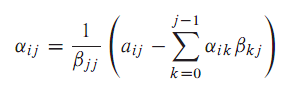1.问题提出
1.前段时间在项目中用到Lists.transform返回的List,在对该list修改后发现修改并没有反映在结果里,研究源码后发现问题还挺大。下面通过单步调试的结果来查看Guava Lists.transform使用过程中需要注意的地方。
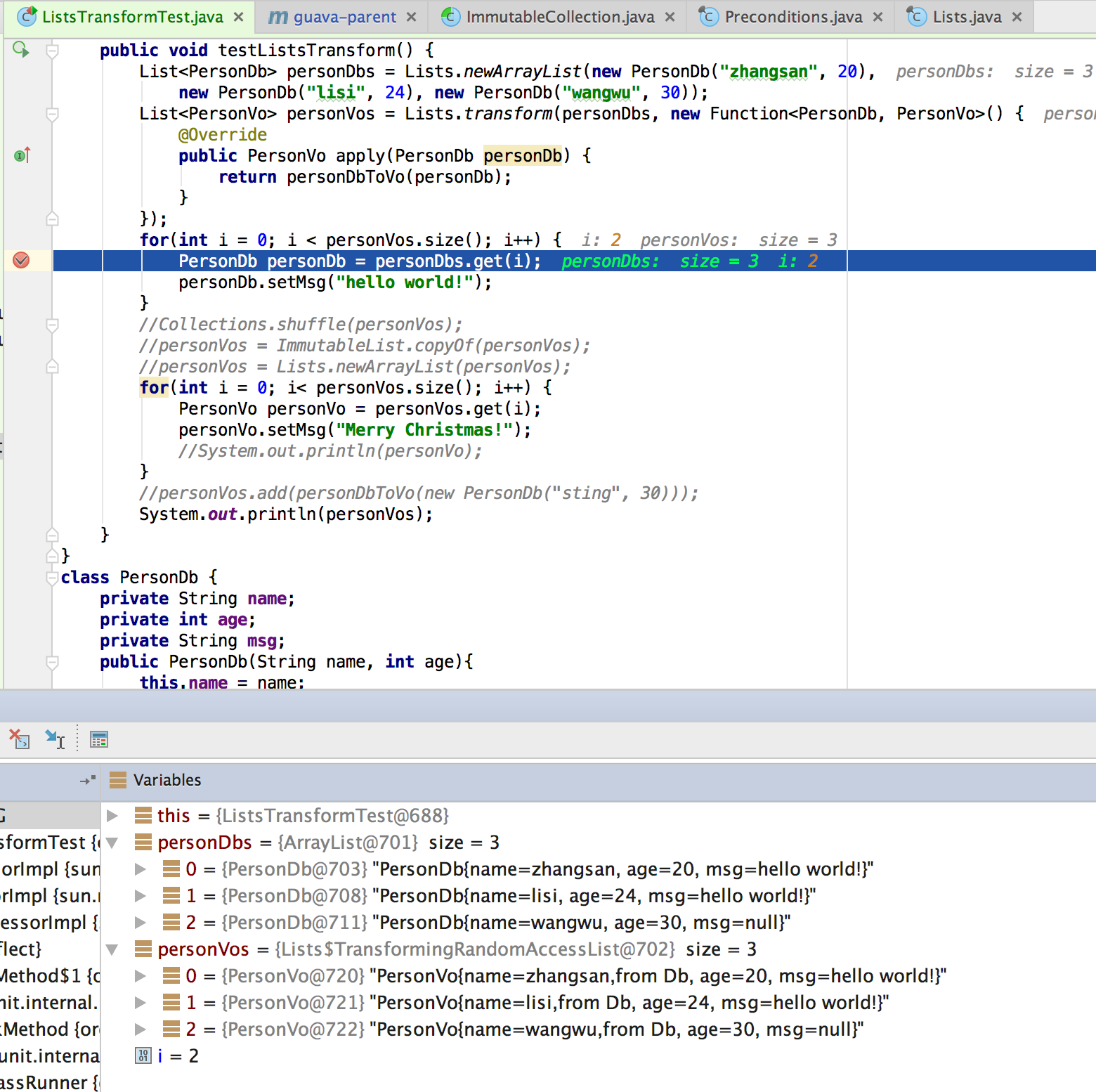
a.对原有的list列表修改会影响Lists.transform已经生成列表
由上图可以看出,对原数据集personDbs的修改会直接影响到Lists.transform方法返回的结果personVos,
这是很危险的,如果在使用的过程中不注意的话会造成很严重的问题,而这种问题又是很隐蔽的,在项目中
无疑是个不定时的炸弹。
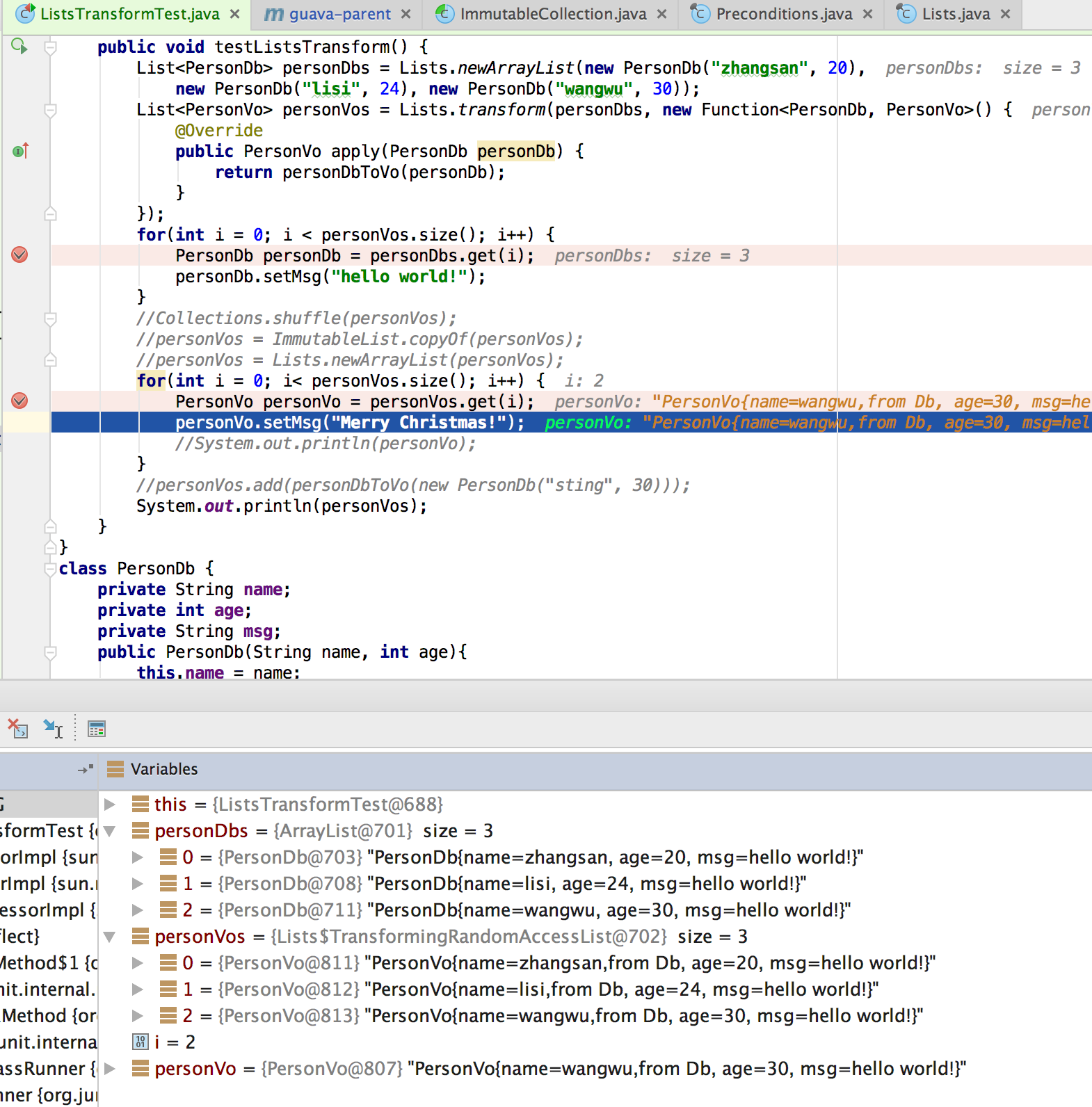
b.对Lists.transform生成的列表的元素进行修改可能无法生效
由上面的调试结果可以看出对Lists.transform返回的List列表中的元素的修改不会"生效",即修改不会反映在list列表中。
c.对returnList调用add、addAll和shuffle等修改returnList的方法会抛异常
对personVos调用Collections.shuffle(personVos);或personVos.add(personDbToVo(new PersonDb("sting", 30)));
都会抛出java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException。
附测试代码:
package com.google.common.base;import com.google.common.collect.Lists;
import org.junit.Test;import java.util.List;/*** @author mnmlist@163.com* @date 2016/12/23* @time 19:31*/
public class ListsTransformTest {public PersonVo personDbToVo(PersonDb personDb) {Preconditions.checkNotNull(personDb, "[PersonDbToVo]personDb为null");PersonVo personVo = new PersonVo();personVo.setName(personDb.getName() + ",from Db");personVo.setAge(personDb.getAge());personVo.setMsg(personDb.getMsg());return personVo;}@Testpublic void testListsTransform() {List<PersonDb> personDbs = Lists.newArrayList(new PersonDb("zhangsan", 20),new PersonDb("lisi", 24), new PersonDb("wangwu", 30));List<PersonVo> personVos = Lists.transform(personDbs, new Function<PersonDb, PersonVo>() {@Overridepublic PersonVo apply(PersonDb personDb) {return personDbToVo(personDb);}});for(PersonDb personDb : personDbs) {personDb.setMsg("hello world!");}//Collections.shuffle(personVos);//personVos = ImmutableList.copyOf(personVos);//personVos = Lists.newArrayList(personVos);for(PersonVo personVo : personVos) {personVo.setMsg("Merry Christmas!");}personVos.add(personDbToVo(new PersonDb("sting", 30)));System.out.println(personVos);}
}
class PersonDb {private String name;private int age;private String msg;public PersonDb(String name, int age){this.name = name;this.age = age;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}public String getMsg() {return msg;}public void setMsg(String msg) {this.msg = msg;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return MoreObjects.toStringHelper(this).add("name", name).add("age", age).add("msg", msg).toString();}
}
class PersonVo {private String name;private int age;private String msg;public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}public String getMsg() {return msg;}public void setMsg(String msg) {this.msg = msg;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return MoreObjects.toStringHelper(this).add("name", name).add("age", age).add("msg", msg).toString();}
}2.源码解读和异常分析
带着上面的三个问题去查看源码 /*** Returns a list that applies {@code function} to each element of {@code* fromList}. The returned list is a transformed view of {@code fromList};* changes to {@code fromList} will be reflected in the returned list and vice* versa.** <p>Since functions are not reversible, the transform is one-way and new* items cannot be stored in the returned list. The {@code add},* {@code addAll} and {@code set} methods are unsupported in the returned* list.** <p>The function is applied lazily, invoked when needed. This is necessary* for the returned list to be a view, but it means that the function will be* applied many times for bulk operations like {@link List#contains} and* {@link List#hashCode}. For this to perform well, {@code function} should be* fast. To avoid lazy evaluation when the returned list doesn't need to be a* view, copy the returned list into a new list of your choosing.