目录
(1)什么是八叉树
(2)PCL中八叉树的体素形成和PCL中基于八叉树的点云压缩
(3)基于八叉树的k邻域搜索、半径搜索和体素近邻搜索
(4)基于八叉树和基于 kd-tree 的k邻域搜索、半径搜索性能比较
(5)基于八叉树的空间变化检测
(1)什么是八叉树
八叉树(Octree)是一种用于描述三维空间的树状数据结构。想象一个正方体,我们最少可以切成多少个相同等分的小正方体?答案就是8个。再想象我们有一个房间,房间里某个角落藏着一枚金币,我们想很快的把金币找出来,怎么找最高效?我们可以把房间当成一个立方体,先切成八个小立方体,然后排除掉没有放任何东西的小立方体,再把有可能藏金币的小立方体继续切八等份….如此下去,平均在Log8(房间内的所有物品数)的时间内就可找到金币。因此,八叉树就是用在3D空间中的场景管理,可以很快地知道物体在3D场景中的位置,或侦测与其它物体是否有碰撞以及是否在可视范围内。
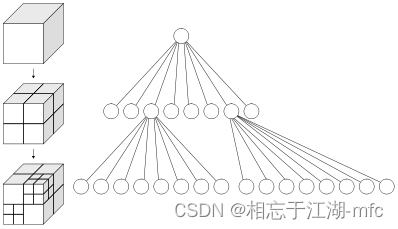
以下是跟八叉树有关的几个概念的解释:
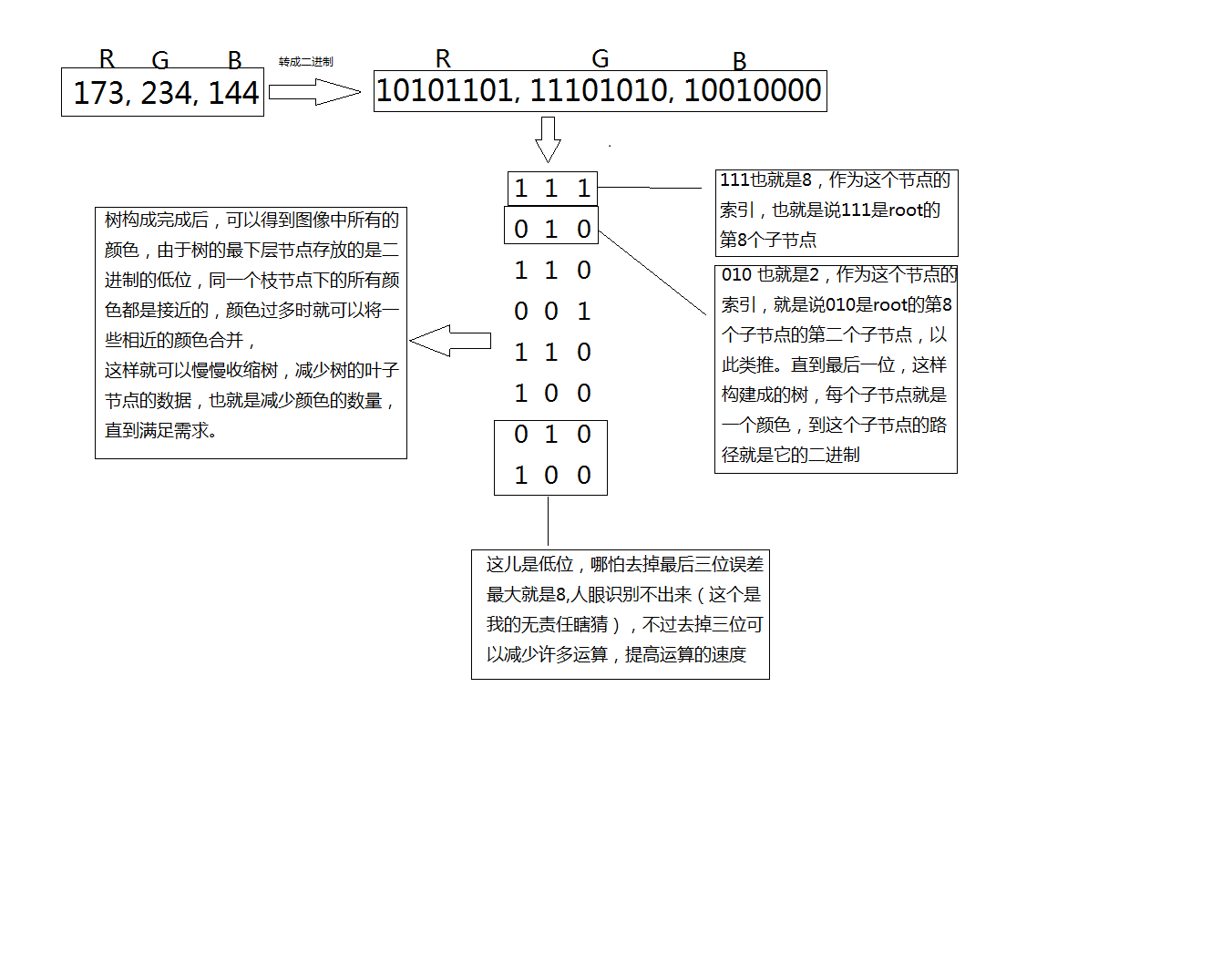
体素:如上图所示,一个正方体空间被分割2次,形成64个边长相等的小正方体,这每个小正方体就被称为该八叉树的体素;
深度:深度=正方体被切割的次数+1。如上图所示,一个正方体空间被分割2次,因此,该八叉树的深度就是3;
分辨率:八叉树的分辨率就是体素的边长。如上图所示,假设大正方体的边长为1m,那么,该八叉树的体素的边长是0.25m,即,该八叉树的分辨率就是0.25。注意,PCL中点的距离单位默认就是m,因此,当进行点云压缩时,如果说给定的分辨率参数是5cm,那么,编程传入的参数就是0.05。
(2)PCL中八叉树的体素形成和PCL中基于八叉树的点云压缩
点云由庞大的数据集组成,这些数据集通过距离、颜色、法线等附加信息来描述空间三维点。这么庞大的数据集要被高效的创建出来,需要占用相当大的存储资源,而一旦点云需要被存储或者通过速率受限制的通信信道进行传输,就需要对点云数据集进行压缩编码,以减少需要存储或者传输的数据量。
PCL提供了点云压缩功能,它允许压缩编码所有类型的点云,包括“无序”点云,它具有无参考点和变化的尺寸、分辨率、分布密度和点顺序等结构特征。
PCL进行点云的编码压缩之前,会将点云视为一个大的正方体,然后,将这个大的正方体按按八叉树的结构分割成多个小正方体组成的大正方体,这些小正方体就是八叉树的叶子节点,也被称为体素。PCL进行点云的压缩编码就是对这些体素分别进行编码,从而达到压缩的目的。
PCL根据点云数据形成体素的方法是这样,首先,找出点云中3个坐标(x、y、z)的值最小的点作为参考点(xmin、ymin、zmin),然后以参考点为起点,分别沿3个坐标轴(x轴、y轴、z轴)的正方向画直线段,该直线段作为大正方体的3条棱边。直线段的长度是多少呢?这个直线段的长度这样计算,找出点云中3个坐标(x、y、z)的值最大的点(xmax、ymax、zmax),分别计算:
xlen = xmax - xmin;
ylen = ymax - ymin;
zlen = zmax - zmin;
然后,取最大值 len = max(xlen, ylen, zlen);
创建PCL的八叉树对象时,会要求传入一个参数,参数名为“八叉树的分辨率”,记做octreeResolution,该参数就是体素(小正方体)的棱长。PCL会计算出八叉树的深度值n(n>=0,八叉树的深度就是大立方体被切割的层次数,第1层是1个立方体变8个立方体,第2层是8个立方体变64个立方体......),使之满足
octreeResolution * 2 ^ n >= len;
满足上式的最小n即为PCL创建的八叉树的深度。
下面,编写2个小程序验证一下:
创建Qt Console程序,
#.pro文件 加上头文件引用和库引用INCLUDEPATH += C:\PCL1.12.1\include\pcl-1.12 \C:\PCL1.12.1\3rdParty\FLANN\include \C:\PCL1.12.1\3rdParty\Boost\include\boost-1_78 \C:\PCL1.12.1\3rdParty\Eigen\eigen3 \C:\PCL1.12.1\include\pcl-1.12 \C:\PCL1.12.1\3rdParty\FLANN\include \C:\PCL1.12.1\3rdParty\Boost\include\boost-1_78 \C:\PCL1.12.1\3rdParty\Eigen\eigen3 \C:\PCL1.12.1\3rdParty\VTK\include\vtk-9.1 \C:\Qt\Qt6.3\6.3.0\msvc2019_64\include\QtOpenGLWidgets \C:\Qt\Qt6.3\6.3.0\msvc2019_64\include\QtOpenGL win32:LIBS += $$quote(C:\PCL1.12.1\lib\pcl_commond.lib)win32:LIBS += $$quote(C:\PCL1.12.1\3rdParty\FLANN\lib\flann_s.lib)
win32:LIBS += $$quote(C:\PCL1.12.1\3rdParty\FLANN\lib\flann_cpp_s.lib)win32:LIBS += $$quote(C:\PCL1.12.1\lib\pcl_commond.lib)
win32:LIBS += $$quote(C:\PCL1.12.1\lib\pcl_visualizationd.lib)
win32:LIBS += $$quote(C:\PCL1.12.1\lib\pcl_iod.lib)
win32:LIBS += $$quote(C:\PCL1.12.1\lib\pcl_octreed.lib)win32:LIBS += $$quote(C:\PCL1.12.1\3rdParty\VTK\lib\vtkCommonCore-9.1d.lib)//main.cpp#include <QCoreApplication>
#include <QDateTime>
#include <QThread>
#include <iostream>
#include <pcl/point_cloud.h>
#include <pcl/visualization/cloud_viewer.h>
#include <pcl/kdtree/kdtree_flann.h>
#include <pcl/compression/compression_profiles.h>
