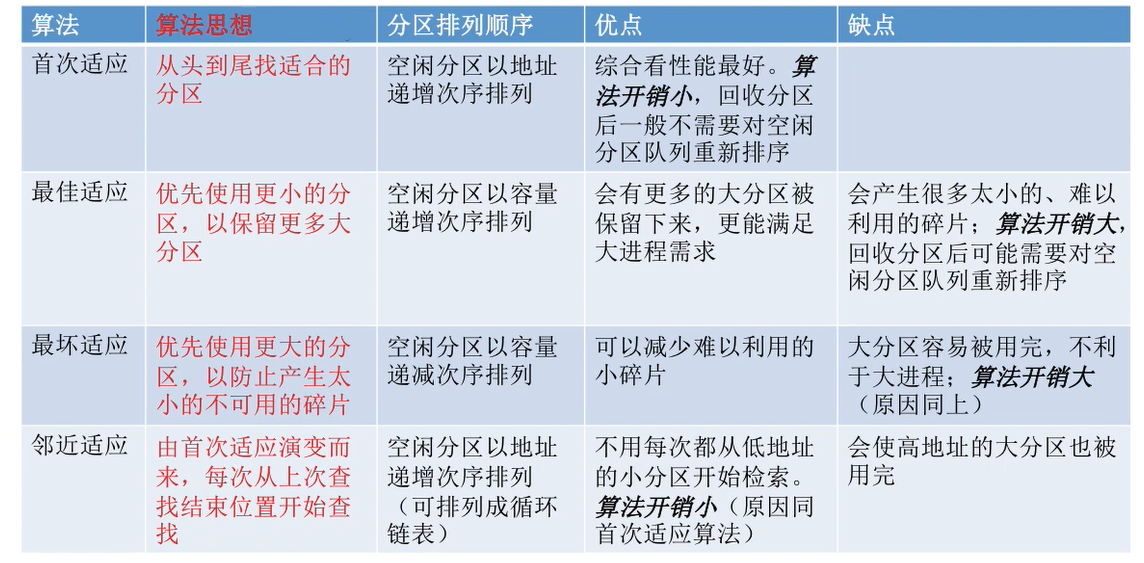
Decoupled Novel Object Captioner
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Methods
- Preliminaries
- Zero-Shot Novel Object Captioning.
- Sequence Model with the Placeholder
- Key-Value Object Memory
- Framework Overview
- Training
- Reference
Reference[原文]: Joselynzhao.top & 夏木青 | Decoupled Novel Object Captioner
(image-text)
Abstract
In this paper, we introduce the zero-shot novel object caption-ing task where the machine generates descriptions without extratraining sentences about the novel object. To tackle the challenging problem, we propose a Decoupled Novel Object Captioner (DNOC)framework that can fully decouple the language sequence model from the object descriptions.
**DNOC has two components. **
- ASequence Model with the Placeholder (SM-P) generates a sen-tence containing placeholders.
占位符的ASequence模型(SM-P)生成一个包含占位符的传感器。
- A key-value object memorybuilt upon the freely available detection model, contains the visualinformation and the corresponding word for each object.
Introduction
The captainingnetworks need a large number of image-sentence paired data totrain a meaningful model.
These captioning models fail in describing the novel objects whichare unseen words in the paired training data.

However, to feed the novel object description into the generatedcaptions, existing approaches either employ the pre-trained lan-guage sequence model [3, 34] or require extra unpaired training sentences of the novel object [41].
**In both cases, the novel objectshave been used in training and, hence, is not really novel. **
A moreprecise meaning of novel in existing works is unseen in the pairedtraining sentences.
In this paper, we tackle the image captioning for novel objects,where we do not need any training sentences containing the object
We utilize a pre-trained object detection model about the novel object. We call it zero-shot novel object captioning to distinguish itfrom the traditional problem setting [3, 34, 41].
In the zero-shot novel object captioning, there are zero training sentences aboutthe novel object .i.e., there is no information about the semanticmeaning, sense, and context of the object
To address this problem, we propose a Decoupled Novel ObjectCaptioner (DNOC) framework that is able to generate natural lan-guage descriptions without extra training sentences of the novelobject.
