本文已收录于专栏
❤️《Redis精通系列》❤️
上千人点赞收藏,全套Redis学习资料,大厂必备技能!
目录
1、简介
2、实现方式
2.1 LRU实现方式
2.2 LFU实现方式
3、LFU使用
3.1 配置文件开启LFU淘汰算法
1、简介
LRU有一个明显的缺点,它无法正确的表示一个Key的热度,如果一个key从未被访问过,仅仅发生内存淘汰的前一会儿被用户访问了一下,在LRU算法中这会被认为是一个热key。
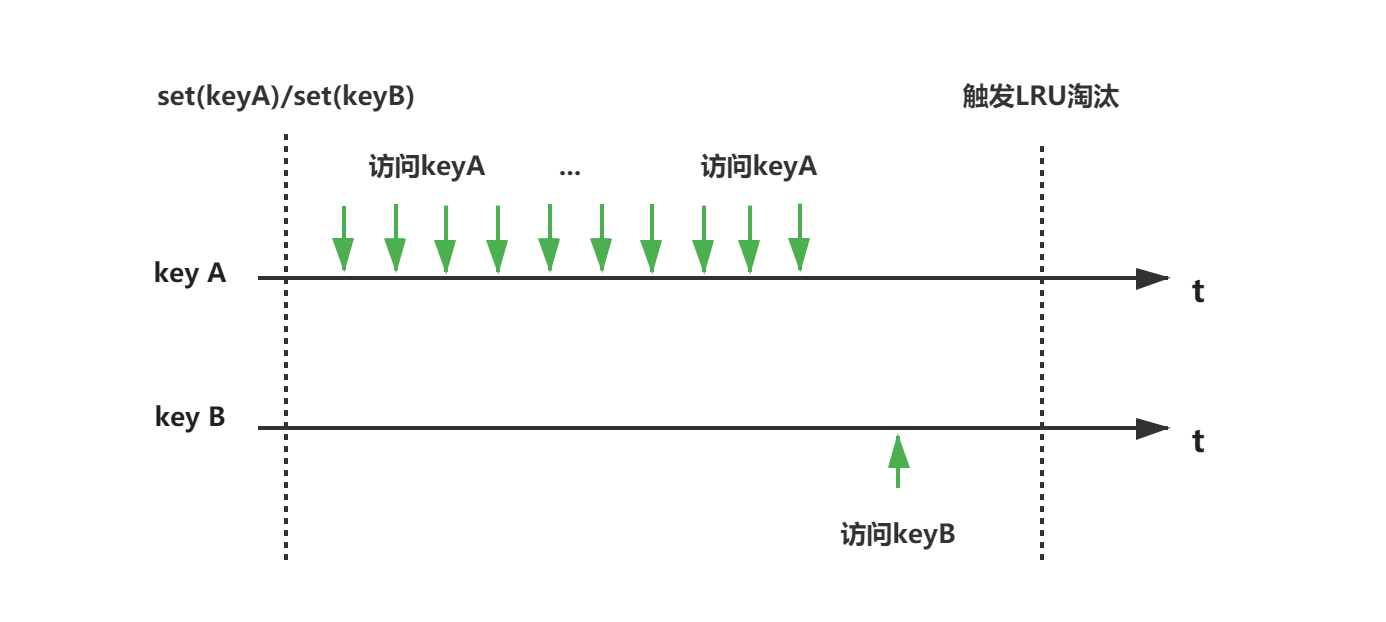
例如如下图,keyA与keyB同时被set到Redis中,在内存淘汰发生之前,keyA被频繁的访问,而keyB只被访问了一次,但是这次访问的时间比keyA的任意一次访问时间都更接近内存淘汰触发的时间,如果keyA与keyB均被Redis选中进行淘汰,keyA将被优先淘汰。我想大家都不太希望keyA被淘汰吧,那么有没有更好的的内存淘汰机制呢?当然有,那就是LFU。
LFU(Least Frequently Used)是Redis 4.0 引入的淘汰算法,它通过key的访问频率比较来淘汰key,重点突出的是Frequently Used。
LRU与LFU的区别:
- LRU -> Recently Used,根据最近一次访问的时间比较
- LFU -> Frequently Used,根据key的访问频率比较
Redis4.0之后为maxmemory_policy淘汰策略添加了两个LFU模式(LRU请看我上一篇文章):
- volatile-lfu:对有过期时间的key采用LFU淘汰算法
- allkeys-lfu:对全部key采用LFU淘汰算法
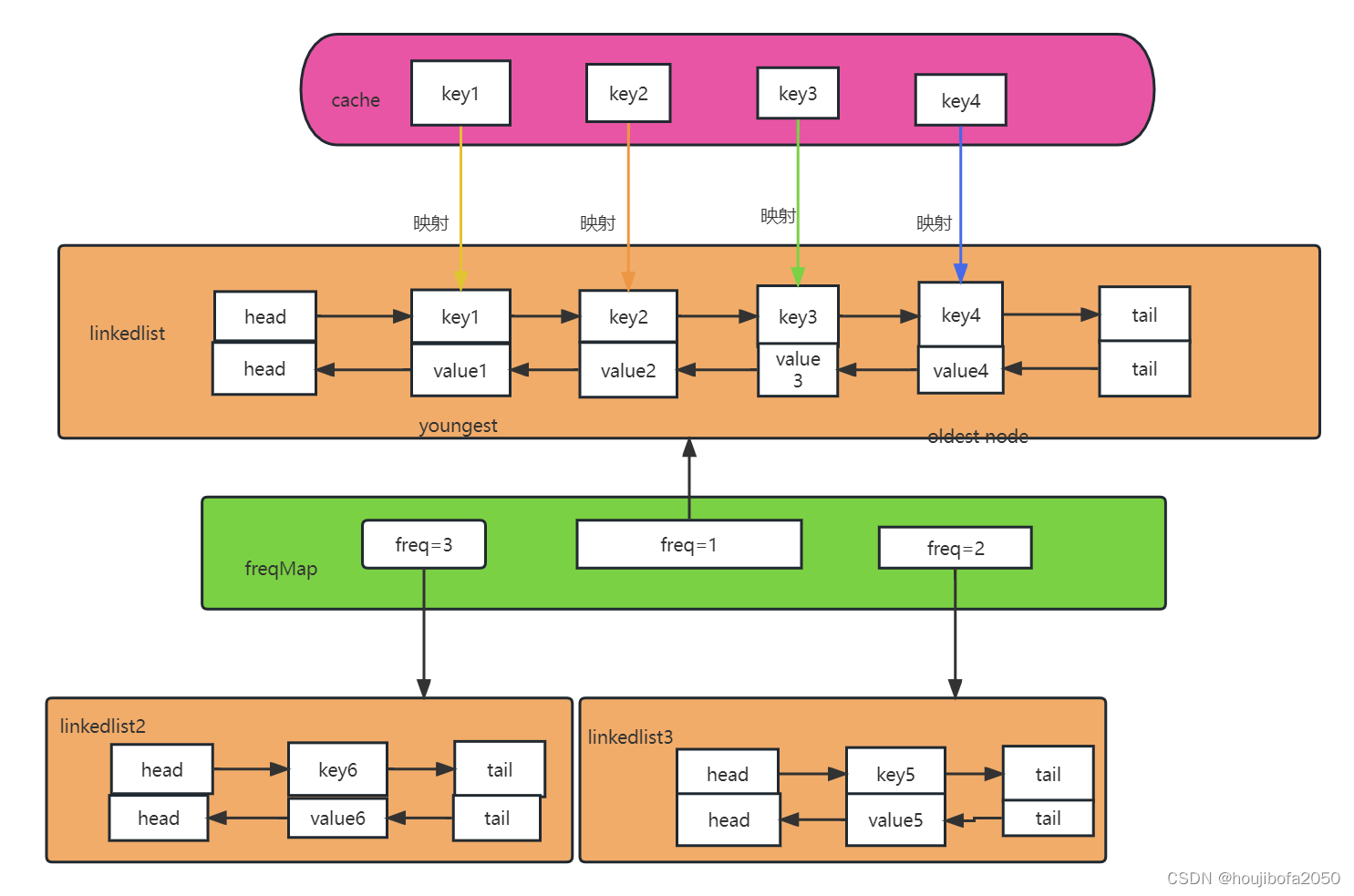
2、实现方式
Redis分配一个字符串的最小空间占用是19字节,16字节(对象头)+3字节(SDS基本字段)。Redis的内存淘汰算法LRU/LFU均依靠其中的对象头中的lru来实现。
Redis对象头的内存结构:
typedef struct redisObject {unsigned type:4; // 4 bits 对象的类型(zset、set、hash等)unsigned encoding:4; // 4 bits 对象的存储方式(ziplist、intset等)unsigned lru:24; // 24bits 记录对象的访问信息int refcount; // 4 bytes 引用计数void *ptr; // 8 bytes (64位操作系统),指向对象具体的存储地址/对象body
}
Redis对象头中的lru字段,在LRU模式下和LFU模式下使用方式并不相同。
2.1 LRU实现方式
在LRU模式,lru字段存储的是key被访问时Redis的时钟server.lrulock(Redis为了保证核心单线程服务性能,缓存了Unix操作系统时钟,默认每毫秒更新一次,缓存的值是Unix时间戳取模2^24)。当key被访问的时候,Redis会更新这个key的对象头中lru字段的值。
因此在LRU模式下,Redis可以根据对象头中的lru字段记录的值,来比较最后一次key的访问时间。
用Java代码演示一个简单的Redis-LRU算法:
- Redis对象头
package com.lizba.redis.lru;/*** <p>* Redis对象头* </p>** @Author: Liziba* @Date: 2021/9/22 22:40*/
