文章目录
- 雪花算法
- 分布式ID
- 分布式ID需要满足的要求
- 全局唯一:
- 高性能:
- 高可用:
- 方便易用:
- 安全:
- 有序递增:
- 要求具体的业务含义:
- 独立部署:
- 组成
- 代码实现
- Java代码实现
- Go语言实现
雪花算法
简介:
-
雪花算法是Twitter开源的分布式ID生成算法 Github仓库地址
-
雪花算法主要用于分布式系统中,数据库的ID生成
-
在自然界中并不存在两片完全一样的雪花,每一片雪花都拥有自己漂亮独特的形状,独一无二.雪花算法也表示生成的分布式id如雪花般独一无二.
分布式ID
随着业务被使用的人越来越多, 单机的数据库已经很难保证业务能够流畅稳定的运行了, 这是我们需要对数据库进行分库分表存储, 使用分布式集群, 但是这样每个表的数据怎么保证ID唯一呢? 如果使用主键递增肯定发生ID不唯一的冲突情况, 所以急需一种可以生成全局唯一ID的算法来解决这个囧境.
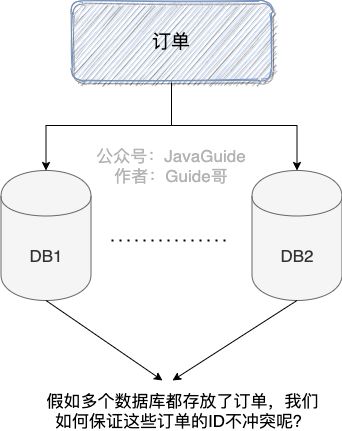
分布式ID需要满足的要求
全局唯一:
- 这是最基本的要求
高性能:
- 不能为了全局唯一就去生成一大长串,肯定需要考虑性能,既要考虑生成的效率,又要考虑查询的效率(即存储的效率).
高可用:
- 生成分布式ID的服务要保证可用性高,无限接近100%
方便易用:
- 拿来即用,使用方便,快速接入!
安全:
- 分布式ID中不应含有敏感信息,否则了解算法的不怀好意之人解码可能会获取到这些敏感信息.
有序递增:
- 如果要把 ID 存放在数据库的话,ID 的有序性可以提升数据库写入速度。并且,很多时候 ,我们还很有可能会直接通过 ID 来进行排序。
要求具体的业务含义:
- 生成的ID如果能有具体的业务含义,可以让定位问题以及开发更透明化(例如根据ID就能确定是哪个业务)
独立部署:
- 也就是分布式系统单独有一个发号器服务,专门用来生成分布式 ID。这样就生成 ID 的服务可以和业务相关的服务解耦。不过,这样同样带来了网络调用消耗增加的问题。总的来说,如果需要用到分布式 ID 的场景比较多的话,独立部署的发号器服务还是很有必要的。(企业级的大型项目中十分有必要)
组成
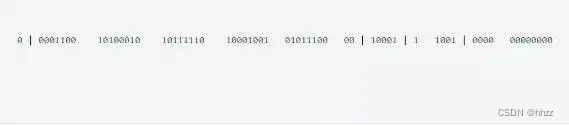
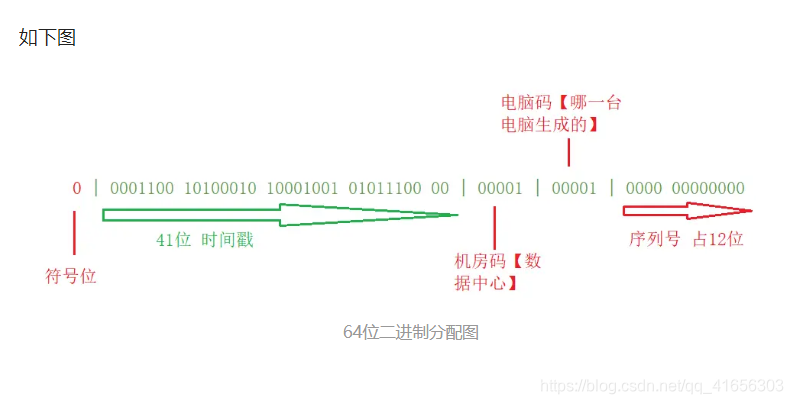
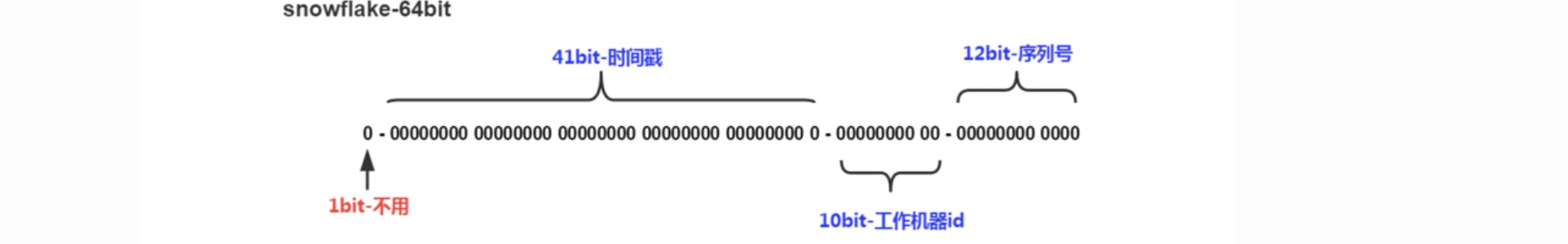
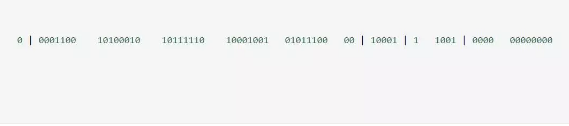
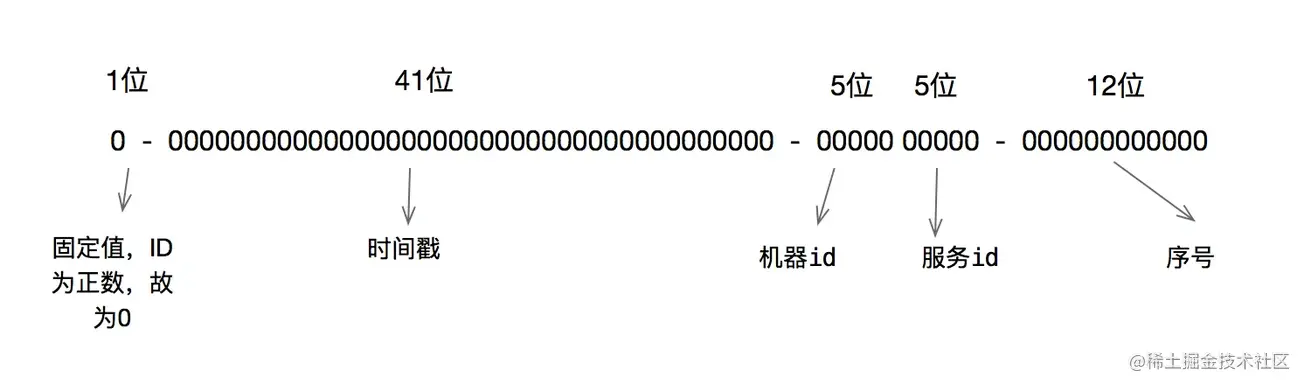
雪花算法生成的ID是一个64bit的long型的数字且按时间趋势递增.大致有首位符号位(无效位), 时间戳插值, 机器编码, 序列号四部分组成.
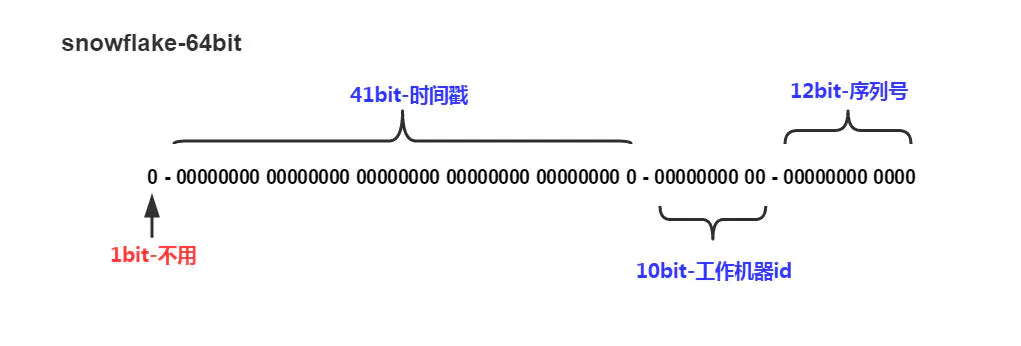
如图:
- 首位无效符: 主要用做为符号位,因为一般都是生成正数,所以符号位统一都是0
- **时间戳:**占用41bit,精确到毫秒. 41bit位最好可以表示2^41-1毫秒, 转化成单位年为69年.