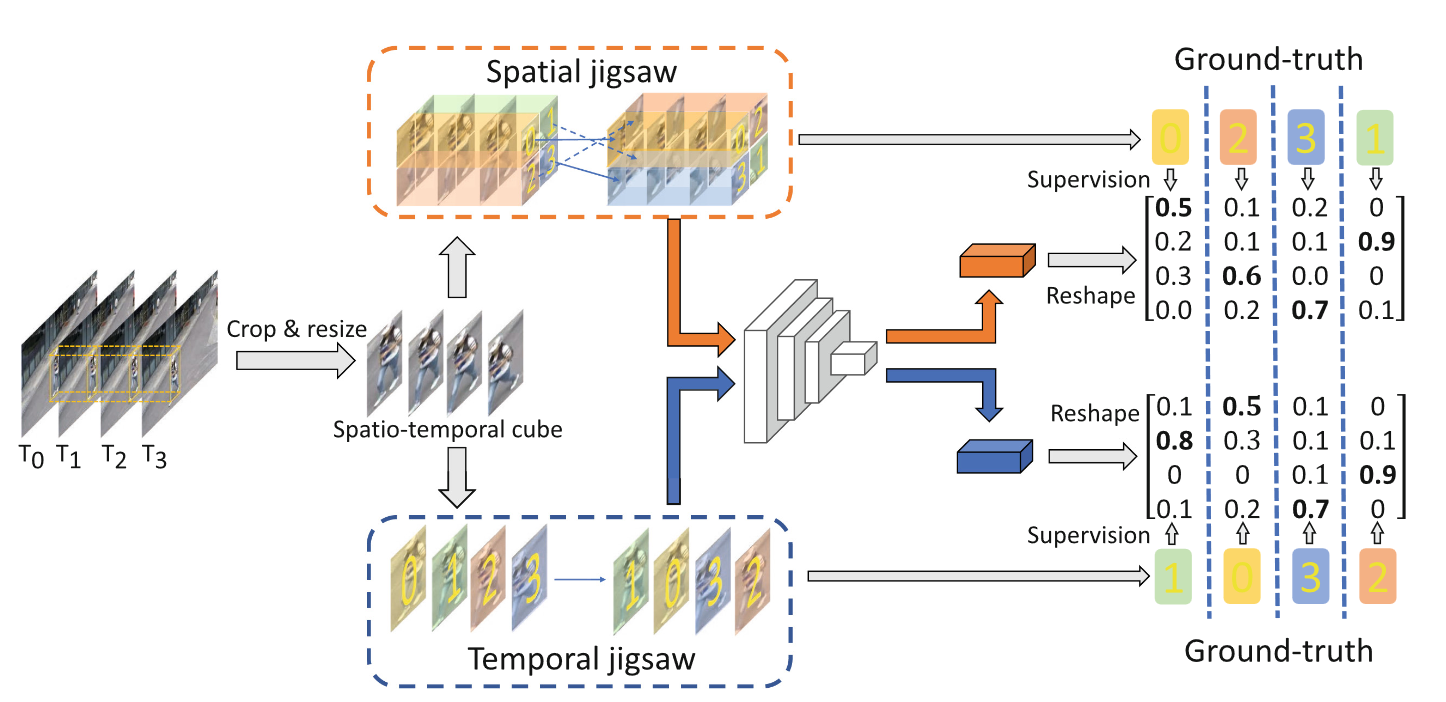
in Fig. 1, our method first generates the captioning sentence bygenerating a placeholder “” to represent any novel object.Then it learns to fill in the placeholder with “zebra” based on thevisual object detection result.
the main contributions of this work are listed asfollows:
- We introduce the zero-shot novel object captioning task
- we design the sequence modelwith the placeholder (SM-P).
- A key-value object memory is introduced to incorporate ex-ternal visual knowledge.
