-
创建异步任务
-
Future.submit
-
supplyAsync / runAsync
-
-
异步回调
-
thenApply / thenApplyAsync
-
thenAccept / thenRun
-
exceptionally
-
whenComplete
-
handle
-
-
组合处理
-
thenCombine / thenAcceptBoth / runAfterBoth
-
applyToEither / acceptEither / runAfterEither
-
thenCompose
-
allOf / anyOf
-
CompletableFuture实现了CompletionStage接口和Future接口,前者是对后者的一个扩展,增加了异步回调、流式处理、多个Future组合处理的能力,使Java在处理多任务的协同工作时更加顺畅便利。
一、创建异步任务
1、Future.submit
通常的线程池接口类ExecutorService,其中execute方法的返回值是void,即无法获取异步任务的执行状态,3个重载的submit方法的返回值是Future,可以据此获取任务执行的状态和结果,示例如下:
@Testpublic void test1() throws Exception {// 创建异步执行任务:ExecutorService executorService= Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();Future<Double> cf = executorService.submit(()->{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());try {Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}if(false){throw new RuntimeException("test");}else{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());return 1.2;}});System.out.println("main thread start,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());//等待子任务执行完成,如果已完成则直接返回结果//如果执行任务异常,则get方法会把之前捕获的异常重新抛出System.out.println("run result->"+cf.get());System.out.println("main thread exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());}执行结果如下:
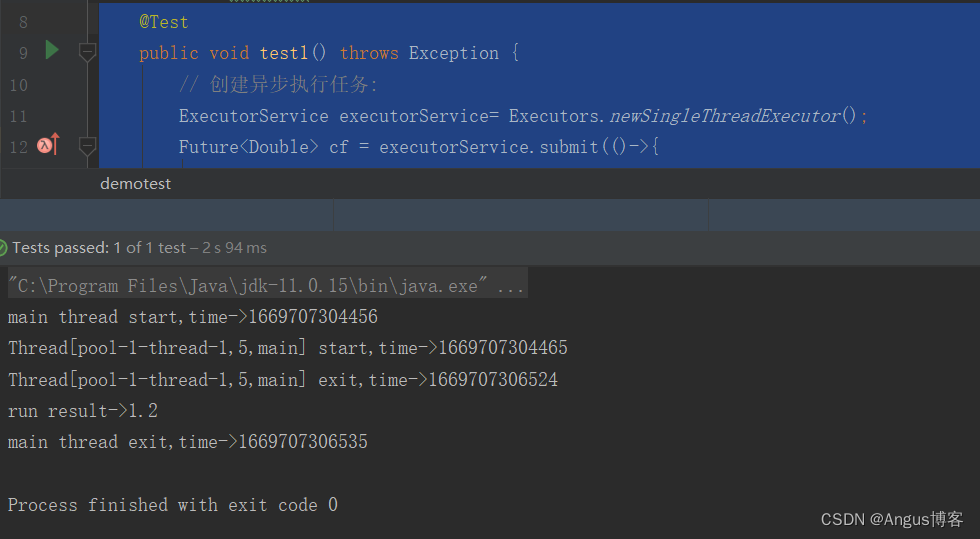
子线程是异步执行的,主线程休眠等待子线程执行完成,子线程执行完成后唤醒主线程,主线程获取任务执行结果后退出。
很多博客说使用不带等待时间限制的get方法时,如果子线程执行异常了会导致主线程长期阻塞,这其实是错误的,子线程执行异常时其异常会被捕获,然后修改任务的状态为异常结束并唤醒等待的主线程,get方法判断任务状态发生变更,就终止等待了,并抛出异常。将上述用例中if(false)改成if(true) ,执行结果如下:
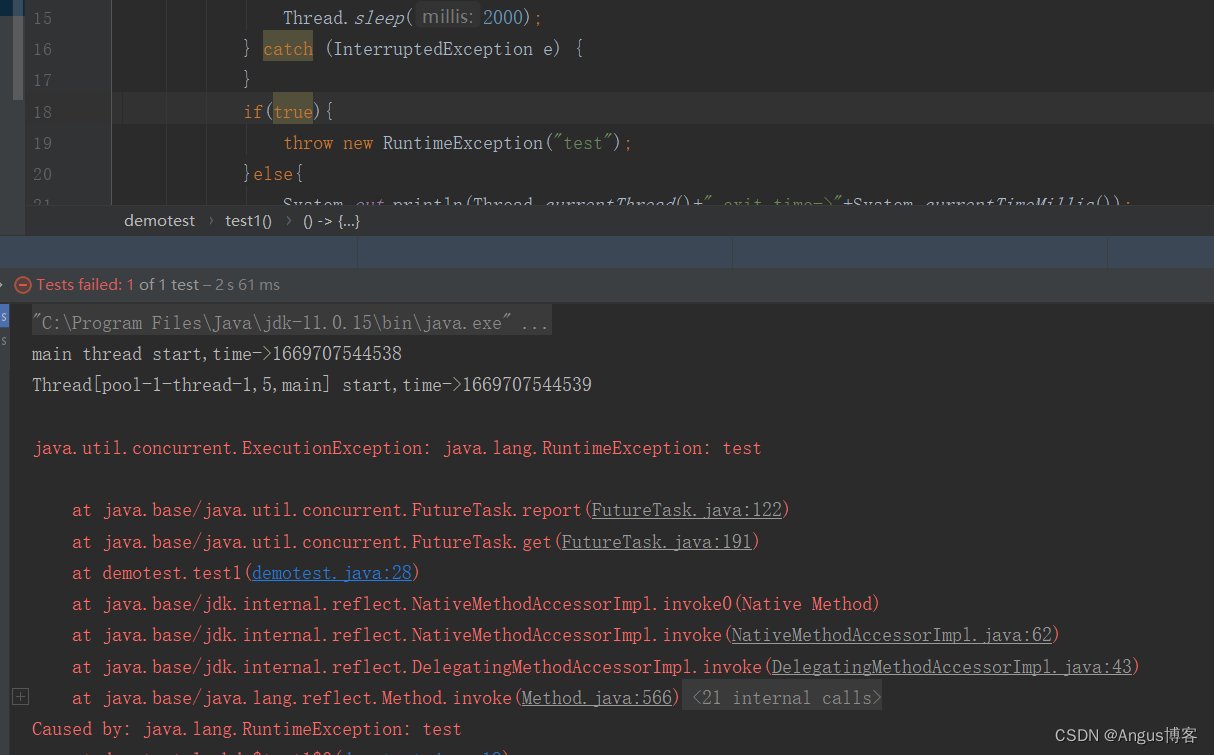
get方法抛出异常导致主线程异常终止。
2、supplyAsync / runAsync
supplyAsync表示创建带返回值的异步任务的,相当于ExecutorService submit(Callable<T> task) 方法,runAsync表示创建无返回值的异步任务,相当于ExecutorService submit(Runnable task)方法,这两方法的效果跟submit是一样的,测试用例如下:
@Testpublic void test2() throws Exception {// 创建异步执行任务,有返回值CompletableFuture<Double> cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());try {Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}if(true){throw new RuntimeException("test");}else{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());return 1.2;}});System.out.println("main thread start,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());//等待子任务执行完成System.out.println("run result->"+cf.get());System.out.println("main thread exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());}@Testpublic void test3() throws Exception {// 创建异步执行任务,无返回值CompletableFuture cf = CompletableFuture.runAsync(()->{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());try {Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}if(false){throw new RuntimeException("test");}else{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());}});System.out.println("main thread start,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());//等待子任务执行完成System.out.println("run result->"+cf.get());System.out.println("main thread exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());}这两方法各有一个重载版本,可以指定执行异步任务的Executor实现,如果不指定,默认使用ForkJoinPool.commonPool(),如果机器是单核的,则默认使用ThreadPerTaskExecutor,该类是一个内部类,每次执行execute都会创建一个新线程。测试用例如下:
