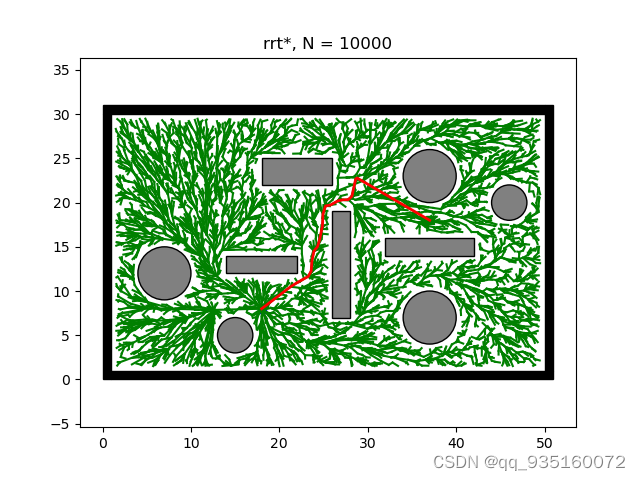
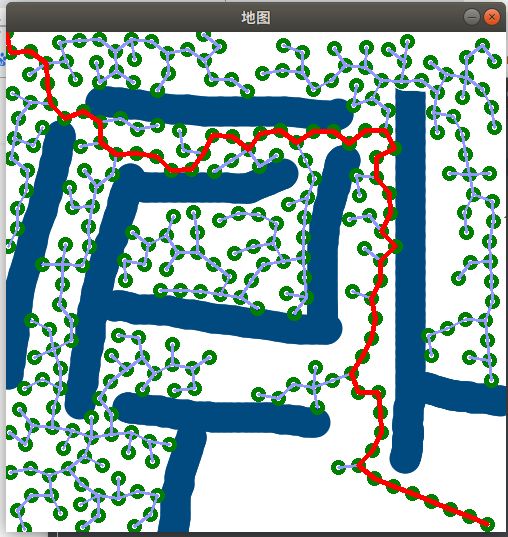
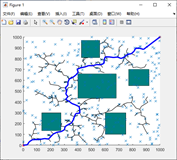
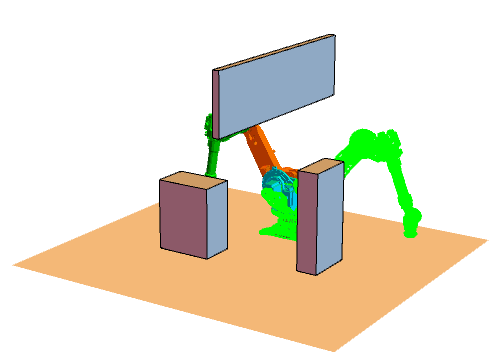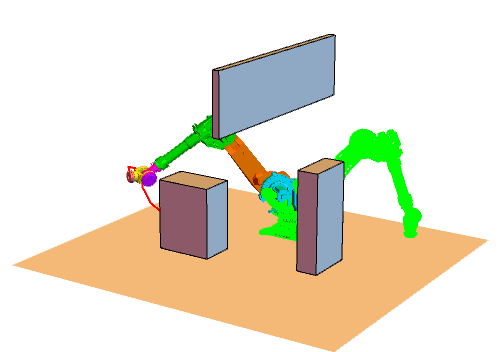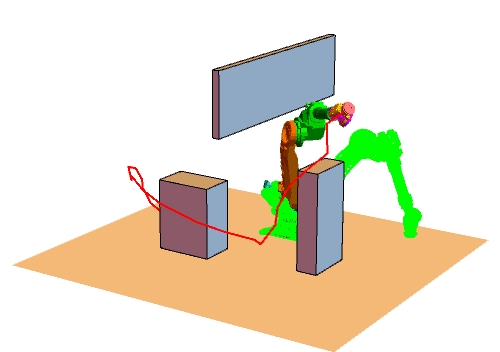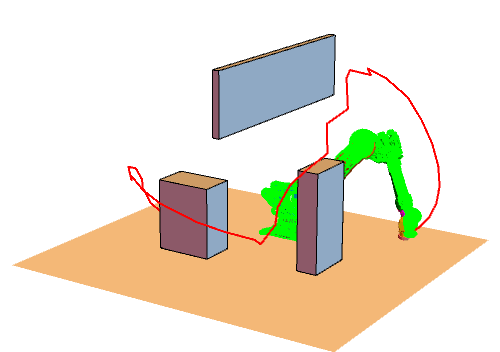
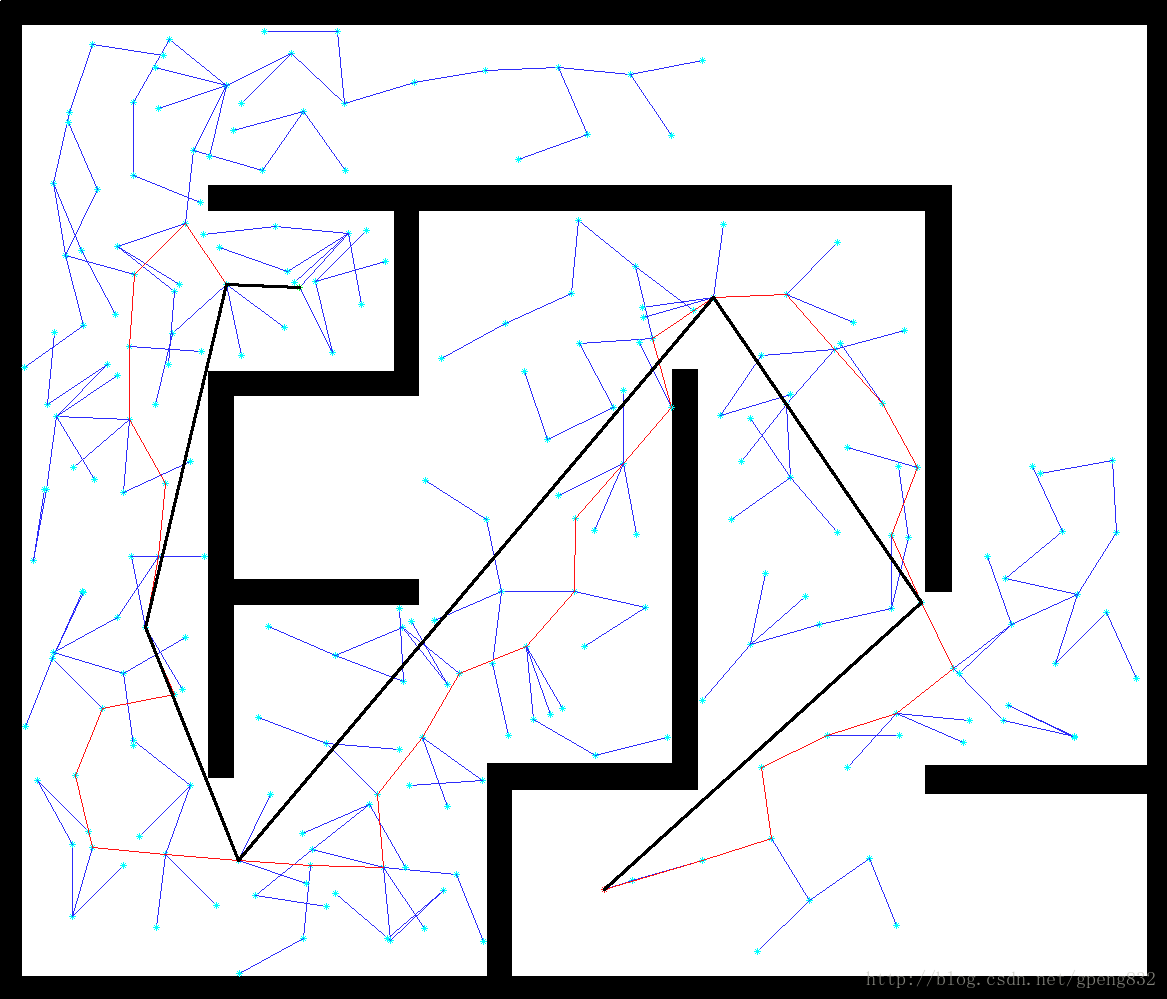
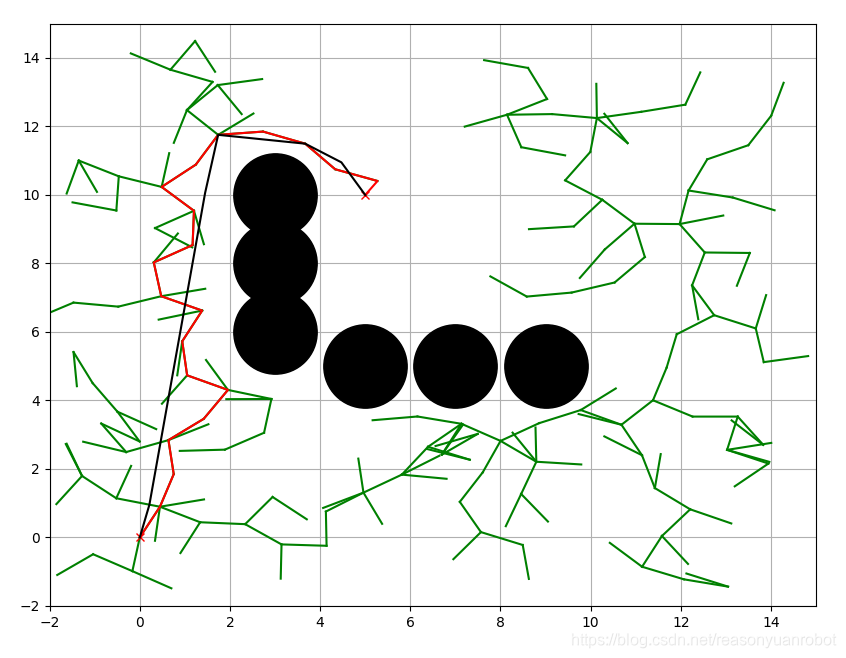
首先我们得明白算法的原理,然后写出步骤。根据步骤可以写出主函数包括每一步的输入输出,怎么表示(基本的伪代码表示,当然如果可以也可以写成汉字形式的),最后一步一步写出代码,调试工作是必须的(建议:子函数尽量分开写,功能分明,便于调试)。好了,差不多就这样,开始做吧^-^
1建立地图,设置起始点,目标点,(障碍带)
2初始化参数:
顶点vertices=起始点q_start;
边edges=空集empty;
设置采样数目k;
初始化启发概率p——>q_goal;
3主循环
For k in range
3.1判断是否到达目标点isGoalOnQNearQNewEdge()
输入:q_new,q_goal,delta_q
输出:返回类型:布尔型。1到达,0未到达
操作内容:判断q_goal与q_new距离在delta_q范围内;
If q_new == q_goal
Break;
End For
3.2if rand<p q_rand = q_goal;elseq_rand=p(map_x,map,y),生成随机采样点
3.3在顶点表中寻找离q_rand最近的顶点q_near,根据delta_q距离得到新的子节点——q_new
输入:vertices,delta_q, q_rand
输出:q_new,q_near
操作内容:根据q_rand与vertices的每个点的欧式距离得出q_near,然后根据方向向量得出q_new
3.4 判断是否加入顶点列表中isAddInVerticesList()
输入:map,q_new,vertices,edges
输出:返回类型:布尔型。1加入0不加入
操作内容:
将它与父节点连接成边edge1,然后将其分解为10个点,间隔总长/10;
If 1
将新节点加入vertices
将edge1加入edges边集合[q_new,q_parent]
Else
Continue;
EndIf
4根据边集合中,返回顶点索引【行向量】,根据行向量索引在顶点集合中,返回路径
path=Findpathnode(q_goal,q_star vertices);
plot(path)
5 path_smooth = smooth(path,vertices,map)%光滑采用的是贪心策略
此处遇到的问题是由于从目标点向起点进行判断连接成的边是否在障碍区内
所以此时增加插值点个数50个