Methods
Preliminaries
given an input image I , the goal is to generate an as-sociated natural language sentence s of length nl, denoted as s =
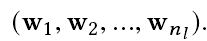




Zero-Shot Novel Object Captioning.
We denote Wunseen as the vocabulary for the novelobject words which are unseen in training.
A notable challenge for this task is to deal with the out-of-vocabulary (OOV) words.
The learned word embedding function ϕw is unable to encode the unseen words, since these word cannot simply be found in Wpaired.
We denote these extra training sentences as Sunpaired.
Sequence Model with the Placeholder

To solve this problem, we design a newtoken, denoted as “<PL>”.
“<PL>” is the placeholder that representsany novel words ˜w ∈ Wunseen .
We add the token“” into the paired vocabulary Wpair edto learn the embedding.
our model utilizes theexternal knowledge from the object detection model to replace it
we use the LSTM as the backbone of our SM-P
Instead, the SM-P model outputs the “”token when it needs to generate a word.
The “” token will be replaced by the novel word generatedby the key-value object memory.
Key-Value Object Memory
we exploit a pre-trained object detection model tobuild the key-value object memory.




Framework Overview

** For an input image with novel objects, we have thefollowing steps to generate the captioning sentence**:
- (i) We first exploit the SM-P to generate a captioning sentencewith some placeholders. Each placeholder represents an un-seen word/phrase for a novel object;
- (ii) We then build a key-value object memory Mobjfor each inputbased on the detection feature-label pairs {fi , li } on the image;
- (iii) Finally, we replace the placeholders of the sentence by corre-sponding object descriptions.
Training





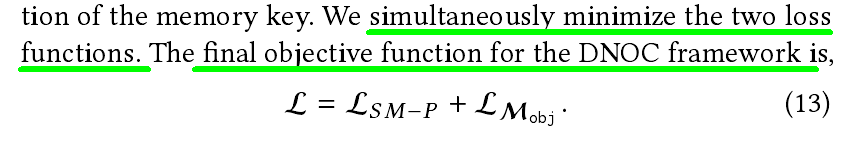
source code: https://github.com/Yu-Wu/Decoupled-Novel-Object-Captioner
Reference
[1] Martín Abadi, Paul Barham, Jianmin Chen, Zhifeng Chen, Andy Davis, JeffreyDean, Matthieu Devin, Sanjay Ghemawat, Geoffrey Irving, Michael Isard, et al.2016. TensorFlow: A System for Large-Scale Machine Learning… In OSDI, Vol. 16.265–283.
[2] Peter Anderson, Basura Fernando, Mark Johnson, and Stephen Gould. 2017.Guided open vocabulary image captioning with constrained beam search. InEMNLP.
[3] Lisa Anne Henzdricks, Subhashini Venugopalan, Marcus Rohrbach, RaymondMooney, Kate Saenko, Trevor Darrell, Junhua Mao, Jonathan Huang, AlexanderToshev, Oana Camburu, et al. 2016. Deep compositional captioning: Describingnovel object categories without paired training data. In CVPR.
[4] Satanjeev Banerjee and Alon Lavie. 2005. METEOR: An automatic metric for MTevaluation with improved correlation with human judgments. In ACL-W. 65–72.
[5] Samy Bengio, Oriol Vinyals, Navdeep Jaitly, and Noam Shazeer. 2015. Scheduledsampling for sequence prediction with recurrent neural networks. In NIPS. 1171–1179.
[6] Jeffrey Donahue, Lisa Anne Hendricks, Sergio Guadarrama, Marcus Rohrbach,Subhashini Venugopalan, Kate Saenko, and Trevor Darrell. 2015. Long-termrecurrent convolutional networks for visual recognition and description. In CVPR.2625–2634.
[7] Xuanyi Dong, Linchao Zhu, De Zhang, Yi Yang, and Fei Wu. 2018. Fast ParameterAdaptation for Few-shot Image Captioning and Visual Question Answering. InACM on Multimedia.