- 机器编码: 占用10bit,其中高位5bit是数据中心ID,低位5bit是工作节点ID,最多可以容纳1024个节点.
- **序列号:**占用12bit,每个节点每毫秒0开始不断累加,最多可以累加到2^12-1,一共可以生成4096个ID(包括了0)
代码实现
提供了Java和Golang两种编程语言的实现方式
Java代码实现
snowFlake.java
package com.dyw.snowFlake;/*** @author Devil* @create 2022-04-04 14:25*/
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public class IDWorker {//十位的工作机器码private long workerId; //工作id 五位private long datacenterId; //数据中心id 五位//12位序列号private long sequence = 0L;//初始时间戳private final long twEpoch = 1288834974657L;//长度为5位private final long workerIdBits = 5L;private final long datacenterIdBits = 5L;//最大值private final long maxWorkerId = ~(-1L << workerIdBits);private final long maxDatacenterId = ~(-1L << datacenterIdBits);//序列号id长度private final long sequenceBits = 12L;private final long sequenceMask = ~(-1L << sequenceBits);//工作id需要左移的位数, 12位(序列号的位长)private final long workerIdShift = sequenceBits;//数据中心id需要左移的位数 序列号长+工作id长private final long datacenterIdShift = sequenceBits + workerIdBits;//时间戳左移位数 = 序列号长+工作id长+工作位长private final long timestampLeftShift = sequenceBits + workerIdBits + datacenterIdBits;//上次时间戳, 初始值位负值private long lastTimestamp = -1L;/*** 构造方法* @param workerId 工作节点id* @param datacenterId 数据中心id*/public IDWorker(long workerId, long datacenterId) {//检查参数的合法性if (workerId > maxWorkerId || workerId < 0) {throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("worker Id can't be greater than %d or less than 0", maxWorkerId));}if (datacenterId > maxDatacenterId || datacenterId < 0) {throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("datacenter Id can't be greater than %d or less than 0", maxDatacenterId));}System.out.printf("worker starting. timestamp left shift %d, datacenter id bits %d, worker id bits %d, sequence bits %d, workerid %d",timestampLeftShift, datacenterIdBits, workerIdBits, sequenceBits, workerId);this.workerId = workerId;this.datacenterId = datacenterId;}public long getWorkerId() {return workerId;}public long getDatacenterId() {return datacenterId;}public long getSequence() {return sequence;}/*** //下一个ID生成算法* @return snowflakeId*/public synchronized long nextId() {//先获取当前系统时间long timestamp = timeGen();//如果当前系统时间比上次获取id时间戳小就抛出异常 时钟往后移动可能会出现同样id所以这里必须抛异常结束执行if (timestamp < lastTimestamp) {System.err.printf("clock is moving backwards. Rejecting requests until %d.",lastTimestamp);throw new RuntimeException(String.format("Clock moved backwards. Refusing to generate id for %d milliseconds",lastTimestamp - timestamp));}//获取当前时间戳如果等于上次时间戳(同一毫秒内),则在序列号加一,否则序列号赋值为0, 从零开始if(timestamp==lastTimestamp){//这是使用&sequenceMask是为了防止sequence溢出12位(前面要求了sequence的长度只能是12位)sequence = (sequence+1)&sequenceMask;//如果防止刚好移除经过&sequenceMask后 会变成0 可能会发生重复的情况//所以此时需要再次获取时间戳,并于上次时间戳作比较 直到与上次时间戳不一致返回当前时间戳避免重复if(sequence==0){timestamp = tilNextMillis(lastTimestamp);}}//如果不在同一个时间戳中 代表该序列刚开始计数所以初始为0else{sequence = 0;}//将上次时间戳值更新lastTimestamp = timestamp;/** 返回结果:* (timestamp - TwEpoch) << timestampLeftShift) 表示将时间戳减去初始时间戳,再左移相应位数* (datacenterId << datacenterIdShift) 表示将数据id左移相应位数* (workerId << workerIdShift) 表示将工作id左移相应位数* | 是按位或运算符,例如:x | y,只有当x,y都为0的时候结果才为0,其它情况结果都为1。* 因为个部分只有相应位上的值有意义,其它位上都是0,所以将各部分的值进行 | 运算就能得到最终拼接好的id*/return ((timestamp - twEpoch)<<timestampLeftShift) |(datacenterId<<datacenterIdShift) |(workerId<<workerIdShift)|sequence;}/*** 获取时间戳,并于上次时间戳作比较* @param lastTimestamp 上一次获取的时间戳* @return timestamp 更新后的系统时间*/private long tilNextMillis(long lastTimestamp){long timestamp = timeGen();while(timestamp<=lastTimestamp){timestamp = timeGen();}return timestamp;}/*** 获取系统时间戳* @return 系统时间戳*/private long timeGen() {return System.currentTimeMillis();}}