#include <pcl/compression/octree_pointcloud_compression.h>int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{QCoreApplication a(argc, argv);//创建3个点的点云pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGB>::Ptr clound(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGB>());clound->width = 3;clound->height = 1;clound->resize(clound->width * clound->height);//将点云的点赋值为(-1, -1, -1)、(0.5, 0.5, 0.5)和(1.5, 1.5, 1.5)int index = 0;clound->points[index].x = -1;clound->points[index].y = -1;clound->points[index].z = -1;clound->points[index].r = 255;clound->points[index].g = 0;clound->points[index].b = 0;index = 1;clound->points[index].x = 0.5;clound->points[index].y = 0.5;clound->points[index].z = 0.5;clound->points[index].r = 255;clound->points[index].g = 0;clound->points[index].b = 0;index = 2;clound->points[index].x = 1.5;clound->points[index].y = 1.5;clound->points[index].z = 1.5;clound->points[index].r = 255;clound->points[index].g = 0;clound->points[index].b = 0;//显示点云for(int kk = 0; kk < clound->points.size(); ++kk){std::cout << "Old cloud pt " << (kk + 1) << " : ( " << clound->points[kk].x << " , " << clound->points[kk].y << " , " << clound->points[kk].z << " )" << std::endl;}pcl::visualization::CloudViewer * viewer = new pcl::visualization::CloudViewer("ss1");viewer->showCloud(clound, "ss1");if(!viewer->wasStopped()){//创建八叉树点云压缩对象pcl::io::compression_Profiles_e pro = pcl::io::MANUAL_CONFIGURATION;pcl::io::OctreePointCloudCompression<pcl::PointXYZRGB> * enc = new pcl::io::OctreePointCloudCompression<pcl::PointXYZRGB>(pro, true, 0.01, 1, true);std::stringstream ss;//编码压缩enc->encodePointCloud(clound->makeShared(), ss);int octee_depth = enc->getTreeDepth();std::cout << "enc->getTreeDepth() : " << octee_depth << std::endl;//编码压缩后的点云pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGB>::Ptr clound_out(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGB>());enc->decodePointCloud(ss, clound_out);for(int kk = 0; kk < clound_out->points.size(); ++kk){clound_out->points[kk].r = 0;clound_out->points[kk].g = 255;clound_out->points[kk].b = 0;std::cout << "New cloud pt " << (kk + 1) << " : ( " << clound_out->points[kk].x << " , " << clound_out->points[kk].y << " , " << clound_out->points[kk].z << " )" << std::endl;}//显示压缩后的点云viewer->showCloud(clound_out, "ss2");}while(!viewer->wasStopped()){}delete viewer;viewer = nullptr;return a.exec();
}以上代码中,创建的点云压缩对象 pcl::io::OctreePointCloudCompression,该类的构造函数有如下几个参数:
/** \brief Constructor* \param compressionProfile_arg: define compression profile* \param octreeResolution_arg: octree resolution at lowest octree level* \param pointResolution_arg: precision of point coordinates* \param doVoxelGridDownDownSampling_arg: voxel grid filtering* \param iFrameRate_arg: i-frame encoding rate* \param doColorEncoding_arg: enable/disable color coding* \param colorBitResolution_arg: color bit depth* \param showStatistics_arg: output compression statistics*/OctreePointCloudCompression (compression_Profiles_e compressionProfile_arg = MED_RES_ONLINE_COMPRESSION_WITH_COLOR,bool showStatistics_arg = false,const double pointResolution_arg = 0.001,const double octreeResolution_arg = 0.01,bool doVoxelGridDownDownSampling_arg = false,const unsigned int iFrameRate_arg = 30,bool doColorEncoding_arg = true,const unsigned char colorBitResolution_arg = 6) :参数 compressionProfile_arg :压缩配置,代码中设置为 pcl::io::MANUAL_CONFIGURATION ,表示自己设置参数,不用默认参数;