[8] Ali Farhadi, Mohsen Hejrati, Mohammad Amin Sadeghi, Peter Young, CyrusRashtchian, Julia Hockenmaier, and David Forsyth. 2010. Every picture tells astory: Generating sentences from images. In ECCV. 15–29.
[9] Chelsea Finn, Pieter Abbeel, and Sergey Levine. 2017. Model-Agnostic Meta-Learning for Fast Adaptation of Deep Networks. In ICML. 1126–1135.
[10] Sepp Hochreiter and Jürgen Schmidhuber. 1997. Long short-term memory. Neuralcomputation 9, 8 (1997), 1735–1780.
[11] Jonathan Huang, Vivek Rathod, Chen Sun, Menglong Zhu, Anoop Korattikara,Alireza Fathi, Ian Fischer, Zbigniew Wojna, Yang Song, Sergio Guadarrama, et al.2017. Speed/accuracy trade-offs for modern convolutional object detectors. InCVPR.
[12] Lu Jiang, Shoou-I Yu, Deyu Meng, Teruko Mitamura, and Alexander G Haupt-mann. 2015. Bridging the ultimate semantic gap: A semantic search engine forinternet videos. In ICMR. 27–34.
[13] Lu Jiang, Shoou-I Yu, Deyu Meng, Yi Yang, Teruko Mitamura, and Alexander GHauptmann. 2015. Fast and accurate content-based semantic search in 100minternet videos. In ACM on Multimedia. 49–5
[14] Justin Johnson, Andrej Karpathy, and Li Fei-Fei. 2016. Densecap: Fully convolu-tional localization networks for dense captioning. In CVPR. 4565–4574.
[15] Andrej Karpathy and Li Fei-Fei. 2015. Deep visual-semantic alignments forgenerating image descriptions. In CVPR. 3128–3137.
[16] Diederik P Kingma and Jimmy Ba. 2015. Adam: A method for stochastic opti-mization. In ICLR.
[17] Ryan Kiros, Ruslan Salakhutdinov, and Rich Zemel. 2014. Multimodal neurallanguage models. In ICML. 595–603.
[18] Girish Kulkarni, Visruth Premraj, Vicente Ordonez, Sagnik Dhar, Siming Li, YejinChoi, Alexander C Berg, and Tamara L Berg. 2013. Babytalk: Understanding andgenerating simple image descriptions. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis andMachine Intelligence 35, 12 (2013), 2891–2903.
[19] Christoph H Lampert, Hannes Nickisch, and Stefan Harmeling. 2014. Attribute-based classification for zero-shot visual object categorization. IEEE Transactionson Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 36, 3 (2014), 453–465.
[20] Tsung-Yi Lin, Michael Maire, Serge Belongie, James Hays, Pietro Perona, DevaRamanan, Piotr Dollár, and C Lawrence Zitnick. 2014. Microsoft coco: Commonobjects in context. In ECCV. 740–755.
[21] Jiasen Lu, Jianwei Yang, Dhruv Batra, and Devi Parikh. 2018. Neural Baby Talk.In CVPR. 7219–7228.
[22] Junhua Mao, Xu Wei, Yi Yang, Jiang Wang, Zhiheng Huang, and Alan L Yuille.2015. Learning like a child: Fast novel visual concept learning from sentencedescriptions of images. In ICCV. 2533–2541.
[23] Junhua Mao, Wei Xu, Yi Yang, Jiang Wang, Zhiheng Huang, and Alan Yuille. 2015.Deep Captioning with Multimodal Recurrent Neural Networks (m-RNN). ICLR(2015).
[24] George A Miller, Richard Beckwith, Christiane Fellbaum, Derek Gross, and Kather-ine J Miller. 1990. Introduction to WordNet: An on-line lexical database. Interna-tional journal of lexicography 3, 4 (1990), 235–244.
[25] Margaret Mitchell, Xufeng Han, Jesse Dodge, Alyssa Mensch, Amit Goyal, AlexBerg, Kota Yamaguchi, Tamara Berg, Karl Stratos, and Hal Daumé III. 2012.Midge: Generating Image Descriptions From Computer Vision Detections. InEACL. 747–756.
