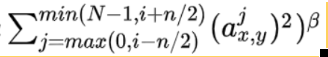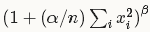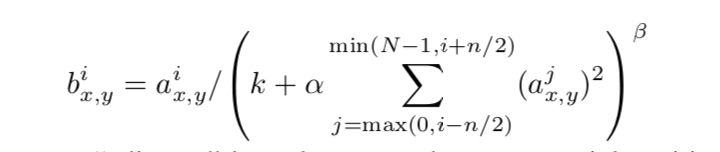2012年 多伦多大学Hinton提出的
AlexNet
AlexNet是第一个large-scale CNN, 从AlexNet之后CNN开始变得火了起来
贡献是提出了用多层最小卷积叠加来替换单个大卷积
AlexNet首次引入了dropout
AlexNet 该模型一共分为八层,5个卷积层, 以及3个全连接层 (注意这个8层是没算pooling层的)
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1575745
这里我们主要写模型,数据加载、训练等类似的步骤就直接用LeNet5的了
虽然论⽂中AlexNet使⽤ImageNet数据集,但因为ImageNet数据集训练时间较⻓,我们仍⽤CIFAR-10数据集来演⽰AlexNet。但用transforms.Resize([227, 227])把它拉到[227,227]上,但是这么做会让图片有点失真的
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)中inplace的作用
inplace-选择是否进行覆盖运算
nn.ReLU(inplace=True) 的意思就是对从上层网络Conv2d中传递下来的tensor直接进行修改,这样能够节省运算内存,不用多存储其他变量。否则就需要花费内存去多存储一个变量
nn.Dropout()
nn.Dropout(p), 默认p=0.5
Dropout的目的是防止过拟合
dropout层不会影响模型的shape
因为输入数据是[3,227,227], 我的4G显存的GPU只能容纳batch_size=32,再大就爆了
import torch import torch.nn as nn import torchvision import torchvision.transforms as transforms import torch.utils.data.dataloader as dataloader import pdb import os from torchvision.transforms import ToPILImage import matplotlib.pyplot as pltclass AlexNet(nn.Module):def __init__(self):super(AlexNet, self).__init__()self.features = nn.Sequential(# x的输入: [b,3,227,227] 3是彩色图片三通道nn.Conv2d(3, 96, kernel_size=(11,11), stride=4, padding=1),#[b,96,55,55]nn.ReLU(inplace=True),# [b,96,55,55]nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=(3,3), stride=2),# [b,96,27,27]nn.Conv2d(96, 256, kernel_size=(5,5), stride=1, padding=2),# [b,256,27,27]nn.ReLU(inplace=True),# [b,256,27,27]nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=(3,3), stride=2),#[b,256,13,13]nn.Conv2d(256, 384, kernel_size=(3,3), stride=1, padding=1),# [b,384,13,13]nn.ReLU(inplace=True),# [b,384,13,13]nn.Conv2d(384, 384, kernel_size=(3,3), stride=1, padding=1),# [b,384,13,13]nn.ReLU(inplace=True),# [b,384,13,13]nn.Conv2d(384, 256, kernel_size=(3,3), padding=1),# [b,256,13,13]nn.ReLU(inplace=True),# [b,256,13,13]nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=(3,3), stride=2),# [b,256,6,6])self.classifier = nn.Sequential(nn.Dropout(),nn.Linear(256 * 6 * 6, 4096),nn.ReLU(inplace=True),nn.Dropout(),nn.Linear(4096, 4096),nn.ReLU(inplace=True),nn.Linear(4096, 10),)def forward(self, x):x = self.features(x)x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)x = self.classifier(x)return xtransform = transforms.Compose([transforms.Resize([227, 227]),transforms.ToTensor(),transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))] )batch_size = 32 train_set = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root="dataset/",download=True,train=True,transform=transform )train_loader = dataloader.DataLoader(dataset=train_set,batch_size=batch_size,shuffle=False )test_set = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root="dataset/",download=True,train=False,transform=transform ) test_loader = dataloader.DataLoader(dataset=test_set,batch_size=batch_size,shuffle=True )device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu") model = AlexNet() model.to(device)lr = 1e-3 criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=lr)show = ToPILImage()train_loss = []if os.path.isfile('params.pth'):model.load_state_dict(torch.load('params.pth'))print('load model parameters from params.pth') else:for epoch in range(2):for i, (images, labels) in enumerate(train_loader):images = images.to(device)labels = labels.to(device)output = model(images)#output是[b,10]# print(output.shape)loss = criterion(output, labels)optimizer.zero_grad()loss.backward()optimizer.step()train_loss.append(loss)if i % 100 == 0:print('{} {}, Loss: {:.4f}'.format(epoch, i, loss.item()))print('Finished Training')torch.save(model.state_dict(), 'params.pth')print('model has been save into params.pth.')plt.plot(range(0,len(train_loss)), train_loss, color='blue')plt.legend(['value'], loc='upper right')plt.xlabel('step')plt.ylabel('value')plt.show()with torch.no_grad():correct = 0total = 0for (images, labels) in test_loader:images, labels = images.to(device), labels.to(device)output = model(images)_, predicted = torch.max(output.data, 1)total += labels.size(0)#pdb.set_trace()correct += (predicted == labels).sum().item()print("The accuracy of total {} images: {}%".format(total, 100 * correct / total))
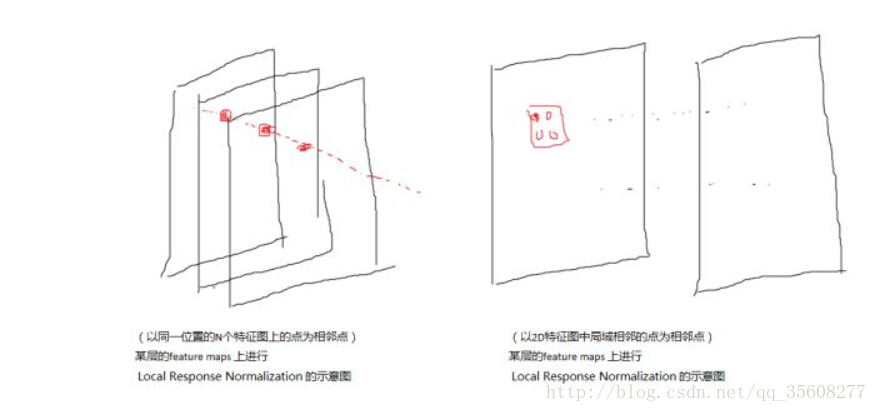
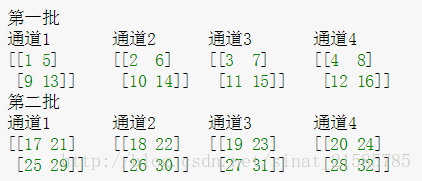
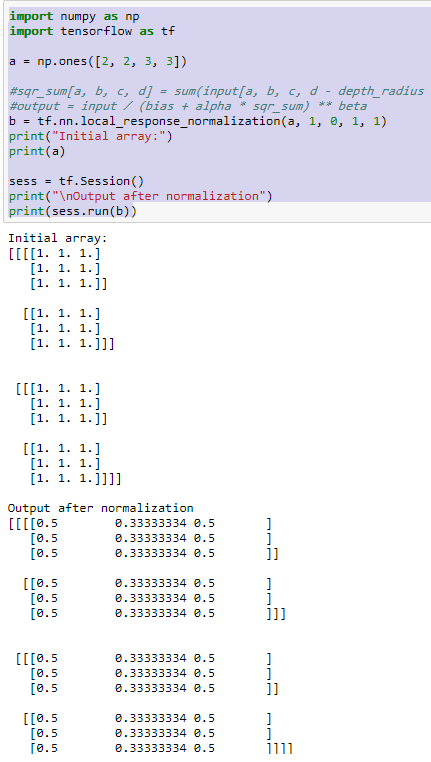
LRN(local response normalization)局部响应标准化
LRN函数类似DROPOUT和数据增强作为relu激励之后防止数据过拟合而提出的一种处理方法。这个函数很少使用,基本上被类似DROPOUT这样的方法取代,见最早的出处AlexNet论文对它的定义