** <p>If {@code fromList} implements {@link RandomAccess}, so will the* returned list. The returned list is threadsafe if the supplied list and* function are.** <p>If only a {@code Collection} or {@code Iterable} input is available, use* {@link Collections2#transform} or {@link Iterables#transform}.** <p><b>Note:</b> serializing the returned list is implemented by serializing* {@code fromList}, its contents, and {@code function} -- <i>not</i> by* serializing the transformed values. This can lead to surprising behavior,* so serializing the returned list is <b>not recommended</b>. Instead,* copy the list using {@link ImmutableList#copyOf(Collection)} (for example),* then serialize the copy. Other methods similar to this do not implement* serialization at all for this reason.*/@CheckReturnValuepublic static <F, T> List<T> transform(List<F> fromList, Function<? super F, ? extends T> function) {return (fromList instanceof RandomAccess)? new TransformingRandomAccessList<F, T>(fromList, function): new TransformingSequentialList<F, T>(fromList, function);}private static class TransformingRandomAccessList<F, T> extends AbstractList<T>implements RandomAccess, Serializable {final List<F> fromList;final Function<? super F, ? extends T> function;TransformingRandomAccessList(List<F> fromList, Function<? super F, ? extends T> function) {this.fromList = checkNotNull(fromList);this.function = checkNotNull(function);}@Overridepublic void clear() {fromList.clear();}@Overridepublic T get(int index) {return function.apply(fromList.get(index));}@Overridepublic Iterator<T> iterator() {return listIterator();}@Overridepublic ListIterator<T> listIterator(int index) {return new TransformedListIterator<F, T>(fromList.listIterator(index)) {@OverrideT transform(F from) {return function.apply(from);}};}@Overridepublic boolean isEmpty() {return