Google guava
Guava是对Java API的补充,对Java开发中常用功能进行更优雅的实现,使得编码更加轻松,代码容易理解。Guava使用了多种设计模式,同时经过了很多测试,得到了越来越多开发团队的青睐。Java最新版本的API采纳了Guava的部分功能,但依旧无法替代。
特点
- 高效设计良好的API,被Google的开发者设计,实现和使用
- 遵循高效的java语法实践
- 使代码更刻度,简洁,简单
- 节约时间,资源,提高生产力 Guava工程包含了若干被Google的 Java项目广泛依赖的核心库
核心库例如:
- 集合 [collections]
- 缓存 [caching]
- 原生类型支持 [primitives support]
- 并发库 [concurrency libraries]
- 通用注解 [common annotations]
- 字符串处理 [string processing]
- I/O 等等。
github地址
https://github.com/google/guava![]() https://github.com/google/guava
https://github.com/google/guava
使用
依赖引入
<dependencies><dependency><groupId>com.google.guava</groupId><artifactId>guava</artifactId><version>28.1-jre</version></dependency></dependencies>Guava 集合工具类
Lists
官网文档:
Lists (Guava: Google Core Libraries for Java 27.0.1-jre API)![]() https://guava.dev/releases/27.0.1-jre/api/docs/com/google/common/collect/Lists.html对应于List集合接口, 在com.google.common.collect包下
https://guava.dev/releases/27.0.1-jre/api/docs/com/google/common/collect/Lists.html对应于List集合接口, 在com.google.common.collect包下
Lists 接口的声明如下:
@GwtCompatible(emulated=true)
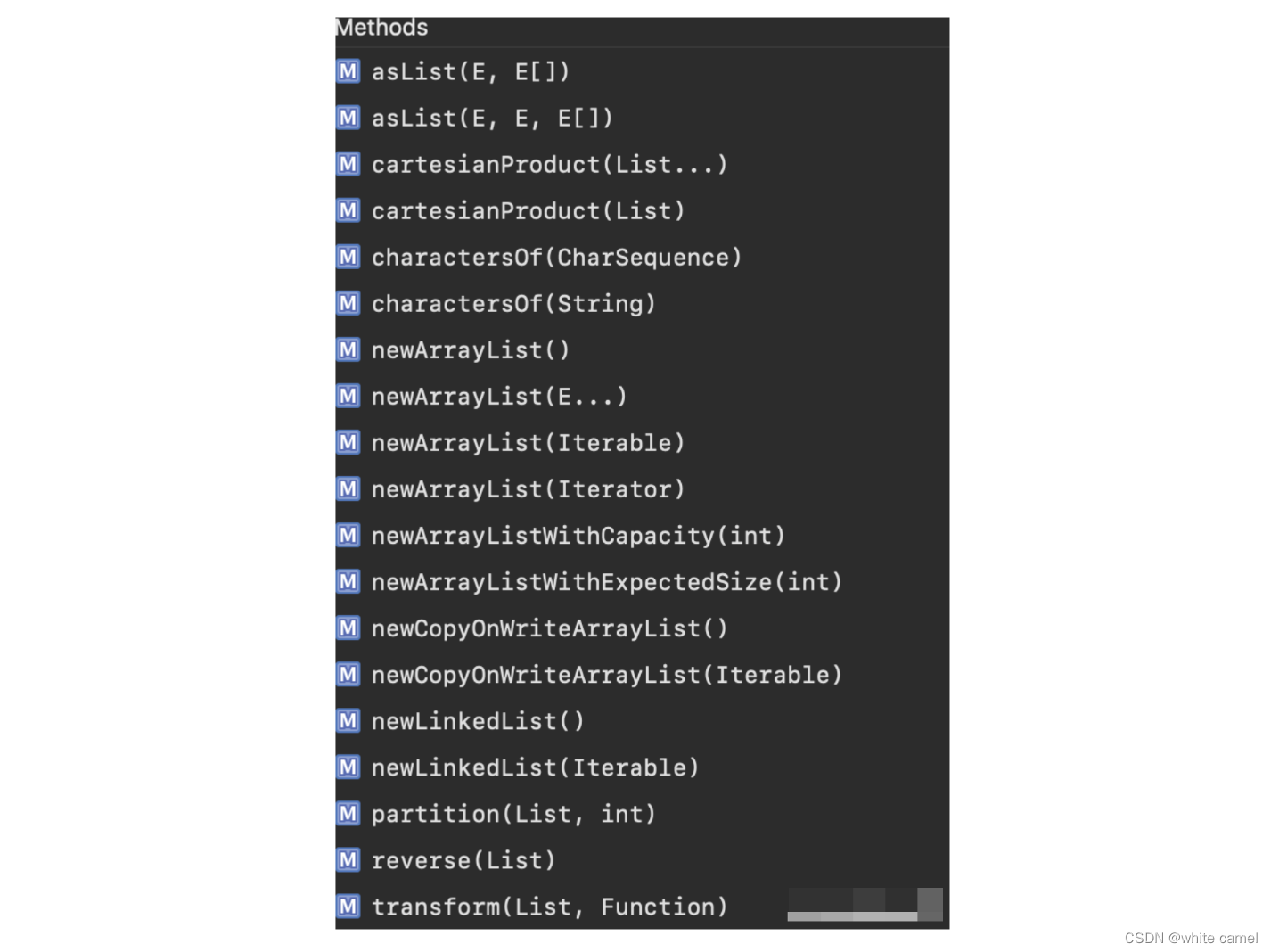
public final class Listsextends Object Lists 类主要提供了对List类的子类构造以及操作的静态方法。在Lists类中支持构造 ArrayList、LinkedList 以及 newCopyOnWriteArrayList 对象的方法。其中提供了以下构造ArrayList的函数:下面四个构造一个 ArrayList 对象,但是不显式的给出申请空间的大小:
newArrayList()
newArrayList(E... elements)
newArrayList(Iterable<? extends E> elements)
newArrayList(Iterator<? extends E> elements)测试
ArrayList<Object> objects = Lists.newArrayList();objects.add("张三");objects.add(20);System.out.println("--- newArrayList test ---");System.out.println(objects);System.out.println("--- newArrayList test ---");ArrayList<Object> objects1 = Lists.newArrayList(objects);System.out.println(objects1);System.out.println("--- newArrayList test ---");ArrayList<String> strings = Lists.newArrayList("张三", "北京市海淀区");System.out.println(strings);
以下两个函数在构造 ArrayList 对象的时候给出了需要分配空间的大小:
newArrayListWithCapacity(int initialArraySize)
newArrayListWithExpectedSize(int estimatedSize) //如果你事先知道元素的个数,可以用 newArrayListWithCapacity 函数;如果你不能确定元素的个数,可以用newArrayListWithExpectedSize函数//这个方法就是直接返回一个10的数组。ArrayList<Object> objects = Lists.newArrayListWithCapacity(10);objects.add("123");System.out.println(objects);ArrayList<Object> objects1 = Lists.newArrayListWithExpectedSize(10);objects1.add("123");System.out.println(objects1);
在 newArrayListWithExpectedSize 函数里面调用了 computeArrayListCapacity(int arraySize) 函数,其实现如下:
@VisibleForTesting
