文章目录
- 决策树的介绍
- CART决策树算法简介
- 基尼指数
- CART决策树生成算法及Python代码实现
决策树的介绍
决策树是以树的结构将决策或者分类过程展现出来,其目的是根据若干输入变量的值构造出一个相适应的模型,来预测输出变量的值。预测变量为离散型时,为分类树;连续型时,为回归树。
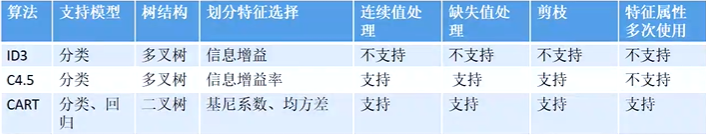
常用的决策树算法:
| 算法 | 简介 |
|---|---|
| ID3 | 使用信息增益作为分类标准 ,处理离散数据,仅适用于分类树。 |
| CART | 使用基尼系数作为分类标准,离散、连续数据均可,适用于分类树,回归树。 |
| C4.5 | 使用信息增益和增益率相结合作为分类标准,离散、连续数据均可,但效率较低,适用于分类树 |
| C5.0 | 是C4.5用于大数据集的拓展,效率较高 |
CART决策树算法简介
- CART算法是二分类常用的方法,由CART算法生成的决策树是二叉树,而 ID3 以及 C4.5 算法生成的决策树是多叉树,从运行效率角度考虑,二叉树模型会比多叉树运算效率高。
- CART算法通过基尼(Gini)指数来选择最优特征。
基尼指数
基尼系数代表模型的不纯度,基尼系数越小,则不纯度越低。
CART决策树使用“基尼指数”来选择划分属性,数据集D的纯度可以用基尼值来度量:
直观来说,G i n i ( D )反映了从数据集D中随机抽取两个样本,其类别标记不一致的概率。因此,G i n i ( D ) 越小,则数据集D 的纯度越高.
属性a的基尼指数定义为
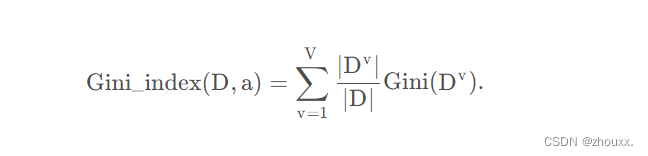
所以我们在候选属性集合A中,选择那个使得划分后基尼指数最小的属性作为最优划分属性,即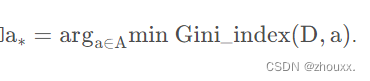
假设使用特征 A 将数据集 D 划分为两部分 D1 和 D2,此时按照特征 A 划分的数据集的基尼系数为:
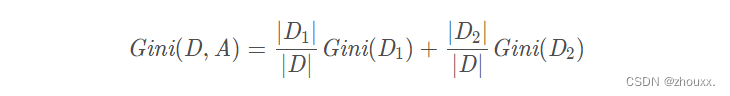
CART决策树生成算法及Python代码实现
输入:训练数据集D,停止计算的条件
输出:CART决策树
(1)构造训练数据集(人的年龄、工作、房产以及信誉)
# 构造数据集
def create_dataset():dataset = [['youth', 'no', 'no', 'just so-so', 'no'],['youth', 'no', 'no', 'good', 'no'],['youth', 'yes', 'no', 'good', 'yes'],['youth', 'yes', 'yes', 'just so-so', 'yes'],['youth', 'no', 'no', 'just so-so', 'no'],['midlife', 'no', 'no', 'just so-so', 'no'],['midlife', 'no', 'no', 'good', 'no'],['midlife', 'yes', 'yes', 'good', 'yes'],['midlife', 'no', 'yes', 'great', 'yes'],['midlife', 'no', 'yes', 'great', 'yes'],['geriatric', 'no', 'yes', 'great', 'yes'],['geriatric', 'no', 'yes', 'good', 'yes'],['geriatric', 'yes', 'no', 'good', 'yes'],['geriatric', 'yes', 'no', 'great', 'yes'],['geriatric', 'no', 'no', 'just so-so', 'no']]features = ['age', 'work', 'house', 'credit']return dataset, features
(2)根据公式计算现有特征对该数据集的基尼指数
计算当前集合的Gini指数:
# 计算当前集合的Gini系数
def calcGini(dataset):# 求总样本数num_of_examples = len(dataset)labelCnt = {}# 遍历整个样本集合for example in dataset:# 当前样本的标签值是该列表的最后一个元素currentLabel = example[-1]# 统计每个标签各出现了几次if currentLabel not in labelCnt.keys():labelCnt[currentLabel] = 0labelCnt[currentLabel] += 1# 得到了当前集合中每个标签的样本个数后,计算它们的p值for key in labelCnt:labelCnt[key] /= num_of_exampleslabelCnt[key] = labelCnt[key] * labelCnt[key]# 计算Gini系数Gini = 1 - sum(labelCnt.values())return Gini
将当前样本集分割成特征i取值为value的一部分和取值不为value的一部分(二分):
def split_dataset(dataset, index, value):sub_dataset1 = []sub_dataset2 = []for example in dataset:current_list = []if example[index] == value:current_list = example[:index]current_list.extend(example[index + 1 :])sub_dataset1.append(current_list)else:current_list = example[:index]current_list.extend(example[index + 1 :])sub_dataset2.append(current_list)return sub_dataset1, sub_dataset2
(3)选择基尼指数最小的值对应的特征为最优特征,对应的切分点为最优切分点(若最小值对应的特征或切分点有多个,随便取一个即可)
def choose_best_feature(dataset):# 特征总数numFeatures = len(dataset[0]) - 1# 当只有一个特征时if numFeatures == 1:return 0# 初始化最佳基尼系数bestGini = 1# 初始化最优特征index_of_best_feature = -1# 遍历所有特征,寻找最优特征和该特征下的最优切分点for i in range(numFeatures):# 去重,每个属性值唯一uniqueVals = set(example[i] for example in dataset)# Gini字典中的每个值代表以该值对应的键作为切分点对当前集合进行划分后的Gini系数Gini = {}# 对于当前特征的每个取值for value in uniqueVals:# 先求由该值进行划分得到的两个子集sub_dataset1, sub_dataset2 = split_dataset(dataset,i,value)# 求两个子集占原集合的比例系数prob1 prob2prob1 = len(sub_dataset1) / float(len(dataset))prob2 = len(sub_dataset2) / float(len(dataset))# 计算子集1的Gini系数Gini_of_sub_dataset1 = calcGini(sub_dataset1)# 计算子集2的Gini系数Gini_of_sub_dataset2 = calcGini(sub_dataset2)# 计算由当前最优切分点划分后的最终Gini系数Gini[value] = prob1 * Gini_of_sub_dataset1 + prob2 * Gini_of_sub_dataset2# 更新最优特征和最优切分点if Gini[value] < bestGini:bestGini = Gini[value]index_of_best_feature = ibest_split_point = valuereturn index_of_best_feature, best_split_point
(4)按照最优特征和最优切分点,从现结点生成两个子结点,将训练数据集中的数据按特征和属性分配到两个子结点中;
删除某特征值为value值的样本后获取到的数据集:
# 提取子集合
# 功能:从dataSet中先找到所有第axis个标签值 = value的样本
# 然后将这些样本删去第axis个标签值,再全部提取出来成为一个新的样本集
def create_sub_dataset(dataset, index, value):sub_dataset = []for example in dataset:current_list = []if example[index] == value:current_list = example[:index]current_list.extend(example[index + 1 :])sub_dataset.append(current_list)return sub_dataset
(5)对两个子结点递归地调用(2)(3)(4),直至满足停止条件。
(6)生成CART树。
算法停止的条件:结点中的样本个数小于预定阈值,或样本集的基尼指数小于预定阈值(样本基本属于同一类,如完全属于同一类则为0),或者特征集为空。
特征被使用完毕返回处理:
# 返回具有最多样本数的那个标签的值('yes' or 'no')
def find_label(classList):# 初始化统计各标签次数的字典# 键为各标签,对应的值为标签出现的次数labelCnt = {}for key in classList:if key not in labelCnt.keys():labelCnt[key] = 0labelCnt[key] += 1# 将classCount按值降序排列# 例如:sorted_labelCnt = {'yes': 9, 'no': 6}sorted_labelCnt = sorted(labelCnt.items(), key = lambda a:a[1], reverse = True)# 下面这种写法有问题# sortedClassCount = sorted(labelCnt.iteritems(), key=operator.itemgetter(1), reverse=True)# 取sorted_labelCnt中第一个元素中的第一个值,即为所求return sorted_labelCnt[0][0]
生成决策树的代码:
def create_decision_tree(dataset, features):# 求出训练集所有样本的标签# 对于初始数据集,其label_list = ['no', 'no', 'yes', 'yes', 'no', 'no', 'no', 'yes', 'yes', 'yes', 'yes', 'yes', 'yes', 'yes', 'no']label_list = [example[-1] for example in dataset]# 先写两个递归结束的情况:# 若当前集合的所有样本标签相等(即样本已被分“纯”)# 则直接返回该标签值作为一个叶子节点if label_list.count(label_list[0]) == len(label_list):return label_list[0]# 若训练集的所有特征都被使用完毕,当前无可用特征,但样本仍未被分“纯”# 则返回所含样本最多的标签作为结果if len(dataset[0]) == 1:return find_label(label_list)# 下面是正式建树的过程# 选取进行分支的最佳特征的下标和最佳切分点index_of_best_feature, best_split_point = choose_best_feature(dataset)# 得到最佳特征best_feature = features[index_of_best_feature]# 初始化决策树decision_tree = {best_feature: {}}# 使用过当前最佳特征后将其删去del(features[index_of_best_feature])# 子特征 = 当前特征(因为刚才已经删去了用过的特征)sub_labels = features[:]# 递归调用create_decision_tree去生成新节点# 生成由最优切分点划分出来的二分子集sub_dataset1, sub_dataset2 = split_dataset(dataset,index_of_best_feature,best_split_point)# 构造左子树decision_tree[best_feature][best_split_point] = create_decision_tree(sub_dataset1, sub_labels)# 构造右子树decision_tree[best_feature]['others'] = create_decision_tree(sub_dataset2, sub_labels)return decision_tree
利用训练好的决策树对新的样本进行分类测试:
# 用上面训练好的决策树对新样本分类
def classify(decision_tree, features, test_example):# 根节点代表的属性first_feature = list(decision_tree.keys())[0]# second_dict是第一个分类属性的值(也是字典)second_dict = decision_tree[first_feature]# 树根代表的属性,所在属性标签中的位置,即第几个属性index_of_first_feature = features.index(first_feature)# 对于second_dict中的每一个keyfor key in second_dict.keys():# 不等于'others'的keyif key != 'others':if test_example[index_of_first_feature] == key:# 若当前second_dict的key的value是一个字典if type(second_dict[key]).__name__ == 'dict':# 则需要递归查询classLabel = classify(second_dict[key], features, test_example)# 若当前second_dict的key的value是一个单独的值else:# 则就是要找的标签值classLabel = second_dict[key]# 如果测试样本在当前特征的取值不等于key,就说明它在当前特征的取值属于'others'else:# 如果second_dict['others']的值是个字符串,则直接输出if isinstance(second_dict['others'],str):classLabel = second_dict['others']# 如果second_dict['others']的值是个字典,则递归查询else:classLabel = classify(second_dict['others'], features, test_example)return classLabel
main函数:
if __name__ == '__main__':dataset, features = create_dataset()decision_tree = create_decision_tree(dataset, features)# 打印生成的决策树print(decision_tree)# 对新样本进行分类测试features = ['age', 'work', 'house', 'credit']test_example = ['midlife', 'yes', 'no', 'great']print(classify(decision_tree, features, test_example))运行结果解析:
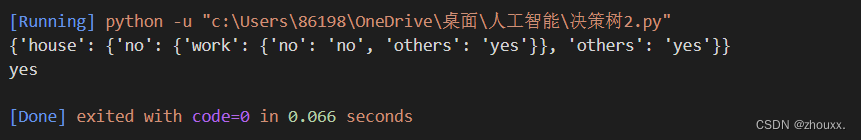
根据结果画出的决策树:
对样本分类测试的结果:
yes。