Java常用API
StringBuffer
为了解决String字符串操作导致的内存冗余,提高效率,Java中提供了StringBuffer和StringBuilder来操作字符串,并且提供了很多方法,便于程序员开发
StringBuffer和StringBuilder中都有char类型可变长数组作为字符串的保存空间,使用到的方法类型和ArrayList类似
- StringBuffer 线程安全,效率较低
- StringBuilder 线程不安全,效率较高
StringBuffer构造方法
构造方法Constructor
-
StringBuffer();
创建一个未存储任何字符串信息的空StringBuffer空间,底层初始化一个16个字符char类型数组
-
StringBuffer(String str);
根据提供的String类型字符串创建对应的StringBuffer空间,底层char类型数组的容量会根据str.length + 16决定,并且保存对应的str
添加方法
- append() 在缓冲区的尾部添加新的文本对象
- insert() 在指定下标位置添加新的文本对象
package cn.ocean888;public class Demo1 {public static void main(String[] args) {StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer("ocean, ocean, ocean, ocean");stringBuffer.append("AAAA");stringBuffer.append("BBBB");System.out.println(stringBuffer);StringBuilder stringBuiler = new StringBuilder("ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQISTUVWXYZ");stringBuiler.insert(3, "CCCC");System.out.println(stringBuiler);}
}

查看方法
-
String toString();
将底层的char类型数组保存的字符内容转换成对应的String类型字符串返回
-
int length();
返回底层char类型数组中有多少有效元素
-
String substring(int begin);
从指定位置开始获取到char’类型数组有效元素末尾对应的字符串截取操作
-
String substring(int begin, int end);
从指定位置begin开始到end结束,获取对应的字符串,要头不要尾
-
int indexOf(String str);
指定元素字符串所在下标位置
-
int lastIndexOf(String str);
指定元素字符串最后一次所在下标位置
修改方法
-
replace(int start, int end, String str);
从指定位置start开始,到end结束,start <= n <= end,使用str替换
-
setChar(int index, char ch)
将指定位置设置为char字符
package cn.ocean888;public class Demo1 {public static void main(String[] args) {StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer("ocean, ocean, ocean, ocean");stringBuffer.replace(1, 6, "888");System.out.println(stringBuffer);stringBuffer.setCharAt(1, 'Y');System.out.println(stringBuffer);}
}

删除方法
-
delete(int start, int end);
删除指定范围以内的字符
-
deleteCharAt(int index);
删除指定下标的字符
逆序方法
-
reverse();
逆序
Math数学类
-
public static double abs(double a);
返回值为绝对值
-
public static double ceil(double a);
向上取整
-
public static double floor(double a);
向下取整
-
public static double round(double a);
四舍五入
-
public static double random();
随机数 0.0 <= n <= 1.0

-3.6相对距离-4为0.4所以舍去,结果为-4
Date类
获取当前系统时间-大部分构造方法已经过时
构造方法
-
Date();
创建一个Date,对应当前时间,精度在毫秒值
-
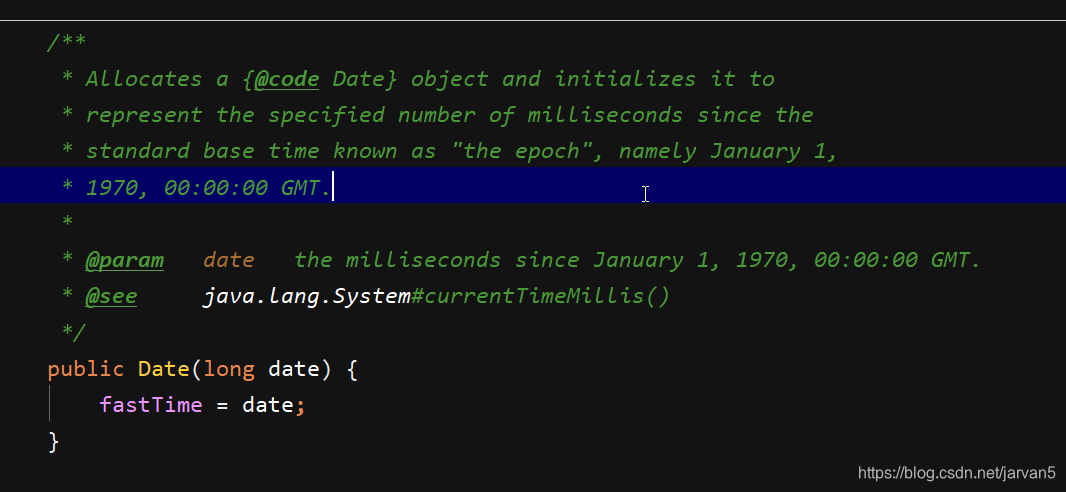
Date(long date);
根据时间戳毫秒数,创建对应的Date对象,时间戳是从1970-01-01 00:00:00 GMT
常用方法
-
long getTime();
通过Date类对象获取对应当前时间的毫秒数
System.currentTimeMillis();
可以获取当前系统时间戳毫秒数
DateFormat时间格式
-
DateFormat是一个abstract修饰的类,用于转换时间格式
-
DateFormat不能直接使用,一般使用DateFormat子类SimpleDataFormat来使用
-
SimpleDataFormat构造方法中需要的参数是一个String,String类型的参数有特定的要求
-
String format(Date data);
根据指定匹配要求,转换Date格式成为字符串
-
Date parse(String format);
按照指定的匹配规则,解析对应的字符串,返回一个Date数据