@Testpublic void test4() throws Exception {ForkJoinPool pool=new ForkJoinPool();// 创建异步执行任务:CompletableFuture<Double> cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());try {Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}if(true){throw new RuntimeException("test");}else{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());return 1.2;}},pool);System.out.println("main thread start,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());//等待子任务执行完成System.out.println("run result->"+cf.get());System.out.println("main thread exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());}@Testpublic void test5() throws Exception {ExecutorService executorService= Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();// 创建异步执行任务:CompletableFuture cf = CompletableFuture.runAsync(()->{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());try {Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}if(false){throw new RuntimeException("test");}else{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());}},executorService);System.out.println("main thread start,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());//等待子任务执行完成System.out.println("run result->"+cf.get());System.out.println("main thread exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());}二、异步回调
1、thenApply / thenApplyAsync
thenApply 表示某个任务执行完成后执行的动作,即回调方法,会将该任务的执行结果即方法返回值作为入参传递到回调方法中,测试用例如下:
@Testpublic void test6() throws Exception {ForkJoinPool pool=new ForkJoinPool();// 创建异步执行任务:CompletableFuture<Double> cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job1,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());try {Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job1,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());return 1.2;},pool);//cf关联的异步任务的返回值作为方法入参,传入到thenApply的方法中//thenApply这里实际创建了一个新的CompletableFuture实例CompletableFuture<String> cf2=cf.thenApply((result)->{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job2,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());try {Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job2,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());return "test:"+result;});System.out.println("main thread start cf.get(),time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());//等待子任务执行完成System.out.println("run result->"+cf.get());System.out.println("main thread start cf2.get(),time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());System.out.println("run result->"+cf2.get());System.out.println("main thread exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());}其执行结果如下:

