Define
Clustering Coefficient:聚类系数
Clustering Coefficient measures the degree to which nodes in a network tend to cluster or form triangles.
——聚类系数衡量网络中节点倾向于聚类或形成三角形的程度
Triadic Closure
三元闭包
The tendency of people who share connections in a social network to become connected
“Triadic Closure would say that those edges that closed triangles are good candidate for edges that may show up next”
那些能形成闭合三角形的边,往往被认为是下一个会出现的边
但我们并不会总是有时间戳,也并不是总是知道边缘进入网路的顺序
Another way of referring to Triadic Closure is Clustering.
——另一种指代三元闭包的方式是聚类
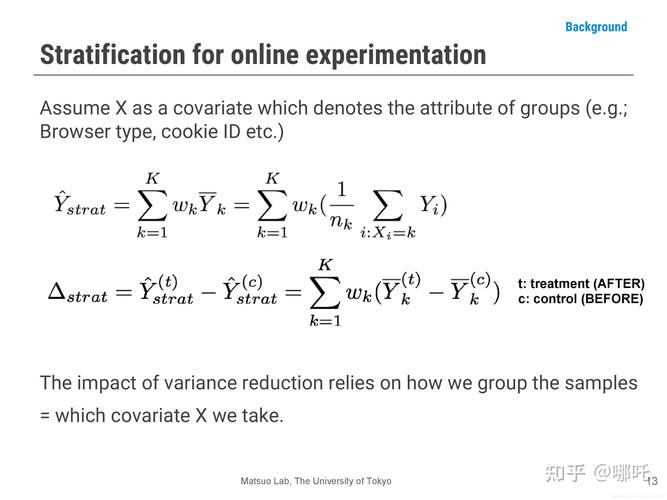
Local Clustering Coefficient
局部聚类系数
We’re going to be measuring Clustering from the point of view of a single node.
——从单个顶点的角度测量聚类
- define:
Fraction of pairs of the node’s friends that are friends with each other.
# o f p a i r s o f C ′ s f r i e n d s w h o a r e f r i e n d s # o f p a i r s o f C ′ f r i e n d s \frac{\#\,\,\,of\,\,\,pairs\,\,\,of\,\,\,C's\,friends\,\,\,who \,\,\,are\,\,\,friends}{\#\,\,\,of \,\,\,pairs\,\,\,of\,\,\,C'\,friends} #ofpairsofC′friends#ofpairsofC′sfriendswhoarefriends

i n s t a n c e # o f C ′ f r i e n d s = d c = 4 ( t h e d e g r e e o f C ) # o f p a i r s o f C ′ f r i e n d s = d c ( d c − 1 ) 2 = 12 2 = 6 # o f p a i r s o f C ′ s f r i e n d s w h o a r e f r i e n d s = 2 L o c a l c l u s t e r i n g c o e f f i c e n t o f C = 2 6 = 1 3 instance\\ \#\,\,\,of\,\,\,C'\,friends=d_c=4(the\,\,\,degree\,\,\,of\,\,\,C)\\ \#\,\,\,of \,\,\,pairs\,\,\,of\,\,\,C'\,friends=\frac{d_c(d_c-1)}{2}=\frac{12}{2}=6\\ \#\,\,\,of\,\,\,pairs\,\,\,of\,\,\,C's\,friends\,\,\,who \,\,\,are\,\,\,friends=2\\ Local\,\,\,clustering\,\,\,coefficent\,\,\,of\,\,\,C=\frac{2}{6}=\frac{1}{3} instance#ofC′friends=dc=4(thedegreeofC)#ofpairsofC′friends=2dc(dc−1)=212=6#ofpairsofC′sfriendswhoarefriends=2LocalclusteringcoefficentofC=62=31
解释
- C结点一共有4个结点
- 4个结点能形成6对朋友
- 但真正存在的朋友是AB和EF两对
When we look at the node J,we will find we have a trouble because we cannot divide by zero.
# o f J ′ f r i e n d s = d c = 1 ( t h e d e g r e e o f J ) # o f p a i r s o f J ′ f r i e n d s = 0 \#\,\,\,of\,\,\,J'\,friends=d_c=1(the\,\,\,degree\,\,\,of\,\,\,J)\\ \#\,\,\,of \,\,\,pairs\,\,\,of\,\,\,J'\,friends=0 #ofJ′friends=dc=1(thedegreeofJ)#ofpairsofJ′friends=0
In this situation,we will assume that the local clustering coefficient of a node of degree less than 2 to be 0.
我们将入度少于2的点,认为其局部聚类系数为0
import networkx as nxG=nx.Graph()
G.add_edges_from([('A','K'),('A','B'),('A','C'),('B','C'),('B','K'),('C','E'),
('C','F'),('D','E'),('E','F'),('E','H'),('F','G'),('I','J')])print(nx.clustering(G,'F'))
#>>0.3333333333333333print(nx.clustering(G,'J'))
#>>0
Global Clustering Coefficient
全局聚类系数
Approach One
Average local clustering coefficient over all nodes in the graph
——图中所有结点的平均局部聚类系数
print(nx.average_clustering(G))
#>>0.28787878787878785
Approach Two
Measuring clustering on the whole network
Percentage of “open triads” that are triangles in a network
- Triangles are simply three nodes that are connected by three edges.
- open triads are three nodes that are connected by only two edges.
T r a n s i t i v i t y = 3 ∗ N u m b e r o f c l o s e d t r i a d s N u m b e r o f o p e n t r i a d s Transitivity=\frac{3*Number\,\,\,of\,\,\,closed\,\,\,triads}{Number\,\,\,of\,\,\,open\,\,\,triads} Transitivity=Numberofopentriads3∗Numberofclosedtriads
Transitivity:Ratio of number of triangles and number of “open triads” in a network
——网络中三角形数量与“开放三元组”数量之比
print(nx.transitivity(G))
#>>0.4090909090909091
Approach Diff
-
Both try to measure the tendency for the edges to form triangles
-
Transitivity weights the nodes with a larger degree higher.
——Transitivity 对具有高入度的结点给予更高的权重
E x a m p l e − 1 Example-1 Example−1

-
Most nodes have a pretty high LCC(Local Clustering Coefficient)
外面那圈结点的LCC都是1
-
The high degree node has low LCC
中间结点是高入度的结点,LCC偏低为 1 11 \frac{1}{11} 111
O u t C o m e OutCome OutCome
- Ave.clustering coeff.=0.93
- Transitivity=0.23
E x a m p l e − 2 Example -2 Example−2

-
Most nodes have low LCC
外围的结点度数为0
-
The high degree node has low LCC
中间部分的结点是完全图,LCC高
O u t C o m e OutCome OutCome
- Ave.clustering coeff.=0.25
- Transitivity=0.86