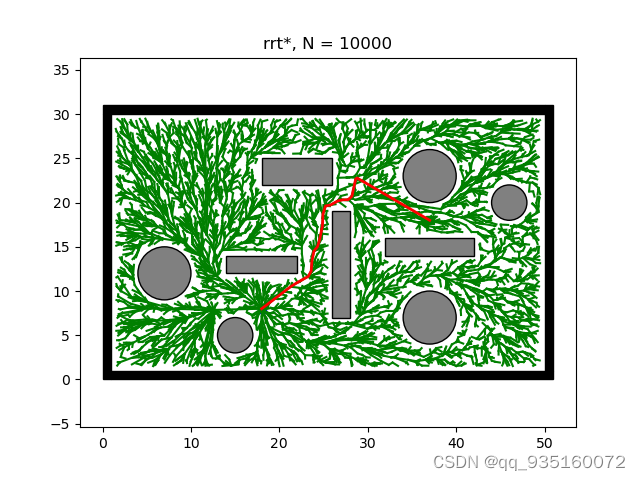
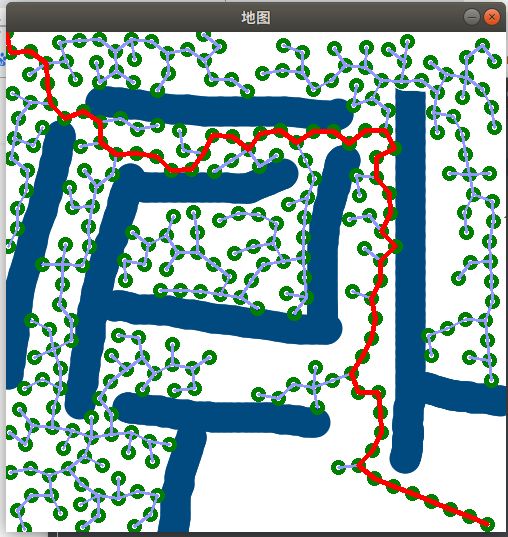
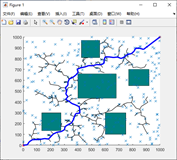
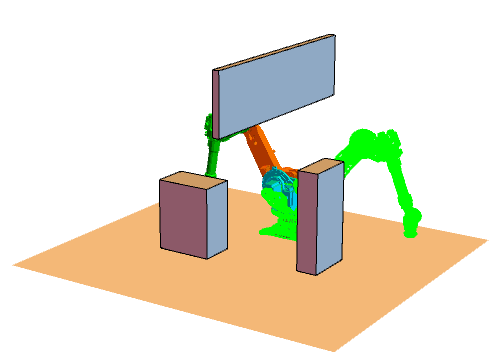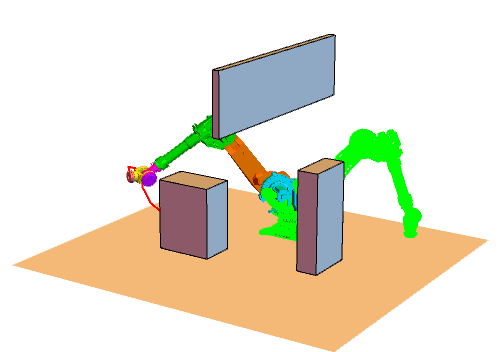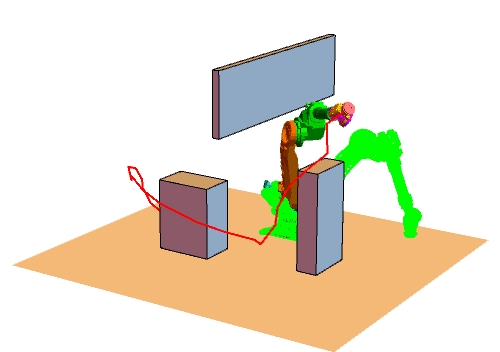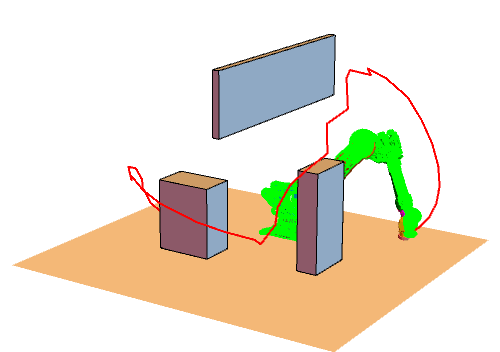
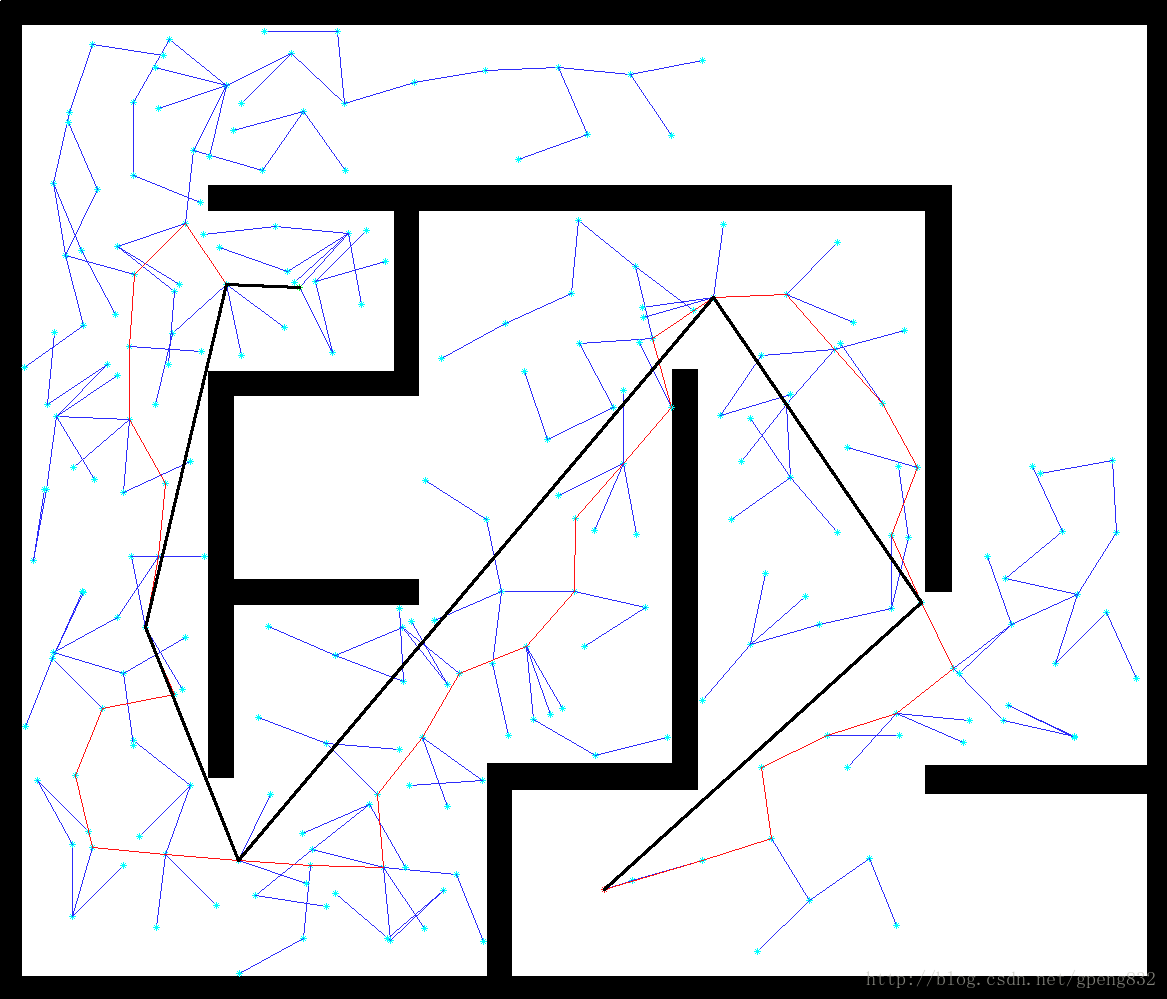
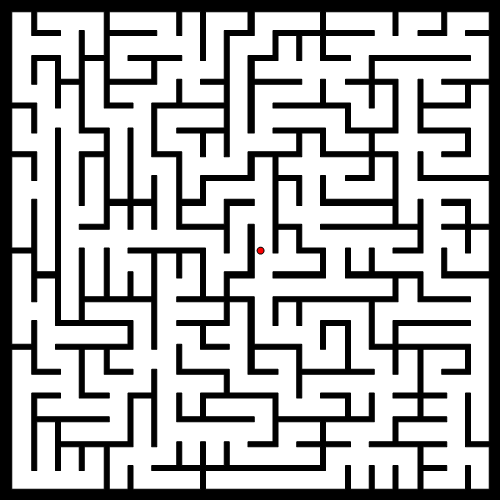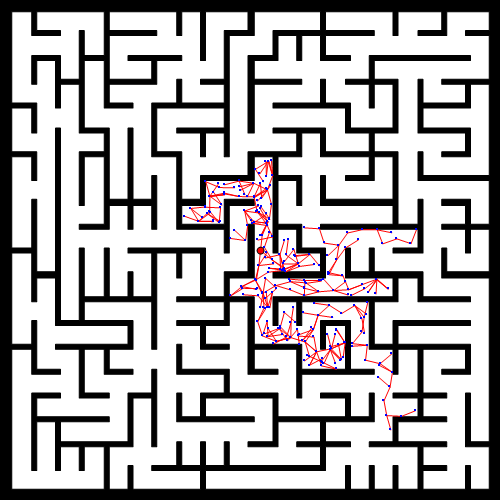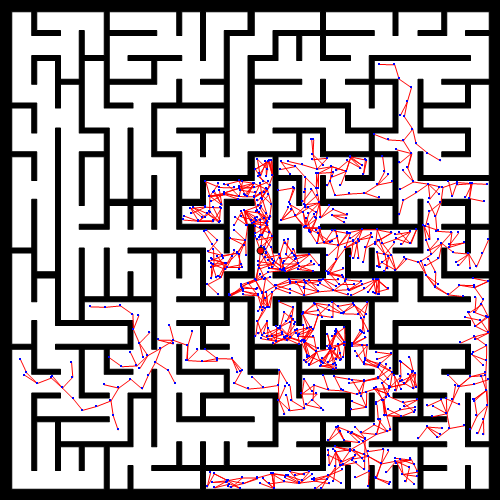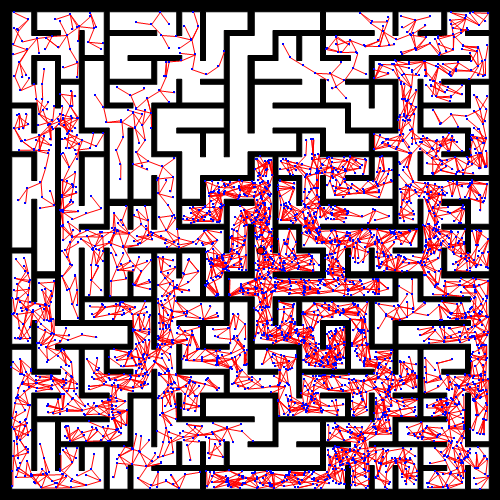
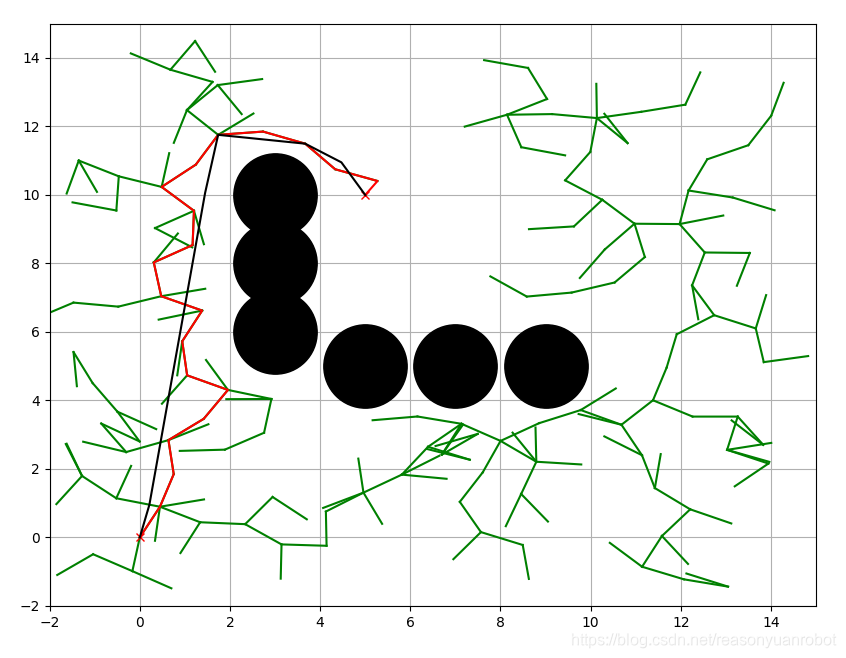
RRT大致流程
1.初始化随机树tree,以空的随机树开始添加节点,最开始只有Qinit。
2.执行sample函数,在地图中获得一个随机点Qrand。
3.遍历tree中所有节点,找出与Qrand之间代价最小的点Qnearest。
4.执行extend函数,获得Qnearest向Qrand方向上的指定长度的扩展点Qnew。并对Qnew进行碰撞检测,若碰撞检测为真,则结束此次循环,重新选择拓展点。若为假则将Qnearest指定为Qnew的父节点,连接两点之间的连线。
5.判断Qnew是否已经到达指定目标范围,若已经到达,则结束循环,否则继续执行循环知道找到目标范围。
其中sample函数用于,在地图中生成随机点;
def Sample(self, a, b):Q = [random.randint(0, a), random.randint(0, b)]return Q
extend函数用于找到拓展点,函数中c为步长。
# 获取Q与最近节点之间的拓展点def extend(self, a, b, c = 10):d = [0, 0]d[0] = a[0] + int(c * (b[0] - a[0]) / math.sqrt((a[0] - b[0]) ** 2 + (a[1] - b[1]) ** 2))d[1] = a[1] + int(c * (b[1] - a[1]) / math.sqrt((a[0] - b[0]) ** 2 + (a[1] - b[1]) ** 2))return d
整个代码段以输入图片作为地图,以灰度读入作为checkMap,用以碰撞检测;再以正常读入作为drawMap用以画出点与路径。

RRT*找Qnew之前的流程与RTT相同,找到Qnew,判断其有效性后。不直接连接Qnew与Qnearest,而是运行函数nearToNew,寻找在指定范围r内的所有节点,遍历所有得到的节点Qnear,判断Qnear中到Qnew与Qnear到Qinit代价和最小的节点,指定其为Qnew的父节点连接两点连线。
再执行函数rewire,遍历剩下的节点Qnear,判断如果以Qnew为父节点,其代价是否会小于原来的代价,若小于,则更改其父节点为Qnew。
其中nearToNew用来寻找距离给定点一定范围内的各个节点返回为一个list;
# 获取指定点周围一定范围内的节点def nearToNew(self, new):nearTonew = []nearCost = []for item in self.tree:costToNew = self.cost(item.loc, new)if costToNew < self.step * 2:# 判断两点之间的连线是否穿过障碍物if self.is_block(item.loc, new):continuenearTonew.append(item)nearCost.append(int(costToNew) + int(item.cost))return nearTonew,nearCost
函数rewire用来重新规划Qnew周围的路径:
# 重新规划新节点new与其周围节点之间的路径def rewire(self, nearTonew, newPoint):for item2 in nearTonew:costToNew = self.cost(item2.loc, newPoint.loc)if costToNew + newPoint.cost < item2.cost:# 判断两点之间路线是否穿过障碍物if self.is_block(item2.loc, newPoint.loc):continuecv2.line(self.map.drawMap, tuple(item2.loc), tuple(item2.fatherPoint.loc), (255, 255, 255))item2.fatherPoint = newPointitem2.cost = costToNew + newPoint.costcv2.line(self.map.drawMap, tuple(item2.loc), tuple(item2.fatherPoint.loc), (0, 255, 0))cv2.imshow("route", self.map.drawMap)cv2.waitKey(self.speed)
以上代码都是我在整个RRT*代码中截取出来的片段,仅供参考大致思路。
以下是RRT*完整代码,初写代码,可能不太标准,仅供参考,也算是对于自己学习的记录。
# -*- coding = utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2021/4/14 9:07import random
import cv2
import math
import copy
import time
from numpy import meanclass Point(object):def __init__(self,loc, cost, fatherPoint = None):self.loc = locself.cost = costself.fatherPoint = fatherPointclass Map(object):point = []def __init__(self, img):self.drawMap = cv2.imread(img)self.checkMaps = cv2.imread(img, cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)self.width = self.checkMaps.shape[1]self.height = self.checkMaps.shape[0]def on_EVENT_LBUTTONDOWN(self,event, x, y, flags, param):# point = []if event == cv2.EVENT_LBUTTONDOWN:xy = '%d,%d' % (x, y)# global pointself.point.append([x,y])# print('x, y = {}, {}'.format(x, y))cv2.circle(self.drawMap, (x, y), 1, (255, 0, 0), thickness=-1)cv2.putText(self.drawMap, xy, (x, y), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN,1.0, (0, 0, 0), thickness=1)cv2.imshow('image', self.drawMap)def start_end(self):cv2.namedWindow('image')cv2.imshow('image', self.checkMaps)cv2.setMouseCallback('image', self.on_EVENT_LBUTTONDOWN)cv2.waitKey(0)cv2.destroyAllWindows()print("起点:", self.point[0], "终点:", self.point[1])return self.pointdef is_block(self,a):if self.checkMaps[a[1], a[0]] == 0:return Trueelse:return Falsedef Route(self,point,v):a = point.locb = point.fatherPoint.loccv2.line(self.drawMap,tuple(a),tuple(b),(0,0,255),3)cv2.imshow('route', self.drawMap)cv2.waitKey(v)return point.fatherPointclass RRTStar(object):tree = []def __init__(self,map,step,speed = 10):self.step = stepself.map = mapself.speed = speedreturn# 获得随机点Q的坐标def Sample(self, a, b):Q = [random.randint(0, a), random.randint(0, b)]return Q# 计算两点之间的代价def cost(self, a, b):c = math.sqrt((a[0] - b[0])**2 + (a[1] - b[1])**2)return c# 找到离随机点Q最近的节点def nearest(self, q, tree):a = []for item in tree:a.append(self.cost(q, item.loc))b = tree[a.index(min(a))]return b# 获取Q与最近节点之间的拓展点def extend(self, a, b, c = 10):d = [0, 0]d[0] = a[0] + int(c * (b[0] - a[0]) / math.sqrt((a[0] - b[0]) ** 2 + (a[1] - b[1]) ** 2))d[1] = a[1] + int(c * (b[1] - a[1]) / math.sqrt((a[0] - b[0]) ** 2 + (a[1] - b[1]) ** 2))return d# 取得指定点之间的的碰撞监测点def checkPoint(self, point1, point2):a = copy.deepcopy(point1)b = copy.deepcopy(point2)if a[0] > b[0]:a[0],b[0] = b[0],a[0]a[1],b[1] = b[1],a[1]q = 3c = []if a[0] == b[0]:if a[1] > b[1]:a[1],b[1] = b[1],a[1]for i in range(a[1] - q, b[1] + q):c.append([a[0], i])c.append([a[0] - q, i])c.append([a[0] + q, i])else:for i in range(a[0] - q,b[0] + q):d = (b[1] - a[1])/(b[0] - a[0]) * (i - a[0]) + a[1]e = (b[1] - a[1])/(b[0] - a[0]) * (i - a[0]) + a[1] + qf = (b[1] - a[1])/(b[0] - a[0]) * (i - a[0]) + a[1] - qc.append([i, int(d)])c.append([i, int(e)])c.append([i, int(f)])return c# 利用梯度下降法生对路径进行平滑处理def smoothPoint(self,path, weight_data=0.5, weight_smooth=0.5, tolerance=0.00001):N = len(path)newpath = copy.deepcopy(path)err = 2 * tolerancewhile err > tolerance:err = 0.for i in range(1, N - 1):for j in range(2):delta = weight_data * (path[i][j] - newpath[i][j]) + \weight_smooth * (newpath[(i - 1) % N][j] + newpath[(i + 1) % N][j] - 2.0 * newpath[i][j])newpath[i][j] += deltaerr += abs(delta)return newpath# 碰撞检测def is_block(self, a, b):for i in self.checkPoint(a, b):if 0 < i[0] < self.map.width and 0 < i[1] < self.map.height:if self.map.is_block(i):return Trueelse:return Truereturn False# 获取指定点周围一定范围内的节点def nearToNew(self, new):nearTonew = []nearCost = []for item in self.tree:costToNew = self.cost(item.loc, new)if costToNew < self.step * 2:# 判断两点之间的连线是否穿过障碍物if self.is_block(item.loc, new):continuenearTonew.append(item)nearCost.append(int(costToNew) + int(item.cost))return nearTonew,nearCost# 重新规划新节点new与其周围节点之间的路径def rewire(self, nearTonew, newPoint):for item2 in nearTonew:costToNew = self.cost(item2.loc, newPoint.loc)if costToNew + newPoint.cost < item2.cost:# 判断两点之间路线是否穿过障碍物if self.is_block(item2.loc, newPoint.loc):continuecv2.line(self.map.drawMap, tuple(item2.loc), tuple(item2.fatherPoint.loc), (255, 255, 255))item2.fatherPoint = newPointitem2.cost = costToNew + newPoint.costcv2.line(self.map.drawMap, tuple(item2.loc), tuple(item2.fatherPoint.loc), (0, 255, 0))cv2.imshow("route", self.map.drawMap)cv2.waitKey(self.speed)# 在图上画出路径def drawRoute(self, point):routePoint = []c = pointroutePoint.append(point.loc)while True:c = self.map.Route(c, self.speed)routePoint.append(c.loc)if c.loc == start:breakreturn routePoint# 在图上画出平滑处理后的路径def Smooth(self, routePoint):s = self.smoothPoint(routePoint)for i in range(len(s)):if i == len(s) - 1:breakx = (int(s[i][0]), int(s[i][1]))y = (int(s[i + 1][0]), int(s[i + 1][1]))cv2.line(self.map.drawMap, x, y, (0, 0, 255), 2)cv2.imshow("route", self.map.drawMap)cv2.waitKey(self.speed)cv2.imshow("route", self.map.drawMap)cv2.waitKey(0)def Path(self, start, end):speed = self.speedtree = self.treetree.append(Point(start,0))t = 0while t < 2000:tag = 0# 取得随机点qq = self.Sample(self.map.width, self.map.height)# 取得离随机点最近的点nearest = self.nearest(q, tree)if q == nearest.loc:continue# 获得拓展点newnew = self.extend(nearest.loc, q, self.step)# 获得在拓展点两个步长范围内的所有点,取得其中到拓展点代价最小的点,作为拓展点父节点nearTonew,nearCost = self.nearToNew(new)#如果拓展点附近没有复合要求的点,则结束此次循环,重新选择拓展点if nearCost:passelse:continueminCostPoint = nearTonew[nearCost.index(min(nearCost))]nearTonew.remove(minCostPoint)newPoint = Point(new, min(nearCost), minCostPoint)t += 1# 标出拓展点位置,画出拓展点与其父节点之间的线cv2.circle(self.map.drawMap, tuple(new), 2, (255, 0, 0), thickness=-1)cv2.line(self.map.drawMap, tuple(newPoint.loc), tuple(newPoint.fatherPoint.loc), (0, 255, 0))tree.append(newPoint)cv2.imshow("route", self.map.drawMap)cv2.waitKey(speed)# 浏览拓展点周围的其他点,判断以拓展点为父节点的代价与原本的代价的大小,若小于原本的代价,则将拓展点改为其父节点self.rewire(nearTonew, newPoint)# 判断是否到达终点,画出路径,并进行平滑处理if abs(new[0] - end[0]) < 20 and abs(new[1] - end[1]) < 20:tag = 1routePoint = self.drawRoute(newPoint)# self.Smooth(routePoint)breakif tag == 1:print("RRT*寻路成功")else:print("RRT*寻路失败")if __name__ == "__main__":t0 = 0T = []while t0 < 10:map = Map("../work/testmap.png")time1 = time.time()start = [50, 50]end = [800, 400]cv2.circle(map.drawMap, (start[0], start[1]), 2, (255, 0, 0), thickness=-1)cv2.rectangle(map.drawMap, (end[0] - 20, end[1] - 20), (end[0] + 20, end[1] + 20), (255, 0, 0))a = RRTStar(map, 30, 1)print(len(a.tree))a.Path(start, end)a.tree.clear()time2 = time.time()T.append(time2 - time1)t0 += 1cv2.destroyAllWindows()print(mean(T))print(T)
效果图