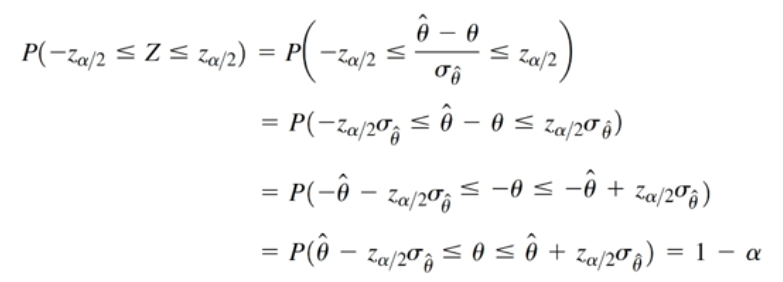1.1.ResNet的提出
残差网络(ResNet) 是由来自Microsoft Research的4位学者提出的卷积神经网络,在2015年的ImageNet大规模视觉识别竞赛(ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge, ILSVRC)中获得了图像分类和物体识别的优胜。
网络出自论文《Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition》
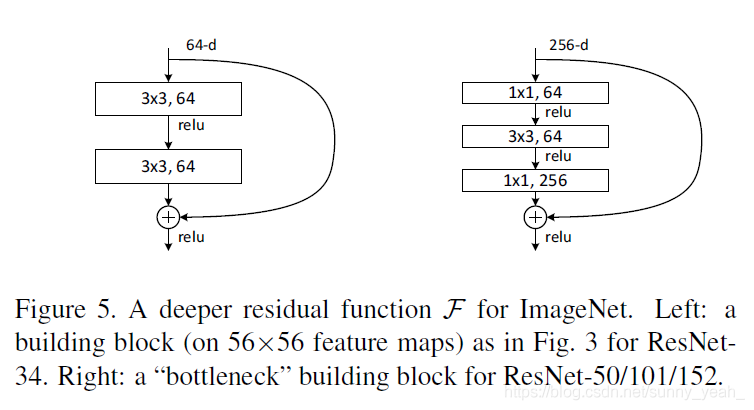
resnet18、resnet34、resnet50、resnet101、resnet152结构
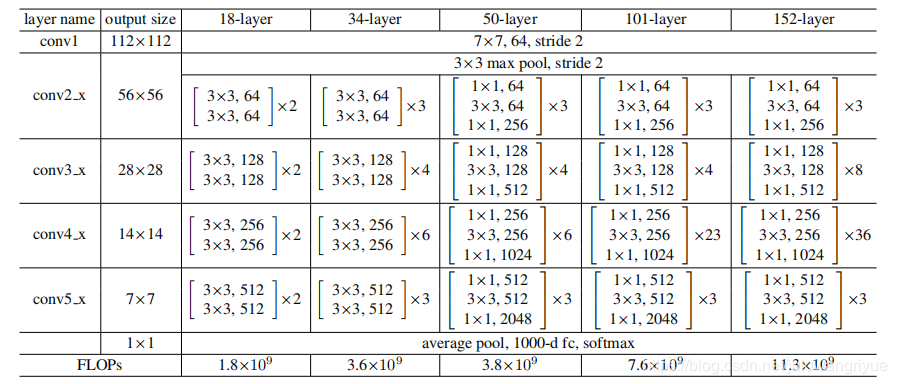
经常看到别人手推网络,很是羡慕,于是决定自己也手推一把。
就拿resnet18来推导吧。
上面这个图是简单示意图,一般分类任务输入图像224*224.
卷积输出,池化输出公式:
o_w =( i_w + 2*p - k)/s + 1
o_h =( i_h + 2*p - k)/s + 1
其中:
o_w、o_h:分别代表输出的宽和高;
i_w、i_h:分别代表输入的宽和高;
k: 卷积或池化的核大小;
p: padding的核大小;
s: stride 步长大小。
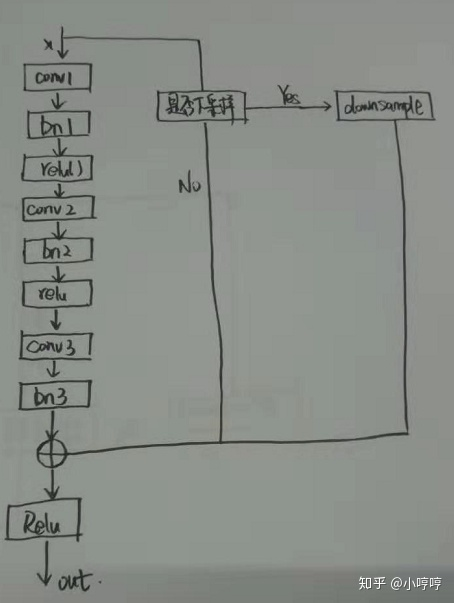
上图标识
1. conv1 实际代表了Convolution、BatchNormal、ReLU操作,只有卷积影响尺寸。
输出尺寸 = (224 + 2 * 3 - 7)/ 2 + 1 = 112
2. maxpool
输出尺寸 = (112 + 2 * 1 - 3)/ 2 + 1 = 56
**BasicBlock类,可以对比结构图中的resnet18和resnet34,类中expansion =1,其表示block内部最后一个卷积的输出channel与第一个卷积的输出channel比值,即:**
expansion=last_block_channel / first_block_channel
接下来是ResNet类,其和我们通常定义的模型差不多一个__init__()+forward(),代码有点长,我们一步步来分析:
- 参考前面的结构图,所有的resnet的第一个conv层都是一样的,输出channel=64
- 然后到了self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 64, layers[0]),这里的layers[0]=2,然后我们进入到_make_layer函数,由于stride=1或当前的输入channel和上一个块的输出channel一样,因而可以直接相加
- self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 128, layers[1], stride=2),此时planes=128而self.inplanes=64(上一个box_block的输出channel),此时channel不一致,需要对输出的x扩维后才能相加,而downsample 实现的就是该功能(ps:这里只有box_block中的第一个block需要downsample,为何?看图4)
- self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 256, layers[2], stride=2),此时planes=256而self.inplanes=128为,此时也需要扩维后才能相加,layer4 同理。


1.2.ResNet的特性
容易优化,并且能够通过增加相当的深度来提高准确率。其内部的残差块使用了跳跃连接,缓解了在深度神经网络中增加深度带来的梯度消失问题。
pytorch官方的ResNet实现:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from .utils import load_state_dict_from_url__all__ = ['ResNet', 'resnet18', 'resnet34', 'resnet50', 'resnet101','resnet152', 'resnext50_32x4d', 'resnext101_32x8d','wide_resnet50_2', 'wide_resnet101_2']model_urls = {'resnet18': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet18-5c106cde.pth','resnet34': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet34-333f7ec4.pth','resnet50': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet50-19c8e357.pth','resnet101': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet101-5d3b4d8f.pth','resnet152': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet152-b121ed2d.pth','resnext50_32x4d': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnext50_32x4d-7cdf4587.pth','resnext101_32x8d': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnext101_32x8d-8ba56ff5.pth','wide_resnet50_2': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/wide_resnet50_2-95faca4d.pth','wide_resnet101_2': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/wide_resnet101_2-32ee1156.pth',
}def conv3x3(in_planes, out_planes, stride=1, groups=1, dilation=1):"""3x3 convolution with padding"""return nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride,padding=dilation, groups=groups, bias=False, dilation=dilation)def conv1x1(in_planes, out_planes, stride=1):"""1x1 convolution"""return nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False)class BasicBlock(nn.Module):expansion = 1def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None, groups=1,base_width=64, dilation=1, norm_layer=None):super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()if norm_layer is None:norm_layer = nn.BatchNorm2dif groups != 1 or base_width != 64:raise ValueError('BasicBlock only supports groups=1 and base_width=64')if dilation > 1:raise NotImplementedError("Dilation > 1 not supported in BasicBlock")# Both self.conv1 and self.downsample layers downsample the input when stride != 1self.conv1 = conv3x3(inplanes, planes, stride)self.bn1 = norm_layer(planes)self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)self.conv2 = conv3x3(planes, planes)self.bn2 = norm_layer(planes)self.downsample = downsampleself.stride = stridedef forward(self, x):identity = xout = self.conv1(x)out = self.bn1(out)out = self.relu(out)out = self.conv2(out)out = self.bn2(out)if self.downsample is not None:identity = self.downsample(x)out += identityout = self.relu(out)return outclass Bottleneck(nn.Module):# Bottleneck in torchvision places the stride for downsampling at 3x3 convolution(self.conv2)# while original implementation places the stride at the first 1x1 convolution(self.conv1)# according to "Deep residual learning for image recognition"https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.03385.# This variant is also known as ResNet V1.5 and improves accuracy according to# https://ngc.nvidia.com/catalog/model-scripts/nvidia:resnet_50_v1_5_for_pytorch.expansion = 4def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None, groups=1,base_width=64, dilation=1, norm_layer=None):super(Bottleneck, self).