public class RedisHead {/** 时间 */private Long lru;/** 具体数据 */private Object body;public RedisHead setLru(Long lru) {this.lru = lru;return this;}public RedisHead setBody(Object body) {this.body = body;return this;}public Long getLru() {return lru;}public Object getBody() {return body;}}
- Redis LRU实现代码
package com.lizba.redis.lru;import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;/*** <p>* Redis中LRU算法的实现demo* </p>** @Author: Liziba* @Date: 2021/9/22 22:36*/
public class RedisLruDemo {/*** 缓存容器*/private ConcurrentHashMap<String, RedisHead> cache;/*** 初始化大小*/private int initialCapacity;public RedisLruDemo(int initialCapacity) {this.initialCapacity = initialCapacity;this.cache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(initialCapacity);;}/*** 设置key/value 设置的时候更新LRU** @param key* @param body*/public void set(String key, Object body) {// 触发LRU淘汰synchronized (RedisLruDemo.class) {if (!cache.containsKey(key) && cache.size() >= initialCapacity) {this.flushLruKey();}}RedisHead obj = this.getRedisHead().setBody(body).setLru(System.currentTimeMillis());cache.put(key, obj);}/*** 获取key,存在则更新LRU** @param key* @return*/public Object get(String key) {RedisHead result = null;if (cache.containsKey(key)) {result = cache.get(key);result.setLru(System.currentTimeMillis());}return result;}/*** 清除LRU key*/private void flushLruKey() {List<String> sortData = cache.keySet().stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(key -> cache.get(key).getLru())).collect(Collectors.toList());String removeKey = sortData.get(0);System.out.println( "淘汰 -> " + "lru : " + cache.get(removeKey).getLru() + " body : " + cache.get(removeKey).getBody());cache.remove(removeKey);if (cache.size() >= initialCapacity) {this.flushLruKey();}return;}/*** 获取所有数据测试用** @return*/public List<RedisHead> getAll() {return cache.keySet().stream().map(key -> cache.get(key)).collect(Collectors.toList());}private RedisHead getRedisHead() {return new RedisHead();}}
