学习心得
task2学习GYH大佬的回归CART树,并在此基础上改为分类CART树。
更新ing。。
这里做一些对决策树分裂依据更深入的思考引导:我们在task1证明离散变量信息增益非负时曾提到,信息增益本质上就是联合分布和边缘分布乘积的kl散度,而事实上kl散度属于f-divergence(https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/F-divergence)中的一类特殊情况,由于在分裂时我们衡量的是这两个分布的差异到底有多大,因此f-divergence中的任意一种距离度量都可以用来作为分裂依据,那么在树结构上进行分裂,这些散度究竟对树的生长结果产生了怎样的影响,似乎还没有看到文章讨论过这些(可以试图充分地讨论它们之间的一些理论性质和联系)
(1)可能会发现在与sklearn对比时,有时会产生两者结果预测部分不一致的情况,这种现象主要来自于当前节点在分裂的时候不同的特征和分割点组合产生了相同的信息增益,但由于遍历特征的顺序(和sklearn内的遍历顺序)不一样,因此在预测时会产生差异,并不是算法实现上有问题。
(2)对比的时候作差后要取绝对值,(np.abs(res1-res2)<1e-8).mean()。
文章目录
- 学习心得
- 一、回顾决策树算法
- 二、代码实践
- Reference
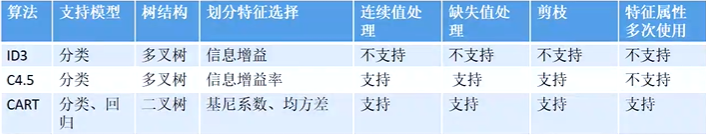
一、回顾决策树算法
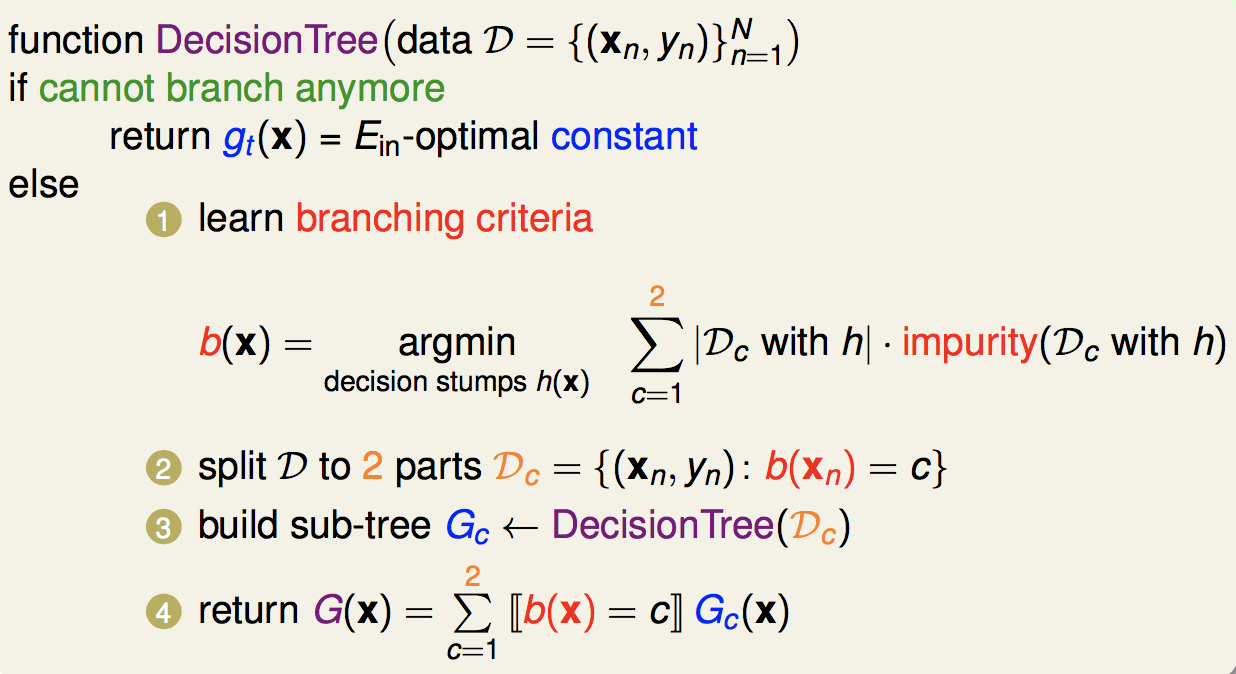
二、代码实践
from CART import DecisionTreeRegressor
from CARTclassifier import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor as dt
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier as dc
from sklearn.datasets import make_regression
from sklearn.datasets import make_classificationif __name__ == "__main__":# 模拟回归数据集X, y = make_regression(n_samples=200, n_features=10, n_informative=5, random_state=0)# 回归树my_cart_regression = DecisionTreeRegressor(max_depth=2)my_cart_regression.fit(X, y)res1 = my_cart_regression.predict(X)importance1 = my_cart_regression.feature_importances_sklearn_cart_r = dt(max_depth=2)sklearn_cart_r.fit(X, y)res2 = sklearn_cart_r.predict(X)importance2 = sklearn_cart_r.feature_importances_# 预测一致的比例print(((res1-res2)<1e-8).mean())# 特征重要性一致的比例print(((importance1-importance2)<1e-8).mean())# 模拟分类数据集X, y = make_classification(n_samples=200, n_features=10, n_informative=5, random_state=0)# 分类树my_cart_classification = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=2)my_cart_classification.fit(X, y)res3 = my_cart_classification.predict(X)importance3 = my_cart_classification.feature_importances_sklearn_cart_c = dc(max_depth=2)sklearn_cart_c.fit(X, y)res4 = sklearn_cart_c.predict(X)importance4 = sklearn_cart_c.feature_importances_# 预测一致的比例print(((res3-res4)<1e-8).mean())# 特征重要性一致的比例print(((importance3-importance4)<1e-8).mean())
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Sun Oct 17 10:46:08 2021@author: 86493
"""
import numpy as np
from collections import Counterdef MSE(y):return ((y - y.mean())**2).sum() / y.shape[0]# 基尼指数
def Gini(y):c = Counter(y)return 1 - sum([(val / y.shape[0]) ** 2 for val in c.values()])class Node:def __init__(self, depth, idx):self.depth = depthself.idx = idxself.left = Noneself.right = Noneself.feature = Noneself.pivot = Noneclass Tree:def __init__(self, max_depth):self.max_depth = max_depthself.X = Noneself.y = Noneself.feature_importances_ = Nonedef _able_to_split(self, node):return (node.depth < self.max_depth) & (node.idx.sum() >= 2)def _get_inner_split_score(self, to_left, to_right):total_num = to_left.sum() + to_right.sum()left_val = to_left.sum() / total_num * Gini(self.y[to_left])right_val = to_right.sum() / total_num * Gini(self.y[to_right])return left_val + right_valdef _inner_split(self, col, idx):data = self.X[:, col]best_val = np.inftyfor pivot in data[:-1]:to_left = (idx==1) & (data<=pivot)to_right = (idx==1) & (~to_left)if to_left.sum() == 0 or to_left.sum() == idx.sum():continueHyx = self._get_inner_split_score(to_left, to_right)if best_val > Hyx:best_val, best_pivot = Hyx, pivotbest_to_left, best_to_right = to_left, to_rightreturn best_val, best_to_left, best_to_right, best_pivotdef _get_conditional_entropy(self, idx):best_val = np.inftyfor col in range(self.X.shape[1]):Hyx, _idx_left, _idx_right, pivot = self._inner_split(col, idx)if best_val > Hyx:best_val, idx_left, idx_right = Hyx, _idx_left, _idx_rightbest_feature, best_pivot = col, pivotreturn best_val, idx_left, idx_right, best_feature, best_pivotdef split(self, node):# 首先判断本节点是不是符合分裂的条件if not self._able_to_split(node):return None, None, None, None# 计算H(Y)entropy = Gini(self.y[node.idx==1])# 计算最小的H(Y|X)(conditional_entropy,idx_left,idx_right,feature,pivot) = self._get_conditional_entropy(node.idx)# 计算信息增益G(Y, X)info_gain = entropy - conditional_entropy# 计算相对信息增益relative_gain = node.idx.sum() / self.X.shape[0] * info_gain# 更新特征重要性self.feature_importances_[feature] += relative_gain# 新建左右节点并更新深度node.left = Node(node.depth+1, idx_left)node.right = Node(node.depth+1, idx_right)self.depth = max(node.depth+1, self.depth)return idx_left, idx_right, feature, pivotdef build_prepare(self):self.depth = 0self.feature_importances_ = np.zeros(self.X.shape[1])self.root = Node(depth=0, idx=np.ones(self.X.shape[0]) == 1)def build_node(self, cur_node):if cur_node is None:returnidx_left, idx_right, feature, pivot = self.split(cur_node)cur_node.feature, cur_node.pivot = feature, pivotself.build_node(cur_node.left)self.build_node(cur_node.right)def build(self):self.build_prepare()self.build_node(self.root)def _search_prediction(self, node, x):if node.left is None and node.right is None:# return self.y[node.idx].mean()return self.y[node.idx].min()if x[node.feature] <= node.pivot:node = node.leftelse:node = node.rightreturn self._search_prediction(node, x)def predict(self, x):return self._search_prediction(self.root, x)class DecisionTreeClassifier:"""max_depth控制最大深度,类功能与sklearn默认参数下的功能实现一致"""def __init__(self, max_depth):self.tree = Tree(max_depth=max_depth)def fit(self, X, y):self.tree.X = Xself.tree.y = yself.tree.build()self.feature_importances_ = (self.tree.feature_importances_ / self.tree.feature_importances_.sum())return selfdef predict(self, X):return np.array([self.tree.predict(x) for x in X])
输出结果如下,可见在误差范围内,实现的分类树和回归树均和sklearn实现的模块近似。
1.0
1.0
1.0
1.0
Reference
(0)datawhale notebook
(1)CART决策树(Decision Tree)的Python源码实现
(2)https://github.com/RRdmlearning/Decision-Tree
(3)《机器学习技法》—决策树