数据描述:
该数据集包含来自数千项投资的真实历史数据的特征。你的挑战是预测与做出交易决策相关的模糊指标的价值。
Your challenge is to predict the value of an obfuscated metric relevant for making trading decisions.
这是一个代码竞赛,它依赖于时间序列 API 来确保模型不会及时向前窥视。要使用该 API,请按照评估页面上的说明进行操作。当您提交笔记本时,它将在未见过的测试中重新运行这也是一场预测比赛,最终的私人排行榜将使用训练期结束后收集的数据来确定。



import os
import gc
import sys
import joblib
import random
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from pathlib import Path
from tqdm.auto import tqdm
from datetime import datetime
from argparse import Namespace
from collections import defaultdict
from scipy.signal import find_peaksimport seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.dates as mdates
from scipy.stats import pearsonr
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler, StandardScaler
from sklearn.model_selection import TimeSeriesSplit, StratifiedKFold, GroupKFold, train_test_split, KFoldimport lightgbm as lgbimport warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
pd.set_option('max_columns', 64)def seed_everything(seed: int = 42) -> None:random.seed(seed)np.random.seed(seed)os.environ["PYTHONHASHSEED"] = str(seed)
def reduce_mem_usage(df):""" iterate through all the columns of a dataframe and modify the data typeto reduce memory usage. """start_mem = df.memory_usage().sum() / 1024**2print('Memory usage of dataframe is {:.2f} MB'.format(start_mem))for col in df.columns:col_type = df[col].dtypeif col_type != object:c_min = df[col].min()c_max = df[col].max()if str(col_type)[:3] == 'int':if c_min > np.iinfo(np.int8).min and c_max < np.iinfo(np.int8).max:df[col] = df[col].astype(np.int8)elif c_min > np.iinfo(np.int16).min and c_max < np.iinfo(np.int16).max:df[col] = df[col].astype(np.int16)elif c_min > np.iinfo(np.int32).min and c_max < np.iinfo(np.int32).max:df[col] = df[col].astype(np.int32)elif c_min > np.iinfo(np.int64).min and c_max < np.iinfo(np.int64).max:df[col] = df[col].astype(np.int64) else:if c_min > np.finfo(np.float16).min and c_max < np.finfo(np.float16).max:df[col] = df[col].astype(np.float16)elif c_min > np.finfo(np.float32).min and c_max < np.finfo(np.float32).max:df[col] = df[col].astype(np.float32)else:df[col] = df[col].astype(np.float64)else:df[col] = df[col].astype('category')end_mem = df.memory_usage().sum() / 1024**2print('Memory usage after optimization is: {:.2f} MB'.format(end_mem))print('Decreased by {:.1f}%'.format(100 * (start_mem - end_mem) / start_mem))return df# https://www.kaggle.com/joelqv/grouptimeseriescv-catboost-gpu
from sklearn.model_selection._split import _BaseKFold, indexable, _num_samples
from sklearn.utils.validation import _deprecate_positional_args# https://github.com/getgaurav2/scikit-learn/blob/d4a3af5cc9da3a76f0266932644b884c99724c57/sklearn/model_selection/_split.py#L2243
class GroupTimeSeriesSplit(_BaseKFold):"""Time Series cross-validator variant with non-overlapping groups.Provides train/test indices to split time series data samplesthat are observed at fixed time intervals according to athird-party provided group.In each split, test indices must be higher than before, and thus shufflingin cross validator is inappropriate.This cross-validation object is a variation of :class:`KFold`.In the kth split, it returns first k folds as train set and the(k+1)th fold as test set.The same group will not appear in two different folds (the number ofdistinct groups has to be at least equal to the number of folds).Note that unlike standard cross-validation methods, successivetraining sets are supersets of those that come before them.Read more in the :ref:`User Guide <cross_validation>`.Parameters----------n_splits : int, default=5Number of splits. Must be at least 2.max_train_size : int, default=NoneMaximum size for a single training set.Examples-------->>> import numpy as np>>> from sklearn.model_selection import GroupTimeSeriesSplit>>> groups = np.array(['a', 'a', 'a', 'a', 'a', 'a',\'b', 'b', 'b', 'b', 'b',\'c', 'c', 'c', 'c',\'d', 'd', 'd'])>>> gtss = GroupTimeSeriesSplit(n_splits=3)>>> for train_idx, test_idx in gtss.split(groups, groups=groups):... print("TRAIN:", train_idx, "TEST:", test_idx)... print("TRAIN GROUP:", groups[train_idx],\"TEST GROUP:", groups[test_idx])TRAIN: [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5] TEST: [6, 7, 8, 9, 10]TRAIN GROUP: ['a' 'a' 'a' 'a' 'a' 'a']\TEST GROUP: ['b' 'b' 'b' 'b' 'b']TRAIN: [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10] TEST: [11, 12, 13, 14]TRAIN GROUP: ['a' 'a' 'a' 'a' 'a' 'a' 'b' 'b' 'b' 'b' 'b']\TEST GROUP: ['c' 'c' 'c' 'c']TRAIN: [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14]\TEST: [15, 16, 17]TRAIN GROUP: ['a' 'a' 'a' 'a' 'a' 'a' 'b' 'b' 'b' 'b' 'b' 'c' 'c' 'c' 'c']\TEST GROUP: ['d' 'd' 'd']"""@_deprecate_positional_argsdef __init__(self, n_splits=5, *, max_train_size=None):super().__init__(n_splits, shuffle=False, random_state=None)self.max_train_size = max_train_sizedef split(self, X, y=None, groups=None):"""Generate indices to split data into training and test set.Parameters----------X : array-like of shape (n_samples, n_features)Training data, where n_samples is the number of samplesand n_features is the number of features.y : array-like of shape (n_samples,)Always ignored, exists for compatibility.groups : array-like of shape (n_samples,)Group labels for the samples used while splitting the dataset intotrain/test set.Yields------train : ndarrayThe training set indices for that split.test : ndarrayThe testing set indices for that split."""if groups is None:raise ValueError("The 'groups' parameter should not be None")X, y, groups = indexable(X, y, groups)n_samples = _num_samples(X)n_splits = self.n_splitsn_folds = n_splits + 1group_dict = {}u, ind = np.unique(groups, return_index=True)unique_groups = u[np.argsort(ind)]n_samples = _num_samples(X)n_groups = _num_samples(unique_groups)for idx in np.arange(n_samples):if groups[idx] in group_dict:group_dict[groups[idx]].append(idx)else:group_dict[groups[idx]] = [idx]if n_folds > n_groups:raise ValueError(("Cannot have number of folds={0} greater than"" the number of groups={1}").format(n_folds, n_groups))group_test_size = n_groups // n_foldsgroup_test_starts = range(n_groups - n_splits * group_test_size, n_groups, group_test_size)for group_test_start in group_test_starts:train_array = []test_array = []for train_group_idx in unique_groups[:group_test_start]:train_array_tmp = group_dict[train_group_idx]train_array = np.sort(np.unique(np.concatenate((train_array, train_array_tmp)), axis=None),axis=None,)train_end = train_array.sizeif self.max_train_size and self.max_train_size < train_end:train_array = train_array[train_end - self.max_train_size : train_end]for test_group_idx in unique_groups[group_test_start : group_test_start + group_test_size]:test_array_tmp = group_dict[test_group_idx]test_array = np.sort(np.unique(np.concatenate((test_array, test_array_tmp)), axis=None),axis=None,)yield [int(i) for i in train_array], [int(i) for i in test_array]from sklearn.utils import check_random_state
from sklearn.utils.multiclass import type_of_target
from sklearn.utils.validation import _num_samples, column_or_1dclass StratifiedGroupKFold(_BaseKFold):"""Stratified K-Folds iterator variant with non-overlapping groups.This cross-validation object is a variation of StratifiedKFold attempts toreturn stratified folds with non-overlapping groups. The folds are made bypreserving the percentage of samples for each class.The same group will not appear in two different folds (the number ofdistinct groups has to be at least equal to the number of folds).The difference between GroupKFold and StratifiedGroupKFold is thatthe former attempts to create balanced folds such that the number ofdistinct groups is approximately the same in each fold, whereasStratifiedGroupKFold attempts to create folds which preserve thepercentage of samples for each class as much as possible given theconstraint of non-overlapping groups between splits.Read more in the :ref:`User Guide <cross_validation>`.Parameters----------n_splits : int, default=5Number of folds. Must be at least 2.shuffle : bool, default=FalseWhether to shuffle each class's samples before splitting into batches.Note that the samples within each split will not be shuffled.This implementation can only shuffle groups that have approximately thesame y distribution, no global shuffle will be performed.random_state : int or RandomState instance, default=NoneWhen `shuffle` is True, `random_state` affects the ordering of theindices, which controls the randomness of each fold for each class.Otherwise, leave `random_state` as `None`.Pass an int for reproducible output across multiple function calls.See :term:`Glossary <random_state>`.Examples-------->>> import numpy as np>>> from sklearn.model_selection import StratifiedGroupKFold>>> X = np.ones((17, 2))>>> y = np.array([0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0])>>> groups = np.array([1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 4, 5, 5, 5, 5, 6, 6, 7, 8, 8])>>> cv = StratifiedGroupKFold(n_splits=3)>>> for train_idxs, test_idxs in cv.split(X, y, groups):... print("TRAIN:", groups[train_idxs])... print(" ", y[train_idxs])... print(" TEST:", groups[test_idxs])... print(" ", y[test_idxs])TRAIN: [1 1 2 2 4 5 5 5 5 8 8][0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0]TEST: [3 3 3 6 6 7][1 1 1 0 0 0]TRAIN: [3 3 3 4 5 5 5 5 6 6 7][1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]TEST: [1 1 2 2 8 8][0 0 1 1 0 0]TRAIN: [1 1 2 2 3 3 3 6 6 7 8 8][0 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0]TEST: [4 5 5 5 5][1 0 0 0 0]Notes-----The implementation is designed to:* Mimic the behavior of StratifiedKFold as much as possible for trivialgroups (e.g. when each group contains only one sample).* Be invariant to class label: relabelling ``y = ["Happy", "Sad"]`` to``y = [1, 0]`` should not change the indices generated.* Stratify based on samples as much as possible while keepingnon-overlapping groups constraint. That means that in some cases whenthere is a small number of groups containing a large number of samplesthe stratification will not be possible and the behavior will be closeto GroupKFold.See also--------StratifiedKFold: Takes class information into account to build folds whichretain class distributions (for binary or multiclass classificationtasks).GroupKFold: K-fold iterator variant with non-overlapping groups."""def __init__(self, n_splits=5, shuffle=False, random_state=None):super().__init__(n_splits=n_splits, shuffle=shuffle, random_state=random_state)def _iter_test_indices(self, X, y, groups):# Implementation is based on this kaggle kernel:# https://www.kaggle.com/jakubwasikowski/stratified-group-k-fold-cross-validation# and is a subject to Apache 2.0 License. You may obtain a copy of the# License at http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0# Changelist:# - Refactored function to a class following scikit-learn KFold# interface.# - Added heuristic for assigning group to the least populated fold in# cases when all other criteria are equal# - Swtch from using python ``Counter`` to ``np.unique`` to get class# distribution# - Added scikit-learn checks for input: checking that target is binary# or multiclass, checking passed random state, checking that number# of splits is less than number of members in each class, checking# that least populated class has more members than there are splits.rng = check_random_state(self.random_state)y = np.asarray(y)type_of_target_y = type_of_target(y)allowed_target_types = ("binary", "multiclass")if type_of_target_y not in allowed_target_types:raise ValueError("Supported target types are: {}. Got {!r} instead.".format(allowed_target_types, type_of_target_y))y = column_or_1d(y)_, y_inv, y_cnt = np.unique(y, return_inverse=True, return_counts=True)if np.all(self.n_splits > y_cnt):raise ValueError("n_splits=%d cannot be greater than the"" number of members in each class." % (self.n_splits))n_smallest_class = np.min(y_cnt)if self.n_splits > n_smallest_class:warnings.warn("The least populated class in y has only %d"" members, which is less than n_splits=%d."