- 测试代码
package com.lizba.redis.lru;import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;/*** <p>* 测试LRU* </p>** @Author: Liziba* @Date: 2021/9/22 22:51*/
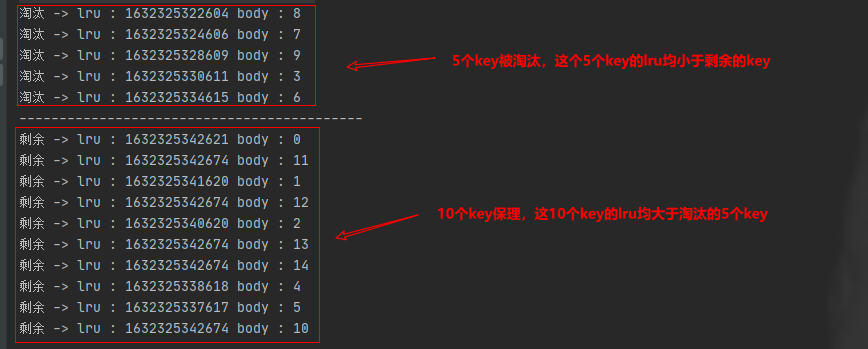
public class TestRedisLruDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {RedisLruDemo demo = new RedisLruDemo(10);// 先加入10个key,此时cache达到容量,下次加入会淘汰keyfor (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {demo.set(i + "", i);}// 随机访问前十个key,这样可以保证下次加入时随机淘汰for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {int nextInt = new Random().nextInt(10);TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);demo.get(nextInt + "");}// 再次添加5个key,此时每次添加都会触发淘汰for (int i = 10; i < 15; i++) {demo.set(i + "", i);}System.out.println("-------------------------------------------");demo.getAll().forEach( redisHead -> System.out.println("剩余 -> " + "lru : " + redisHead.getLru() + " body : " + redisHead.getBody()));}}
- 测试结果
2.2 LFU实现方式
在LFU模式下,Redis对象头的24bit lru字段被分成两段来存储,高16bit存储ldt(Last Decrement Time),低8bit存储logc(Logistic Counter)。

2.2.1 ldt(Last Decrement Time)
高16bit用来记录最近一次计数器降低的时间,由于只有8bit,存储的是Unix分钟时间戳取模2^16,16bit能表示的最大值为65535(65535/24/60≈45.5),大概45.5天会折返(折返指的是取模后的值重新从0开始)。
Last Decrement Time计算的算法源码:
/* Return the current time in minutes, just taking the least significant* 16 bits. The returned time is suitable to be stored as LDT (last decrement* time) for the LFU implementation. */
// server.unixtime是Redis缓存的Unix时间戳
