目录
- 什么是八叉树(八叉树的数据结构)
- 八叉树的图例
- 八叉树的实现算法
- 八叉树的场景管理器代码实现
- 八叉树的应用场景
1.什么是八叉树——八叉树的数据结构
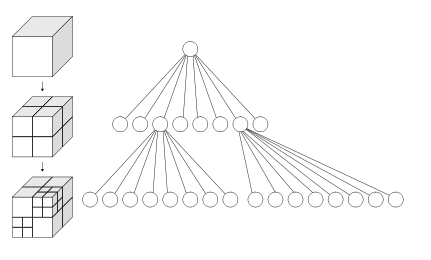
八叉树是一个树形结构,它的特点就是每个节点正好拥有八个子节点。它的这个结构特点正好能把空间立方体平均分成对称八份。利用这个特性,八叉树经常用在3D图形学中或者3D游戏中的碰撞检测,场景管理等。
Each node in an octree subdivides the space it represents into eight octants. In a point region (PR) octree, the node stores an explicit three-dimensional point, which is the “center” of the subdivision for that node; the point defines one of the corners for each of the eight children. In a matrix based (MX) octree, the subdivision point is implicitly the center of the space the node represents. The root node of a PR octree can represent infinite space; the root node of an MX octree must represent a finite bounded space so that the implicit centers are well-defined. Note that Octrees are not the same as k-d trees: k-d trees split along a dimension and octrees split around a point. Also k-d trees are always binary, which is not the case for octrees. By using a depth-first search the nodes are to be traversed and only required surfaces are to be viewed.
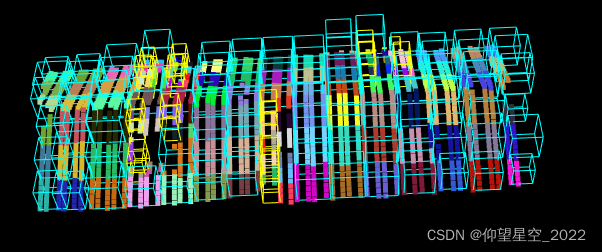
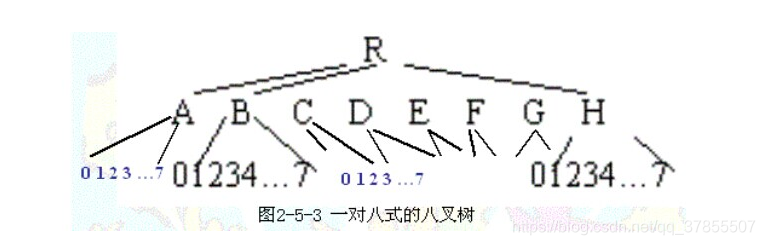
2.八叉树的图例

- 图片来自wikipedia
3.八叉树的实现算法
- 设定最大递归深度
- 找出场景的最大尺寸,并以此尺寸建立第一个立方体
- 依序将单位元元素丢入能被包含且没有子节点的立方体
- 若没有达到最大递归深度,就进行细分八等份,再将该立方体所装的单位元元素全部分担给八个子立方体
- 若发现子立方体所分配到的单位元元素数量不为零且跟父立方体是一样的,则该子立方体停止细分,因为跟据空间分割理论,细分的空间所得到的分配必定较少,若是一样数目,则再怎么切数目还是一样,会造成无穷切割的情形。
- 重复3,直到达到最大递归深度。
- 选自百度百科
我们逐条分析下:
- 设定最大递归深度即设置树的最大深度。
1层深度只有一个根节点,2层深度1个根节点和8个子节点,3层深度则对2层8个节点再生成8^8个节点……可见节点的个数随着层数的增加呈(8)指数增长,那么计算量也会指数增加。 - 找出场景的最大尺寸,并以此尺寸简历第一个立方体。
这个比较好理解,即创建最大尺寸的立方体,这个立方体必须包含场景中所有的物体,接下来再对这个立方体进行八叉树细分。 - 第三和第四条的意思就是从根节点开始,对场景物体进行分类,根据位置和大小丢进八叉树的叶子节点中。第五条是一个优化方案,即如果子节点和父节点被分到的物体一样多,那么就相当于这个节点所有物体的位置大小都差不多,没有必要再细分下去(这里我有疑问,我的观点是没有到叶子节点都不能认为"再怎么切数目还是一样")。
- 递归。
4.八叉树的场景管理器代码实现
对于八叉树的代码实现,github上找到一个非常简单的实现
我把主要实现代码贴在这里:
#ifndef Octree_H
#define Octree_H#include <cstddef>
#include <vector>
#include "OctreePoint.h"namespace brandonpelfrey {/**!**/class Octree {// Physical position/size. This implicitly defines the bounding // box of this nodeVec3 origin; //! The physical center of this nodeVec3 halfDimension; //! Half the width/height/depth of this node// The tree has up to eight children and can additionally store// a point, though in many applications only, the leaves will store data.Octree *children[8]; //! Pointers to child octantsOctreePoint *data; //! Data point to be stored at a node/*Children follow a predictable pattern to make accesses simple.Here, - means less than 'origin' in that dimension, + means greater than.child: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7x: - - - - + + + +y: - - + + - - + +z: - + - + - + - +*/public:Octree(const Vec3& origin, const Vec3& halfDimension) : origin(origin), halfDimension(halfDimension), data(NULL) {// Initially, there are no childrenfor(int i=0; i<8; ++i) children[i] = NULL;}Octree(const Octree& copy): origin(copy.origin), halfDimension(copy.halfDimension), data(copy.data) {}~Octree() {// Recursively destroy octantsfor(int i=0; i<8; ++i) delete children[i];}// Determine which octant of the tree would contain 'point'int getOctantContainingPoint(const