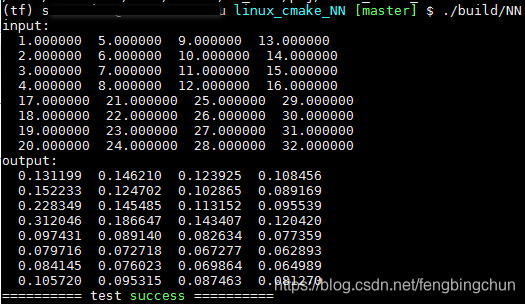
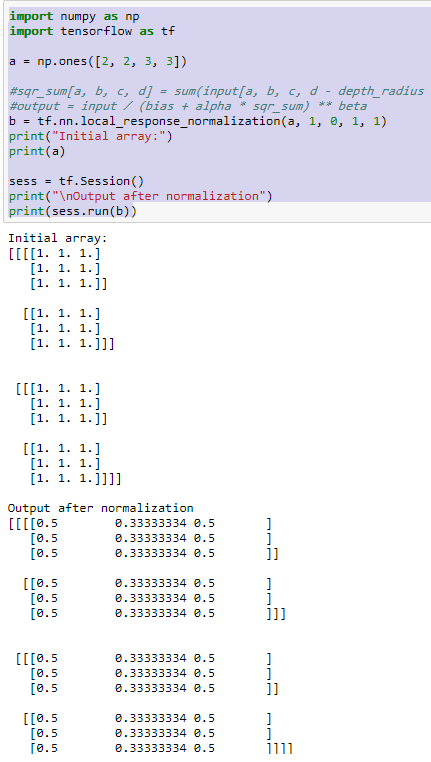
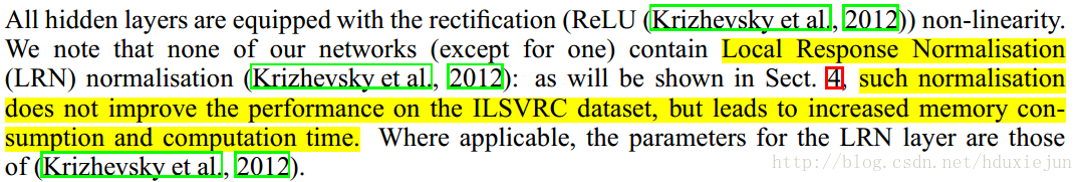
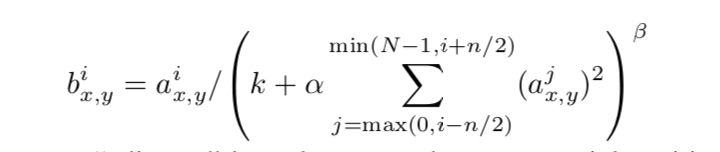昨日面试,被问道BN层和LRN层,一直以来用的都是bn,所以当时对LRN只剩下点印象,事后弥补了一下这边知识点的不足,浅谈自己对LRN层的理解,如果误导,欢迎指正.
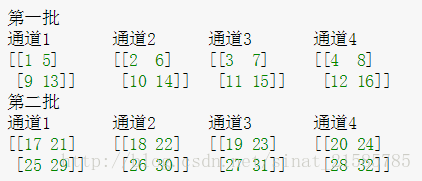
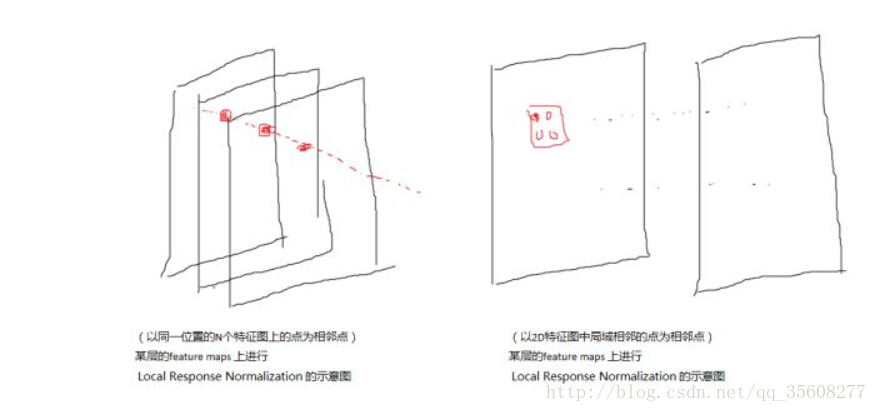
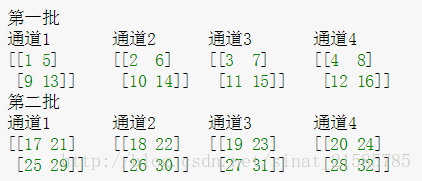
LRN层的作用是对局部区域进行归一化,对响应比较大的值变得更大,对响应比较小的值抑制.先看一下caffe的代码
可以看到四个参数.