补充:代码及地图数据地址https://download.csdn.net/download/qinze5857/10901150
——下面是自写代码,用matlab发布形式粘贴的哈
Contents
- color map
- rrt tree %行是y坐标,列是x坐标
- sub function
function My_RRT
My_RRT
clc
clear
close all
all
color map
load maze.mat map
[map_height,map_width]=size(map); %行是高y,列是宽x
q_start = [206, 198]; %q s t a r t ( 1 ) : x宽 , q s t a r t ( 2 ) : y高
q_goal = [416, 612];
colormap=[1 1 10 0 01 0 00 1 00 0 1];
imshow(uint8(map),colormap)
hold on
maze.mat map
[map_height,map_width]=size(map); %行是高y,列是宽x
q_start = [206, 198]; %q s t a r t ( 1 ) : x宽 , q s t a r t ( 2 ) : y高
q_goal = [416, 612];
colormap=[1 1 10 0 01 0 00 1 00 0 1];
imshow(uint8(map),colormap)
hold on
警告: 图像太大,无法在屏幕上显示;将以
67% 显示
rrt tree %行是y坐标,列是x坐标
%initial
vertices=q_start;
edges = [];
K=10000;
delta_q=50;
p=0.3;
q_rand=[];
q_near=[];
q_new=[];
%main loop
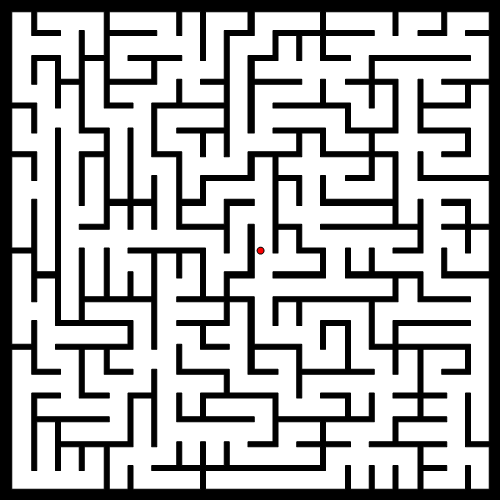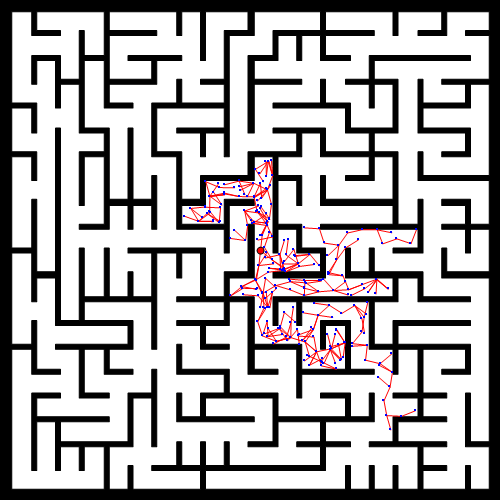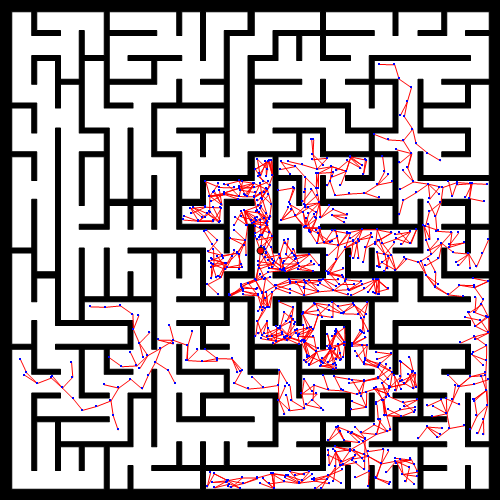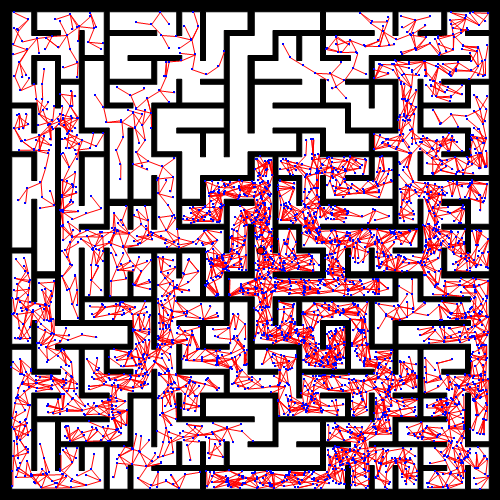
plot(q_start(2),q_start(1),'*b')
plot(q_goal(2),q_goal(1),'*y')
for k = 1:Karrived=is_goal_arrived(vertices,q_goal,delta_q);if arrivedvertices=[vertices;q_goal];edges = [edges;[size(vertices,1),size(vertices,1)-1]];break;endif rand <= pq_rand = q_goal;%q(1)宽x,q(2)高yelseq_rand = [randi(map_height),randi(map_width)];endif map( q_rand(1,1),q_rand(1,2) ) == 1 %map(1)height,map(2)widthcontinue;end[q_new,q_near,q_near_ind,vector_dir] = get_qnew_qnear(delta_q,q_rand,vertices);add_qnew = is_add_in_veritces(map,q_new,q_near,vector_dir,10);if add_qnewvertices=[vertices;q_new];r_v = size(vertices,1);edges = [edges;[r_v,q_near_ind]];elsecontinue;end
