简介
RRT 算法(快速扩展随机树,rapidly exploring random tree)是一种随机性算法,它可以直接应用于非完整约束系统的规划,不需进行路径转换,所以它的算法复杂度较小,尤为适用于高维多自由度的系统。
缺点是得到的路径质量不是很好。需要后处理进一步优化。
思想是快速扩张一群像树一样的路径以探索(填充)空间的大部分区域,伺机找到可行的路径。
RRT 的基本步骤是:
1. 起点作为一颗种子,从它开始生长枝丫;
2. 在机器人的“构型”空间中,生成一个随机点X;
3. 在树上找到距离X最近的那个点,记为Y吧;
4. 朝着X的方向生长,如果没有碰到障碍物就把生长后的树枝和端点添加到树上,返回 2;
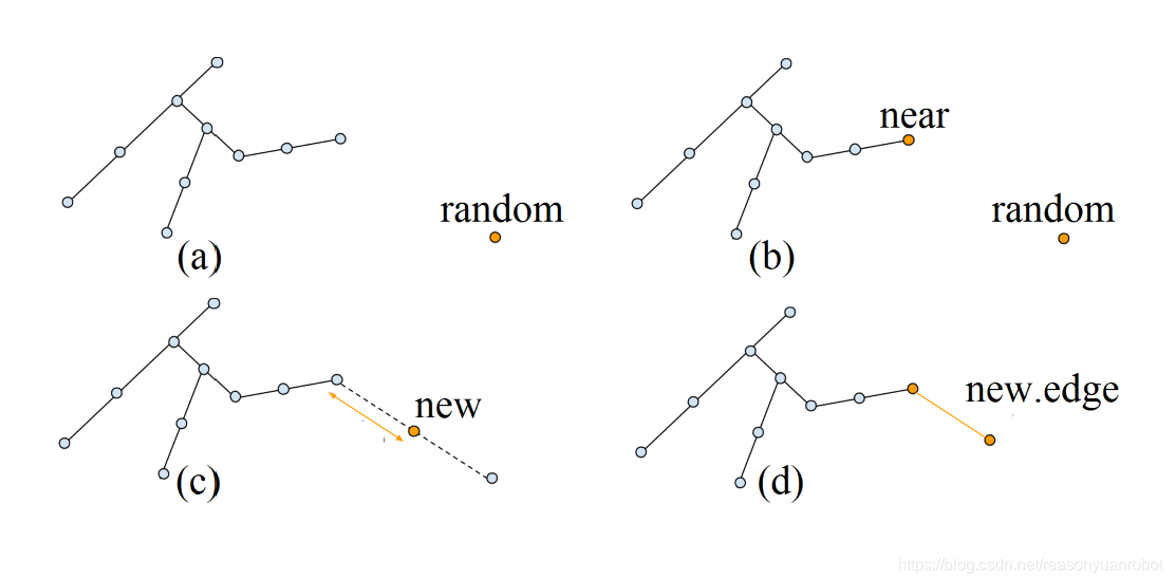
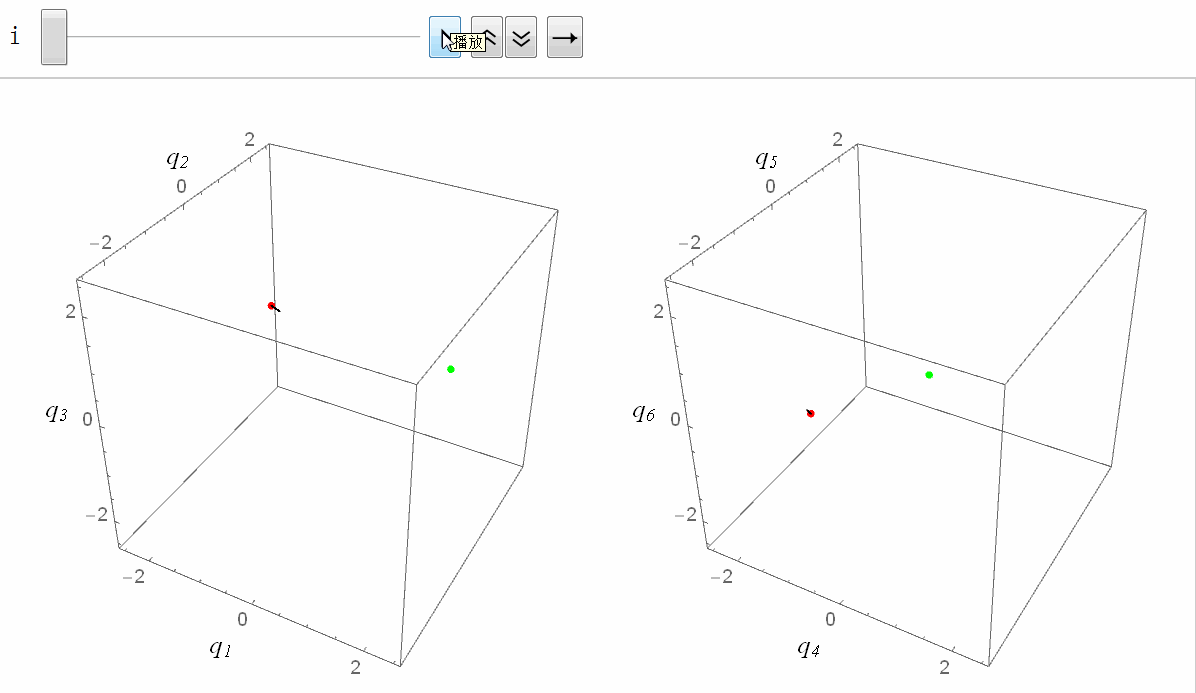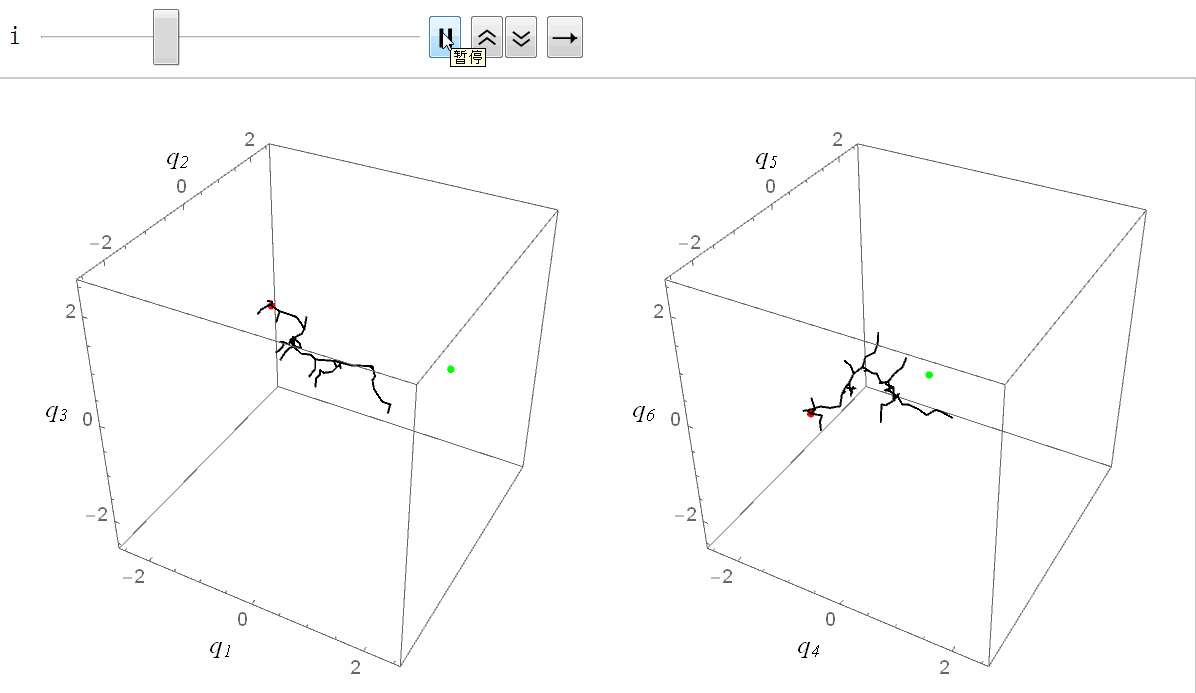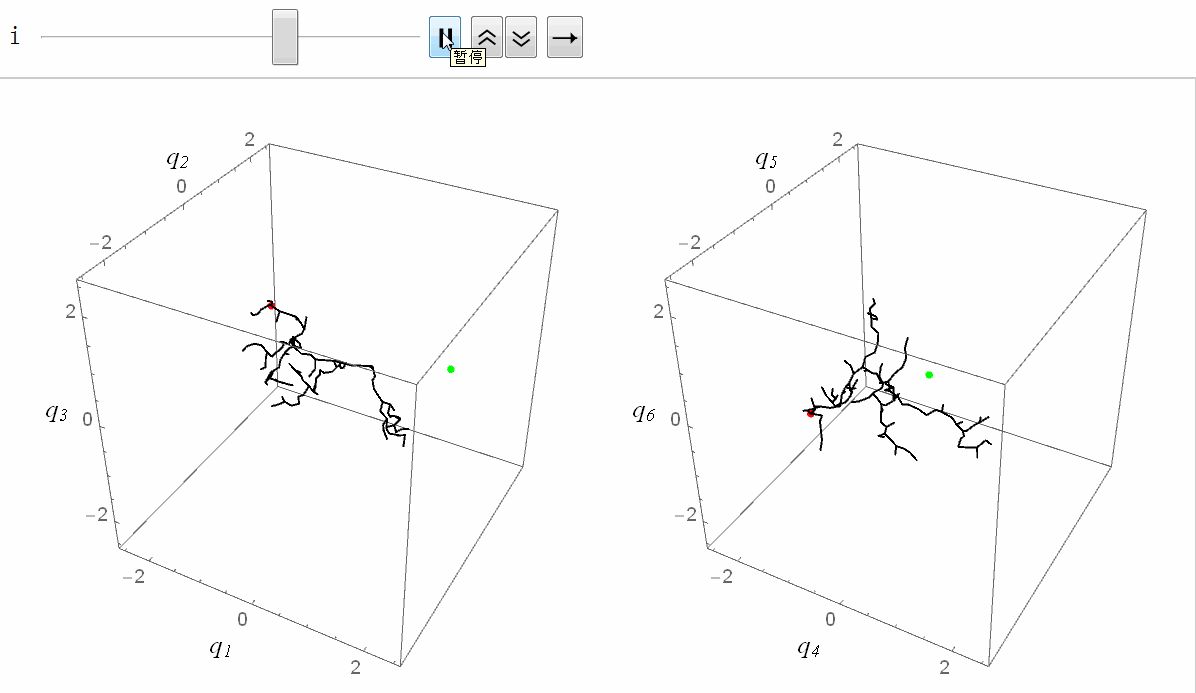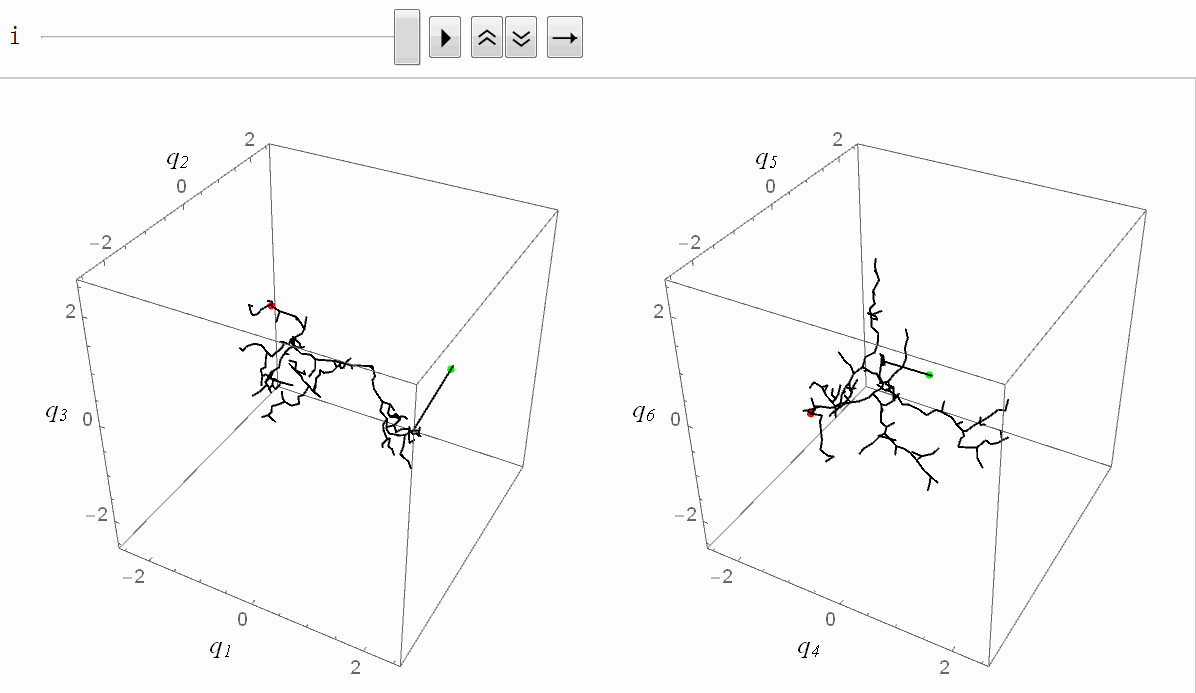
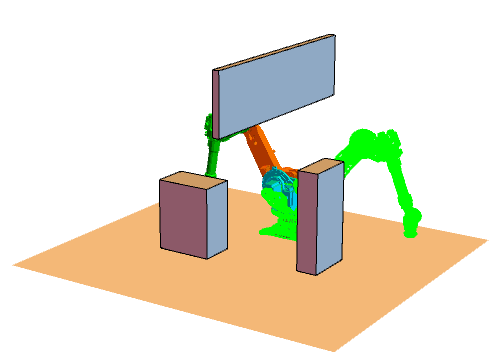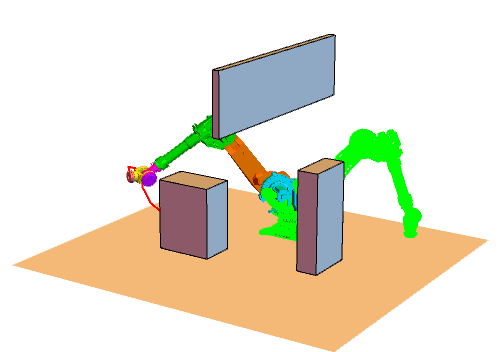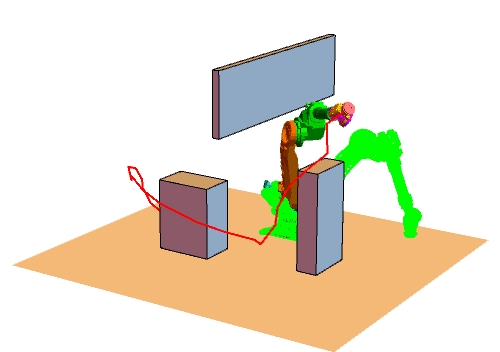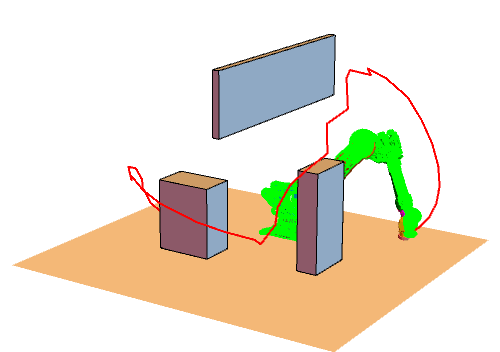
六维空间的RRT
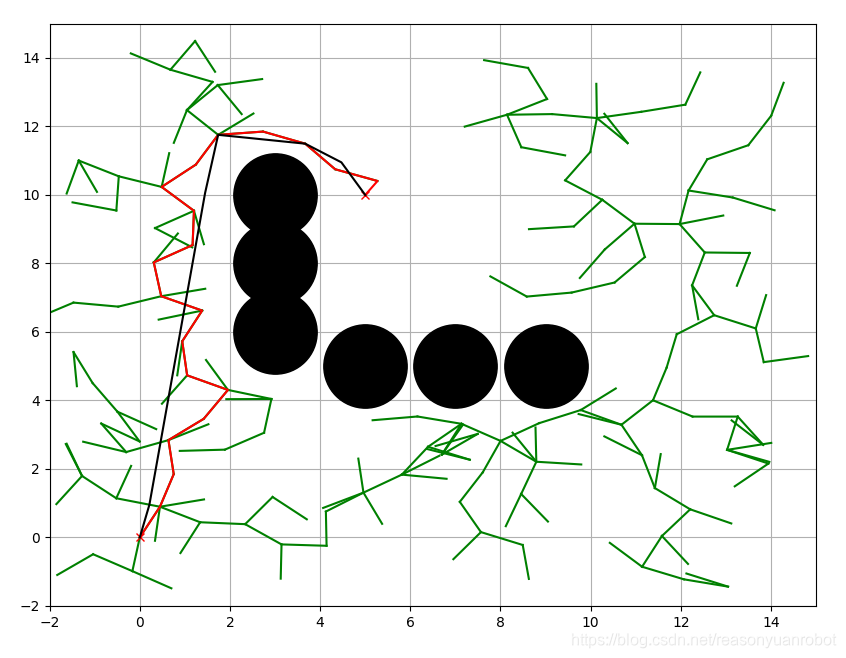
实际效果如图。
伪代码