fromList.isEmpty();}@Overridepublic T remove(int index) {return function.apply(fromList.remove(index));}@Overridepublic int size() {return fromList.size();}private static final long serialVersionUID = 0;}源码的解释很清楚,Lists.transform返回的是一个新的类TransformingRandomAccessList,该类有两个变量
final List<F> fromList;
final Function<? super F, ? extends T> function;@Override
public T get(int index) {return function.apply(fromList.get(index));
}由于functions不具有可逆性,transform是单向的,无法向结果列表中添加新元素,因此Lists.transform返回的l
ist不支持add和addAll方法。这可以解释异常c。
The returned list is a transformed view of fromList; changes to fromList will be reflected in the returned list
and vice versa.源码的注释表明对fromList的修改会反映到returnList上,对returnList的修改也会同样影响fromList,
这是不正确的,对returnList的修改不一定样影响fromList,没有必然的联系,这取决于Function对象中的转换方法,如
本测试方法用到的PersonDb向PersonVo转换方法personDbToVo,遍历returnList时每次都会调用personDbToVo,然后每次都会调用
PersonVo personVo = new PersonVo();生成新的对象,所以对结果列表returnList修改只会影响该局部变量personVo,而不会
影响到原来的fromList,这可以解释异常b。
public PersonVo personDbToVo(PersonDb personDb) {Preconditions.checkNotNull(personDb, "[PersonDbToVo]personDb为null");PersonVo personVo = new PersonVo();personVo.setName(personDb.getName() + ",from Db");personVo.setAge(personDb.getAge());personVo.setMsg(personDb.getMsg());return personVo;
}3.问题避免
a.刚开始看Guava代码觉着Lists.transform是个好方法,很强大,但在使用的过程中发现其坑也是挺多的,不注意的话可能会出现很严重的bug。所以考虑在只有在很必要的情况下才考虑用Lists.transform,即使用Lists.transform可以极大地减少代码量并
使得程序更清晰易懂。在使用复杂的开源类库前还是很有必要仔细阅读下源码的,在不清楚知道自己在干什么的时候最好还是
用成熟的解决方案去解决遇到的问题。
b.如果非要使用Lists.transform方法来实现集合转换,最好对returnList进行下后处理,如使用ImmutableList.copyOf和Lists.newArrayList
对返回结果进行下加工,这样就不用担心不可以对returnList结果进行必要修改了。但如果真的对returnList做上述处理,是否还真的有必要
调用Lists.transform?直接循环遍历过程中生成新的resultList是不是更好呢。
//personVos = ImmutableList.copyOf(personVos);
//personVos = Lists.newArrayList(personVos);//我认为直接循环遍历、转换生成resultList在时间和空间复杂度上会更好。