static int computeArrayListCapacity(int arraySize) {checkArgument(arraySize >= 0);// TODO(kevinb): Figure out the right behavior, and document itreturn Ints.saturatedCast(5L + arraySize + (arraySize / 10));
} 返回的容量大小为 5L + arraySize + (arraySize / 10),当 arraySize 比较大的时候,给定大小和真正分配的容量之比为 10/11。
Lists 类还支持构造 LinkedList、newCopyOnWriteArrayList 对象,其函数接口为:
newLinkedList()
newLinkedList(Iterable<? extends E> elements)
newCopyOnWriteArrayList()
newCopyOnWriteArrayList(Iterable<? extends E> elements) /* newLinkedList()newLinkedList(Iterable<? extends E> elements) newCopyOnWriteArrayList()newCopyOnWriteArrayList(Iterable<? extends E> elements) */LinkedList<Object> objects = Lists.newLinkedList();objects.add("张三");objects.add("李四");System.out.println("--- newLinkedList ---");System.out.println(objects);ArrayList<Object> objects1 = Lists.newArrayList(objects);System.out.println("--- newLinkedList ---");System.out.println(objects1);System.out.println("--- newCopyOnWriteArrayList ---");CopyOnWriteArrayList<Object> objects2 = Lists.newCopyOnWriteArrayList();objects2.add("王五");objects2.add("张三");System.out.println(objects2);System.out.println("--- newCopyOnWriteArrayList ---");CopyOnWriteArrayList<Object> objects3 = Lists.newCopyOnWriteArrayList(objects2);System.out.println(objects3);
我们还可以将两个(或三个)类型相同的数据存放在一个list中,这样可以传入到只有一个参数的函数或者需要减少参数的函数中,这些函数如下:
asList(@Nullable E first, E[] rest)
asList(@Nullable E first, @Nullable E second, E[] rest) String str = "i love u";String[] strs = {"i like u", "i miss u"};List<String> strings = Lists.asList(str, strs);System.out.println(strings);
Lists 类中 transform 函数可以根据传进来的 function 对 fromList 进行相应的处理,并将处理得到的结果存入到新的list对象中,这样有利于我们进行分析,函数接口如下:
public static <F, T> List<T> transform(List<F> fromList, Function<? super F, ? extends T> function) Function<String, Integer> strlen = new Function<String, Integer>() {public Integer apply(String from) {Preconditions.checkNotNull(from);return from.length();}};List<String> from = Lists.newArrayList("abc", "defg", "hijkl");List<Integer> to = Lists.transform(from, strlen);for (int i = 0; i < from.size(); i++) {System.out.printf("%s has length %d\n", from.get(i), to.get(i));}
Maps
官方文档
Maps (Guava: Google Core Libraries for Java 27.0.1-jre API)![]() https://guava.dev/releases/27.0.1-jre/api/docs/com/google/common/collect/Maps.html
https://guava.dev/releases/27.0.1-jre/api/docs/com/google/common/collect/Maps.html com.google.common.collect.Maps 接口的声明:
@GwtCompatible(emulated=true)
public final class Mapsextends ObjectnewHashMap
newHashMapWithExpectedSize
newLinkedHashMap
ImmutableMap
difference
transformValues测试
newHashMap
HashMap<Object, Object> hashMap = Maps.newHashMap();for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {hashMap.put(i, i);}System.out.println("hashMap:" + hashMap);HashMap<Object, Object> hashMap1 = Maps.newHashMap(hashMap);System.out.println("hashMap1:" + hashMap1);
newHashMapWithExpectedSize
Map<Integer, Integer> map = Maps.newHashMapWithExpectedSize(3);map.put(1, 1);map.put(2, 2);map.put(3, 3);System.out.println("map:" + map); // map:{1=1, 2=2, 3=3} 
newLinkedHashMap
Map<Integer, Integer> map = Maps.newLinkedHashMap();map.put(11, 11);System.out.println("map:" + map);LinkedHashMap<Integer, Integer> map1 = Maps.newLinkedHashMap(map);System.out.println("map1:" + map1);
ImmutableMap
ImmutableMap<String, String> a = ImmutableMap.of("a", "1");System.out.println(a); 
difference
Map<Integer, Integer> map = Maps.newHashMap();map.put(10, 10);Map<Integer, Integer> map1 = Maps.newHashMap();map1.put(10, 10);map1.put(20, 20);MapDifference<Integer, Integer> difference = Maps.difference(map, map1);System.out.println(difference.areEqual());System.out.println(difference.entriesInCommon());System.out.println(difference.entriesOnlyOnRight());System.out.println(difference.entriesOnlyOnLeft());System.out.println(difference.entriesDiffering());System.out.println(difference);transformValues
Map<String, Boolean> fromMap = Maps.newHashMap();fromMap.put("key", true);fromMap.put("value", false);// 对传入的元素取反System.out.println(Maps.transformValues(fromMap, (Function<Boolean, Object>) input -> !input));// value为假,则key变大写Maps.EntryTransformer<String, Boolean, String> entryTransformer = (key, value) -> value ? key : key.toUpperCase();System.out.println(Maps.transformEntries(fromMap, entryTransformer));Sets
官方文档
Sets (Guava: Google Core Libraries for Java 27.0.1-jre API)![]() https://guava.dev/releases/27.0.1-jre/api/docs/com/google/common/collect/Sets.html
https://guava.dev/releases/27.0.1-jre/api/docs/com/google/common/collect/Sets.htmlcom.google.common.collect.Sets 接口的声明:
@GwtCompatible(emulated=true)
public final class Setsextends ObjectnewHashSet
filter
difference
symmetricDifference
intersection
union
cartesianProduct
powerSetnewHashSet
HashSet<Object> objects = Sets.newHashSet();objects.add("张三");objects.add("李四");System.out.println(objects); 
filter
/*** filter:返回传入Set集合unfiltered中满足给定Predicate的元素集合Set*/@Testpublic void testFilter() {Set<String> set = Sets.newHashSet("i like u", "i miss u", "i love u");Predicate<String> predicate = new Predicate<String>() {@Overridepublic boolean apply(String input) {//过滤包含字母l的元素return input.contains("l");}};System.out.println(Sets.filter(set, predicate)); // [i like u, i love u]System.out.println(Sets.filter(set, input -> input.contains("l"))); // [i like u, i love u]}
difference
/*** difference:返回两个set集合的差的不可修改SetView* A,B是两个集合,则所有属于A且不属于B的元素构成的集合,叫做A与B的差集*/@Testpublic void testDifference() {Set<Integer> set1 = Sets.newHashSet(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);Set<Integer> set2 = Sets.newHashSet(1, 3, 5, 7, 9);System.out.println(Sets.difference(set1, set2)); // [2, 4]} 
symmetricDifference
/*** symmetricDifference:返回两个set集合的对称差的不可修改SetView* 对称差,即两个集合的对称差是只属于其中一个集合,而不属于另一个集合的元素组成的集合*/@Testpublic void testSymmetricDifference() {Set<Integer> set1 = Sets.newHashSet(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);Set<Integer> set2 = Sets.newHashSet(1, 3, 5, 7, 9);System.out.println(Sets.symmetricDifference(set1, set2)); // [2, 4, 9, 7]} 
intersection
/*** intersection:返回两个set集合的交集的不可修改SetView* 两个集合A和集合B的交集是指含有所有既属于A又属于B的元素,而没有其他元素的集合*/@Testpublic void testIntersection() {Set<Integer> set1 = Sets.newHashSet(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);Set<Integer> set2 = Sets.newHashSet(1, 3, 5, 7, 9);System.out.println(Sets.intersection(set1, set2)); // [1, 3, 5]}
Union
/*** Union:返回两个set集合的并集的不可修改SetView* 若A和B是集合,则A和B并集是有所有A的元素和所有B的元素,而没有其他元素的集合*/@Testpublic void testUnion() {Set<Integer> set1 = Sets.newHashSet(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);Set<Integer> set2 = Sets.newHashSet(1, 3, 5, 7, 9);System.out.println(Sets.union(set1, set2)); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 9, 7]}
cartesianProduct
/*** cartesianProduct:返回通过从各给定集中选择一个元素所形成每一个可能的集合*/@Testpublic void testCartesianProduct() {Set<String> set1 = Sets.newHashSet("i love u", "i hate u");Set<String> set2 = Sets.newHashSet("tom", "jerry");Set<List<String>> sets = Sets.cartesianProduct(set1, set2);System.out.println(sets); // [[i hate u, tom], [i hate u, jerry], [i love u, tom], [i love u, jerry]]}
powerSet
/*** powerSet:返回一个set,包含给定set的所有可能父级集合*/@Testpublic void testPowerSet() {Set<String> set1 = Sets.newHashSet("A", "B", "C");Set<Set<String>> sets = Sets.powerSet(set1);
// for (Set<String> set : sets) {
// System.out.println(set);
// }System.out.println(Arrays.toString(sets.toArray())); // [[], [A], [B], [A, B], [C], [A, C], [B, C], [A, B, C]]}
完整代码
maven项目里用junit进行单元测试
import com.google.common.base.Predicate;
import com.google.common.collect.Sets;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;public class TestSets {/*** filter:返回传入Set集合unfiltered中满足给定Predicate的元素集合Set*/@Testpublic void testFilter() {Set<String> set = Sets.newHashSet("i like u", "i miss u", "i love u");Predicate<String> predicate = new Predicate<String>() {@Overridepublic boolean apply(String input) {//过滤包含字母l的元素return input.contains("l");}};System.out.println(Sets.filter(set, predicate)); // [i like u, i love u]System.out.println(Sets.filter(set, input -> input.contains("l"))); // [i like u, i love u]}/*** difference:返回两个set集合的差的不可修改SetView* A,B是两个集合,则所有属于A且不属于B的元素构成的集合,叫做A与B的差集*/@Testpublic void testDifference() {Set<Integer> set1 = Sets.newHashSet(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);Set<Integer> set2 = Sets.newHashSet(1, 3, 5, 7, 9);System.out.println(Sets.difference(set1, set2)); // [2, 4]}/*** symmetricDifference:返回两个set集合的对称差的不可修改SetView* 对称差,即两个集合的对称差是只属于其中一个集合,而不属于另一个集合的元素组成的集合*/@Testpublic void testSymmetricDifference() {Set<Integer> set1 = Sets.newHashSet(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);Set<Integer> set2 = Sets.newHashSet(1, 3, 5, 7, 9);System.out.println(Sets.symmetricDifference(set1, set2)); // [2, 4, 9, 7]}/*** intersection:返回两个set集合的交集的不可修改SetView* 两个集合A和集合B的交集是指含有所有既属于A又属于B的元素,而没有其他元素的集合*/@Testpublic void testIntersection() {Set<Integer> set1 = Sets.newHashSet(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);Set<Integer> set2 = Sets.newHashSet(1, 3, 5, 7, 9);System.out.println(Sets.intersection(set1, set2)); // [1, 3, 5]}/*** Union:返回两个set集合的并集的不可修改SetView* 若A和B是集合,则A和B并集是有所有A的元素和所有B的元素,而没有其他元素的集合*/@Testpublic void testUnion() {Set<Integer> set1 = Sets.newHashSet(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);Set<Integer> set2 = Sets.newHashSet(1, 3, 5, 7, 9);System.out.println(Sets.union(set1, set2)); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 9, 7]}/*** cartesianProduct:返回通过从各给定集中选择一个元素所形成每一个可能的集合*/@Testpublic void testCartesianProduct() {Set<String> set1 = Sets.newHashSet("i love u", "i hate u");Set<String> set2 = Sets.newHashSet("tom", "jerry");Set<List<String>> sets = Sets.cartesianProduct(set1, set2);System.out.println(sets); // [[i hate u, tom], [i hate u, jerry], [i love u, tom], [i love u, jerry]]}/*** powerSet:返回一个set,包含给定set的所有可能父级集合*/@Testpublic void testPowerSet() {Set<String> set1 = Sets.newHashSet("A", "B", "C");Set<Set<String>> sets = Sets.powerSet(set1);
// for (Set<String> set : sets) {
// System.out.println(set);
// }System.out.println(Arrays.toString(sets.toArray())); // [[], [A], [B], [A, B], [C], [A, C], [B, C], [A, B, C]]}}