% plot(q_near(1,1),q_near(2,1),'*b');plot([q_near(1,2),q_new(1,2)],[q_near(1,1),q_new(1,1)],'-b')drawnow
end
path =find_path_node(edges);
%plot base path
plot(vertices(path,2),vertices(path,1),'-r')
%smooth
path_smooth = smooth(path,vertices,map);
%plot smooth path
plot(vertices(path_smooth,2),vertices(path_smooth,1),'-g');
vertices=q_start;
edges = [];
K=10000;
delta_q=50;
p=0.3;
q_rand=[];
q_near=[];
q_new=[];
%main loop
plot(q_start(2),q_start(1),'*b')
plot(q_goal(2),q_goal(1),'*y')
for k = 1:Karrived=is_goal_arrived(vertices,q_goal,delta_q);if arrivedvertices=[vertices;q_goal];edges = [edges;[size(vertices,1),size(vertices,1)-1]];break;endif rand <= pq_rand = q_goal;%q(1)宽x,q(2)高yelseq_rand = [randi(map_height),randi(map_width)];endif map( q_rand(1,1),q_rand(1,2) ) == 1 %map(1)height,map(2)widthcontinue;end[q_new,q_near,q_near_ind,vector_dir] = get_qnew_qnear(delta_q,q_rand,vertices);add_qnew = is_add_in_veritces(map,q_new,q_near,vector_dir,10);if add_qnewvertices=[vertices;q_new];r_v = size(vertices,1);edges = [edges;[r_v,q_near_ind]];elsecontinue;end
% plot(q_near(1,1),q_near(2,1),'*b');plot([q_near(1,2),q_new(1,2)],[q_near(1,1),q_new(1,1)],'-b')drawnow
end
path =find_path_node(edges);
