ThreadPoolExecutor
ThreadPoolExecutor构造函数的五大参数
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,int maximumPoolSize,long keepAliveTime,TimeUnit unit,BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue) {this(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue,Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), defaultHandler);}
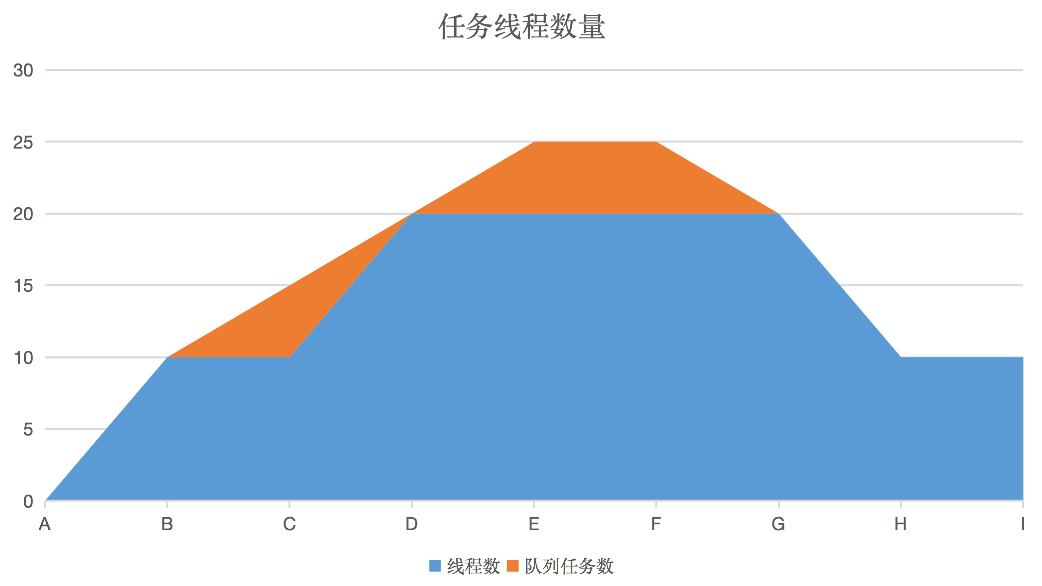
- corePoolSize 核心线程数,表示线程池支持的最小线程数
- maximumPoolSize 最大线程数,当线程数大于核心线程数后,并且有界队列里存放能时,线程池还能接受maximumPoolSize - corePoolSize个线程
- keepAliveTime 保持存活时间,空闲线程的存活时间,为了更好的复用线程
- unit 线程存活时间的单位
- workQueue 队列,等待线程存放的队列
提问:如下线程池同一时间最多能接受多少个线程?
ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2,5,10L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(5));
答案是10个,等待队列里5个,最大线程数5个,多的线程请求将会被拒绝,异常如下

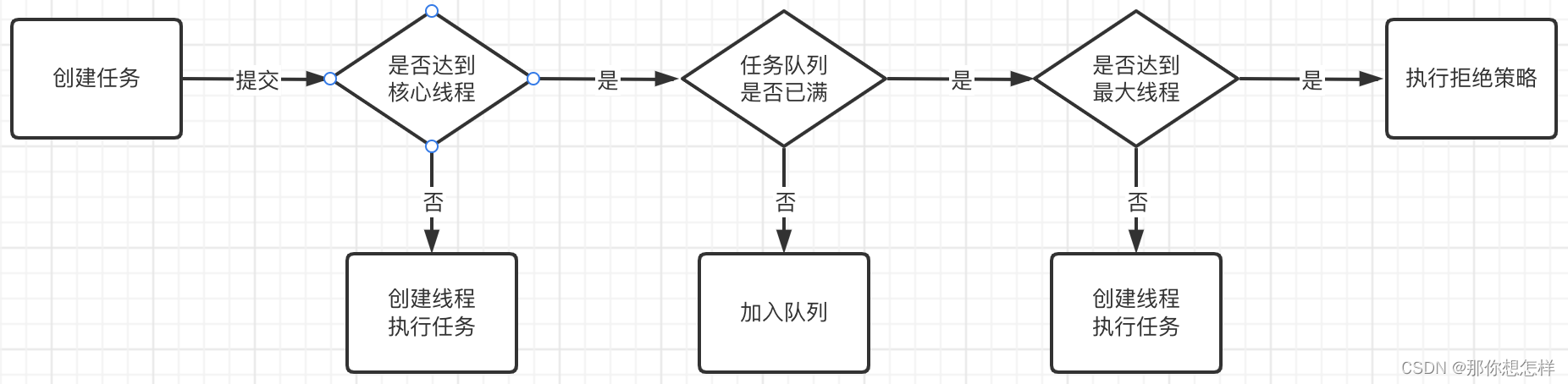
线程池的处理流程:

逻辑流程图

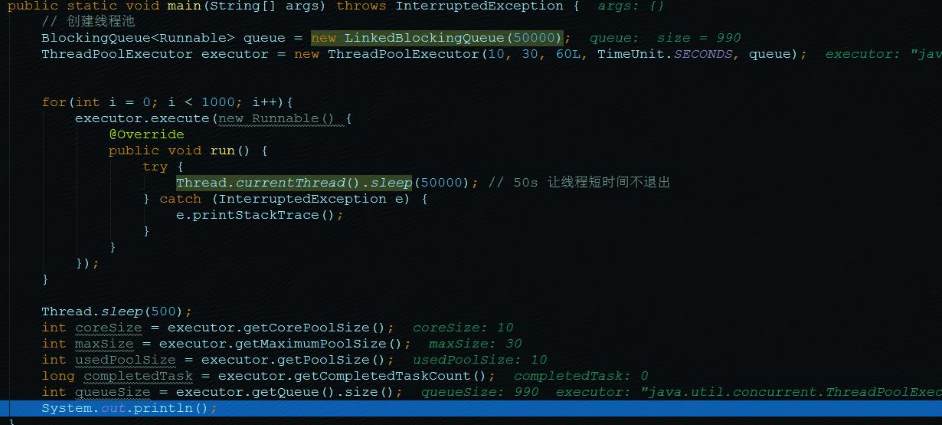
写个demo压测下线程池
public class ThreadPoolDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(80,150,10L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(200));long start = System.currentTimeMillis() / 1000;IntStream.range(0,500).forEach(i ->{pool.submit(new MyThread());try {Thread.sleep(3L);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}});pool.shutdown();System.out.println("use time " + (System.currentTimeMillis() / 1000 - start) + "秒");}static class MyThread implements Runnable{@Overridepublic void run() {try {Thread.sleep(500L);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" run ....");} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}
}
执行结果

执行500个耗时0.5秒的操作用时2秒,速度提升了125倍。
注意
线程池的参数设置一定要甚重,当并发过高时,等待队列和最大线程数都到极限时,线程池就会采用一定的拒绝策略拒绝任务,这个一定要根据业务场景考虑。
另外还有一点队列尽量选用有界队列,否则最大线程数是没有意义的,潜在风险就是内存会爆。
【以上仅是个人观点,如有错误欢迎指证】
关注个人公众号