Go语言实现
snowFlake.go
package alimport ("errors""fmt""sync""time"
)var mutex = sync.Mutex{}const (//初始时间戳twEpoch int64 = 1288834974657//长度为5位workerIdBits int64 = 5datacenterIdBits int64 = 5//最大值maxWorkerId int64 = -1 ^ (-1 << workerIdBits)maxDatacenterId int64 = -1 ^ (-1 << datacenterIdBits)//序列号id长度sequenceBits int64 = 12sequenceMask = -1 ^ (-1 << sequenceBits)//工作id需要左移的位数, 12位(序列号的位长)workerIdShift = sequenceBits//数据中心id需要左移的位数 序列号长+工作id长datacenterIdShift = sequenceBits + workerIdBits//时间戳左移位数 = 序列号长+工作id长+工作位长timestampLeftShift = sequenceBits + workerIdBits + datacenterIdBits
)//上次时间戳, 初始值位负值
var lastTimestamp int64 = -1type IDWorker struct {//十位的工作机器码workerId int64 //工作id 五位datacenterId int64 //数据中心id 五位//12位序列号sequence int64
}func InitIDWorker(workerId, datacenterId int64) (*IDWorker, error) {//检查参数合法性if workerId > maxWorkerId || workerId < 0 {var err = errors.New(fmt.Sprintf("worker Id can't be greater than %d or less than 0", maxWorkerId))return nil, err}if datacenterId > maxDatacenterId || datacenterId < 0 {var err = errors.New(fmt.Sprintf("datacenter Id can't be greater than %d or less than 0", maxDatacenterId))return nil, err}fmt.Printf("worker starting. timestamp left shift %d, datacenter id bits %d, worker id bits %d, sequence bits %d, workerid %d",timestampLeftShift, datacenterIdBits, workerIdBits, sequenceBits, workerId)return &IDWorker{datacenterId: datacenterId,workerId: workerId,}, nil
}/*下一个ID生成算法
*/
func (i *IDWorker) NextId() (id int64, err error) {//上锁mutex.Lock()//程序结束 释放锁defer mutex.Unlock()//先获取当前系统时间var timestamp = timeGen()//如果当前系统时间比上次获取id时间戳小就抛出异常 时钟往后移动可能会出现同样id所以这里必须抛异常结束执行if timestamp < lastTimestamp {fmt.Printf("clock is moving backwards. Rejecting requests until %d.", lastTimestamp)err = errors.New(fmt.Sprintf("Clock moved backwards. Refusing to generate id for %d milliseconds",lastTimestamp-timestamp))}//获取当前时间戳如果等于上次时间戳(同一毫秒内),则在序列号加一,否则序列号赋值为0, 从零开始if timestamp == lastTimestamp {//这是使用&sequenceMask是为了防止sequence溢出12位(前面要求了sequence的长度只能是12位)i.sequence = (i.sequence + 1) & sequenceMask//如果防止刚好移除经过&sequenceMask后 会变成0 可能会发生重复的情况//所以此时需要再次获取时间戳,并于上次时间戳作比较 直到与上次时间戳不一致返回当前时间戳避免重复if i.sequence == 0 {timestamp = tilNextMillis(lastTimestamp)}} else {//如果不在同一个时间戳中 代表该序列刚开始计数所以初始为0i.sequence = 0}//将上次时间戳值更新lastTimestamp = timestamp//返回雪花算法生成的idid = ((timestamp - twEpoch) << timestampLeftShift) |(i.datacenterId << datacenterIdShift) |(i.workerId << workerIdShift) |i.sequencereturn
}func (i IDWorker) WorkerId() int64 {return i.workerId
}
func (i IDWorker) DatacenterId() int64 {return i.datacenterId
}func (i IDWorker) Sequence() int64 {return i.sequence
}/*获取系统时间戳
*/
func timeGen() int64 {return time.Now().UnixMilli()
}/*获取时间戳,并于上次时间戳作比较
*/
func tilNextMillis(lastTimestamp int64) int64 {var timestamp = timeGen()for timestamp <= lastTimestamp {timestamp = timeGen()}return timestamp
}