%plot base path
plot(vertices(path,2),vertices(path,1),'-r')
%smooth
path_smooth = smooth(path,vertices,map);
%plot smooth path
plot(vertices(path_smooth,2),vertices(path_smooth,1),'-g');
<span style="color:#0000ff">end</span>
sub function
function arrived=is_goal_arrived(vertices,q_goal,delta_q)
%判断是否到达终点
dist=pdist2(vertices(end,:),q_goal);
if dist <= delta_qarrived=1;
elsearrived=0;
end
endfunction [q_new,q_near,q_near_ind,vector_dir] = get_qnew_qnear(delta_q,q_rand,vertices)
%获得节点中最近的和新节点
dist_rand = pdist2(vertices,q_rand);
[dist_min,q_near_ind]=min(dist_rand);
q_near=vertices(q_near_ind,:);
vector_dir =q_rand-q_near;
vector_dir = vector_dir./dist_min;
if dist_min > delta_q %随机点到最近点的距离不确定q_new = floor( q_near+delta_q*vector_dir );
elseq_new=q_rand;
end
endfunction add_qnew = is_add_in_veritces(map,q_new,q_near,vector_dir,insert_p)
%判断是否加入到列表中,q_new,与edges_new
%输出:add_qnew=1加入 0不加入
%注意:sub2ind,[y高,x宽]=size(map),q_goal=[x宽,y高]
dist_new2near = norm(q_new - q_near);%此处有问题
dist_gap = dist_new2near/insert_p;
ii =1:insert_p;
insert_point = repmat(q_near,insert_p,1)+ii'.*dist_gap* vector_dir;
insert_point =[floor(insert_point);q_new];
insert_num = sub2ind(size(map),insert_point(:,1),insert_point(:,2));
or =find( map(insert_num)==1 );
if ~isempty(or)add_qnew=0;
elseadd_qnew=1;
endendfunction path =find_path_node(edges)
%返回路径 ,path代表在顶点中的行数,返回的是行向量
e=edges(end,2);
path = edges(end,:);