layer {name: "norm1"type: "LRN"bottom: "conv1"top: "norm1"lrn_param {// norm_region:ACROSS_CHANNELS,表示相邻通道求和归一化,局部区域块形状为//local_size*1*1,如果是WITHIN_CHANNEL表示一个通道内部求和归一,局部区域形状为//1*local_zie*local_size// local_size: 5//默认值5,如果是跨通道的,表示求和的通道数;如果在通道内,表示求和正方形区域长度alpha: 0.0001//公式的参数,默认为1beta: 0.75//公式的参数,默认为5}
}归一化时,每个输入值都将除以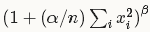
#include <vector>#include "caffe/layers/lrn_layer.hpp"
#include "caffe/util/math_functions.hpp"namespace caffe {template <typename Dtype>
void LRNLayer<Dtype>::LayerSetUp(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {size_ = this->layer_param_.lrn_param().local_size();//提取size_的值CHECK_EQ(size_ % 2, 1) << "LRN only supports odd values for local_size";//检查是否为奇数,不是则报错pre_pad_ = (size_ - 1) / 2; //计算pad值,前后各补一半0alpha_ = this->layer_param_.lrn_param().alpha();//提取alphabeta_ = this->layer_param_.lrn_param().beta();//提取betak_ = this->layer_param_.lrn_param().k();//提取kif (this->layer_param_.lrn_param().norm_region() ==//如果是within_channel模式,还需要初始化一系列中间层,暂且不关注LRNParameter_NormRegion_WITHIN_CHANNEL) {// Set up split_layer_ to use inputs in the numerator and denominator.split_top_vec_.clear();split_top_vec_.push_back(&product_input_);split_top_vec_.push_back(&square_input_);LayerParameter split_param;split_layer_.reset(new SplitLayer<Dtype>(split_param));split_layer_->SetUp(bottom, split_top_vec_);// Set up square_layer_ to square the inputs.square_bottom_vec_.clear();square_top_vec_.clear();square_bottom_vec_.push_back(&square_input_);square_top_vec_.push_back(&square_output_);LayerParameter square_param;square_param.mutable_power_param()->set_power(Dtype(2));square_layer_.reset(new PowerLayer<Dtype>(square_param));square_layer_->SetUp(square_bottom_vec_, square_top_vec_);// Set up pool_layer_ to sum over square neighborhoods of the input.pool_top_vec_.clear();pool_top_vec_.push_back(&pool_output_);LayerParameter pool_param;pool_param.mutable_pooling_param()->set_pool(PoolingParameter_PoolMethod_AVE);pool_param.mutable_pooling_param()->set_pad(pre_pad_);pool_param.mutable_pooling_param()->set_kernel_size(size_);pool_layer_.reset(new PoolingLayer<Dtype>(pool_param));pool_layer_->SetUp(square_top_vec_, pool_top_vec_);// Set up power_layer_ to compute (1 + alpha_/N^2 s)^-beta_, where s is// the sum of a squared neighborhood (the output of pool_layer_).power_top_vec_.clear();power_top_vec_.push_back(&power_output_);LayerParameter power_param;power_param.mutable_power_param()->set_power(-beta_);power_param.mutable_power_param()->set_scale(alpha_);power_param.mutable_power_param()->set_shift(Dtype(1));power_layer_.reset(new PowerLayer<Dtype>(power_param));power_layer_->SetUp(pool_top_vec_, power_top_vec_);// Set up a product_layer_ to compute outputs by multiplying inputs by the// inverse demoninator computed by the power layer.product_bottom_vec_.clear();product_bottom_vec_.push_back(&product_input_);product_bottom_vec_.push_back(&power_output_);LayerParameter product_param;EltwiseParameter* eltwise_param = product_param.mutable_eltwise_param();eltwise_param->set_operation(EltwiseParameter_EltwiseOp_PROD);product_layer_.reset(new EltwiseLayer<Dtype>(product_param));product_layer_->SetUp(product_bottom_vec_, top);}
}template <typename Dtype>
void LRNLayer<Dtype>::Reshape(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {CHECK_EQ(4, bottom[0]->num_axes()) << "Input must have 4 axes, "<< "corresponding to (num, channels, height, width)";num_ = bottom[0]->num();channels_ = bottom[0]->channels();height_ = bottom[0]->height();width_ = bottom[0]->width();//初始化n\c\h\w的值switch (this->layer_param_.lrn_param().norm_region()) {//看参数normal_region选的是什么case LRNParameter_NormRegion_ACROSS_CHANNELS://如果是通道间归一化top[0]->Reshape(num_, channels_, height_, width_);//将top尺寸和bottom尺寸设置成一样大,这样归一化时,只需要
//scale_值乘bottom值就可以得到相应的top值scale_.Reshape(num_, channels_, height_, width_);break;case LRNParameter_NormRegion_WITHIN_CHANNEL://如果是空间区域归一化split_layer_->Reshape(bottom, split_top_vec_);square_layer_->Reshape(square_bottom_vec_, square_top_vec_);pool_layer_->Reshape(square_top_vec_, pool_top_vec_);power_layer_->Reshape(pool_top_vec_, power_top_vec_);product_layer_->Reshape(product_bottom_vec_, top);break;}
}template <typename Dtype>
void LRNLayer<Dtype>::Forward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {switch (this->layer_param_.lrn_param().norm_region()) {case LRNParameter_NormRegion_ACROSS_CHANNELS:CrossChannelForward_cpu(bottom, top);break;case LRNParameter_NormRegion_WITHIN_CHANNEL:WithinChannelForward(bottom, top);break;default:LOG(FATAL) << "Unknown normalization region.";}
}template <typename Dtype>
void LRNLayer<Dtype>::CrossChannelForward_cpu(
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom, vector<Blob<Dtype>*>* top) {
const Dtype* bottom_data = bottom[0]->cpu_data();
Dtype* top_data = (*top)[0]->mutable_cpu_data();
Dtype* scale_data = scale_.mutable_cpu_data();//用指针获取每个Blob对象的内存地址,便于后面操作
// start with the constant value
for (int i = 0; i < scale_.count(); ++i) {//初始化值为1.0
scale_data[i] = 1.;
}
Blob<Dtype> padded_square(1, channels_ + size_ - 1, height_, width_);//补零后的Blob,第三维尺寸比bottom大了size_ - 1;
Dtype* padded_square_data = padded_square.mutable_cpu_data();
caffe_set(padded_square.count(), Dtype(0), padded_square_data);//先清零
Dtype alpha_over_size = alpha_ / size_;//预先计算公式中的alpha/n
// go through the images
for (int n = 0; n < num_; ++n) {//bottom的第四维尺寸num_,需要分解为单个来做归一化
// compute the padded square
caffe_sqr(channels_ * height_ * width_,bottom_data + bottom[0]->offset(n),padded_square_data + padded_square.offset(0, pre_pad_));//计算bottom的平方,放入padded_square矩阵中,前pre_pad_个位置依旧0
// Create the first channel scale
for (int c = 0; c < size_; ++c) {//对n个通道平方求和并乘以预先算好的(alpha/n),累加至scale_中(实现计算 1 + sum_under_i(x_i^2))caffe_axpy<Dtype>(height_ * width_, alpha_over_size,padded_square_data + padded_square.offset(0, c),scale_data + scale_.offset(n, 0));
}
for (int c = 1; c < channels_; ++c) {//这里使用了类似FIFO的形式计算其余scale_参数,每次向后移动一个单位,加头去尾,避免重复计算求和// copy previous scalecaffe_copy<Dtype>(height_ * width_,scale_data + scale_.offset(n, c - 1),scale_data + scale_.offset(n, c));// add headcaffe_axpy<Dtype>(height_ * width_, alpha_over_size,padded_square_data + padded_square.offset(0, c + size_ - 1),scale_data + scale_.offset(n, c));// subtract tailcaffe_axpy<Dtype>(height_ * width_, -alpha_over_size,padded_square_data + padded_square.offset(0, c - 1),scale_data + scale_.offset(n, c));
}
}// In the end, compute output
caffe_powx<Dtype>(scale_.count(), scale_data, -beta_, top_data);//计算求指数,由于将除法转换为乘法,故指数变负
caffe_mul<Dtype>(scale_.count(), top_data, bottom_data, top_data);//bottom .* scale_ -> top
}template <typename Dtype>
void LRNLayer<Dtype>::WithinChannelForward(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {split_layer_->Forward(bottom, split_top_vec_);square_layer_->Forward(square_bottom_vec_, square_top_vec_);pool_layer_->Forward(square_top_vec_, pool_top_vec_);power_layer_->Forward(pool_top_vec_, power_top_vec_);product_layer_->Forward(product_bottom_vec_, top);
}template <typename Dtype>
void LRNLayer<Dtype>::Backward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top,const vector<bool>& propagate_down, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom) {switch (this->layer_param_.lrn_param().norm_region()) {case LRNParameter_NormRegion_ACROSS_CHANNELS:CrossChannelBackward_cpu(top, propagate_down, bottom);break;case LRNParameter_NormRegion_WITHIN_CHANNEL:WithinChannelBackward(top, propagate_down, bottom);break;default:LOG(FATAL) << "Unknown normalization region.";}
}template <typename Dtype>
void LRNLayer<Dtype>::CrossChannelBackward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top, const vector<bool>& propagate_down,const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom) {const Dtype* top_diff = top[0]->cpu_diff();const Dtype* top_data = top[0]->cpu_data();const Dtype* bottom_data = bottom[0]->cpu_data();const Dtype* scale_data = scale_.cpu_data();Dtype* bottom_diff = bottom[0]->mutable_cpu_diff();Blob<Dtype> padded_ratio(1, channels_ + size_ - 1, height_, width_);Blob<Dtype> accum_ratio(1, 1, height_, width_);Dtype* padded_ratio_data = padded_ratio.mutable_cpu_data();Dtype* accum_ratio_data = accum_ratio.mutable_cpu_data();// We hack a little bit by using the diff() to store an additional resultDtype* accum_ratio_times_bottom = accum_ratio.mutable_cpu_diff();caffe_set(padded_ratio.count(), Dtype(0), padded_ratio_data);Dtype cache_ratio_value = 2. * alpha_ * beta_ / size_;caffe_powx<Dtype>(scale_.count(), scale_data, -beta_, bottom_diff);caffe_mul<Dtype>(scale_.count(), top_diff, bottom_diff, bottom_diff);// go through individual dataint inverse_pre_pad = size_ - (size_ + 1) / 2;for (int n = 0; n < num_; ++n) {int block_offset = scale_.offset(n);// first, compute diff_i * y_i / s_icaffe_mul<Dtype>(channels_ * height_ * width_,top_diff + block_offset, top_data + block_offset,padded_ratio_data + padded_ratio.offset(0, inverse_pre_pad));caffe_div<Dtype>(channels_ * height_ * width_,padded_ratio_data + padded_ratio.offset(0, inverse_pre_pad),scale_data + block_offset,padded_ratio_data + padded_ratio.offset(0, inverse_pre_pad));// Now, compute the accumulated ratios and the bottom diffcaffe_set(accum_ratio.count(), Dtype(0), accum_ratio_data);for (int c = 0; c < size_ - 1; ++c) {caffe_axpy<Dtype>(height_ * width_, 1.,padded_ratio_data + padded_ratio.offset(0, c), accum_ratio_data);}for (int c = 0; c < channels_; ++c) {caffe_axpy<Dtype>(height_ * width_, 1.,padded_ratio_data + padded_ratio.offset(0, c + size_ - 1),accum_ratio_data);// compute bottom diffcaffe_mul<Dtype>(height_ * width_,bottom_data + top[0]->offset(n, c),accum_ratio_data, accum_ratio_times_bottom);caffe_axpy<Dtype>(height_ * width_, -cache_ratio_value,accum_ratio_times_bottom, bottom_diff + top[0]->offset(n, c));caffe_axpy<Dtype>(height_ * width_, -1.,padded_ratio_data + padded_ratio.offset(0, c), accum_ratio_data);}}
}template <typename Dtype>
void LRNLayer<Dtype>::WithinChannelBackward(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top, const vector<bool>& propagate_down,const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom) {if (propagate_down[0]) {vector<bool> product_propagate_down(2, true);product_layer_->Backward(top, product_propagate_down, product_bottom_vec_);power_layer_->Backward(power_top_vec_, propagate_down, pool_top_vec_);pool_layer_->Backward(pool_top_vec_, propagate_down, square_top_vec_);square_layer_->Backward(square_top_vec_, propagate_down,square_bottom_vec_);split_layer_->Backward(split_top_vec_, propagate_down, bottom);}
}#ifdef CPU_ONLY
STUB_GPU(LRNLayer);
STUB_GPU_FORWARD(LRNLayer, CrossChannelForward);
STUB_GPU_BACKWARD(LRNLayer, CrossChannelBackward);
#endifINSTANTIATE_CLASS(LRNLayer);} // namespace caffe