Vec3& point) const {int oct = 0;if(point.x >= origin.x) oct |= 4;if(point.y >= origin.y) oct |= 2;if(point.z >= origin.z) oct |= 1;return oct;}bool isLeafNode() const {// This is correct, but overkill. See below./*for(int i=0; i<8; ++i)if(children[i] != NULL) return false;return true;*/// We are a leaf iff we have no children. Since we either have none, or // all eight, it is sufficient to just check the first.return children[0] == NULL;}void insert(OctreePoint* point) {// If this node doesn't have a data point yet assigned // and it is a leaf, then we're done!if(isLeafNode()) {if(data==NULL) {data = point;return;} else {// We're at a leaf, but there's already something here// We will split this node so that it has 8 child octants// and then insert the old data that was here, along with // this new data point// Save this data point that was here for a later re-insertOctreePoint *oldPoint = data;data = NULL;// Split the current node and create new empty trees for each// child octant.for(int i=0; i<8; ++i) {// Compute new bounding box for this childVec3 newOrigin = origin;newOrigin.x += halfDimension.x * (i&4 ? .5f : -.5f);newOrigin.y += halfDimension.y * (i&2 ? .5f : -.5f);newOrigin.z += halfDimension.z * (i&1 ? .5f : -.5f);children[i] = new Octree(newOrigin, halfDimension*.5f);}// Re-insert the old point, and insert this new point// (We wouldn't need to insert from the root, because we already// know it's guaranteed to be in this section of the tree)children[getOctantContainingPoint(oldPoint->getPosition())]->insert(oldPoint);children[getOctantContainingPoint(point->getPosition())]->insert(point);}} else {// We are at an interior node. Insert recursively into the // appropriate child octantint octant = getOctantContainingPoint(point->getPosition());children[octant]->insert(point);}}// This is a really simple routine for querying the tree for points// within a bounding box defined by min/max points (bmin, bmax)// All results are pushed into 'results'void getPointsInsideBox(const Vec3& bmin, const Vec3& bmax, std::vector<OctreePoint*>& results) {// If we're at a leaf node, just see if the current data point is inside// the query bounding boxif(isLeafNode()) {if(data!=NULL) {const Vec3& p = data->getPosition();if(p.x>bmax.x || p.y>bmax.y || p.z>bmax.z) return;if(p.x<bmin.x || p.y<bmin.y || p.z<bmin.z) return;results.push_back(data);}} else {// We're at an interior node of the tree. We will check to see if// the query bounding box lies outside the octants of this node.for(int i=0; i<8; ++i) {// Compute the min/max corners of this child octantVec3 cmax = children[i]->origin + children[i]->halfDimension;Vec3 cmin = children[i]->origin - children[i]->halfDimension;// If the query rectangle is outside the child's bounding box, // then continueif(cmax.x<bmin.x || cmax.y<bmin.y || cmax.z<bmin.z) continue;if(cmin.x>bmax.x || cmin.y>bmax.y || cmin.z>bmax.z) continue;// At this point, we've determined that this child is intersecting // the query bounding boxchildren[i]->getPointsInsideBox(bmin,bmax,results);} }}};
}#ifndef OctreePoint_H
#define OctreePoint_H#include "Vec3.h"// Simple point data type to insert into the tree.