// 可以看出使用的Unix的分钟时间戳,取模2^16
unsigned long LFUGetTimeInMinutes(void) {return (server.unixtime/60) & 65535;
}/* Given an object last access time, compute the minimum number of minutes* that elapsed since the last access. Handle overflow (ldt greater than* the current 16 bits minutes time) considering the time as wrapping* exactly once. */
unsigned long LFUTimeElapsed(unsigned long ldt) {// 获取系统当前的LFU timeunsigned long now = LFUGetTimeInMinutes();// 如果now >= ldt 直接取差值 if (now >= ldt) return now-ldt;// 如果now < ldt 增加上65535// 注意Redis 认为折返就只有一次折返,多次折返也是一次,我思考了很久感觉这个应该是可以接受的,本身Redis的淘汰算法就带有随机性 return 65535-ldt+now;
}
2.2.2 logc(Logistic Counter)
低8位用来记录访问频次,8bit能表示的最大值为255,logc肯定无法记录真实的Rediskey的访问次数,其实从名字可以看出存储的是访问次数的对数值,每个新加入的key的logc初始值为5(LFU_INITI_VAL),这样可以保证新加入的值不会被首先选中淘汰;logc每次key被访问时都会更新;此外,logc会随着时间衰减。
2.2.3 logc 算法调整
redis.conf 提供了两个配置项,用于调整LFU的算法从而控制Logistic Counter的增长和衰减。
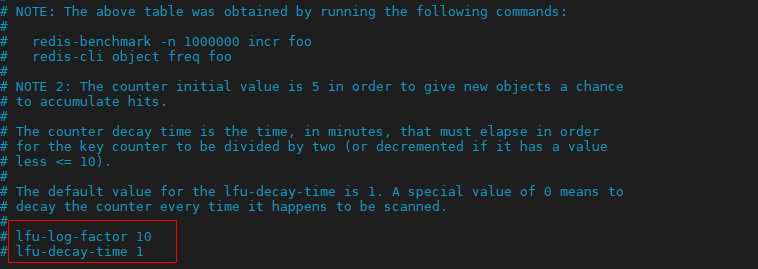
- lfu-log-factor 用于调整Logistic Counter的增长速度,lfu-log-factor值越大,Logistic Counter增长越慢。
Redis Logistic Counter增长的源代码:
/* Logarithmically increment a counter. The greater is the current counter value* the less likely is that it gets really implemented. Saturate it at 255. */
uint8_t LFULogIncr(uint8_t counter) {// Logistic Counter最大值为255 if (counter == 255) return 255;// 取一个0~1的随机数r double r = (double)rand()/RAND_MAX;// counter减去LFU_INIT_VAL (LFU_INIT_VAL为每个key的Logistic Counter初始值,默认为5)double baseval = counter - LFU_INIT_VAL;// 如果衰减之后已经小于5了,那么baseval < 0取0if (baseval < 0) baseval = 0;// lfu-log-factor在这里被使用// 可以看出如果lfu_log_factor的值越大,p越小// r < p的概率就越小,Logistic Counter增加的概率就越小(因此lfu_log_factor越大增长越缓慢)double p = 1.0/(baseval*server.lfu_log_factor+1);if (r < p) counter++;return counter;
}
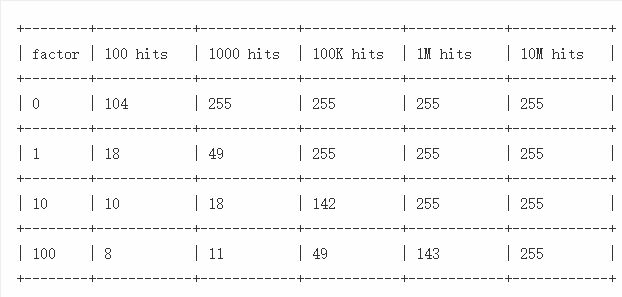
如下是官网提供lfu-log-factor在不同值下,key随着访问次数的增加的Logistic Counter变化情况的数据:
- lfu-decay-time 用于调整Logistic Counter的衰减速度,它是一个以分钟为单位的数值,默认值为1,;lfu-decay-time值越大,衰减越慢。
Redis Logistic Counter衰减的源代码:
/* If the object decrement time is reached decrement the LFU counter but* do not update LFU fields of the object, we update the access time* and counter in an explicit way when the object is really accessed.* And we will times halve the counter according to the times of* elapsed time than server.lfu_decay_time.* Return the object frequency counter.** This function is used in order to scan the dataset for the best object* to fit: as we check for the candidate, we incrementally decrement the* counter of the scanned objects if needed. */
unsigned long LFUDecrAndReturn(robj *o) {// 获取lru的高16位,也就是ldtunsigned long ldt = o->lru >> 8; // 获取lru的低8位,也就是logc unsigned long counter = o->lru & 255;// 根据配置的lfu-decay-time计算Logistic Counter需要衰减的值unsigned long num_periods = server.lfu_decay_time ? LFUTimeElapsed(ldt) / server.lfu_decay_time : 0;if (num_periods)counter = (num_periods > counter) ? 0 : counter - num_periods;return counter;
}
2.2.4 LFU 优化
LFU 与 LRU 有一个共同点,当内存达到max_memory时,选择key是随机抓取的,因此Redis为了使这种随机性更加准确,设计了一个淘汰池,这个淘汰池对于LFU和LRU算的都适应,只是淘汰池的排序算法有区别而已。
Redis 3.0就对这一块进行了优化(来自redis.io):

3、LFU使用
3.1 配置文件开启LFU淘汰算法
修改redis.conf配置文件,设置maxmemory-policy volatile-lfu/allkeys-lfu
重启Redis,连接客户端通过info指令查看maxmemory_policy的配置信息

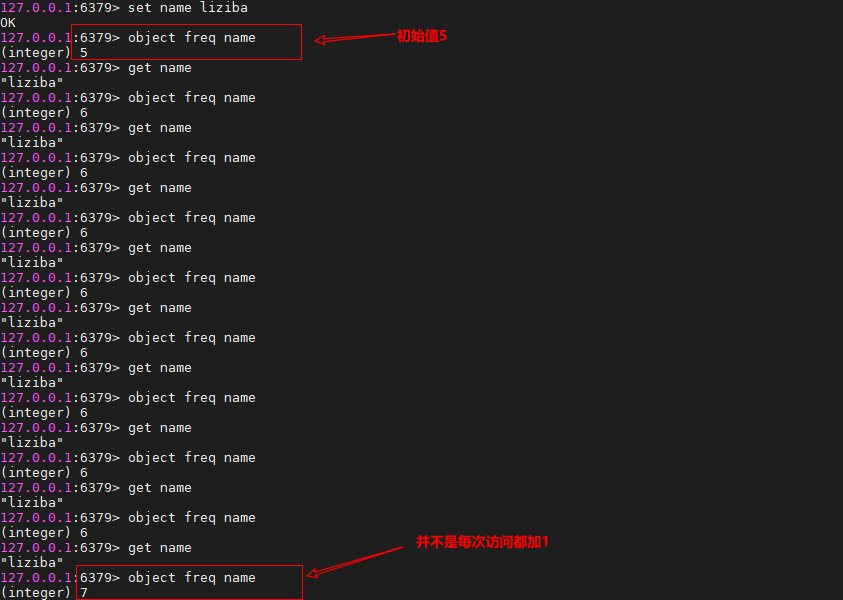
通过object freq key 获取对象的LFU的Logistic Counter值