job1执行结束后,将job1的方法返回值作为入参传递到job2中并立即执行job2。
thenApplyAsync与thenApply的区别在于,前者是将job2提交到线程池中异步执行,实际执行job2的线程可能是另外一个线程,后者是由执行job1的线程立即执行job2,即两个job都是同一个线程执行的。将上述测试用例中thenApply改成thenApplyAsync后,执行结果如下:

从输出可知,执行job1和job2是两个不同的线程。thenApplyAsync有一个重载版本,可以指定执行异步任务的Executor实现,如果不指定,默认使用ForkJoinPool.commonPool()。
下述的多个方法,每个方法都有两个以Async结尾的方法,一个使用默认的Executor实现,一个使用指定的Executor实现,不带Async的方法是由触发该任务的线程执行该任务,带Async的方法是由触发该任务的线程将任务提交到线程池,执行任务的线程跟触发任务的线程不一定是同一个。
2、thenAccept / thenRun
thenAccept 同 thenApply 接收上一个任务的返回值作为参数,但是无返回值;thenRun 的方法没有入参,也买有返回值,测试用例如下:
@Testpublic void test7() throws Exception {ForkJoinPool pool=new ForkJoinPool();// 创建异步执行任务:CompletableFuture<Double> cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job1,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());try {Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job1,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());return 1.2;},pool);//cf关联的异步任务的返回值作为方法入参,传入到thenApply的方法中CompletableFuture cf2=cf.thenApply((result)->{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job2,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());try {Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job2,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());return "test:"+result;}).thenAccept((result)-> { //接收上一个任务的执行结果作为入参,但是没有返回值System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job3,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());try {Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}System.out.println(result);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job3,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());}).thenRun(()->{ //无入参,也没有返回值System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job4,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());try {Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}System.out.println("thenRun do something");System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job4,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());});System.out.println("main thread start cf.get(),time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());//等待子任务执行完成System.out.println("run result->"+cf.get());System.out.println("main thread start cf2.get(),time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());//cf2 等待最后一个thenRun执行完成System.out.println("run result->"+cf2.get());System.out.println("main thread exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());}其执行结果如下:
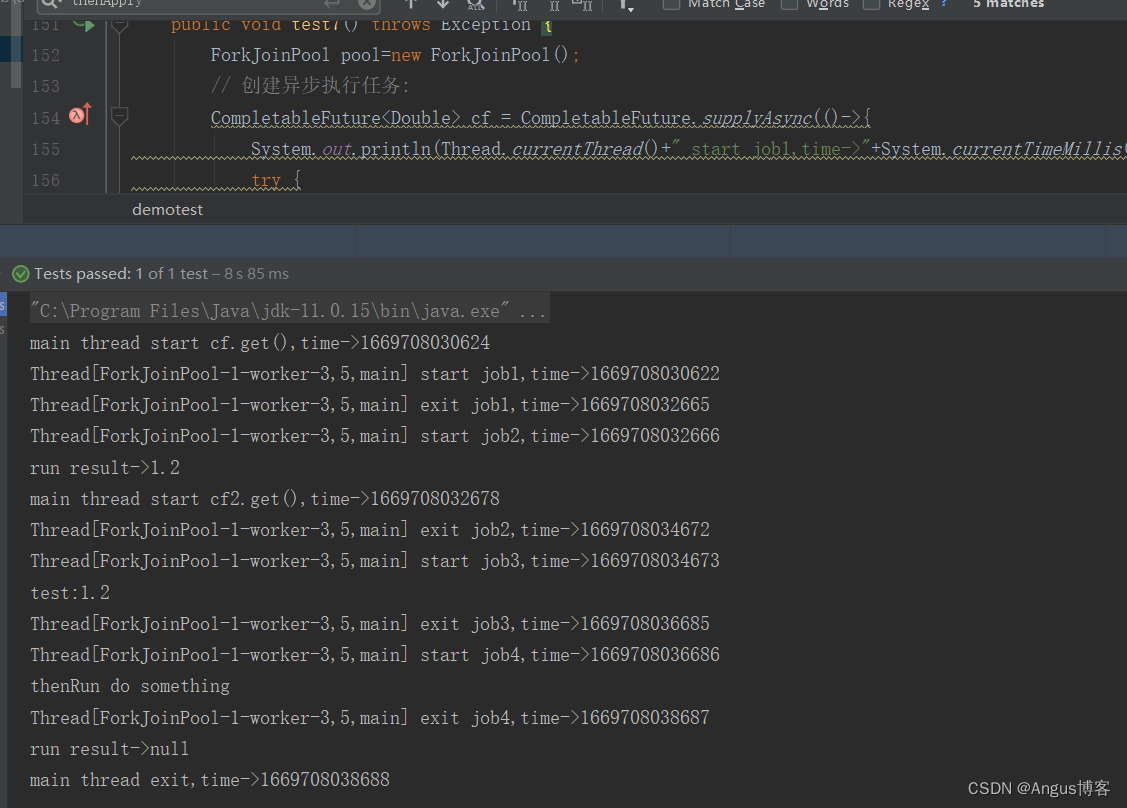
3、 exceptionally
exceptionally方法指定某个任务执行异常时执行的回调方法,会将抛出异常作为参数传递到回调方法中,如果该任务正常执行则会exceptionally方法返回的CompletionStage的result就是该任务正常执行的结果,测试用例如下:
@Testpublic void test8() throws Exception {ForkJoinPool pool=new ForkJoinPool();// 创建异步执行任务:CompletableFuture<Double> cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"job1 start,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());try {Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}if(true){throw new RuntimeException("test");}else{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"job1 exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());return 1.2;}},pool);//cf执行异常时,将抛出的异常作为入参传递给回调方法CompletableFuture<Double> cf2= cf.exceptionally((param)->{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());try {Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}System.out.println("error stack trace->");param.printStackTrace();System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());return -1.1;});//cf正常执行时执行的逻辑,如果执行异常则不调用此逻辑CompletableFuture cf3=cf.thenAccept((param)->{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"job2 start,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());try {Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}System.out.println("param->"+param);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"job2 exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());});System.out.println("main thread start,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());//等待子任务执行完成,此处无论是job2和job3都可以实现job2退出,主线程才退出,如果是cf,则主线程不会等待job2执行完成自动退出了//cf2.get时,没有异常,但是依然有返回值,就是cf的返回值System.out.println("run result->"+cf2.get());System.out.println("main thread exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());}
其输出如下:
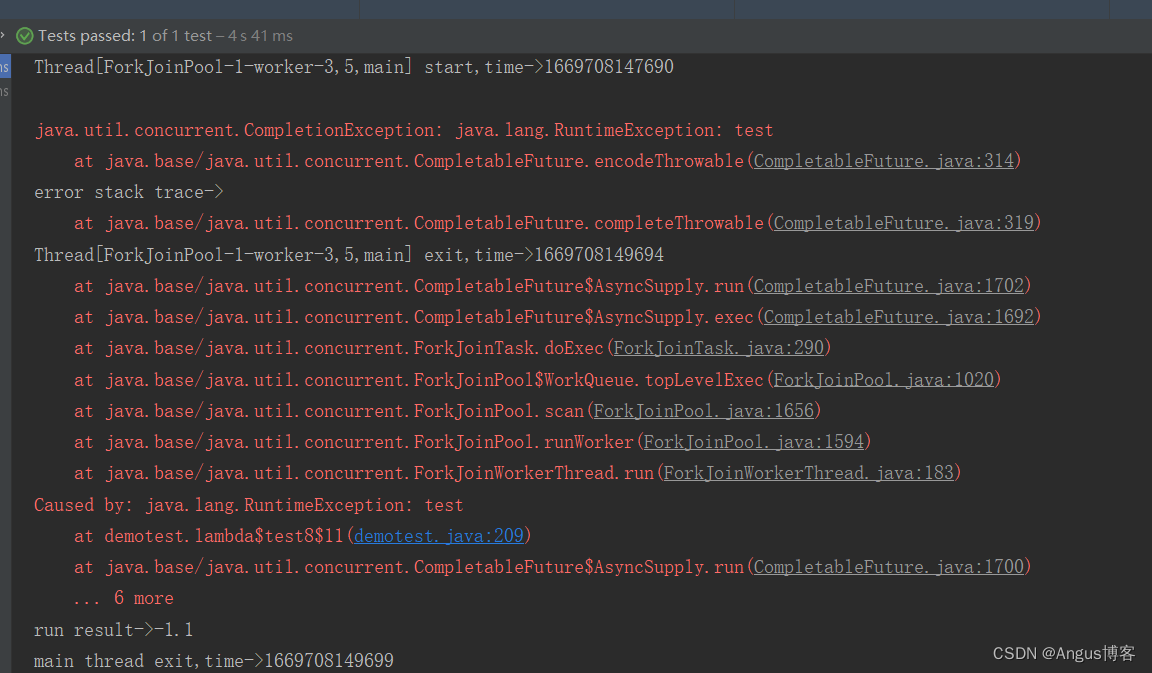
抛出异常后,只有cf2执行了,cf3没有执行。将上述示例中的if(true) 改成if(false),其输出如下:
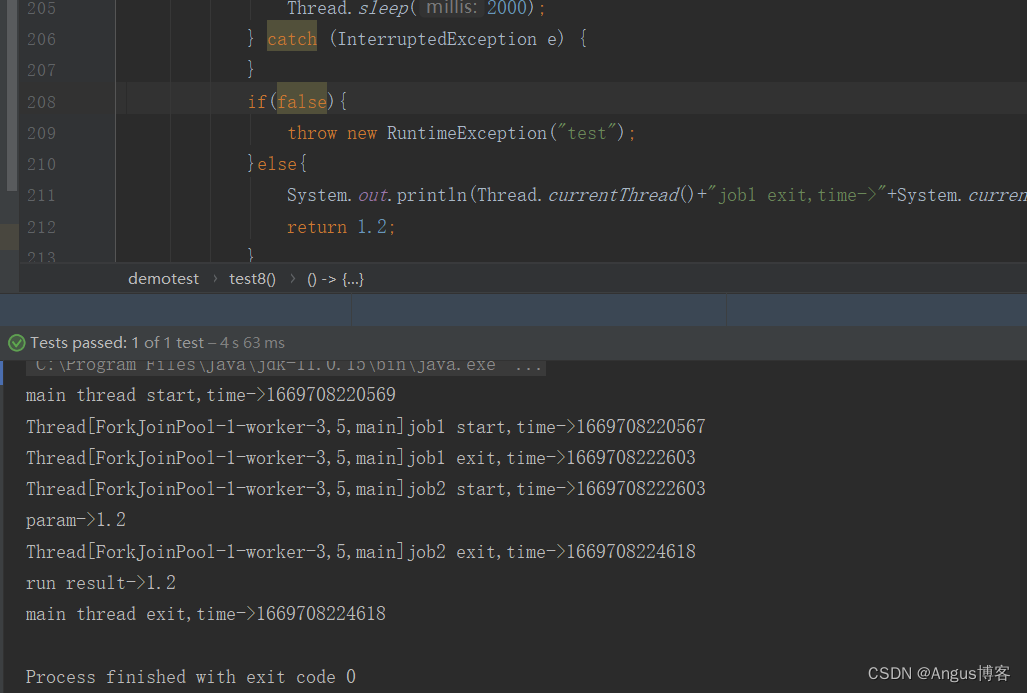
cf2没有指定,其result就是cf执行的结果,理论上cf2.get应该立即返回的,此处是等待了cf3,即job2执行完成后才返回,具体原因且待下篇源码分析时再做探讨。
4、whenComplete
whenComplete是当某个任务执行完成后执行的回调方法,会将执行结果或者执行期间抛出的异常传递给回调方法,如果是正常执行则异常为null,回调方法对应的CompletableFuture的result和该任务一致,如果该任务正常执行,则get方法返回执行结果,如果是执行异常,则get方法抛出异常。测试用例如下:
@Testpublic void test9() throws Exception {// 创建异步执行任务:CompletableFuture<Double> cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"job1 start,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());try {Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}if(false){throw new RuntimeException("test");}else{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"job1 exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());return 1.2;}});//cf执行完成后会将执行结果和执行过程中抛出的异常传入回调方法,如果是正常执行的则传入的异常为nullCompletableFuture<Double> cf2=cf.whenComplete((a,b)->{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"job2 start,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());try {Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}if(b!=null){System.out.println("error stack trace->");b.printStackTrace();}else{System.out.println("run succ,result->"+a);}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"job2 exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());});//等待子任务执行完成System.out.println("main thread start wait,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());//如果cf是正常执行的,cf2.get的结果就是cf执行的结果//如果cf是执行异常,则cf2.get会抛出异常System.out.println("run result->"+cf2.get());System.out.println("main thread exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());}执行结果如下:
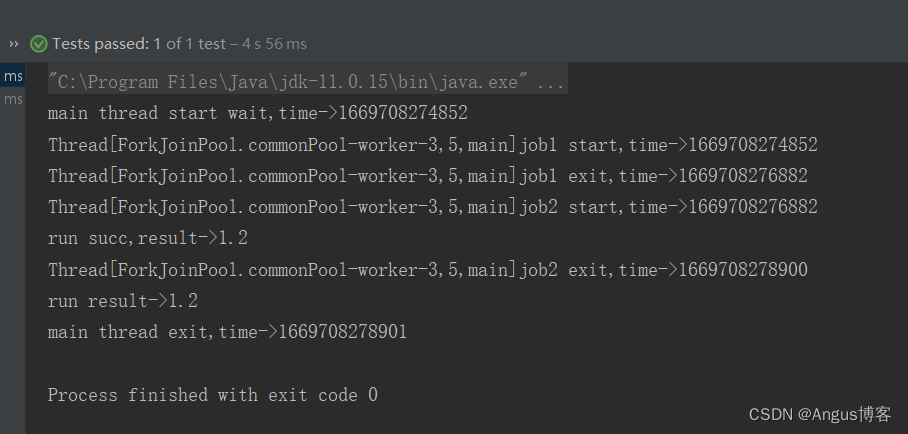
将上述示例中的if(false) 改成if(true),其输出如下:

5、handle
跟whenComplete基本一致,区别在于handle的回调方法有返回值,且handle方法返回的CompletableFuture的result是回调方法的执行结果或者回调方法执行期间抛出的异常,与原始CompletableFuture的result无关了。测试用例如下:
@Testpublic void test10() throws Exception {// 创建异步执行任务:CompletableFuture<Double> cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"job1 start,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());try {Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}if(true){throw new RuntimeException("test");}else{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"job1 exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());return 1.2;}});//cf执行完成后会将执行结果和执行过程中抛出的异常传入回调方法,如果是正常执行的则传入的异常为nullCompletableFuture<String> cf2=cf.handle((a,b)->{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"job2 start,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());try {Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}if(b!=null){System.out.println("error stack trace->");b.printStackTrace();}else{System.out.println("run succ,result->"+a);}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"job2 exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());if(b!=null){return "run error";}else{return "run succ";}});//等待子任务执行完成System.out.println("main thread start wait,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());//get的结果是cf2的返回值,跟cf没关系了System.out.println("run result->"+cf2.get());System.out.println("main thread exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());}其执行结果如下:
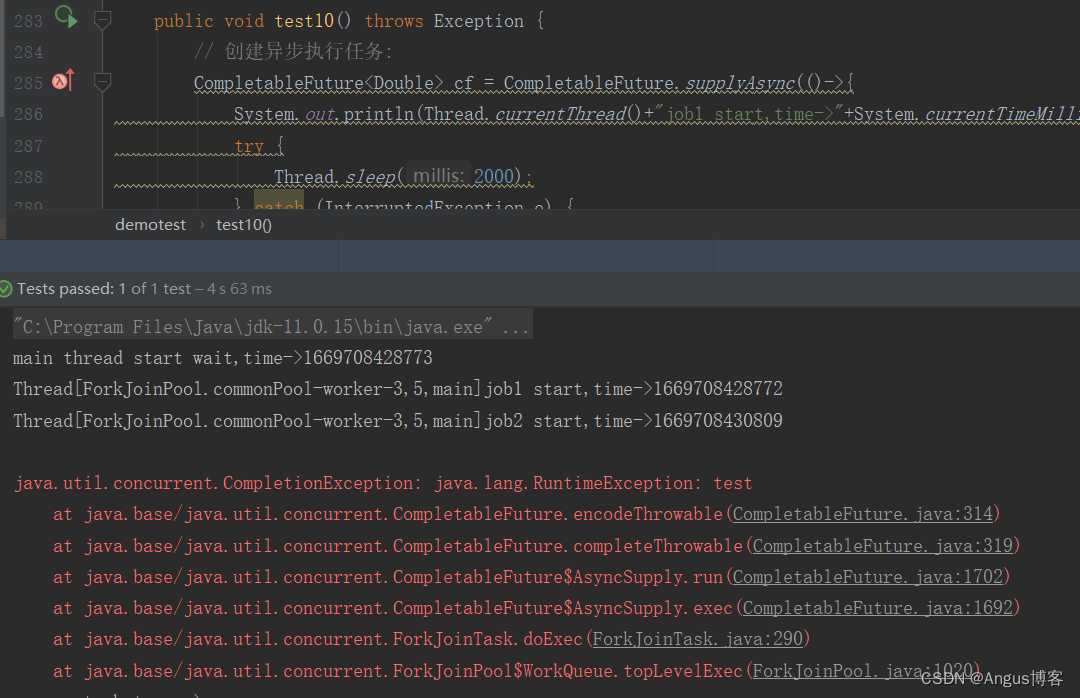
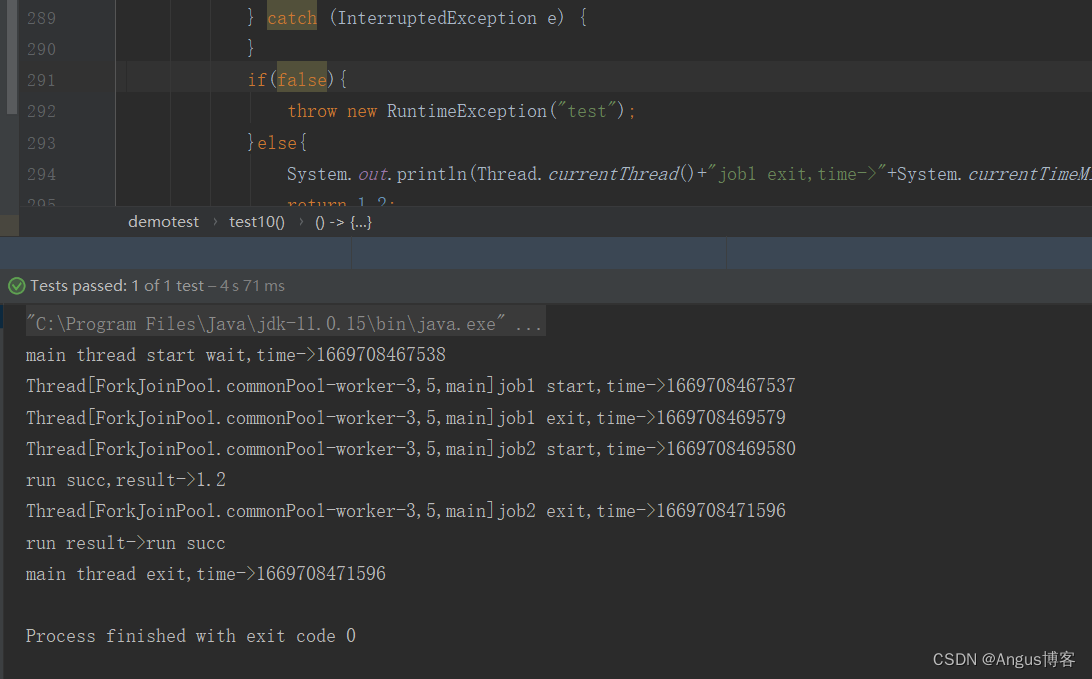
将上述示例中的if(true) 改成if(false),其输出如下:
三、组合处理
1、thenCombine / thenAcceptBoth / runAfterBoth
这三个方法都是将两个CompletableFuture组合起来,只有这两个都正常执行完了才会执行某个任务,区别在于,thenCombine会将两个任务的执行结果作为方法入参传递到指定方法中,且该方法有返回值;
thenAcceptBoth同样将两个任务的执行结果作为方法入参,但是无返回值;runAfterBoth没有入参,也没有返回值。注意两个任务中只要有一个执行异常,则将该异常信息作为指定任务的执行结果。测试用例如下:
@Testpublic void test11() throws Exception {ForkJoinPool pool=new ForkJoinPool();// 创建异步执行任务:CompletableFuture<Double> cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job1,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());try {Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job1,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());return 1.2;});CompletableFuture<Double> cf2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job2,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());try {Thread.sleep(1500);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job2,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());return 3.2;});//cf和cf2的异步任务都执行完成后,会将其执行结果作为方法入参传递给cf3,且有返回值CompletableFuture<Double> cf3=cf.thenCombine(cf2,(a,b)->{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job3,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());System.out.println("job3 param a->"+a+",b->"+b);try {Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job3,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());return a+b;});//cf和cf2的异步任务都执行完成后,会将其执行结果作为方法入参传递给cf3,无返回值CompletableFuture cf4=cf.thenAcceptBoth(cf2,(a,b)->{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job4,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());System.out.println("job4 param a->"+a+",b->"+b);try {Thread.sleep(1500);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job4,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());});//cf4和cf3都执行完成后,执行cf5,无入参,无返回值CompletableFuture cf5=cf4.runAfterBoth(cf3,()->{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job5,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}System.out.println("cf5 do something");System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job5,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());});System.out.println("main thread start cf.get(),time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());//等待子任务执行完成System.out.println("cf run result->"+cf.get());System.out.println("main thread start cf5.get(),time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());System.out.println("cf5 run result->"+cf5.get());System.out.println("main thread exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());}
其运行结果如下:
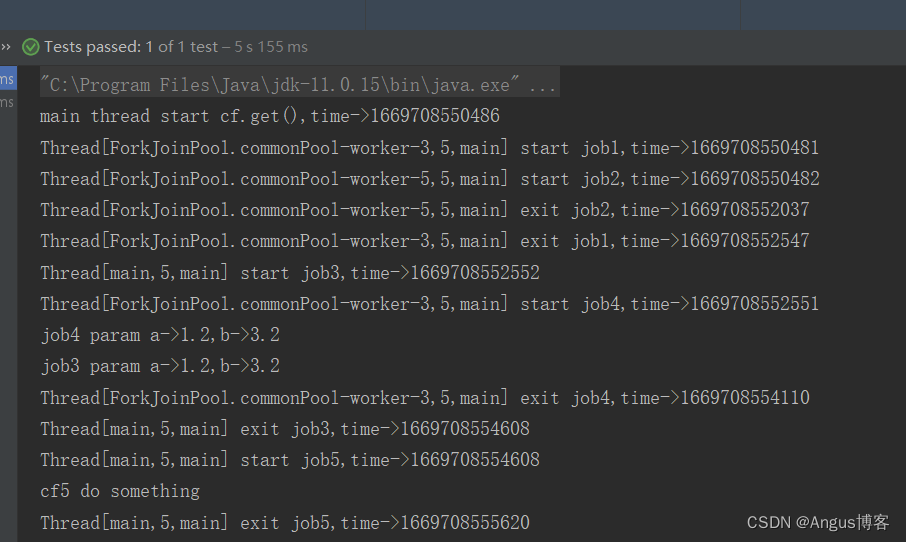
job1 和 job2几乎同时运行,job2比job1先执行完成,等job1退出后,job3和job4几乎同时开始运行,job4先退出,等job3执行完成,job5开始了,等job5执行完成后,主线程退出。
2、applyToEither / acceptEither / runAfterEither
这三个方法都是将两个CompletableFuture组合起来,只要其中一个执行完了就会执行某个任务,其区别在于applyToEither会将已经执行完成的任务的执行结果作为方法入参,并有返回值;
acceptEither同样将已经执行完成的任务的执行结果作为方法入参,但是没有返回值;runAfterEither没有方法入参,也没有返回值。注意两个任务中只要有一个执行异常,则将该异常信息作为指定任务的执行结果。测试用例如下:
@Testpublic void test12() throws Exception {// 创建异步执行任务:CompletableFuture<Double> cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job1,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());try {Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job1,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());return 1.2;});CompletableFuture<Double> cf2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job2,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());try {Thread.sleep(1500);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job2,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());return 3.2;});//cf和cf2的异步任务都执行完成后,会将其执行结果作为方法入参传递给cf3,且有返回值CompletableFuture<Double> cf3=cf.applyToEither(cf2,(result)->{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job3,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());System.out.println("job3 param result->"+result);try {Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job3,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());return result;});//cf和cf2的异步任务都执行完成后,会将其执行结果作为方法入参传递给cf3,无返回值CompletableFuture cf4=cf.acceptEither(cf2,(result)->{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job4,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());System.out.println("job4 param result->"+result);try {Thread.sleep(1500);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job4,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());});//cf4和cf3都执行完成后,执行cf5,无入参,无返回值CompletableFuture cf5=cf4.runAfterEither(cf3,()->{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job5,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}System.out.println("cf5 do something");System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job5,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());});System.out.println("main thread start cf.get(),time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());//等待子任务执行完成System.out.println("cf run result->"+cf.get());System.out.println("main thread start cf5.get(),time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());System.out.println("cf5 run result->"+cf5.get());System.out.println("main thread exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());}其运行结果如下:
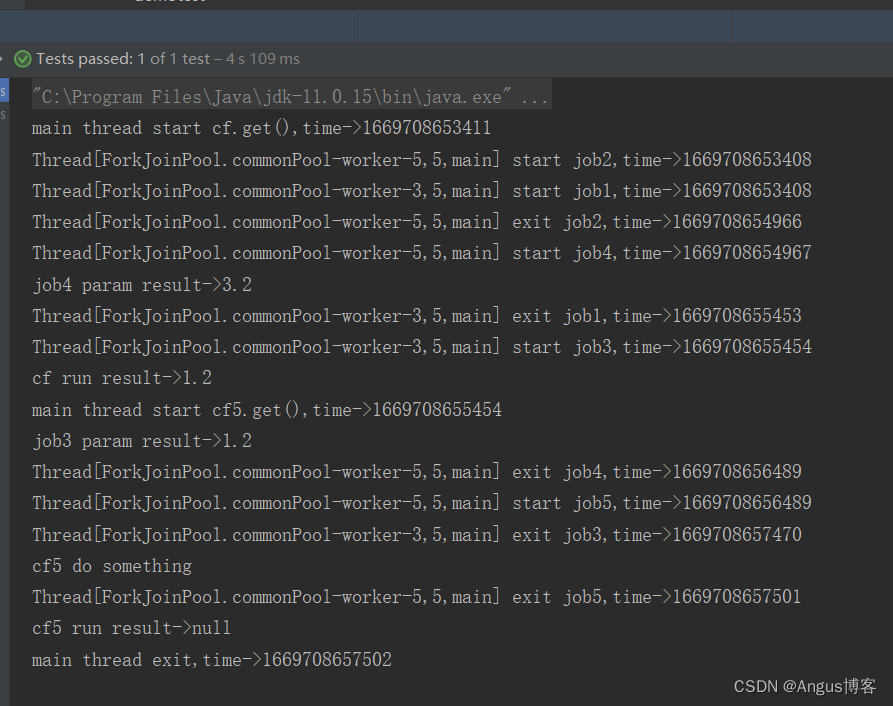
job1 和job2 同时开始运行,job2先执行完成,然后job4开始执行,理论上job3和job4应该同时开始运行,但是此时只有job4开始执行了,job3是等待job1执行完成后才开始执行,job4先于job3执行完成,然后job5开始执行,等job5执行完成后,主线程退出。上述差异且到下篇源码分析时再做探讨。
3、thenCompose
thenCompose方法会在某个任务执行完成后,将该任务的执行结果作为方法入参然后执行指定的方法,该方法会返回一个新的CompletableFuture实例,如果该CompletableFuture实例的result不为null,则返回一个基于该result的新的CompletableFuture实例;如果该CompletableFuture实例为null,则,然后执行这个新任务,测试用例如下:
@Testpublic void test13() throws Exception {// 创建异步执行任务:CompletableFuture<Double> cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job1,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());try {Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job1,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());return 1.2;});CompletableFuture<String> cf2= cf.thenCompose((param)->{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job2,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());try {Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job2,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job3,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());try {Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job3,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());return "job3 test";});});System.out.println("main thread start cf.get(),time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());//等待子任务执行完成System.out.println("cf run result->"+cf.get());System.out.println("main thread start cf2.get(),time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());System.out.println("cf2 run result->"+cf2.get());System.out.println("main thread exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());}其输出如下:
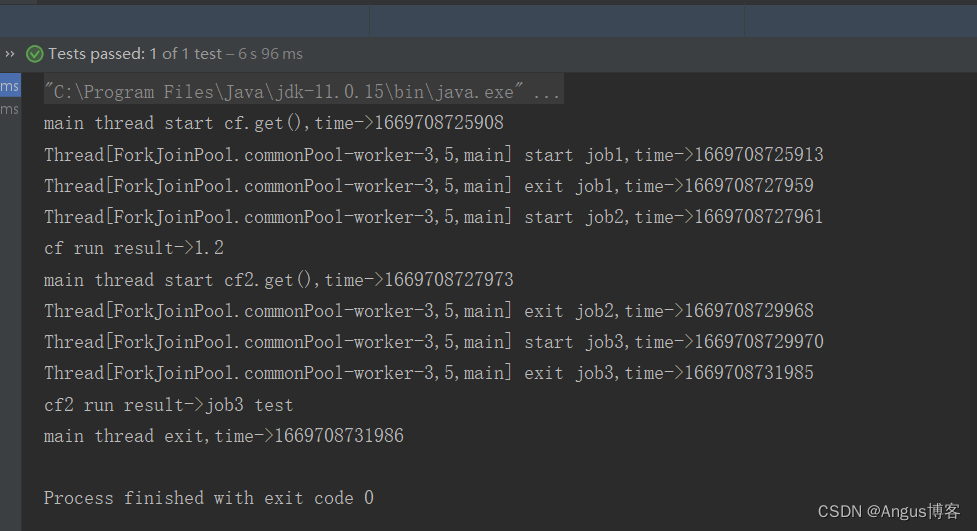
job1执行完成后job2开始执行,等job2执行完成后会把job3返回,然后执行job3,等job3执行完成后,主线程退出。
4、allOf / anyOf
allOf返回的CompletableFuture是多个任务都执行完成后才会执行,只有有一个任务执行异常,则返回的CompletableFuture执行get方法时会抛出异常,如果都是正常执行,则get返回null。
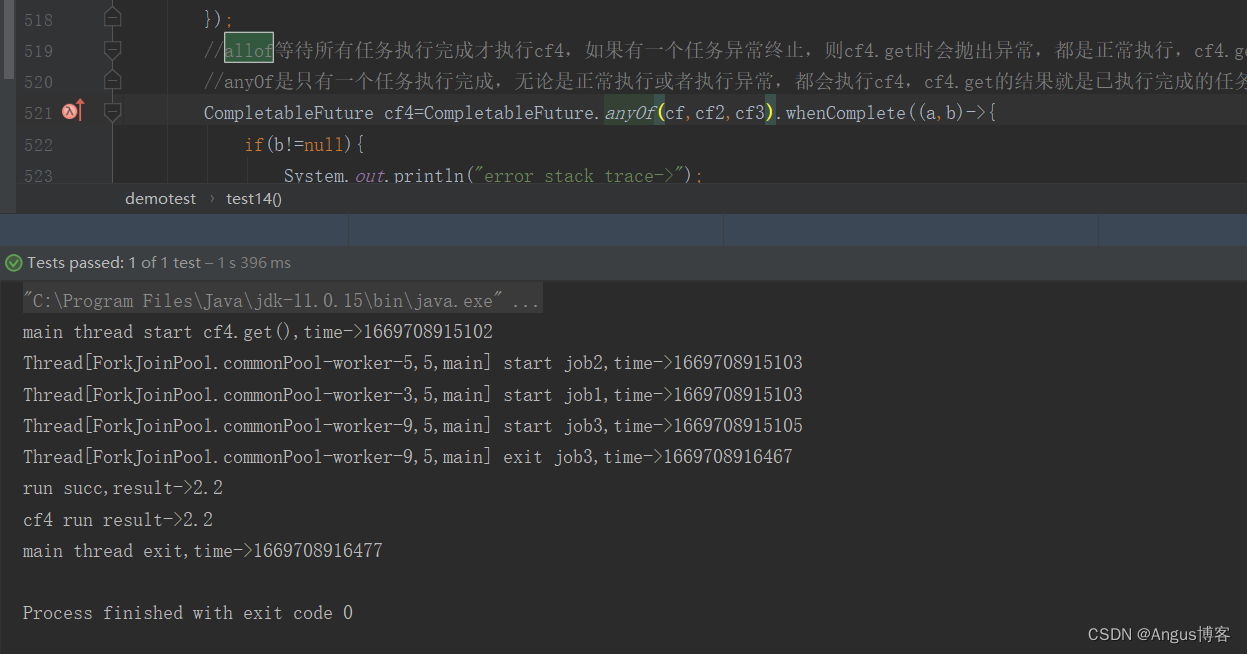
@Testpublic void test14() throws Exception {// 创建异步执行任务:CompletableFuture<Double> cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job1,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());try {Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job1,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());return 1.2;});CompletableFuture<Double> cf2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job2,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());try {Thread.sleep(1500);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job2,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());return 3.2;});CompletableFuture<Double> cf3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job3,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());try {Thread.sleep(1300);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException("test");}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job3,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());return 2.2;});//allof等待所有任务执行完成才执行cf4,如果有一个任务异常终止,则cf4.get时会抛出异常,都是正常执行,cf4.get返回null//anyOf是只有一个任务执行完成,无论是正常执行或者执行异常,都会执行cf4,cf4.get的结果就是已执行完成的任务的执行结果CompletableFuture cf4=CompletableFuture.allOf(cf,cf2,cf3).whenComplete((a,b)->{if(b!=null){System.out.println("error stack trace->");b.printStackTrace();}else{System.out.println("run succ,result->"+a);}});System.out.println("main thread start cf4.get(),time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());//等待子任务执行完成System.out.println("cf4 run result->"+cf4.get());System.out.println("main thread exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());}其输出如下:
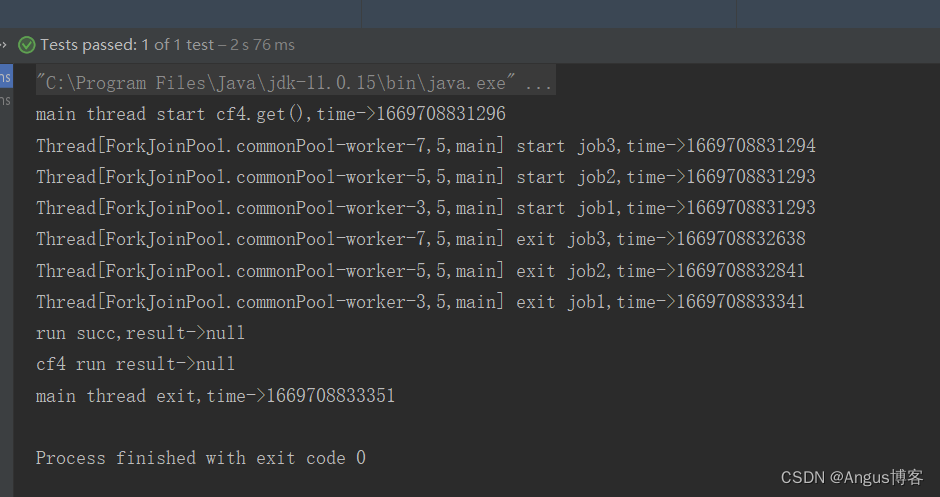
主线程等待最后一个job1执行完成后退出。anyOf返回的CompletableFuture是多个任务只要其中一个执行完成就会执行,其get返回的是已经执行完成的任务的执行结果,如果该任务执行异常,则抛出异常。将上述测试用例中allOf改成anyOf后,其输出如下: