流行病模型(SIR Model)
by : ZhuoFei, Zhou
首先定义一个函数bernoulli(p)
#以概率p判断是否会被感染或恢复
function bernoulli(p::Number)if rand(1)[1] < preturn trueelsereturn falseend
end
bernoulli (generic function with 1 method)
恢复所需的时间函数recovery_time(p)
function recovery_time(p)if p ≤ 0throw(ArgumentError("p must be positive: p = 0 cannot result in a recovery"))endrecovered = falsedays = 0while !recoveredrecovered = bernoulli(p)days+=1endreturn days
end
recovery_time (generic function with 1 method)
测试一下这个函数的运行情况:
其中 p p p为治愈概率, N N N为人数:
function do_experiment(p, N)return [recovery_time(p) for _=1:N]
end
do_experiment(0.5, 20);
Model
每个病原体都有自己的内部状态,模拟其感染状态,即“易感”、“感染”或“恢复”。我们想把它们分别编码为值’ S ', ’ I ‘和’ R ':
@enum InFectionStatus S I R
对于每一个病毒,我们都希望跟踪它的感染状态以及它在模拟过程中感染的其他病毒的数量。定义一个新的数据结构来保存一个个体的所有信息,如下所示:
mutable struct Agentstatus::InFectionStatusnum_infected::Int64
endAgent() = Agent(S,0)
Agent
#Agent状态变化
function set_status!(agent::Agent, new_status::InFectionStatus)agent.status = new_statusreturn agent# your code here
end#Agent 数量变化
function set_num_infected!(agent::Agent, new_num::Int64)agent.num_infected = new_numreturn agent
endfunction generate_agents(N::Integer)agents = [Agent() for _ in 1:N]set_status!(first(rand(agents,1)), I)return agentsend
generate_agents (generic function with 1 method)
#感染概率和恢复概率
abstract type AbstractInfection end
struct InfectionRecovery <: AbstractInfectionp_infectionp_recovery
end
一个类型为S的Agent,类型为I的Agent。它实现了两个人之间的单一(单边)交互:
-
如果“病原体”易受感染,而“来源”具有传染性,则“来源”以既定的感染概率感染“病原体”。如果“源”成功感染了另一个代理,则必须更新其“num_infected”记录。
-
如果“病原体”被感染,则它以相应的概率恢复。
-
否则,什么都不会发生。
function interact!(agent::Agent, source::Agent, infection::InfectionRecovery)if agent.status == S && source.status == Iif bernoulli(infection.p_infection)set_status!(agent,I)set_num_infected!(source,source.num_infected+1)endelseif agent.status == Iif bernoulli(infection.p_recovery)set_status!(agent,R)endend
endfunction step!(agents::Vector{Agent}, infection::AbstractInfection)agent,source = rand(agents,2)interact!(agent,source,infection)return agents
endfunction sweep!(agents::Vector{Agent}, infection::AbstractInfection)for _ in 1:length(agents)step!(agents, infection)endreturn agents
end
sweep! (generic function with 1 method)
模型的模拟函数:
function simulation(N::Integer, T::Integer, infection::AbstractInfection)tot_S = zeros(T)tot_I = zeros(T)tot_R = zeros(T)agents = generate_agents(N)for i in 1:Tsweep!(agents,infection)tot_S[i] = length(filter(agent -> agent.status==S,agents))tot_I[i] = length(filter(agent -> agent.status==I,agents))tot_R[i] = length(filter(agent -> agent.status==R,agents))end# your code herereturn (S=tot_S, I=tot_I, R=tot_R)
end
simulation (generic function with 1 method)
测试:
using Plots
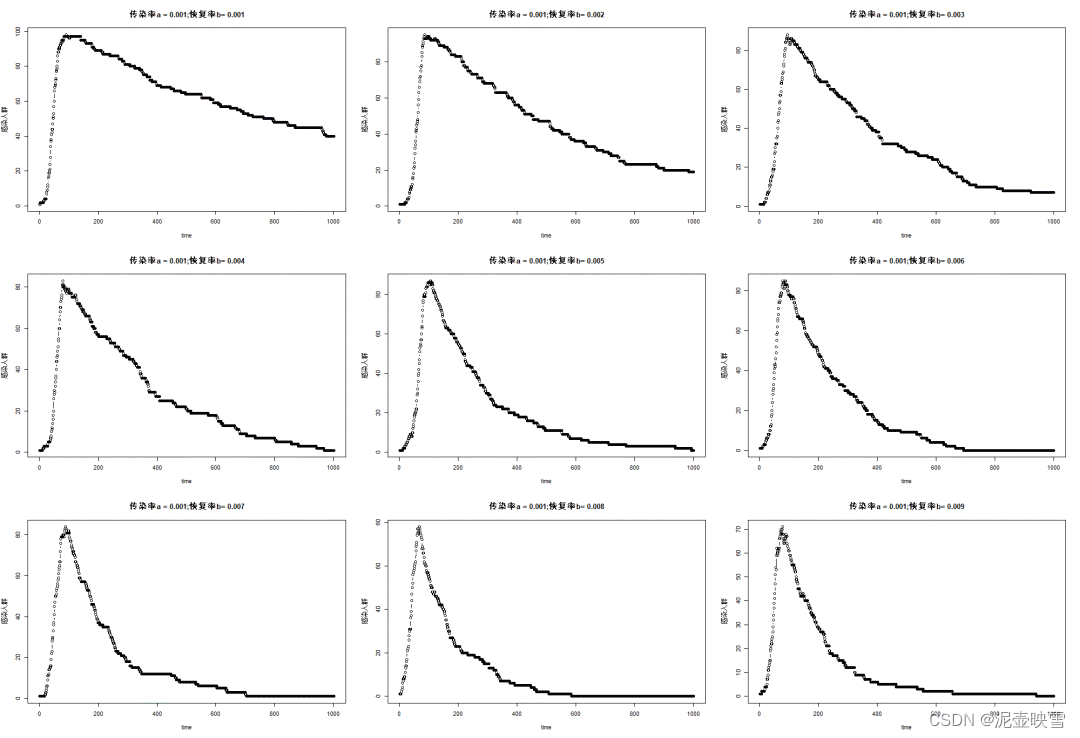
N = 1000
T = 1000
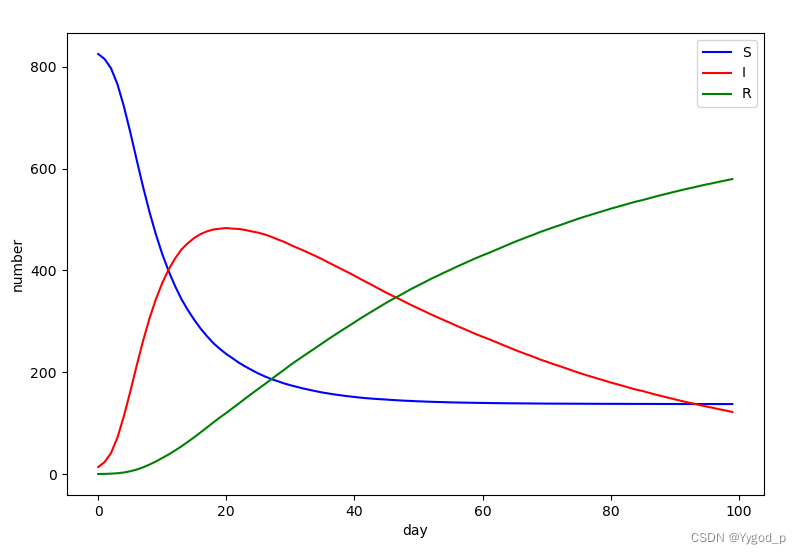
sim = simulation(N, T, InfectionRecovery(0.02, 0.002))result = plot(1:T, sim.S, ylim=(0, N), label="Susceptible")
plot!(result, 1:T, sim.I, ylim=(0, N), label="Infectious")
plot!(result, 1:T, sim.R, ylim=(0, N), label="Recovered")

function repeat_simulations(N, T, infection, num_simulations)N = 100T = 1000map(1:num_simulations) do _simulation(N, T, infection)endendsimulations = repeat_simulations(100, 1000, InfectionRecovery(0.02, 0.002), 20)p = plot()
for sim in simulationsplot!(p, 1:1000, sim.I, alpha=.5, label=nothing)
end
mean_I = sum(reduce(hcat, map(sim -> sim.I, simulations)),dims=2)./length(simulations)
plot!(p, mean_I, linewidth=3, label="mean I")
plot!(p, ylabel = "# of Infectious Agents")
p