__init__()if norm_layer is None:norm_layer = nn.BatchNorm2dwidth = int(planes * (base_width / 64.)) * groups# Both self.conv2 and self.downsample layers downsample the input when stride != 1self.conv1 = conv1x1(inplanes, width)self.bn1 = norm_layer(width)self.conv2 = conv3x3(width, width, stride, groups, dilation)self.bn2 = norm_layer(width)self.conv3 = conv1x1(width, planes * self.expansion)self.bn3 = norm_layer(planes * self.expansion)self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)self.downsample = downsampleself.stride = stridedef forward(self, x):identity = xout = self.conv1(x)out = self.bn1(out)out = self.relu(out)out = self.conv2(out)out = self.bn2(out)out = self.relu(out)out = self.conv3(out)out = self.bn3(out)if self.downsample is not None:identity = self.downsample(x)out += identityout = self.relu(out)return outclass ResNet(nn.Module):def __init__(self, block, layers, num_classes=1000, zero_init_residual=False,groups=1, width_per_group=64, replace_stride_with_dilation=None,norm_layer=None):super(ResNet, self).__init__()if norm_layer is None:norm_layer = nn.BatchNorm2dself._norm_layer = norm_layerself.inplanes = 64self.dilation = 1if replace_stride_with_dilation is None:# each element in the tuple indicates if we should replace# the 2x2 stride with a dilated convolution insteadreplace_stride_with_dilation = [False, False, False]if len(replace_stride_with_dilation) != 3:raise ValueError("replace_stride_with_dilation should be None ""or a 3-element tuple, got {}".format(replace_stride_with_dilation))self.groups = groupsself.base_width = width_per_groupself.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, self.inplanes, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3,bias=False)self.bn1 = norm_layer(self.inplanes)self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 64, layers[0])self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 128, layers[1], stride=2,dilate=replace_stride_with_dilation[0])self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 256, layers[2], stride=2,dilate=replace_stride_with_dilation[1])self.layer4 = self._make_layer(block, 512, layers[3], stride=2,dilate=replace_stride_with_dilation[2])self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1))self.fc = nn.Linear(512 * block.expansion, num_classes)for m in self.modules():if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')elif isinstance(m, (nn.BatchNorm2d, nn.GroupNorm)):nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1)nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)# Zero-initialize the last BN in each residual branch,# so that the residual branch starts with zeros, and each residual block behaves like an identity.# This improves the model by 0.2~0.3% according to https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.02677if zero_init_residual:for m in self.modules():if isinstance(m, Bottleneck):nn.init.constant_(m.bn3.weight, 0)elif isinstance(m, BasicBlock):nn.init.constant_(m.bn2.weight, 0)def _make_layer(self, block, planes, blocks, stride=1, dilate=False):norm_layer = self._norm_layerdownsample = Noneprevious_dilation = self.dilationif dilate:self.dilation *= stridestride = 1if stride != 1 or self.inplanes != planes * block.expansion:downsample = nn.Sequential(conv1x1(self.inplanes, planes * block.expansion, stride),norm_layer(planes * block.expansion),)layers = []layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, stride, downsample, self.groups,self.base_width, previous_dilation, norm_layer))self.inplanes = planes * block.expansionfor _ in range(1, blocks):layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, groups=self.groups,base_width=self.base_width, dilation=self.dilation,norm_layer=norm_layer))return nn.Sequential(*layers)def _forward_impl(self, x):# See note [TorchScript super()]x = self.conv1(x)x = self.bn1(x)x = self.relu(x)x = self.maxpool(x)x = self.layer1(x)x = self.layer2(x)x = self.layer3(x)x = self.layer4(x)x = self.avgpool(x)x = torch.flatten(x, 1)x = self.fc(x)return xdef forward(self, x):return self._forward_impl(x)def _resnet(arch, block, layers, pretrained, progress, **kwargs):model = ResNet(block, layers, **kwargs)if pretrained:state_dict = load_state_dict_from_url(model_urls[arch],progress=progress)model.load_state_dict(state_dict)return modeldef resnet18(pretrained=False, progress=True, **kwargs):r"""ResNet-18 model from`"Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition" <https://arxiv.org/pdf/1512.03385.pdf>`_Args:pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNetprogress (bool): If True, displays a progress bar of the download to stderr"""return _resnet('resnet18', BasicBlock, [2, 2, 2, 2], pretrained, progress,**kwargs)def resnet34(pretrained=False, progress=True, **kwargs):r"""ResNet-34 model from`"Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition" <https://arxiv.org/pdf/1512.03385.pdf>`_Args:pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNetprogress (bool): If True, displays a progress bar of the download to stderr"""return _resnet('resnet34', BasicBlock, [3, 4, 6, 3], pretrained, progress,**kwargs)def resnet50(pretrained=False, progress=True, **kwargs):r"""ResNet-50 model from`"Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition" <https://arxiv.org/pdf/1512.03385.pdf>`_Args:pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNetprogress (bool): If True, displays a progress bar of the download to stderr"""return _resnet('resnet50', Bottleneck, [3, 4, 6, 3], pretrained, progress,**kwargs)def resnet101(pretrained=False, progress=True, **kwargs):r"""ResNet-101 model from`"Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition" <https://arxiv.org/pdf/1512.03385.pdf>`_Args:pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNetprogress (bool): If True, displays a progress bar of the download to stderr"""return _resnet('resnet101', Bottleneck, [3, 4, 23, 3], pretrained, progress,**kwargs)def resnet152(pretrained=False, progress=True, **kwargs):r"""ResNet-152 model from`"Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition" <https://arxiv.org/pdf/1512.03385.pdf>`_Args:pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNetprogress (bool): If True, displays a progress bar of the download to stderr"""return _resnet('resnet152', Bottleneck, [3, 8, 36, 3], pretrained, progress,**kwargs)def resnext50_32x4d(pretrained=False, progress=True, **kwargs):r"""ResNeXt-50 32x4d model from`"Aggregated Residual Transformation for Deep Neural Networks" <https://arxiv.org/pdf/1611.05431.pdf>`_Args:pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNetprogress (bool): If True, displays a progress bar of the download to stderr"""kwargs['groups'] = 32kwargs['width_per_group'] = 4return _resnet('resnext50_32x4d', Bottleneck, [3, 4, 6, 3],pretrained, progress, **kwargs)def resnext101_32x8d(pretrained=False, progress=True, **kwargs):r"""ResNeXt-101 32x8d model from`"Aggregated Residual Transformation for Deep Neural Networks" <https://arxiv.org/pdf/1611.05431.pdf>`_Args:pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNetprogress (bool): If True, displays a progress bar of the download to stderr"""kwargs['groups'] = 32kwargs['width_per_group'] = 8return _resnet('resnext101_32x8d', Bottleneck, [3, 4, 23, 3],pretrained, progress, **kwargs)def wide_resnet50_2(pretrained=False, progress=True, **kwargs):r"""Wide ResNet-50-2 model from`"Wide Residual Networks" <https://arxiv.org/pdf/1605.07146.pdf>`_The model is the same as ResNet except for the bottleneck number of channelswhich is twice larger in every block. The number of channels in outer 1x1convolutions is the same, e.g. last block in ResNet-50 has 2048-512-2048channels, and in Wide ResNet-50-2 has 2048-1024-2048.Args:pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNetprogress (bool): If True, displays a progress bar of the download to stderr"""kwargs['width_per_group'] = 64 * 2return _resnet('wide_resnet50_2', Bottleneck, [3, 4, 6, 3],pretrained, progress, **kwargs)def wide_resnet101_2(pretrained=False, progress=True, **kwargs):r"""Wide ResNet-101-2 model from`"Wide Residual Networks" <https://arxiv.org/pdf/1605.07146.pdf>`_The model is the same as ResNet except for the bottleneck number of channelswhich is twice larger in every block. The number of channels in outer 1x1convolutions is the same, e.g. last block in ResNet-50 has 2048-512-2048channels, and in Wide ResNet-50-2 has 2048-1024-2048.Args:pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNetprogress (bool): If True, displays a progress bar of the download to stderr"""kwargs['width_per_group'] = 64 * 2return _resnet('wide_resnet101_2', Bottleneck, [3, 4, 23, 3],pretrained, progress, **kwargs)
参考:ResNet学习笔记