台大林轩田《机器学习基石》:作业一python实现
台大林轩田《机器学习基石》:作业二python实现
台大林轩田《机器学习基石》:作业三python实现
台大林轩田《机器学习基石》:作业四python实现
完整代码:
https://github.com/xjwhhh/LearningML/tree/master/MLFoundation
欢迎follow和star
在学习和总结的过程中参考了不少别的博文,且自己的水平有限,如果有错,希望能指出,共同学习,共同进步
##13
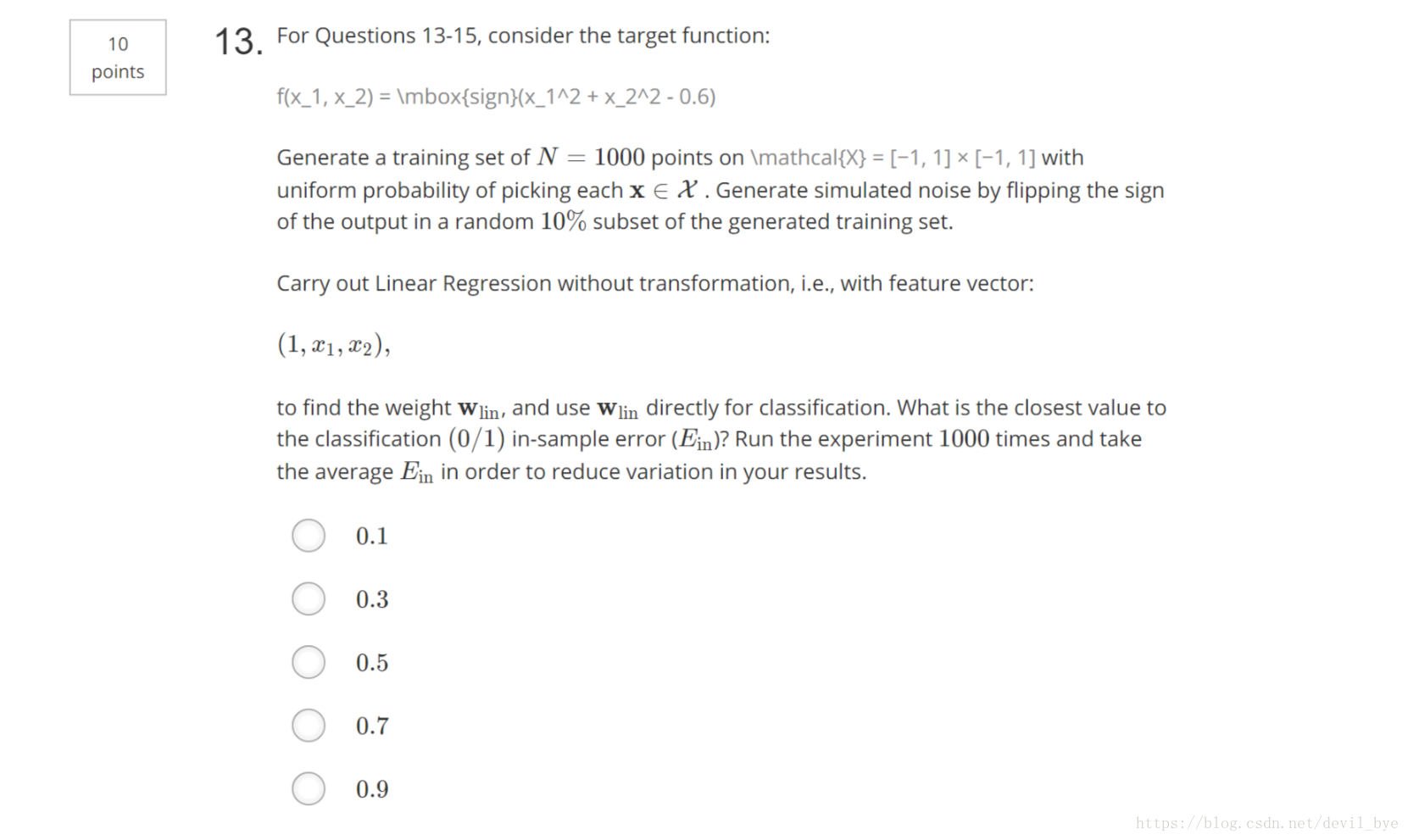
给定target function,我们的工作是在X=[-1,1]x[-1,1]上随机产生1000个点,利用f(x1,x2)计算它的值,然后在基础上添加10%的噪声(二元分类的噪声就是把10%的样本的y值取相反数)。如果不做feacher transform 直接利用数据做线性回归,利用得到的参数做线性分类器,问此时得到的Ein是多少。运行1000次取平均值。
步骤:
1.随机产生训练样本并添加噪声
2.利用训练样本进行线性回归
3.用得到的线性回归参数w作为二元分类器的参数,计算sign(w*x)得到预测值,计算他与y的0/1错误,得到错误率E_in
代码如下:
import random
import numpy as np# target function f(x1, x2) = sign(x1^2 + x2^2 - 0.6)
def target_function(x1, x2):if (x1 * x1 + x2 * x2 - 0.6) >= 0:return 1else:return -1# create train_set
def training_data_with_random_error(num=1000):features = np.zeros((num, 3))labels = np.zeros((num, 1))points_x1 = np.array([round(random.uniform(-1, 1), 2) for i in range(num)])points_x2 = np.array([round(random.uniform(-1, 1), 2) for i in range(num)])for i in range(num):# create random featurefeatures[i, 0] = 1features[i, 1] = points_x1[i]features[i, 2] = points_x2[i]labels[i] = target_function(points_x1[i], points_x2[i])# choose 10% error labelsif i <= num * 0.1:if labels[i] < 0:labels[i] = 1else:labels[i] = -1return features, labelsdef error_rate(features, labels, w):wrong = 0for i in range(len(labels)):if np.dot(features[i], w) * labels[i, 0] < 0:wrong += 1return wrong / (len(labels) * 1.0)def linear_regression_closed_form(X, Y):"""linear regression:model : g(x) = Wt * Xstrategy : squared erroralgorithm : close form(matrix)result : w = (Xt.X)^-1.Xt.Y林老师上课讲的公式"""return np.linalg.inv(np.dot(X.T, X)).dot(X.T).dot(Y)if __name__ == '__main__':# 13error_rate_array = []for i in range(1000):(features, labels) = training_data_with_random_error(1000)w13 = linear_regression_closed_form(features, labels)error_rate_array.append(error_rate(features, labels, w13))# error rate, approximately 0.5avr_err = sum(error_rate_array) / (len(error_rate_array) * 1.0)print("13--Linear regression for classification without feature transform:Average error--", avr_err)
运行结果是0.5079380000000009
##14
在第13题,直接利用逻辑回归做分类是很不理想的,错误率为50%,没有实际意义。但是我们可以先进行特征转换,正确率就会高很多。我们要将特征转换到如题所示
与13题的不同在于多了一个feature_transform(features)方法,在1000次计算中比较得到最好的w
def feature_transform(features):new = np.zeros((len(features), 6))new[:, 0:3] = features[:, :] * 1new[:, 3] = features[:, 1] * features[:, 2]new[:, 4] = features[:, 1] * features[:, 1]new[:, 5] = features[:, 2] * features[:, 2]return new
main方法变为:
# 14
(features, labels) = training_data_with_random_error(1000)
new_features = feature_transform(features)
w14 = linear_regression_closed_form(new_features, labels)
min_error_in = float("inf")
# print(w14)
# plot_dot_pictures(features, labels, w)
error_rate_array = []
for i in range(1000):(features, labels) = training_data_with_random_error(1000)new_features = feature_transform(features)w = linear_regression_closed_form(new_features, labels)error_in = error_rate(new_features, labels, w)if error_in <= min_error_in:w14 = wmin_error_in = error_inerror_rate_array.append(error_in)
print("w14", w14)
运行结果为
w14 [[-0.95043879]
[ 0.02597952]
[ 0.00375311]
[ 0.00370397]
[ 1.54904793]
[ 1.60014614]]
##15
在14题得到的最优w的基础上,我们利用产生训练样本的方法一样产生1000个测试样本,计算误差。重复1000次求平均误差
在14题的main方法里添加:
# 15
error_out = []
for i in range(1000):(features, labels) = training_data_with_random_error(1000)new_features = feature_transform(features)error_out.append(error_rate(new_features, labels, w14))
print("15--Average of E_out is: ", sum(error_out) / (len(error_out) * 1.0))
运行结果为0.1176709999999998
##18
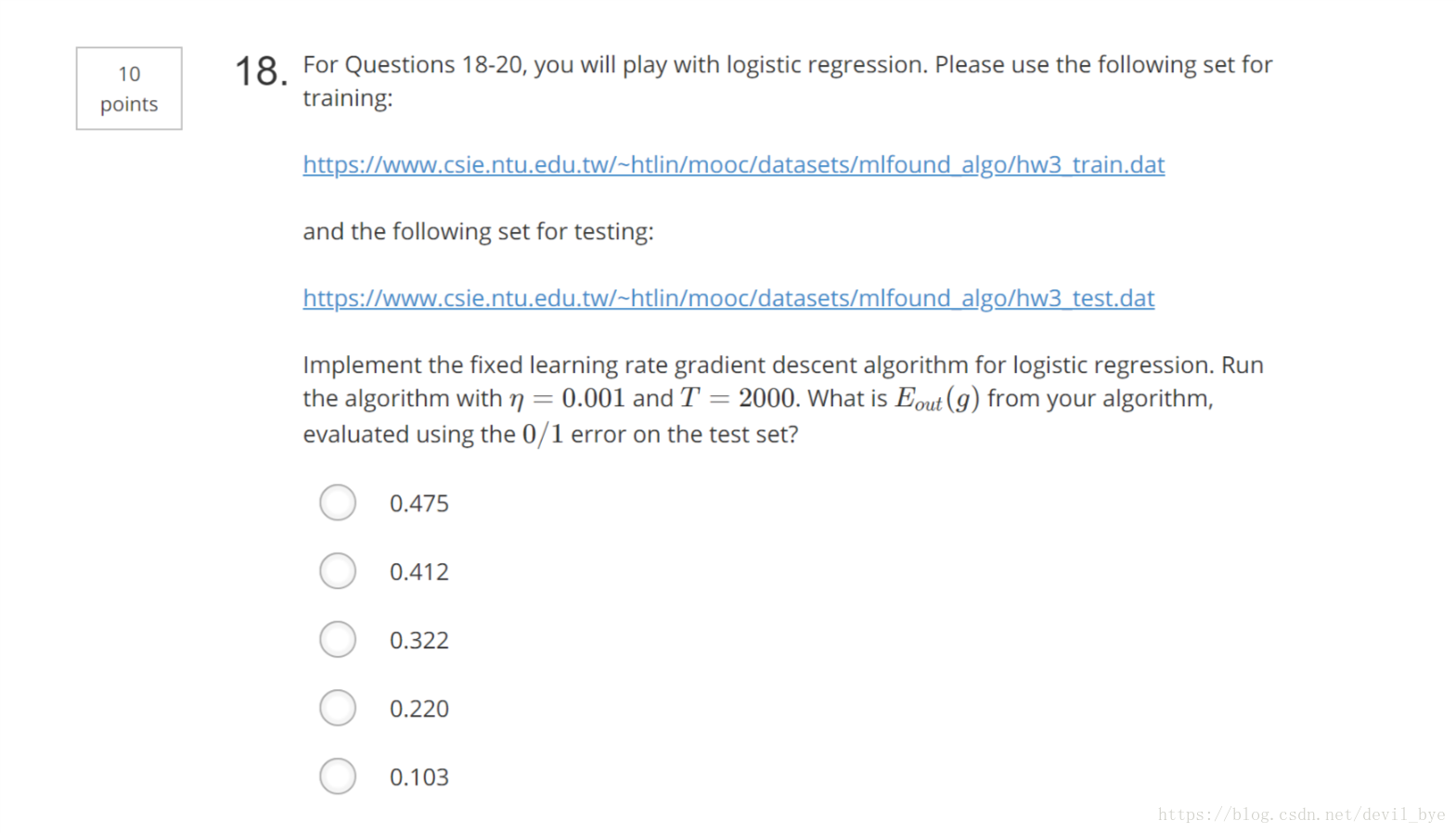
下载训练样本和测试样本,进行逻辑回归。取迭代步长ita = 0.001,迭代次数T=2000,求E_out
梯度下降时注意公式转化为代码
代码如下:
import numpy as npdef data_load(file_path):# open file and read linesf = open(file_path)try:lines = f.readlines()finally:f.close()# create features and labels arrayexample_num = len(lines)feature_dimension = len(lines[0].strip().split())features = np.zeros((example_num, feature_dimension))features[:, 0] = 1labels = np.zeros((example_num, 1))for index, line in enumerate(lines):# items[0:-1]--features items[-1]--labelitems = line.strip().split(' ')# get featuresfeatures[index, 1:] = [float(str_num) for str_num in items[0:-1]]# get labellabels[index] = float(items[-1])return features, labels# gradient descent
def gradient_descent(X, y, w):# -YnWtXntmp = -y * (np.dot(X, w))# θ(-YnWtXn) = exp(tmp)/1+exp(tmp)# weight_matrix = np.array([math.exp(_)/(1+math.exp(_)) for _ in tmp]).reshape(len(X), 1)weight_matrix = np.exp(tmp) / ((1 + np.exp(tmp)) * 1.0)gradient = 1 / (len(X) * 1.0) * (sum(weight_matrix * -y * X).reshape(len(w), 1))return gradient# gradient descent
def stochastic_gradient_descent(X, y, w):# -YnWtXntmp = -y * (np.dot(X, w))# θ(-YnWtXn) = exp(tmp)/1+exp(tmp)# weight = math.exp(tmp[0])/((1+math.exp(tmp[0]))*1.0)weight = np.exp(tmp) / ((1 + np.exp(tmp)) * 1.0)gradient = weight * -y * Xreturn gradient.reshape(len(gradient), 1)# LinearRegression Class
class LinearRegression:def __init__(self):pass# fit modeldef fit(self, X, y, Eta=0.001, max_iteration=2000, sgd=False):# ∂E/∂w = 1/N * ∑θ(-YnWtXn)(-YnXn)self.__w = np.zeros((len(X[0]), 1))# whether use stochastic gradient descentif not sgd:for i in range(max_iteration):self.__w = self.__w - Eta * gradient_descent(X, y, self.__w)else:index = 0for i in range(max_iteration):if (index >= len(X)):index = 0self.__w = self.__w - Eta * stochastic_gradient_descent(np.array(X[index]), y[index], self.__w)index += 1# predictdef predict(self, X):binary_result = np.dot(X, self.__w) >= 0return np.array([(1 if _ > 0 else -1) for _ in binary_result]).reshape(len(X), 1)# get vector wdef get_w(self):return self.__w# score(error rate)def score(self, X, y):predict_y = self.predict(X)return sum(predict_y != y) / (len(y) * 1.0)if __name__ == '__main__':# 18# training model(X, Y) = data_load("hw3_train.dat")lr = LinearRegression()lr.fit(X, Y, max_iteration=2000)# get 0/1 error in test datatest_X, test_Y = data_load("hw3_test.dat")print("E_out: ", lr.score(test_X, test_Y))
运行结果为0.475
##19
把第18题的步长ita=0.001改为0.01,求E_out
只需要更改main函数里的ita
# 19
# training model
(X, Y) = data_load("hw3_train.dat")
lr_eta = LinearRegression()
lr_eta.fit(X, Y, 0.01, 2000)
# get 0/1 error in test data
test_X, test_Y = data_load("hw3_test.dat")
print("E_out: ", lr_eta.score(test_X, test_Y))
运行结果为0.22
##20
ita取0.001,迭代2000次,利用随机梯度下降法(Stostic Gradieng Descent),求迭代2000次后的Eout
我在18题的代码中给出了随机梯度下降的实现,只要在调用方法时将sgd设为True即可
# 20
(X, Y) = data_load("hw3_train.dat")
lr_sgd = LinearRegression()
lr_sgd.fit(X, Y, sgd=True, max_iteration=2000)
# get 0/1 error in test data
test_X, test_Y = data_load("hw3_test.dat")
print("E_out: ", lr_sgd.score(test_X, test_Y))
运行结果为0.473