目录
- 1. 为什么要用CompletableFuture
- 1.1 API
- 2. CompletableFuture Demo
- 1. 创建CompletableFuture
- 2. 定义CompletableFuture完成时和异常时需要回调的实例
- 3. CompletableFuture的优点
- 3. demo:多个CompletableFuture串行执行
- 4. demo:多个CompletableFuture并行执行
- 流程图
- 5. 使用CompletableFuture场景
1. 为什么要用CompletableFuture
使用Future获得异步执行结果时,要么调用阻塞方法get(),要么轮询看isDone()是否为true,这两种方法都不是很好,因为主线程也会被迫等待。
从Java 8开始引入了CompletableFuture,它针对Future做了改进,可以传入回调对象,当异步任务完成或者发生异常时,自动调用回调对象的回调方法。
1.1 API
1. 实例化
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier);
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier, Executor executor);public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable);
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable, Executor executor);
其中supplyAsync()用于有返回值的任务,runAsync()则用于没有返回值的任务。
Executor参数可以手动指定线程池,否则默认ForkJoinPool.commonPool()系统级公共线程池,注意:这些线程都是Daemon线程(守护线程),主线程结束,JVM中不存在其余用户线程,那么CompletableFuture的守护线程会直接退出,造成任务无法完成的问题
2. 获取结果
public T get() //阻塞直到任务完成
public T get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
public T getNow(T valueIfAbsent) //参数valueIfAbsent的意思是当计算结果不存在或者Now时刻没有完成任务,给定一个确定的值。
public T join()
join() 与get() 区别在于join() 返回计算的结果或者抛出一个unchecked异常(CompletionException),而get() 返回一个具体的异常
3. 计算完成后续操作1——complete
public CompletableFuture<T> whenComplete(BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable> action)
public CompletableFuture<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable> action)
public CompletableFuture<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable> action, Executor executor)
public CompletableFuture<T> exceptionally(Function<Throwable,? extends T> fn)
方法1和2的区别在于是否使用异步处理,2和3的区别在于是否使用自定义的线程池,前三个方法都会提供一个返回结果和可抛出异常,我们可以使用lambda表达式的来接收这两个参数,然后自己处理。 方法4,接收一个可抛出的异常,且必须return一个返回值
CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {return 10086;
});
future.whenComplete((result, error) -> {System.out.println("拨打"+result);error.printStackTrace();
});
4. 计算完成后续操作2——handle
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> handle(BiFunction<? super T,Throwable,? extends U> fn)
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> handleAsync(BiFunction<? super T,Throwable,? extends U> fn)
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> handleAsync(BiFunction<? super T,Throwable,? extends U> fn, Executor executor)
handle方法集和上面的complete方法集没有区别,同样有两个参数一个返回结果和可抛出异常,区别就在于返回值,没错,虽然同样返回CompletableFuture类型,但是里面的参数类型,handle方法是可以自定义的。
// 开启一个异步方法
CompletableFuture<List> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add("语文");list.add("数学");// 获取得到今天的所有课程return list;});// 使用handle()方法接收list数据和error异常CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = future.handle((list,error)-> {// 如果报错,就打印出异常error.printStackTrace();// 如果不报错,返回一个包含Integer的全新的CompletableFuturereturn list.size();// 注意这里的两个CompletableFuture包含的返回类型不同});
5. 计算完成的后续操作3——apply
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApply(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn)
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn)
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn, Executor executor)
apply方法和handle方法一样,都是结束计算之后的后续操作,唯一的不同是,handle方法会给出异常,可以让用户自己在内部处理,而apply方法只有一个返回结果,如果异常了,会被直接抛出,交给上一层处理。 如果不想每个链式调用都处理异常,那么就使用apply吧。
6. 计算完成的后续操作4——accept
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenAccept(Consumer<? super T> action)
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action)
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action, Executor executor)
accept()三个方法只做最终结果的消费,注意此时返回的CompletableFuture是空返回。只消费,无返回,有点像流式编程的终端操作。
7. 捕获中间产生的异常——exceptionally
public CompletableFuture<T> exceptionally(Function<Throwable, ? extends T> fn)
exceptionally() 可以帮我们捕捉到所有中间过程的异常,方法会给我们一个异常作为参数,我们可以处理这个异常,同时返回一个默认值,跟服务降级 有点像,默认值的类型和上一个操作的返回值相同。 小贴士 :向线程池提交任务的时候发生的异常属于外部异常,是无法捕捉到的,毕竟还没有开始执行任务。作者也是在触发线程池拒绝策略的时候发现的。exceptionally() 无法捕捉RejectedExecutionException
// 实例化一个CompletableFuture,返回值是Integer
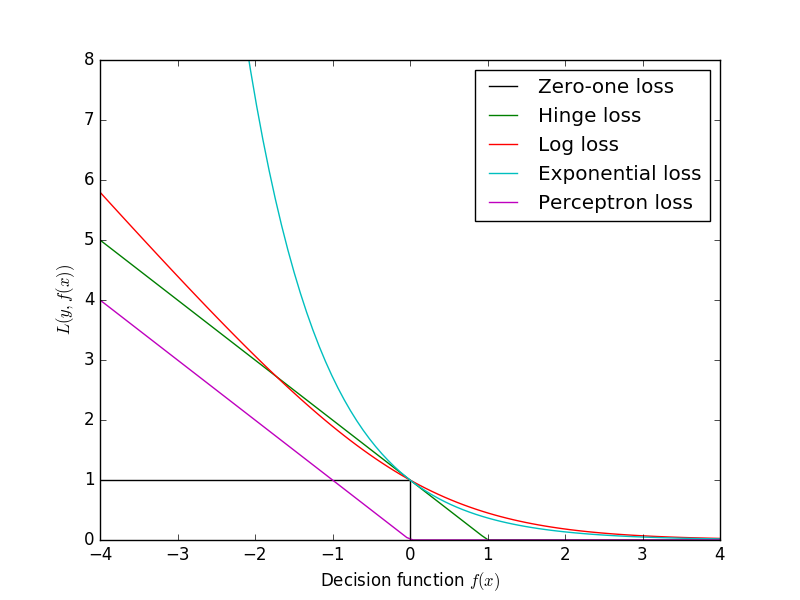
CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {// 返回nullreturn null;});CompletableFuture<String> exceptionally = future.thenApply(result -> {// 制造一个空指针异常NPEint i = result;return i;}).thenApply(result -> {// 这里不会执行,因为上面出现了异常String words = "现在是" + result + "点钟";return words;}).exceptionally(error -> {// 我们选择在这里打印出异常error.printStackTrace();// 并且当异常发生的时候,我们返回一个默认的文字return "出错啊~";});exceptionally.thenAccept(System.out::println);}
8. thenApply()
假设一个场景,我是一个小学生,我想知道今天我需要上几门课程 此时我需要两个步骤,1.根据我的名字获取我的学生信息 2.根据我的学生信息查询课程 我们可以用下面这种方式来链式调用api,使用上一步的结果进行下一步操作
CompletableFuture<List<Lesson>> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {// 根据学生姓名获取学生信息return StudentService.getStudent(name);
}).thenApply(student -> {// 再根据学生信息获取今天的课程return LessonsService.getLessons(student);
});
9. thenCombine()
假设一个场景,我是一个小学生,今天有劳技课和美术课,我需要查询到今天需要带什么东西到学校
CompletableFuture<List<String>> painting = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {// 第一个任务获取美术课需要带的东西,返回一个listList<String> stuff = new ArrayList<>();stuff.add("画笔");stuff.add("颜料");return stuff;
});
CompletableFuture<List<String>> handWork = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {// 第二个任务获取劳技课需要带的东西,返回一个listList<String> stuff = new ArrayList<>();stuff.add("剪刀");stuff.add("折纸");return stuff;
});
CompletableFuture<List<String>> total = painting// 传入handWork列表,然后得到两个CompletableFuture的参数Stuff1和2.thenCombine(handWork, (stuff1, stuff2) -> {// 合并成新的listList<String> totalStuff = Stream.of(stuff1, stuff1).flatMap(Collection::stream).collect(Collectors.toList());return totalStuff;});
System.out.println(JSONObject.toJSONString(total.join()));
10. 获取所有完成结果——allOf
public static CompletableFuture<Void> allOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs)
CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {//使用sleep()模拟耗时操作TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return 1;
});CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {return 2;
});CompletableFuture.allOf(future1, future1);
// 输出3
System.out.println(future1.join()+future2.join());
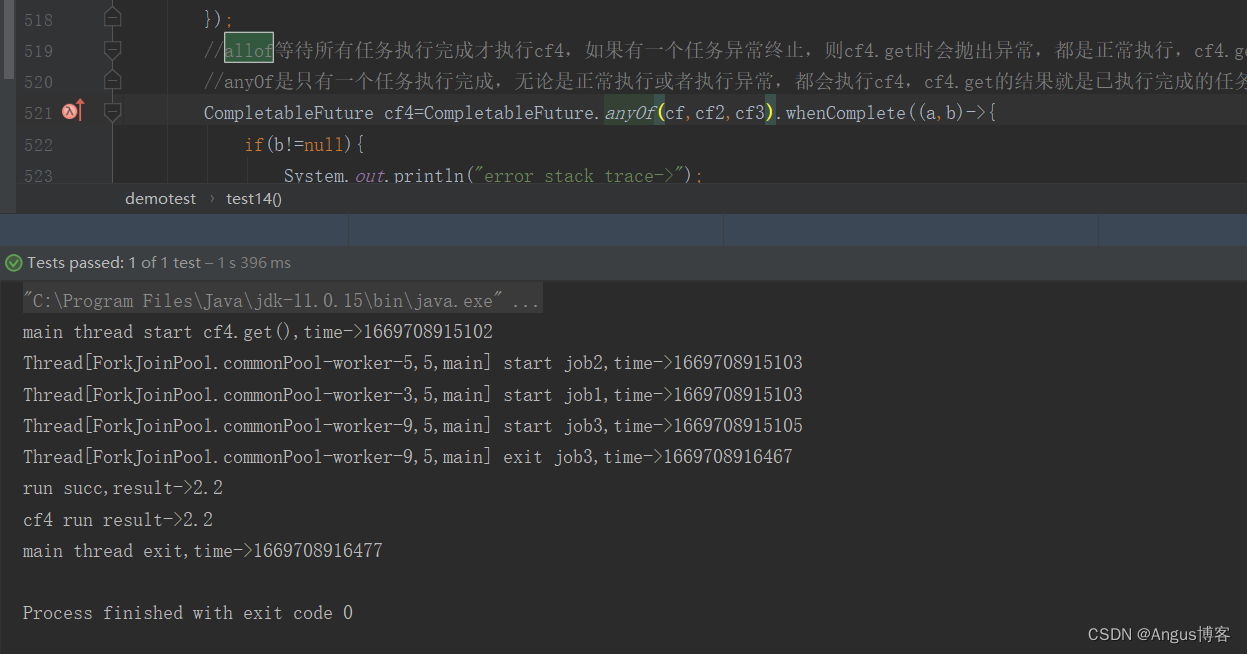
11. 获取率先完成的任务结果——anyOf
仅等待Future集合种最快结束的任务完成(有可能因为他们试图通过不同的方式计算同一个值),并返回它的结果。 小贴士 :如果最快完成的任务出现了异常,也会先返回异常,如果害怕出错可以加个exceptionally() 去处理一下可能发生的异常并设定默认返回值
public static CompletableFuture<Object> anyOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs)
CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {throw new NullPointerException();
});CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {// 睡眠3s模拟延时TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return 1;
});
CompletableFuture<Object> anyOf = CompletableFuture.anyOf(future, future2).exceptionally(error -> {error.printStackTrace();return 2;});
System.out.println(anyOf.join());
thenApplyAsync():用于串行化另一个CompletableFuture;
anyOf()和allOf():用于并行化多个CompletableFuture。
anyOf()可以实现“任意个CompletableFuture只要一个成功”,allOf()可以实现“所有CompletableFuture都必须成功”
2. CompletableFuture Demo
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {// 创建异步执行任务:CompletableFuture<Double> cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(Main::fetchPrice);// 如果执行成功:cf.thenAccept((result) -> {System.out.println("price: " + result);});// 如果执行异常:cf.exceptionally((e) -> {e.printStackTrace();return null;});// 主线程不要立刻结束,否则CompletableFuture默认使用的线程池会立刻关闭:Thread.sleep(200);}static Double fetchPrice() {try {Thread.sleep(100);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}if (Math.random() < 0.3) {throw new RuntimeException("fetch price failed!");}return 5 + Math.random() * 20;}
}
1. 创建CompletableFuture
创建一个CompletableFuture是通过CompletableFuture.supplyAsync()实现的,它需要一个实现了Supplier接口的对象:
public interface Supplier<T> {T get();
}
这里我们用lambda语法简化了一下,直接传入Main::fetchPrice,因为Main.fetchPrice()静态方法的签名符合Supplier接口的定义(除了方法名外)。
2. 定义CompletableFuture完成时和异常时需要回调的实例
完成时,CompletableFuture会调用Consumer对象:
public interface Consumer<T> {void accept(T t);
}
异常时,CompletableFuture会调用Function对象:
public interface Function<T, R> {R apply(T t);
}
3. CompletableFuture的优点
异步任务结束时,会自动回调某个对象的方法;
异步任务出错时,会自动回调某个对象的方法;
主线程设置好回调后,不再关心异步任务的执行。
3. demo:多个CompletableFuture串行执行
例如,定义两个CompletableFuture,第一个CompletableFuture根据证券名称查询证券代码,第二个CompletableFuture根据证券代码查询证券价格,这两个CompletableFuture实现串行操作如下
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {// 第一个任务:CompletableFuture<String> cfQuery = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {return queryCode("中国石油");});// cfQuery成功后继续执行下一个任务:CompletableFuture<Double> cfFetch = cfQuery.thenApplyAsync((code) -> {return fetchPrice(code);});// cfFetch成功后打印结果:cfFetch.thenAccept((result) -> {System.out.println("price: " + result);});// 主线程不要立刻结束,否则CompletableFuture默认使用的线程池会立刻关闭:Thread.sleep(2000);}static String queryCode(String name) {try {Thread.sleep(100);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}return "601857";}static Double fetchPrice(String code) {try {Thread.sleep(100);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}return 5 + Math.random() * 20;}
}
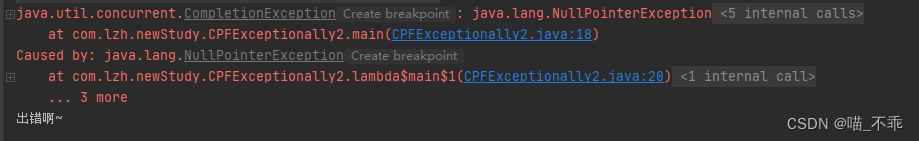
4. demo:多个CompletableFuture并行执行
例如,我们考虑这样的场景:
同时从新浪和网易查询证券代码,只要任意一个返回结果,就进行下一步查询价格,查询价格也同时从新浪和网易查询,只要任意一个返回结果,就完成操作:
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {// 两个CompletableFuture执行异步查询:CompletableFuture<String> cfQueryFromSina = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {return queryCode("中国石油", "https://finance.sina.com.cn/code/");});CompletableFuture<String> cfQueryFrom163 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {return queryCode("中国石油", "https://money.163.com/code/");});// 用anyOf合并为一个新的CompletableFuture:CompletableFuture<Object> cfQuery = CompletableFuture.anyOf(cfQueryFromSina, cfQueryFrom163);// 两个CompletableFuture执行异步查询:CompletableFuture<Double> cfFetchFromSina = cfQuery.thenApplyAsync((code) -> {return fetchPrice((String) code, "https://finance.sina.com.cn/price/");});CompletableFuture<Double> cfFetchFrom163 = cfQuery.thenApplyAsync((code) -> {return fetchPrice((String) code, "https://money.163.com/price/");});// 用anyOf合并为一个新的CompletableFuture:CompletableFuture<Object> cfFetch = CompletableFuture.anyOf(cfFetchFromSina, cfFetchFrom163);// 最终结果:cfFetch.thenAccept((result) -> {System.out.println("price: " + result);});// 主线程不要立刻结束,否则CompletableFuture默认使用的线程池会立刻关闭:Thread.sleep(200);}static String queryCode(String name, String url) {System.out.println("query code from " + url + "...");try {Thread.sleep((long) (Math.random() * 100));} catch (InterruptedException e) {}return "601857";}static Double fetchPrice(String code, String url) {System.out.println("query price from " + url + "...");try {Thread.sleep((long) (Math.random() * 100));} catch (InterruptedException e) {}return 5 + Math.random() * 20;}
}
流程图
除了anyOf()可以实现“任意个CompletableFuture只要一个成功”,allOf()可以实现“所有CompletableFuture都必须成功”,这些组合操作可以实现非常复杂的异步流程控制。
5. 使用CompletableFuture场景
- 执行比较耗时的操作时,尤其是那些依赖一个或多个远程服务的操作,使用异步任务可以改善程序的性能,加快程序的响应速度
- 使用CompletableFuture类,它提供了异常管理的机制,让你有机会抛出、管理异步任务执行种发生的异常
- 如果这些异步任务之间相互独立,或者他们之间的的某一些的结果是另一些的输入,你可以讲这些异步任务构造或合并成一个
来源 :https://www.liaoxuefeng.com/wiki/1252599548343744/1306581182447650
API:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/344431341
美团CompletableFuture详解(未整理):https://tech.meituan.com/2022/05/12/principles-and-practices-of-completablefuture.html