% (n_smallest_class, self.n_splits),UserWarning,)n_classes = len(y_cnt)_, groups_inv, groups_cnt = np.unique(groups, return_inverse=True, return_counts=True)y_counts_per_group = np.zeros((len(groups_cnt), n_classes))for class_idx, group_idx in zip(y_inv, groups_inv):y_counts_per_group[group_idx, class_idx] += 1y_counts_per_fold = np.zeros((self.n_splits, n_classes))groups_per_fold = defaultdict(set)if self.shuffle:rng.shuffle(y_counts_per_group)# Stable sort to keep shuffled order for groups with the same# class distribution variancesorted_groups_idx = np.argsort(-np.std(y_counts_per_group, axis=1), kind="mergesort")for group_idx in sorted_groups_idx:group_y_counts = y_counts_per_group[group_idx]best_fold = self._find_best_fold(y_counts_per_fold=y_counts_per_fold,y_cnt=y_cnt,group_y_counts=group_y_counts,)y_counts_per_fold[best_fold] += group_y_countsgroups_per_fold[best_fold].add(group_idx)for i in range(self.n_splits):test_indices = [idxfor idx, group_idx in enumerate(groups_inv)if group_idx in groups_per_fold[i]]yield test_indicesdef _find_best_fold(self, y_counts_per_fold, y_cnt, group_y_counts):best_fold = Nonemin_eval = np.infmin_samples_in_fold = np.inffor i in range(self.n_splits):y_counts_per_fold[i] += group_y_counts# Summarise the distribution over classes in each proposed foldstd_per_class = np.std(y_counts_per_fold / y_cnt.reshape(1, -1), axis=0)y_counts_per_fold[i] -= group_y_countsfold_eval = np.mean(std_per_class)samples_in_fold = np.sum(y_counts_per_fold[i])is_current_fold_better = (fold_eval < min_evalor np.isclose(fold_eval, min_eval)and samples_in_fold < min_samples_in_fold)if is_current_fold_better:min_eval = fold_evalmin_samples_in_fold = samples_in_foldbest_fold = ireturn best_fold#https://www.kaggle.com/c/ubiquant-market-prediction/discussion/304036
from typing import Tuple
import numpy as npclass GroupTimeSeriesSplit:"""Custom class to create a Group Time Series Split. We ensurethat the time id values that are in the testing data are not a partof the training data & the splits are temporal"""def __init__(self, n_folds: int, holdout_size: int, groups: str) -> None:self.n_folds = n_foldsself.holdout_size = holdout_sizeself.groups = groupsdef split(self, X) -> Tuple[np.array, np.array]:# Take the group column and get the unique valuesunique_time_ids = np.unique(self.groups.values)# Split the time ids into the length of the holdout size# and reverse so we work backwards in time. Also, makes# it easier to get the correct time_id values per# splitarray_split_time_ids = np.array_split(unique_time_ids, len(unique_time_ids) // self.holdout_size)[::-1]# Get the first n_folds valuesarray_split_time_ids = array_split_time_ids[:self.n_folds]for time_ids in array_split_time_ids:# Get test index - time id values that are in the time_idstest_condition = X['time_id'].isin(time_ids)test_index = X.loc[test_condition].index# Get train index - The train index will be the time# id values right up until the minimum value in the test# data - we can also add a gap to this step by# time id < (min - gap)train_condition = X['time_id'] < (np.min(time_ids))train_index = X.loc[train_condition].indexyield train_index, test_indexargs = Namespace(debug=False,seed=21,folds=5,workers=4,min_time_id=None, holdout=False,cv_method="group",num_bins=16,holdout_size=100,outlier_threshold=0.001,trading_days_per_year=250, # chinese stock market trading days per year (roughly)add_investment_id_model=False,data_path=Path("../input/ubiquant-parquet/"),just_eda=True,
)
seed_everything(args.seed)if args.debug:setattr(args, 'min_time_id', 1150)assert args.cv_method in {"kfold", "group", "stratified", "time", "group_time", "time_range"}, "unknown cv method"
assert args.data_path.exists(), "data_path not exists"%%time
train = pd.read_parquet(args.data_path.joinpath("train_low_mem.parquet"))
assert train.isnull().any().sum() == 0, "null exists."
assert train.row_id.str.extract(r"(?P<time_id>\d+)_(?P<investment_id>\d+)").astype(train.time_id.dtype).equals(train[["time_id", "investment_id"]]), "row_id!=time_id_investment_id"
assert train.time_id.is_monotonic_increasing, "time_id not monotonic increasing"![]()




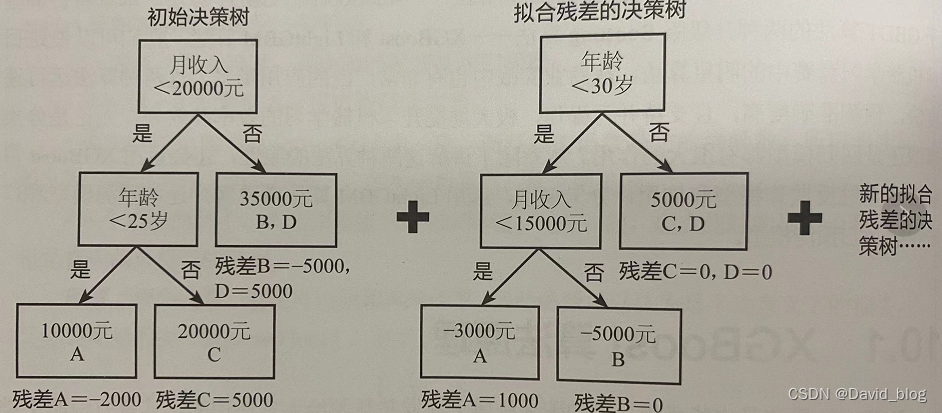
![[机器学习] 模型融合GBDT(xgb/lgbm/rf)+LR 的原理及实践](https://img-blog.csdn.net/201810091707037?watermark/2/text/aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L2Fuc2h1YWlfYXcx/font/5a6L5L2T/fontsize/400/fill/I0JBQkFCMA==/dissolve/70)

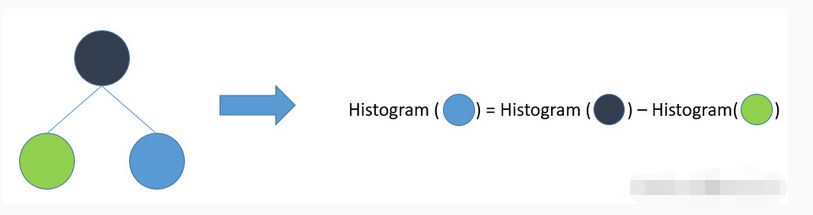


![[C++] OpenCasCade空间几何库的模型展现](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/20190104124903515.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L20wXzM4MTI1Mjc4,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)