package cn.ocean888;import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;public class Demo2 {public static void main(String[] args) {SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日HH:mm:ss E");String format = simpleDateFormat.format(new Date());System.out.println(format);}
}

Calender日历类
替换了很多Date类中的方法,把很多数据都作为静态的属性,通过一些特定的方法来获取,比Date处理日期数据更加方便
Calender是一个abstract修饰的类,没有自己的类对象,这里通过特定的方法getInstance获取Calender日历类对象
public static Calender getInstance();
默认为当前系统时区
常用方法
-
public int get(int field);
返回特定数据的数值
-
public void set(int field, int value);
设置特定字段对应的数据
-
public Date getTime();
返回得到一个Date对象,从计算机元年到现在的毫秒数,保存在date对象中
package cn.ocean888;import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Date;public class Demo3 {public static void main(String[] args) {Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();int year = calendar.get(Calendar.YEAR);int month = calendar.get(Calendar.MONTH)+1;int day = calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);int hour = calendar.get(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY);int minute = calendar.get(Calendar.MINUTE);int second = calendar.get(Calendar.SECOND);int dayOfWeek = calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK);System.out.println(year + "-" + month + "-" + day + " " + hour + ":" + minute + ":" + second + " " + dayOfWeek);calendar.set(Calendar.YEAR, 2008);calendar.set(Calendar.MONTH, 7);calendar.set(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH, 8);Date time = calendar.getTime();System.out.println(time);}
}

System类
System类提供了大量的静态方法,操作的内容和系统有关
- 可以获取当前时间戳 long currentTimeMillis()
- 获取系统属性的方法 Properties getProperties();
- 退出当前程序 exit(int status)
- 数组拷贝方法 arrayCopy(Object src, int srcPos, Object dest, int destPos, int length)
package cn.ocean888;import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Properties;public class Demo4 {public static void main(String[] args) {// 属性类Properties properties = System.getProperties();properties.list(System.out);System.out.println("-----------");// 获取系统对应属性的数据String property = System.getProperty("os.name");System.out.println(property);System.out.println("-----------");// 数组拷贝方法int[] arr = {1, 3, 5, 7};int[] temp = new int[10];System.arraycopy(arr, 0, temp, 0, arr.length);System.out.println(Arrays.toString(temp));System.out.println("-----------");}
}
输出效果

Runtime类
Runtime当前程序运行环境类对象,只要程序启动就又会对应的Runtime存在
获取Runtime对象的方法:
- Runtime Runtime.getRuntime();
需要了解的方法:
- gc(); JVM的GC机制,但是调用了GC方法,也不会立即执行
package cn.ocean888;import java.io.IOException;public class Demo5 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();System.out.println(runtime.totalMemory());System.out.println(runtime.freeMemory());System.out.println(runtime.maxMemory());}
}

包装类
Java中提供了两种数据类型
-
基本数据类型
byte short int long double float boolean char
-
引用数据类型
类对象 数组 字符串

自动装箱和自动拆箱
基本类型和包装类型之间进行转换的操作
- 装箱:从基本类型到包装类
- 拆箱:从包装类到基本类型
package cn.ocean888;public class Demo6 {public static void main(String[] args) {// 自动方式// 基本类型int num = 5;// 基本数据类型赋值给包装类,自动装箱的过程Integer num1 = num;System.out.println(num1);// 包装类转换成基本数据类型,自动拆箱的过程int num2 = num1;System.out.println(num2);// 强行包装Integer i = new Integer(5);Integer ii = Integer.valueOf(5);// 强制拆箱int intValue = i.intValue();}
}

在输出结果上没有差异
包装类和字符串数据转换过程