cluster ck proportional to their proximity. α is a parameter (positive constant) that controls the decay of the response with the magnitude of the distance,α → +∞ setup replicates the original VLAD
【CC】为了通过CNN模仿VLAN,要保证所有层可微;原始VLAD中不可微的就是指示函数ak(xi),我们使用soft指派函数(可微)替换原有的ak(xi),新的a¯k(xi)可以表征xi关于中心店ck的距离权重. α是一个衰减系数,超参,设置成 +∞就退化成了原始的ak(xi)
By expanding the squares in, it is easy to see that the term e−αk xik 2 cancels between the numerator and the denominator resulting in a soft-assignment of the following form:
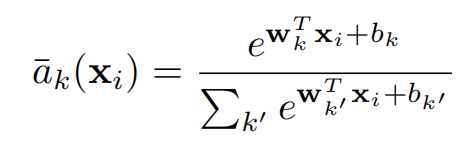
where vector wk = 2αck and scalar bk = −α||ck||2
【CC】展开,分子/分母消掉二次项 , 得到类似线性的式子,将新a¯k(xi)带入到V的计算式中得到如下V的式子
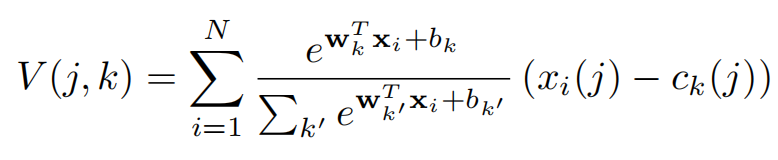
where {wk}, {bk} and {ck} are sets of trainable parameters for each cluster k.
Similarly to the original VLAD descriptor, the NetVLAD layer aggregates the first order statistics of residuals (xi − ck) in different parts of the descriptor space weighted by the soft-assignment a¯k(xi) of descriptor xi to cluster k.
【CC】{wk}, {bk} {ck} 都是NN网络关于K可以训练的参数. 新的V值计算跟老的相比,有相同的于xi - ck残差项,不同在于ak换成了可训练的soft-
three independent sets of parameters {wk}, {bk} and {ck}, compared to just {ck} of the original VLAD. This enables greater flexibility than the original VLAD,show:

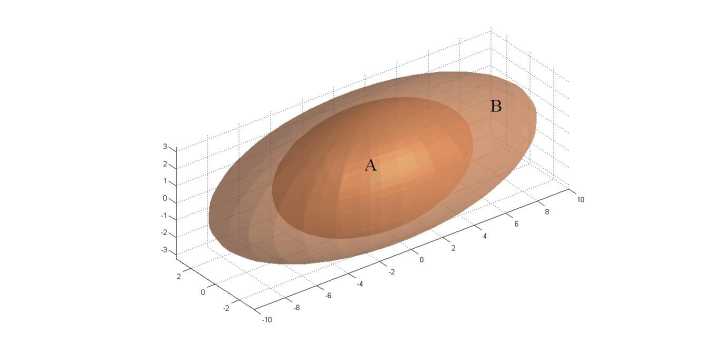
Benefits of supervised VLAD. Red and green circles are local descriptors from two different images, assigned to the same cluster(Voronoi cell). Under the VLAD encoding, their contribution to the similarity score between the two images is the scalar product (as final VLAD vectors are L2-normalized) between the corresponding residuals, where a residual vector is computed as the difference between the descriptor and the cluster’s anchor point. The anchor point ck can be interpreted as the origin of a new coordinate system local to the the specific cluster k. In standard VLAD, the anchor is chosen as the cluster centre (×) in order to evenly distribute the residuals across the database. However, in a supervised setting where the two descriptors are known to belong to images which should not match, it is possible to learn a better anchor (? ) which causes the scalar product between the new residuals to be small
【CC】新的计算式有三个独立参数项{wk}, {bk} {ck}, 比老的更灵活; 上图显示,绿/红点(两张图片的特征值)关于CK 的矢量内积就代表其相似性. 如果采用监督的方式能够学到一个更好的ck点,明知道红点-绿点不是同一个地点,如图Ck点可以从X点到星号点迁移
实际面临的挑战
(i) how to gather enough annotated training data
– Weak supervision from the Time Machine – Google Street View Time Machine
(ii) what is the appropriate loss for the place recognition task.
【CC】第二个才是本文的核心; 至于google的数据这个在国内用不了,百度街景好像没有这个功能,还不知道国内有啥开源的数据集可以用

Google Street View Time Machine examples. Each column shows perspective images generated from panoramas from
nearby locations, taken at different times. A well designed method can use this source of imagery to learn to be invariant to changes in viewpoint and lighting (a-c), and to moderate occlusions (b).It can also learn to suppress confusing visual information such as clouds (a), vehicles and people (b-c), and to chose to either ignore vegetation or to learn a season-invariant vegetation representation(a-c).
【CC】最核心的还是有“真值”-- 知道哪些图片在物理位置上相近的,进而通过NN学习到“局部的不变性”
Therefore, for a given training query q, the GPS information can only be used as a source of (i) potential positives {pqi }, i.e. images that are geographically close to the query, and (ii)definite negatives {nqj}, i.e. images that are geographically far from the query
【CC】这里是关于GPS信息的使用原则:GPS信息只能在确认了是相邻/远离的场景下才能作为属性进行查询,而不能以GPS作为判定的依据
损失函数设计
For a given test query image q, the goal is to rank a database image Ii∗ from a close-by location higher than all other far away images Ii in the database. we wish the Euclidean distance dθ(q, I) between the query q and a close-by image Ii∗ to be smaller than the distance to far away images in the database Ii, i.e. dθ(q, Ii∗) < dθ(q, Ii), for all images Ii further than a certain distance from the query on the map
【CC】给一个待查找的图片q,对图片库进行查找希望找到一个Ii* 使得q到Ii*的欧式距离是所有图片中最小的
We obtain a training dataset of tuples (q, {pqi }, {nqj}), where for each training query image q we have a set of potential positives {pqi } and the set of definite negatives {nqj}.
【CC】数据集中的一次q查询,对应了一组正样本{pqi }和一组负样本{nqj}
the set of potential positives contains at least one positive image that should match the query, but we do not know which one. To address this ambiguity, we propose to identify the best matching potential positive image pqi∗
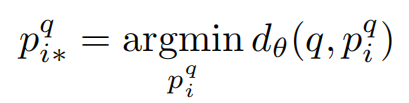
for each training tuple (q, {pqi }, {nqj}). The goal then becomes to learn an image representation fθ so that distance dθ(q, pqi∗) between the training query q and the best matching potential positive pqi∗ is smaller than the distance dθ(q, nqj ) between the query q and all negative images qj :
【CC】如果我们对每次查询q有真值pqi∗,那么我们需要训练的是图像的表达fθ(即本文的描述子网络VLADNET),使得上面的两个式子成立:即真值是所有正样本中距离最小的, 真值的距离比所有的负样本都小
Based on this intuition we define a weakly supervised ranking loss Lθ for a training tuple (q, {pqi }, {nqj}) as
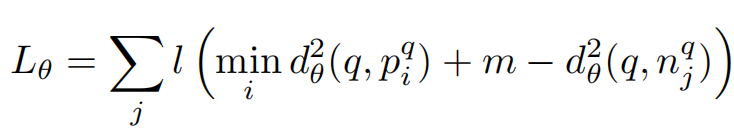
where l is the hinge loss l(x) = max(x, 0), and m is a constant parameter giving the margin
【CC】m是一个超参,代表正负样本距离差能够容忍的最小值,超过m才计算loss,小于这个值loss为0; 有点类似 triplet loss
网络结构

【CC】输入图片后面加了一个卷积层(有各种cnn的比对实现),将WHD的图片抽取成N*D的特征向量x,将x分别塞到(w,b)θ的小卷积网络里面和VLAD里面,本质就是对改进式子(equation4)的实现;可训练的就是两部分fθ(即图片的特征表达层)和(w,b)θ,使得上面的Loss func - Lθ最小