// Have something with more interesting behavior inherit
// from this in order to store other attributes in the tree.
class OctreePoint {Vec3 position;
public:OctreePoint() { }OctreePoint(const Vec3& position) : position(position) { }inline const Vec3& getPosition() const { return position; }inline void setPosition(const Vec3& p) { position = p; }
};#endif#endif
代码很简单,注释也很详细了。在实际的运用过程中还需要优化一下。如果用在场景剔除,那么每个节点具备的属性有AABBox,深度,可见性,孩子节点。如果仅仅是判断场景物体的可见性,那么就不需要先构建八叉树然后再与摄像机进行碰撞判断了,可以在构建的过程中就进行可见性判断。
class HrOctNode
{
public:HrOctNode(const AABBox& aabb, int nDepth, bool bLeafNode = false);~HrOctNode();......void WalkTree(const HrCameraPtr& pCamera, const HrSceneNodePtr& pSceneNode, float fThreshold, int nMaxDepth);......
protected:AABBox m_aabb;//当前深度int m_nDepth;//是否为叶子节点bool m_bLeafNode;//是否重新初始化了AABBbool m_bInitAABB;HrMath::EnumVisibility m_selfNV;std::array<HrOctNode*, 8> m_arrChildren;
};我们把构造函数改为遍历构造,在构造的过程中就进行可见性判断。具体步骤:
- 如果当前节点本来就不可见,那么就不用判断了,不管是否为叶子节点,落在这个节点的所有物体都不可见。
- 如果当前是叶子节点,那么判断摄像机和落在这个节点的物体的碰撞(可见性判断),这里优化空间就是如果当前节点完全可见,那么落在这个几点的物体也全部可见。
- 如果当前节点不是叶子节点并且可见(全可见或者部分可见),那么继续细分
void HrOctNode::WalkTree(const HrCameraPtr& pCamera, const HrSceneNodePtr& pSceneNode, float fThreshold, int nMaxDepth)
{//先判断是否可见 //如果这个节点本身就不可见 //那么就不用初始化了 落在这个区域的物体也不可见if (!DetectNodeVisible(pCamera, fThreshold)){return;}// If this node doesn't have a data point yet assigned // and it is a leaf, then we're done!if (m_nDepth == nMaxDepth){if (DetectDataVisible(pCamera, fThreshold, pSceneNode->GetTransform()->GetWorldAABBox())){if (pSceneNode->GetFrustumVisible() != HrMath::NV_FULL)pSceneNode->SetFrustumVisible(HrMath::NV_FULL);}}else{if (!m_bInitAABB){InitChildrenNode(nMaxDepth);}const float3& parentCenter = m_aabb.Center();const AABBox& aabb = pSceneNode->GetTransform()->GetWorldAABBox();int mark[6];mark[0] = aabb.Min().x() >= parentCenter.x() ? 1 : 0;mark[1] = aabb.Min().y() >= parentCenter.y() ? 2 : 0;mark[2] = aabb.Min().z() >= parentCenter.z() ? 4 : 0;mark[3] = aabb.Max().x() >= parentCenter.x() ? 1 : 0;mark[4] = aabb.Max().y() >= parentCenter.y() ? 2 : 0;mark[5] = aabb.Max().z() >= parentCenter.z() ? 4 : 0;for (int j = 0; j < 8; ++j){if (j == ((j & 1) ? mark[3] : mark[0])+ ((j & 2) ? mark[4] : mark[1])+ ((j & 4) ? mark[5] : mark[2])){m_arrChildren[j]->WalkTree(pCamera, pSceneNode, fThreshold, nMaxDepth);}}}
}
5.八叉树的应用场景
八叉树可以用在一些在"场景"中选取部分物体的场合,例如捕鱼中的子弹碰撞判断,也可以用八叉树来实现,只不过要考虑计算量的问题(每物理帧构建八叉树)。八叉树相对来说构建起来非常快,当然是相对的,如果场景很简单,物体也很少,也没有必要过度设计。八叉树的缺点就是占用空间。
这里有一个关于四叉树八叉树BSP树区别的问题讨论


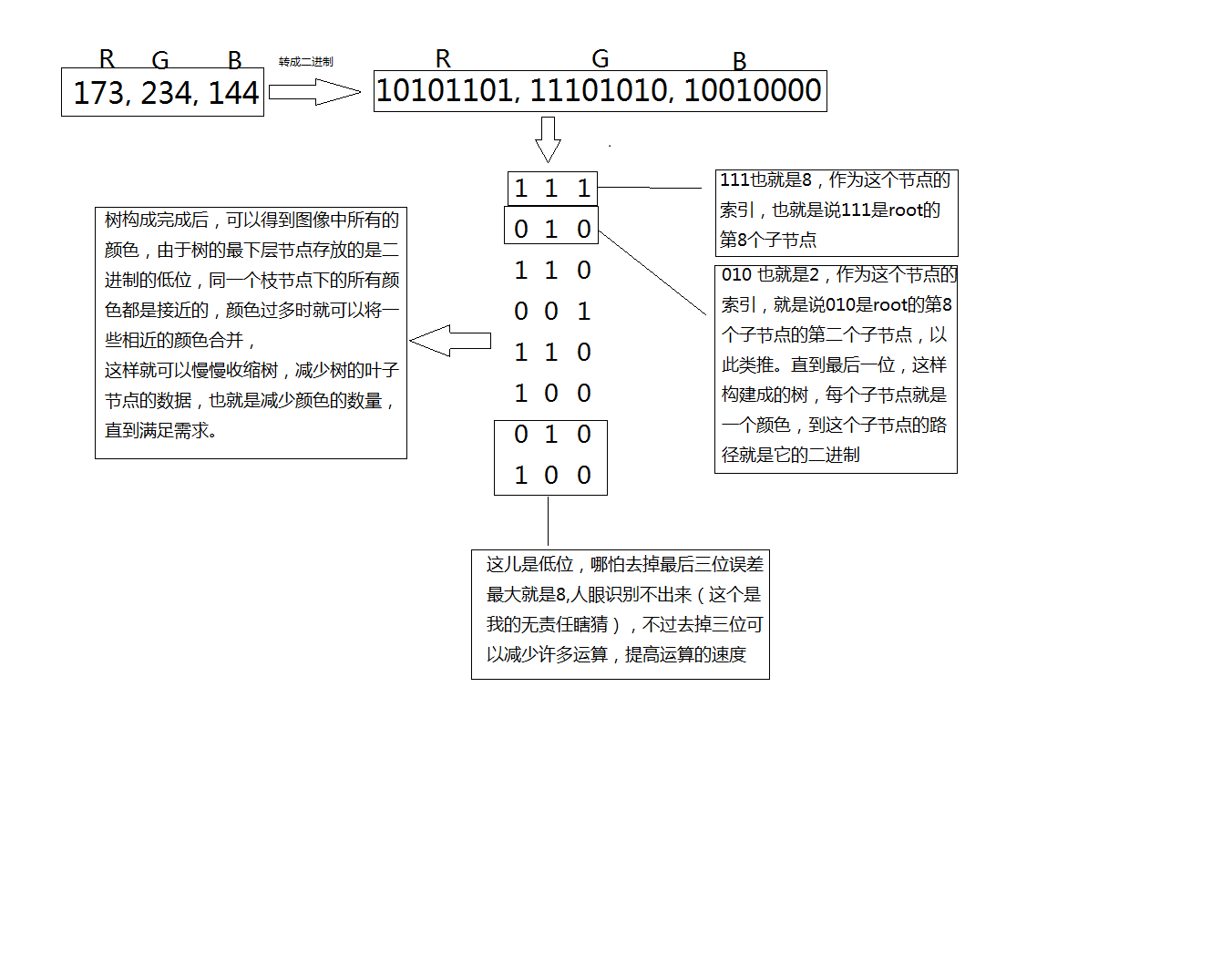


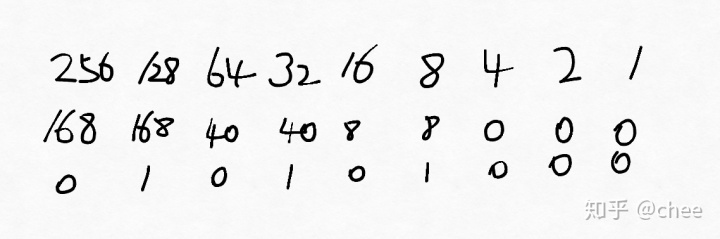

![[学习笔记] 二进制小数表示方法](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/f5bc7c1a5487406f95b1fce456335fbf.jpg#pic_center)