[26] Vicente Ordonez, Girish Kulkarni, and Tamara L Berg. 2011. Im2text: Describingimages using 1 million captioned photographs. In NIPS. 1143–1151
.[27] Marc’Aurelio Ranzato, Sumit Chopra, Michael Auli, and Wojciech Zaremba. 2016.Sequence level training with recurrent neural networks. In ICLR.
[28] Shaoqing Ren, Kaiming He, Ross Girshick, and Jian Sun. 2015. Faster r-cnn:Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In NIPS. 91–99.
[29] Marcus Rohrbach, Michael Stark, and Bernt Schiele. 2011. Evaluating knowledgetransfer and zero-shot learning in a large-scale setting. In CVPR. 1641–1648.
[30] Adam Santoro, Sergey Bartunov, Matthew Botvinick, Daan Wierstra, and TimothyLillicrap. 2016. One-shot learning with memory-augmented neural networks.NIPS-W (2016).
[31] Karen Simonyan and Andrew Zisserman. 2015. Very deep convolutional networksfor large-scale image recognition. In ICLR.
[32] Christian Szegedy, Sergey Ioffe, Vincent Vanhoucke, and Alexander A Alemi.2017. Inception-v4, inception-resnet and the impact of residual connections onlearning. In AAAI.
[33] Hamed R Tavakoliy, Rakshith Shetty, Ali Borji, and Jorma Laaksonen. 2017.Paying Attention to Descriptions Generated by Image Captioning Models. InICCV. 2506–2515.
[34] Subhashini Venugopalan, Lisa Anne Hendricks, Marcus Rohrbach, RaymondMooney, Trevor Darrell, and Kate Saenko. 2017. Captioning Images with DiverseObjects. In CVPR.
[35] Subhashini Venugopalan, Marcus Rohrbach, Jeffrey Donahue, Raymond Mooney,Trevor Darrell, and Kate Saenko. 2015. Sequence to sequence-video to text. InICCV. 4534–4542.
[36] Oriol Vinyals, Charles Blundell, Tim Lillicrap, Daan Wierstra, et al. 2016. Match-ing networks for one shot learning. In NIPS. 3630–3638.
[37] Oriol Vinyals, Alexander Toshev, Samy Bengio, and Dumitru Erhan. 2015. Showand tell: A neural image caption generator. In CVPR. 3156–3164
.[38] O. Vinyals, A. Toshev, S. Bengio, and D. Erhan. 2017. Show and Tell: LessonsLearned from the 2015 MSCOCO Image Captioning Challenge. IEEE Transactionson Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 39, 4 (April 2017), 652–663
.[39] Y. Xian, C. H. Lampert, B. Schiele, and Z. Akata. 2018. Zero-Shot Learning - AComprehensive Evaluation of the Good, the Bad and the Ugly. IEEE Transactionson Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (2018), 1–1. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2857768
[40] Kelvin Xu, Jimmy Ba, Ryan Kiros, Kyunghyun Cho, Aaron Courville, RuslanSalakhudinov, Rich Zemel, and Yoshua Bengio. 2015. Show, attend and tell:Neural image caption generation with visual attention. In ICML. 2048–2057.
[41] Ting Yao, Yingwei Pan, Yehao Li, and Tao Mei. 2017. Incorporating copyingmechanism in image captioning for learning novel objects. In CVPR. 5263–5271
.[42] Quanzeng You, Hailin Jin, Zhaowen Wang, Chen Fang, and Jiebo Luo. 2016. Imagecaptioning with semantic attention. In CVPR. 4651–4659.
[43] Linchao Zhu, Zhongwen Xu, Yi Yang, and Alexander G. Hauptmann. 2017. Un-covering the Temporal Context for Video Question Answering. InternationalJournal of Computer Vision 124, 3 (01 Sep 2017), 409–421. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-017-1033-7Session: FF-4 MM’18, October 22-26, 2018, Seoul, Republic of Korea1037