while trueind= find(edges(:,1)==e);tmp_e = edges(ind,:);e=tmp_e(2);path=[path,e];if e==1break;end
endendfunction path_smooth = smooth(path,vertices,map)
%光滑方法:从起点往前找
% path = fliplr(path);
path_smooth =path(end);
tmp_point = vertices(1,:);
while truel_p = length(path);for i=1:l_pvec = vertices( path(i),:) - tmp_point;vec_dir = vec/norm(vec);or_reduce = is_add_in_veritces(map ,vertices(path(i),: ),tmp_point,vec_dir,60);if or_reduce==1 %可缩减path_smooth = [path_smooth, path(i)];tmp_point = vertices(path(i),: );break;elsecontinue;endendvec_goal = vertices(end,:) - tmp_point;goal_dir = vec_goal/norm(vec_goal);or_goal = is_add_in_veritces(map , vertices(end,: ),tmp_point,goal_dir,60);if or_goal==1 %可以与目标点连接path_smooth = [path_smooth, path(1)];break;elseind_path = find(path==path(i));path=path(1:ind_path);end
endend
arrived=is_goal_arrived(vertices,q_goal,delta_q)
%判断是否到达终点
dist=pdist2(vertices(end,:),q_goal);
if dist <= delta_qarrived=1;
elsearrived=0;
end
endfunction [q_new,q_near,q_near_ind,vector_dir] = get_qnew_qnear(delta_q,q_rand,vertices)
%获得节点中最近的和新节点
dist_rand = pdist2(vertices,q_rand);
[dist_min,q_near_ind]=min(dist_rand);
q_near=vertices(q_near_ind,:);
vector_dir =q_rand-q_near;
vector_dir = vector_dir./dist_min;
if dist_min > delta_q %随机点到最近点的距离不确定q_new = floor( q_near+delta_q*vector_dir );
elseq_new=q_rand;
end
endfunction add_qnew = is_add_in_veritces(map,q_new,q_near,vector_dir,insert_p)
%判断是否加入到列表中,q_new,与edges_new
%输出:add_qnew=1加入 0不加入
%注意:sub2ind,[y高,x宽]=size(map),q_goal=[x宽,y高]
dist_new2near = norm(q_new - q_near);%此处有问题
dist_gap = dist_new2near/insert_p;
ii =1:insert_p;
insert_point = repmat(q_near,insert_p,1)+ii'.*dist_gap* vector_dir;
insert_point =[floor(insert_point);q_new];
insert_num = sub2ind(size(map),insert_point(:,1),insert_point(:,2));
or =find( map(insert_num)==1 );
if ~isempty(or)add_qnew=0;
elseadd_qnew=1;
endendfunction path =find_path_node(edges)
%返回路径 ,path代表在顶点中的行数,返回的是行向量
e=edges(end,2);
path = edges(end,:);
while trueind= find(edges(:,1)==e);tmp_e = edges(ind,:);e=tmp_e(2);path=[path,e];if e==1break;end
endendfunction path_smooth = smooth(path,vertices,map)
%光滑方法:从起点往前找
% path = fliplr(path);
path_smooth =path(end);
tmp_point = vertices(1,:);
while truel_p = length(path);for i=1:l_pvec = vertices( path(i),:) - tmp_point;vec_dir = vec/norm(vec);or_reduce = is_add_in_veritces(map ,vertices(path(i),: ),tmp_point,vec_dir,60);if or_reduce==1 %可缩减path_smooth = [path_smooth, path(i)];tmp_point = vertices(path(i),: );break;elsecontinue;endendvec_goal = vertices(end,:) - tmp_point;goal_dir = vec_goal/norm(vec_goal);or_goal = is_add_in_veritces(map , vertices(end,: ),tmp_point,goal_dir,60);if or_goal==1 %可以与目标点连接path_smooth = [path_smooth, path(1)];break;elseind_path = find(path==path(i));path=path(1:ind_path);end
endend
Published with MATLAB® R2015b