参数 showStatistics_arg :编码压缩过程中,是否在colsole窗口显示压缩信息;
参数 pointResolution_arg :体素编码压缩时的点分辨率,用于体素压缩编码,这个参数只在参数 doVoxelGridDownDownSampling_arg == false 时有效;
参数 octreeResolution_arg :体素(八叉树叶子节点正方体的棱长)的棱长;
参数 doVoxelGridDownDownSampling_arg :false-根据特定公式计算体素压缩编码后的点;true-取体素的中心点作为体素压缩编码后的点;
参数 iFrameRate_arg :用来决定进行I帧编码的频率,如果此数值为30,则每隔30帧进行一次I帧编码,中间的帧则进行P帧编码;
参数 doColorEncoding_arg :false-不会对颜色进行编码;true-进行颜色编码,如果输入的点云文件没有颜色信息,则在解码时赋予其颜色默认值;
参数 colorBitResolution_arg :用来表示颜色的RGB的保留的有效位数。
根据代码中参数给定 pcl::io::OctreePointCloudCompression(pro, true, 0.01, 1, true);
doVoxelGridDownDownSampling_arg == true :不进行体素编码,即取体素中心点作为新点云的点;
octreeResolution_arg == 1 :八叉树分辨率为1,即体素正方体棱长为1。
依据前文的分析,代码中点云最小点(-1, -1, -1),最大点(1.5, 1.5, 1.5), len = 1.5 - ( -1 ) = 2.5;octreeResolution=1,
满足式子 octreeResolution * 2 ^ n >= len 的最小 n == 2。
因此,这段代码会将点云以(-1, -1, -1)为参考点,将棱长为 (octreeResolution * 2 ^ n) == 4 的大正方体,切割2层,形成 64 个棱长为 1 的小正方体(体素),八叉树的深度为 n == 2,然后,因为参数 doVoxelGridDownDownSampling_arg == true ,所以,压缩后的点云将每个包含点的体素取其中心点形成编码压缩后的点云。
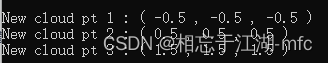
根据 octreeResolution_arg == 1 , 可知源点云的3个点分别位于3个不同的体素,而这3个体素的中心点分别为(-0.5, -0.5, -0.5)、(0.5, 0.5, 0.5)和(1.5, 1.5, 1.5),因此,该代码编码压缩过后的新点云肯定是由这3个点组成。
运行程序查看输出和预期一致:

![]()
(3)基于八叉树的k邻域搜索、半径搜索和体素近邻搜索
基于八叉树的搜索和基于kd-tree的搜索差别不大,主要是创建的搜索对象不一致。
基于八叉树要创建对象 pcl::octree::OctreePointCloudSearch。
k邻域搜索调用 pcl::octree::OctreePointCloudSearch::nearestKSearch;
半径搜索调用 pcl::octree::OctreePointCloudSearch::radiusSearch;
体素近邻搜索调用 pcl::octree::OctreePointCloudSearch::voxelSearch。
以下用一个例子演示这三种搜索函数的调用:
创建Qt Console程序,
#.pro文件 加上头文件引用和库引用INCLUDEPATH += C:\PCL1.12.1\include\pcl-1.12 \C:\PCL1.12.1\3rdParty\FLANN\include \C:\PCL1.12.1\3rdParty\Boost\include\boost-1_78 \C:\PCL1.12.1\3rdParty\Eigen\eigen3 \C:\PCL1.12.1\include\pcl-1.12 \C:\PCL1.12.1\3rdParty\FLANN\include \C:\PCL1.12.1\3rdParty\Boost\include\boost-1_78 \C:\PCL1.12.1\3rdParty\Eigen\eigen3 \C:\PCL1.12.1\3rdParty\VTK\include\vtk-9.1 \C:\Qt\Qt6.3\6.3.0\msvc2019_64\include\QtOpenGLWidgets \C:\Qt\Qt6.3\6.3.0\msvc2019_64\include\QtOpenGLwin32:LIBS += $$quote(C:\PCL1.12.1\lib\pcl_commond.lib)win32:LIBS += $$quote(C:\PCL1.12.1\3rdParty\FLANN\lib\flann_s.lib)
win32:LIBS += $$quote(C:\PCL1.12.1\3rdParty\FLANN\lib\flann_cpp_s.lib)win32:LIBS += $$quote(C:\PCL1.12.1\lib\pcl_commond.lib)
win32:LIBS += $$quote(C:\PCL1.12.1\lib\pcl_visualizationd.lib)
win32:LIBS += $$quote(C:\PCL1.12.1\lib\pcl_iod.lib)
win32:LIBS += $$quote(C:\PCL1.12.1\lib\pcl_octreed.lib)win32:LIBS += $$quote(C:\PCL1.12.1\3rdParty\VTK\lib\vtkCommonCore-9.1d.lib)//main.cpp#include <QCoreApplication>
#include <QDateTime>
#include <QThread>
#include <iostream>
#include <pcl/point_cloud.h>
#include <pcl/visualization/cloud_viewer.h>
#include <pcl/kdtree/kdtree_flann.h>
#include <pcl/compression/compression_profiles.h>
#include <pcl/compression/octree_pointcloud_compression.h>
#include <pcl/octree/octree_search.h>int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{QCoreApplication a(argc, argv);//创建6个点的点云pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr clound(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>());clound->width = 6;clound->height = 1;clound->resize(clound->width *clound->height);int index = 0;clound->points[index].x = -1;clound->points[index].y = -1;clound->points[index].z = -1;index = 1;clound->points[index].x = 0.5;clound->points[index].y = 0.5;clound->points[index].z = 0.5;index = 2;clound->points[index].x = 1.5;clound->points[index].y = 1.5;clound->points[index].z = 1.5;index = 3;clound->points[index].x = 1.8;clound->points[index].y = 1.8;clound->points[index].z = 1.8;index = 4;clound->points[index].x = 1.9;clound->points[index].y = 1.9;clound->points[index].z = 1.9;index = 5;clound->points[index].x = 1.2;clound->points[index].y = 1.2;clound->points[index].z = 1.2;//打印点云qDebug() << "Clound : ";for(int i = 0; i < clound->points.size(); ++i){qDebug() << clound->points[i].x << "," << clound->points[i].y << "," << clound->points[i].z;}//创建八叉树对象,并将点云对象赋值给它float octreeResolution_arg = 1.0f; //体素棱长为1pcl::octree::OctreePointCloudSearch<pcl::PointXYZ> octree(octreeResolution_arg);octree.setInputCloud(clound);octree.addPointsFromInputCloud();//构建八叉树int octee_depth = octree.getTreeDepth();std::cout << "octree.getTreeDepth() : " << octee_depth << std::endl;//输出八叉树深度//体素近邻搜索pcl::PointXYZ search_pt_for_neighbor_in_voxel;search_pt_for_neighbor_in_voxel.x = -0.3;search_pt_for_neighbor_in_voxel.y = -0.4;search_pt_for_neighbor_in_voxel.z = -0.6;std::cout << " Search point(" << search_pt_for_neighbor_in_voxel.x << "," << search_pt_for_neighbor_in_voxel.y << "," << search_pt_for_neighbor_in_voxel.z << ") in voxel 1 : ";std::vector<int> pt_index_for_neighbor_in_voxel;if(octree.voxelSearch(search_pt_for_neighbor_in_voxel, pt_index_for_neighbor_in_voxel)){std::cout << "Points in the same voxel 1 :" << std::endl;for(int i = 0; i < pt_index_for_neighbor_in_voxel.size(); ++i){int pt_index = pt_index_for_neighbor_in_voxel[i];if(i > 0)std::cout << ",";std::cout << " ( " << clound->points[pt_index].x << "," << clound->points[pt_index].y << "," << clound->points[pt_index].z << " ) ";}std::cout << std::endl;}elsestd::cout << "None point in the same voxel 1 ." << std::endl;search_pt_for_neighbor_in_voxel.x = 1.3;search_pt_for_neighbor_in_voxel.y = 1.4;search_pt_for_neighbor_in_voxel.z = 1.6;pt_index_for_neighbor_in_voxel.clear();std::cout << " Search point(" << search_pt_for_neighbor_in_voxel.x << "," << search_pt_for_neighbor_in_voxel.y << "," << search_pt_for_neighbor_in_voxel.z << ") in voxel 2 : ";if(octree.voxelSearch(search_pt_for_neighbor_in_voxel, pt_index_for_neighbor_in_voxel)){std::cout << "Points in the same voxel 2 :" << std::endl;for(int i = 0; i < pt_index_for_neighbor_in_voxel.size(); ++i){int pt_index = pt_index_for_neighbor_in_voxel[i];if(i > 0)std::cout << ",";std::cout << " ( " << clound->points[pt_index].x << "," << clound->points[pt_index].y << "," << clound->points[pt_index].z << " ) ";}std::cout << std::endl;}elsestd::cout << "None point in the same voxel 2 ." << std::endl;//k近邻搜索int K = 4;//最近的4个点pcl::PointXYZ search_pt_for_neighbor_k;search_pt_for_neighbor_k.x = 1.3;search_pt_for_neighbor_k.y = 1.4;search_pt_for_neighbor_k.z = 1.6;std::vector<int> pt_index_for_neighbor_k;std::vector<float> squared_distance_for_neighbor_k;std::cout << " Search point(" << search_pt_for_neighbor_k.x << "," << search_pt_for_neighbor_k.y << "," << search_pt_for_neighbor_k.z << ") for neighbor K( K=" << K << ") : ";if(octree.nearestKSearch(search_pt_for_neighbor_k, K, pt_index_for_neighbor_k, squared_distance_for_neighbor_k)){std::cout << "Points for neighbor K :" << std::endl;for(int i = 0; i < pt_index_for_neighbor_k.size(); ++i){int pt_index = pt_index_for_neighbor_k[i];float sd = squared_distance_for_neighbor_k[i];std::cout << " ( " << clound->points[pt_index].x << "," << clound->points[pt_index].y << "," << clound->points[pt_index].z << " ) "<< "- squared_distance : " << sd << " " << std::endl;}}elsestd::cout << "None point for neighbor K ." << std::endl;//半径近邻搜索double raius = 0.7;//距离为 (radius ^ 2) > (3 * (1.9 - 1.5) ^ 2),保证体素内4个点都在距离范围内pcl::PointXYZ search_pt_for_radius;search_pt_for_radius.x = 1.5;search_pt_for_radius.y = 1.5;search_pt_for_radius.z = 1.5;std::vector<int> pt_index_for_radius;std::vector<float> squared_distance_for_radius;std::cout << " Search point(" << search_pt_for_radius.x << "," << search_pt_for_radius.y << "," << search_pt_for_radius.z << ") for radius( radius=" << raius << ") : ";if(octree.radiusSearch(search_pt_for_radius, raius, pt_index_for_radius, squared_distance_for_radius)){std::cout << "Points for radius :" << std::endl;for(int i = 0; i < pt_index_for_radius.size(); ++i){int pt_index = pt_index_for_radius[i];float sd = squared_distance_for_radius[i];std::cout << " ( " << clound->points[pt_index].x << "," << clound->points[pt_index].y << "," << clound->points[pt_index].z << " ) "<< "- squared_distance : " << sd << " " << std::endl;}}elsestd::cout << "None point for radius ." << std::endl;return a.exec();
}以上程序的输出为:
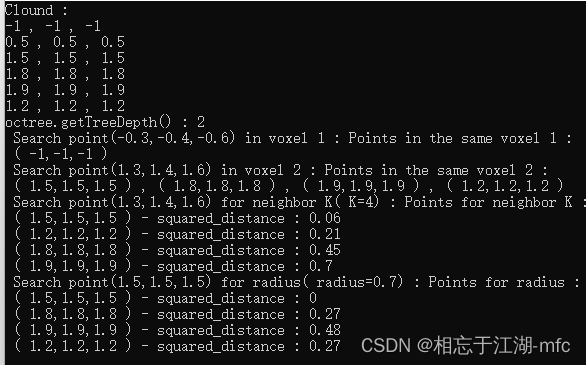
(4)基于八叉树和基于 kd-tree 的k邻域搜索、半径搜索的性能比较
下面通过写一个小程序对比测试一下kd-tree和八叉树的k邻域搜索、半径搜索的性能。
创建Qt Console程序,
#.pro文件 加上头文件引用和库引用INCLUDEPATH += C:\PCL1.12.1\include\pcl-1.12 \C:\PCL1.12.1\3rdParty\FLANN\include \C:\PCL1.12.1\3rdParty\Boost\include\boost-1_78 \C:\PCL1.12.1\3rdParty\Eigen\eigen3 \C:\PCL1.12.1\include\pcl-1.12 \C:\PCL1.12.1\3rdParty\FLANN\include \C:\PCL1.12.1\3rdParty\Boost\include\boost-1_78 \C:\PCL1.12.1\3rdParty\Eigen\eigen3 \C:\PCL1.12.1\3rdParty\VTK\include\vtk-9.1 \C:\Qt\Qt6.3\6.3.0\msvc2019_64\include\QtOpenGLWidgets \C:\Qt\Qt6.3\6.3.0\msvc2019_64\include\QtOpenGLwin32:LIBS += $$quote(C:\PCL1.12.1\lib\pcl_commond.lib)win32:LIBS += $$quote(C:\PCL1.12.1\3rdParty\FLANN\lib\flann_s.lib)
win32:LIBS += $$quote(C:\PCL1.12.1\3rdParty\FLANN\lib\flann_cpp_s.lib)win32:LIBS += $$quote(C:\PCL1.12.1\lib\pcl_commond.lib)
win32:LIBS += $$quote(C:\PCL1.12.1\lib\pcl_visualizationd.lib)
win32:LIBS += $$quote(C:\PCL1.12.1\lib\pcl_iod.lib)
win32:LIBS += $$quote(C:\PCL1.12.1\lib\pcl_octreed.lib)win32:LIBS += $$quote(C:\PCL1.12.1\3rdParty\VTK\lib\vtkCommonCore-9.1d.lib)//main.cpp#include <QCoreApplication>
#include <QDateTime>
#include <QThread>
#include <iostream>
#include <chrono>
#include <pcl/point_cloud.h>
#include <pcl/visualization/cloud_viewer.h>
#include <pcl/kdtree/kdtree_flann.h>
#include <pcl/compression/compression_profiles.h>
#include <pcl/compression/octree_pointcloud_compression.h>
#include <pcl/octree/octree_search.h>int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{QCoreApplication a(argc, argv);//创建1000个点的点云(取值范围为1~RAND_MAX)pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr clound(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>());clound->width = 1000;//10000//100000//1000000clound->height = 1;clound->resize(clound->width *clound->height);for(int i = 0; i < clound->points.size(); ++i){clound->points[i].x = rand();clound->points[i].y = rand();clound->points[i].z = rand();}//kd-treepcl::KdTreeFLANN<pcl::PointXYZ> kdtree;kdtree.setInputCloud(clound);//八叉树float octreeResolution_arg = 1.0f; //体素棱长为1pcl::octree::OctreePointCloudSearch<pcl::PointXYZ> octree(octreeResolution_arg);octree.setInputCloud(clound);octree.addPointsFromInputCloud();//查找点pcl::PointXYZ search_pt;search_pt.x = rand();search_pt.y = rand();search_pt.z = rand();std::vector<int> pt_index;std::vector<float> pt_sqart_dis;std::cout << " Total points count : " << clound->points.size() << std::endl;//K邻域搜索std::cout << " Neighbor K search : " << std::endl;pt_index.clear();pt_sqart_dis.clear();int K = 10;std::chrono::system_clock::time_point start = std::chrono::system_clock::now();kdtree.nearestKSearch(search_pt, K, pt_index, pt_sqart_dis);std::chrono::system_clock::time_point end = std::chrono::system_clock::now();auto nao_time = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::nanoseconds>(end - start);std::cout << " kd-tree consuming time : " << nao_time.count() << " ns " << std::endl;std::cout << "Points :" << std::endl;for(int i = 0; i < pt_index.size(); ++i){int pti = pt_index[i];float sd = pt_sqart_dis[i];std::cout << " ( " << clound->points[pti].x << "," << clound->points[pti].y << "," << clound->points[pti].z << " ) "<< "- squared_distance : " << sd << " ; ";}std::cout << std::endl;pt_index.clear();pt_sqart_dis.clear();K = 10;start = std::chrono::system_clock::now();octree.nearestKSearch(search_pt, K, pt_index, pt_sqart_dis);end = std::chrono::system_clock::now();nao_time = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::nanoseconds>(end - start);std::cout << " octree consuming time : " << nao_time.count() << " ns " << std::endl;std::cout << "Points :" << std::endl;for(int i = 0; i < pt_index.size(); ++i){int pti = pt_index[i];float sd = pt_sqart_dis[i];std::cout << " ( " << clound->points[pti].x << "," << clound->points[pti].y << "," << clound->points[pti].z << " ) "<< "- squared_distance : " << sd << " ; ";}std::cout << std::endl;//半径搜索std::cout << " Radius search : " << std::endl;pt_index.clear();pt_sqart_dis.clear();float radius = 0x1000;start = std::chrono::system_clock::now();kdtree.radiusSearch(search_pt, radius, pt_index, pt_sqart_dis);end = std::chrono::system_clock::now();nao_time = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::nanoseconds>(end - start);std::cout << " kd-tree consuming time : " << nao_time.count() << " ns " << std::endl;std::cout << "Points count : " << pt_index.size() << std::endl;/*for(int i = 0; i < pt_index.size(); ++i){int pti = pt_index[i];float sd = pt_sqart_dis[i];std::cout << " ( " << clound->points[pti].x << "," << clound->points[pti].y << "," << clound->points[pti].z << " ) "<< "- squared_distance : " << sd << " ; ";}std::cout << std::endl;*/pt_index.clear();pt_sqart_dis.clear();radius = 0x1000;start = std::chrono::system_clock::now();octree.radiusSearch(search_pt,radius, pt_index, pt_sqart_dis);end = std::chrono::system_clock::now();nao_time = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::nanoseconds>(end - start);std::cout << " octree consuming time : " << nao_time.count() << " ns " << std::endl;std::cout << "Points count : " << pt_index.size() << std::endl;/*for(int i = 0; i < pt_index.size(); ++i){int pti = pt_index[i];float sd = pt_sqart_dis[i];std::cout << " ( " << clound->points[pti].x << "," << clound->points[pti].y << "," << clound->points[pti].z << " ) "<< "- squared_distance : " << sd << " ; ";}std::cout << std::endl;*/return a.exec();
}
1000个点的计算结果:
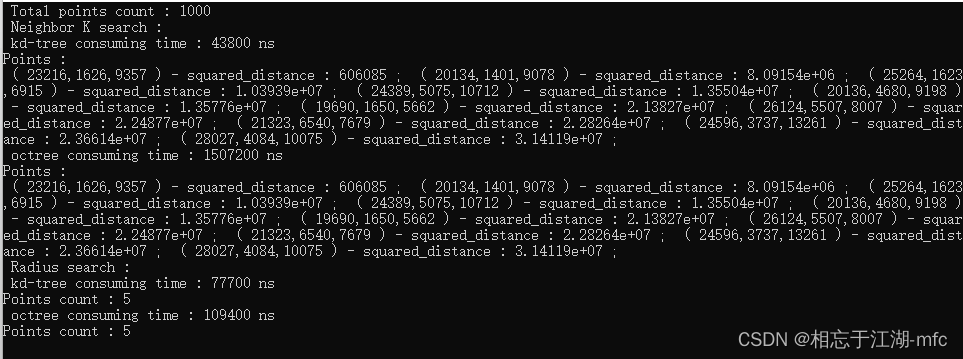
10,000个点的计算结果:
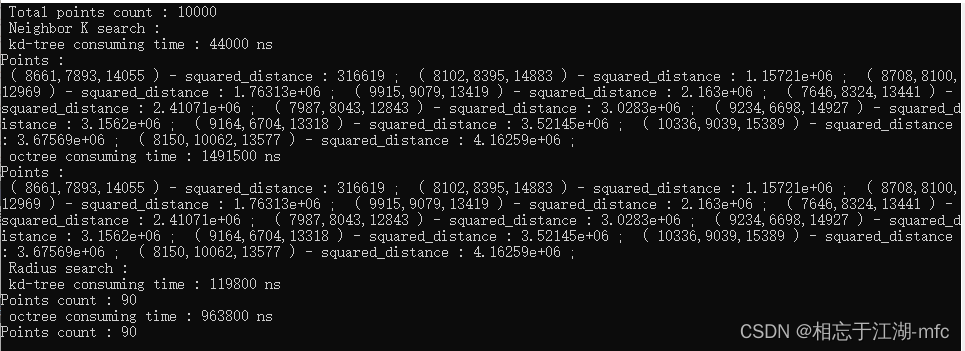
100,000个点的计算结果:
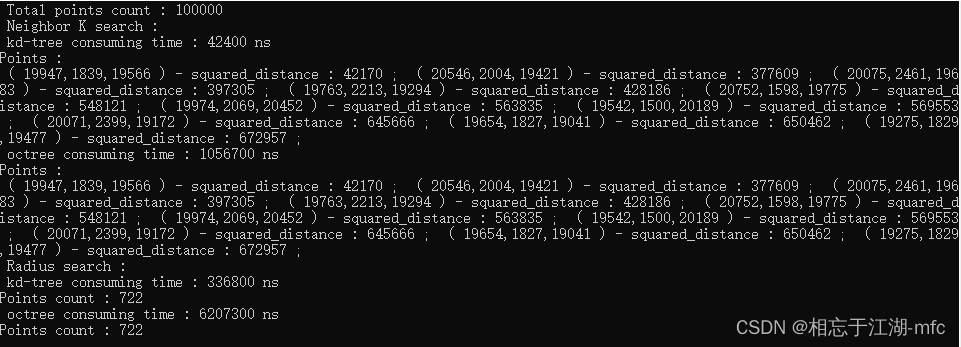
1,000,000个点的计算结果:
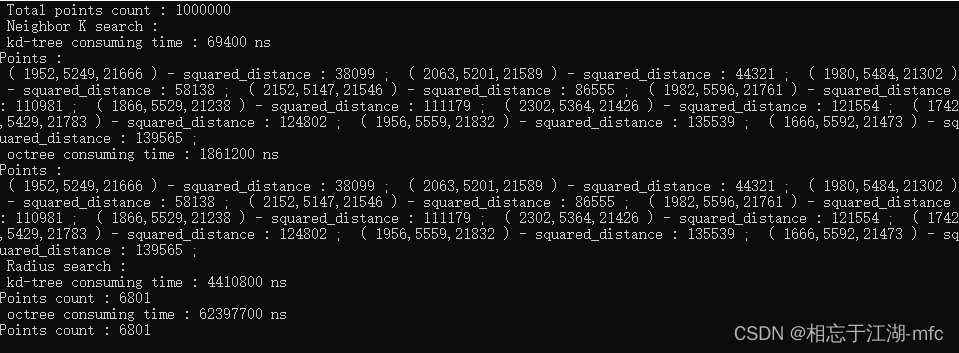
从4次计算结果来看,对于k近邻搜索和半径搜索,kd-tree比八叉树的速度更快一些,性能更好。
(5)基于八叉树的空间变化检测
八叉树是一种管理稀疏3D数据的树状数据结构,可以用于多个无序点云之间的空间变化检测,这些点云可能在尺寸、分辨率、密度和点顺序方面有所差异。
通过递归地比较八叉树的树结构,可以鉴定出由八叉树产生的体素组成之间的区别多代表的空间变化。
以下通过一个小程序看下PCL的八叉树如何检测出点云的体素变化:
创建Qt Console程序,
#.pro文件 加上头文件引用和库引用INCLUDEPATH += C:\PCL1.12.1\include\pcl-1.12 \C:\PCL1.12.1\3rdParty\FLANN\include \C:\PCL1.12.1\3rdParty\Boost\include\boost-1_78 \C:\PCL1.12.1\3rdParty\Eigen\eigen3 \C:\PCL1.12.1\include\pcl-1.12 \C:\PCL1.12.1\3rdParty\FLANN\include \C:\PCL1.12.1\3rdParty\Boost\include\boost-1_78 \C:\PCL1.12.1\3rdParty\Eigen\eigen3 \C:\PCL1.12.1\3rdParty\VTK\include\vtk-9.1 \C:\Qt\Qt6.3\6.3.0\msvc2019_64\include\QtOpenGLWidgets \C:\Qt\Qt6.3\6.3.0\msvc2019_64\include\QtOpenGLwin32:LIBS += $$quote(C:\PCL1.12.1\lib\pcl_commond.lib)win32:LIBS += $$quote(C:\PCL1.12.1\3rdParty\FLANN\lib\flann_s.lib)
win32:LIBS += $$quote(C:\PCL1.12.1\3rdParty\FLANN\lib\flann_cpp_s.lib)win32:LIBS += $$quote(C:\PCL1.12.1\lib\pcl_commond.lib)
win32:LIBS += $$quote(C:\PCL1.12.1\lib\pcl_visualizationd.lib)
win32:LIBS += $$quote(C:\PCL1.12.1\lib\pcl_iod.lib)
win32:LIBS += $$quote(C:\PCL1.12.1\lib\pcl_octreed.lib)win32:LIBS += $$quote(C:\PCL1.12.1\3rdParty\VTK\lib\vtkCommonCore-9.1d.lib)//main.cpp#include <QCoreApplication>
#include <QDateTime>
#include <QThread>
#include <iostream>
#include <chrono>
#include <pcl/point_cloud.h>
#include <pcl/visualization/cloud_viewer.h>
#include <pcl/kdtree/kdtree_flann.h>
#include <pcl/compression/compression_profiles.h>
#include <pcl/compression/octree_pointcloud_compression.h>
#include <pcl/octree/octree_search.h>
#include <pcl/octree/octree_pointcloud_changedetector.h>int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{QCoreApplication a(argc, argv);//创建6个点的无序点云pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr clound(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>());clound->width = 6;clound->height = 1;clound->resize(clound->width *clound->height);int index = 0;clound->points[index].x = -1;clound->points[index].y = -1;clound->points[index].z = -1;index = 1;clound->points[index].x = 0.5;clound->points[index].y = 0.5;clound->points[index].z = 0.5;index = 2;clound->points[index].x = 1.5;clound->points[index].y = 1.5;clound->points[index].z = 1.5;index = 3;clound->points[index].x = 1.8;clound->points[index].y = 1.8;clound->points[index].z = 1.8;index = 4;clound->points[index].x = 1.9;clound->points[index].y = 1.9;clound->points[index].z = 1.9;index = 5;clound->points[index].x = 1.2;clound->points[index].y = 1.2;clound->points[index].z = 1.2;float octreeResolution_arg = 1.0f; //体素棱长为1pcl::octree::OctreePointCloudChangeDetector<pcl::PointXYZ> octree(octreeResolution_arg);octree.setInputCloud(clound); //设置输入点云octree.addPointsFromInputCloud(); //从输入点云构造前台的八叉树//OctreePointCloudChangeDetector从Octree2BufBase继承,该类管理2个八叉树,通过switchBuffers可以切换前/后台的八叉树octree.switchBuffers();//再创建3个点的无序点云pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloundB(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>());cloundB->width = 3;cloundB->height = 1;cloundB->resize(cloundB->width *cloundB->height);index = 0;cloundB->points[index].x = -1;cloundB->points[index].y = -1;cloundB->points[index].z = -1;//cloundB缺少了clound中的点(0.5, 0.5, 0.5)所在的体素index = 1;//clound->points[index].x = 0.5;//clound->points[index].y = 0.5;//clound->points[index].z = 0.5;cloundB->points[index].x = 1.5;cloundB->points[index].y = 1.5;cloundB->points[index].z = 1.5;//cloundB增加了点(2.5, 2.5, 2.5)所在的体素index = 2;cloundB->points[index].x = 2.5;cloundB->points[index].y = 2.5;cloundB->points[index].z = 2.5;octree.setInputCloud(cloundB); //设置输入点云octree.addPointsFromInputCloud(); //从输入点云构造前台的八叉树std::vector<int> indices;//点的索引octree.getPointIndicesFromNewVoxels(indices);std::cout << "Points :" << std::endl;for(int i = 0; i < indices.size(); ++i){int pti = indices[i];std::cout << " ( " << cloundB->points[pti].x << "," << cloundB->points[pti].y << "," << cloundB->points[pti].z << " ) " << " ; ";}std::cout << std::endl;return a.exec();
}程序输出为:
![]()
根据代码中初始化的点云,cloundB形成的八叉树和clound形成的八叉树,在(包含点的)体素上,实际上是减少了一个体素(点(0.5,0.5,0.5)所在的体素)和增加了一个体素(点(2.5,2.5,2.5)所在的体素),但是,程序只给出了增加的体素,并未给出减少的体素。可见,PCL的基于八叉树的控件变化检测,只检测新点云比原点云增加的体素,而不检查新点云比原点云减少的体素。



![[学习笔记] 二进制小数表示方法](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/f5bc7c1a5487406f95b1fce456335fbf.jpg#pic_center)




![【轨迹压缩】Trajectory Simplification: On Minimizing the Direction-based Error [2015] [VLDB]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/be6eda238261421d9b8f96b6adf26c3f.png)