function BuildRRT(qinit, K, Δq)T.init(qinit)for k = 1 to Kqrand = Sample() -- chooses a random configurationqnearest = Nearest(T, qrand) -- selects the node in the RRT tree that is closest to qrandif Distance(qnearest, qgoal) < Threshold thenreturn trueqnew = Extend(qnearest, qrand, Δq) -- moving from qnearest an incremental distance in the direction of qrandif qnew ≠ NULL thenT.AddNode(qnew)return falsefunction Sample() -- Alternatively,one could replace Sample with SampleFree(by using a collision detection algorithm to reject samples in C_obstaclep = Random(0, 1.0)if 0 < p < Prob thenreturn qgoalelseif Prob < p < 1.0 thenreturn RandomNode()
初始化时随机树T只包含一个节点:根节点qinit。首先Sample函数从状态空间中随机选择一个采样点qrand(4行);
然后Nearest函数从随机树中选择一个距离qrand最近的节点qnearest(5行);
最后Extend函数通过从qnearest向qrand扩展一段距离,得到一个新的节点qnew(8行)。如果qnew与障碍物发生碰撞,则Extend函数返回空,放弃这次生长,否则将qnew加入到随机树中。重复上述步骤直到qnearest和目标点qgaol距离小于一个阈值,则代表随机树到达了目标点,算法返回成功(6~7行)。为了使算法可控,可以设定运行时间上限或搜索次数上限(3行)。如果在限制次数内无法到达目标点,则算法返回失败。
为了加快随机树到达目标点的速度,简单的改进方法是:在随机树每次的生长过程中,根据随机概率来决定qrand是目标点还是随机点。在Sample函数中设定参数Prob (probability),每次得到一个0到1.0的随机值p,当0<p<Prob的时候,随机树朝目标点生长;当Prob<p<1.0时,随机树朝一个随机方向生长。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/a735148617/article/details/103644670

上图说明了RRT在有障碍物和没有障碍物的情况下探索自由空间的能力。这种特性通常被称为RRT的Voronoi偏差。作为均匀采样的结果,规划器更有可能在更大的Voronoi区域中选择样本,并且树朝着那个自由空间递增地快速增长。
RRT路径规划算法
https://blog.csdn.net/aoyousihaiqiuqihuang/article/details/100147478 matlab实现,包括后处理smooth
- 关于后处理,有不同的策略,文中采用的贪心策略,是相对简单的一种
一种后处理smooth策略:
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
import numpy as np
import random
import mathclass Smoother(object):"""@desc; 在规划好的path中,随机选择两个point(中间至少间隔一个point),对选中的两个point采用固定长度的线性插值,若中间插值点未发生碰撞,则用该path替换之前两点之间的path"""def __init__(self):passdef __linecdchecker(self, start, goal):""":param start::param goal::return:"""nps = np.array(start).reshape(-1,1)npg = np.array(goal).reshape(-1,1)nele = math.ceil((abs(npg-nps)/self.__expanddis).max())ratio = np.linspace(0, 1, nele, endpoint=False)jointslist = (nps+(npg-nps)*ratio).T.tolist()for joints in jointslist:iscollided = self.__iscollidedcallback(joints, self.__obstaclelist, self.__robot, self.__cdchecker)if iscollided:return False, []return True, jointslistdef pathsmoothing(self, path, planner, maxiter):"""the path and planner are necessary parametersthe following member variables of planner will be used for smoothing1. jointlimits2. iscollidedcallback3. cdchecker4. robot5. expanddis6. obstaclelist:param path::param planner::return:"""self.__jointlimits = planner.jointlimitsself.__iscollidedcallback = planner.iscollidedcallbackself.__cdchecker = planner.cdcheckerself.__robot = planner.robotself.__expanddis = planner.expanddisself.__obstaclelist = planner.obstaclelistpathlength = len(path)if pathlength <= 3:return pathfor i in range(maxiter):pickpoint0 = random.randint(0, pathlength-3)pickpoint1 = random.randint(pickpoint0+1, pathlength-1)result, addpath = self.__linecdchecker(path[pickpoint0], path[pickpoint1])if result:path = path[:pickpoint0]+addpath+path[pickpoint1:]pathlength = len(path)return path
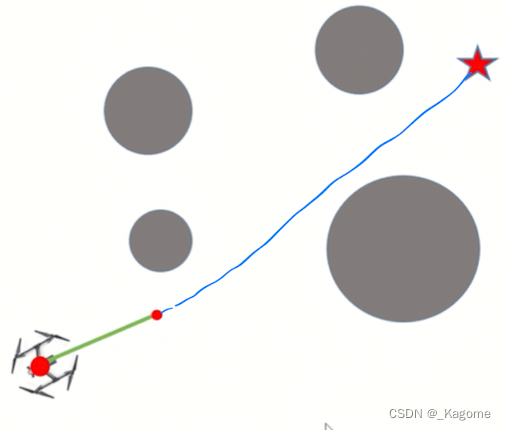
smooth效果: