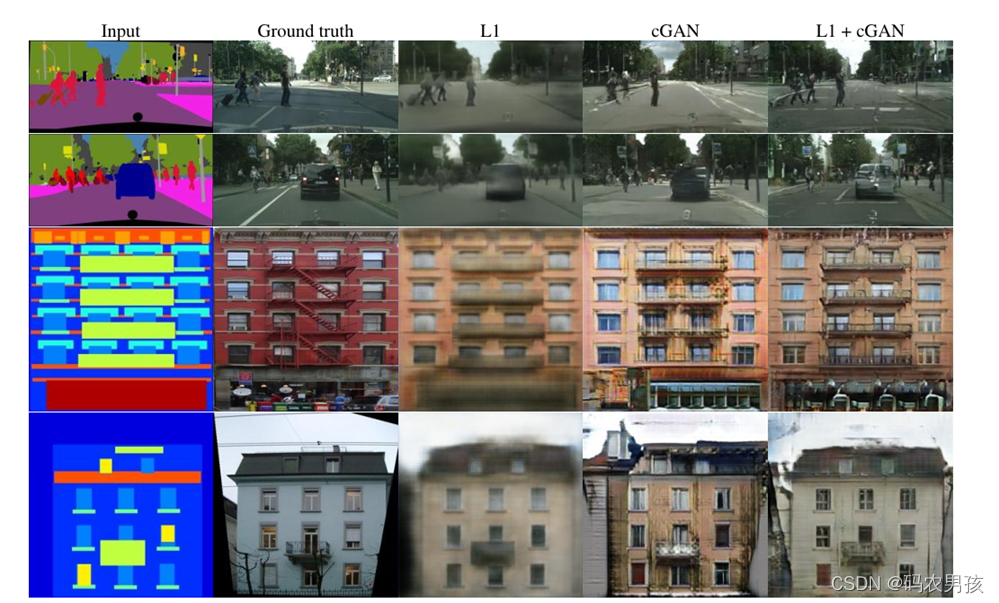
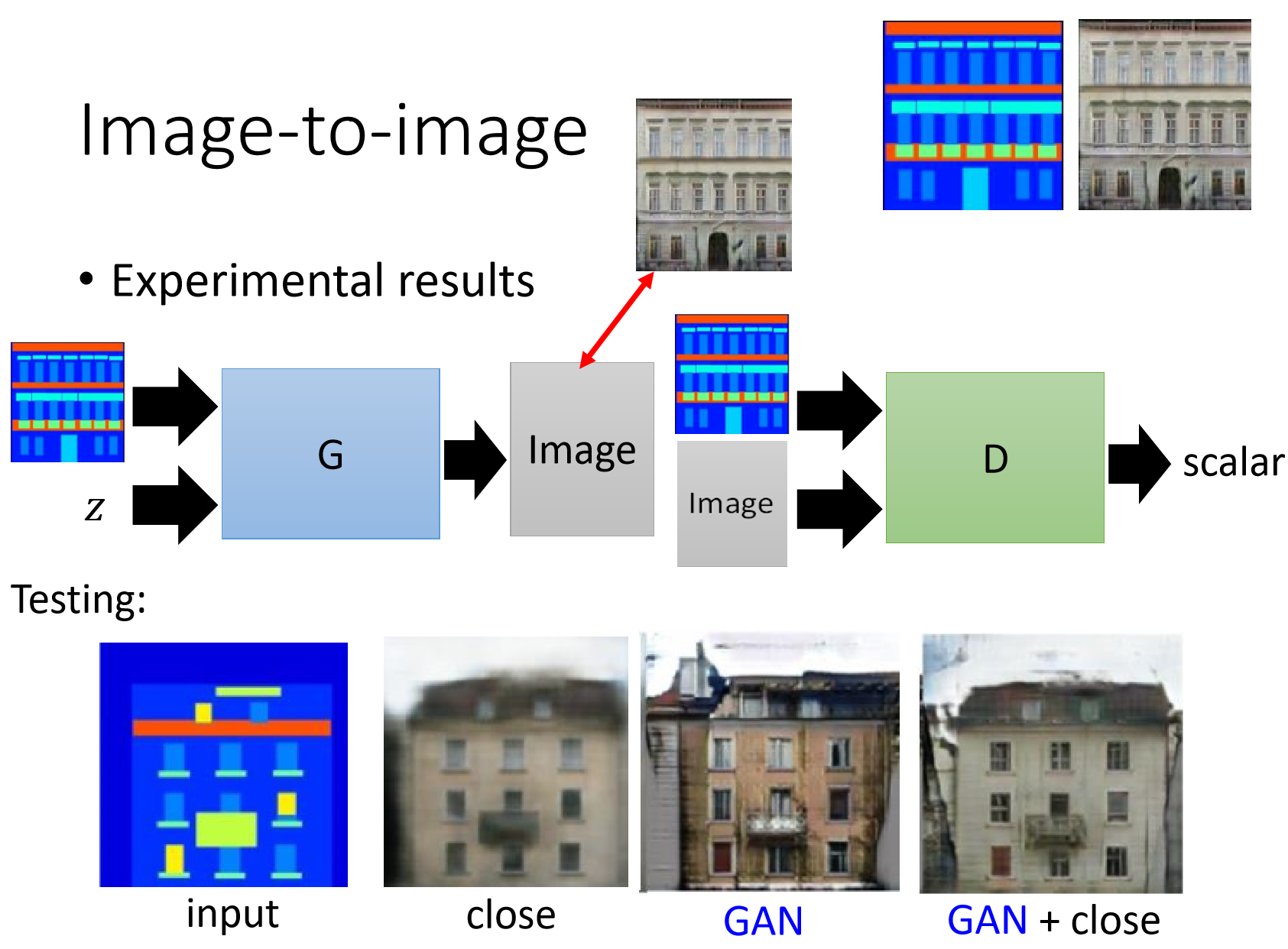
Pix2pix算法(Image-to-Image Translation,图像翻译),它的核心技术有三点:基于条件GAN的损失函数,基于U-Net的生成器和基于PatchGAN的判别器。Pix2Pix能够在诸多图像翻译任务上取得令人惊艳的效果,但因为它的输入是图像对,因此它得到的模型还是有偏的。这里的有偏指的是模型能够在与数据集近似的 的情况下得到令人满意的生成内容,但是如果输入 与训练集的偏差过大,Pix2Pix得到的结果便不那么理想了。
条件GAN
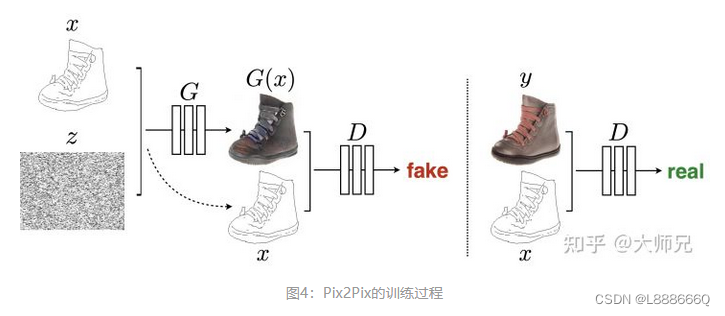
如图,鉴别器D学习对假图片(由生成器合成)和真实图片组进行分类。生成器G,学会欺骗鉴别器。与普通GAN不同,生成器和鉴别器都观察输入的轮廓图与生成图片或真实图片,普通GAN直接输入生成图片或真实图片。
输入图像用y表示,输入图像的边缘图像用x表示,pix2pix在训练时需要成对的图像(x和y)。x作为生成器G的输入(随机噪声z,去掉z不会对生成效果有太大影响,但假如将x和z合并在一起作为G的输入,可以得到更多样的输出)得到生成图像G(x),然后将G(x)和x基于通道维度合并在一起,最后作为判别器D的输入得到预测概率值,该预测概率值表示输入是否是一对真实图像,概率值越接近1表示判别器D越肯定输入是一对真实图像。另外真实图像y和x也基于通道维度合并在一起,作为判别器D的输入得到概率预测值。因此判别器D的训练目标就是在输入不是一对真实图像(x和G(x))时输出小的概率值(比如最小是0),在输入是一对真实图像(x和y)时输出大的概率值(比如最大是1)。生成器G的训练目标就是使得生成的G(x)和x作为判别器D的输入时,判别器D输出的概率值尽可能大,这样就相当于成功欺骗了判别器D。
U-Net
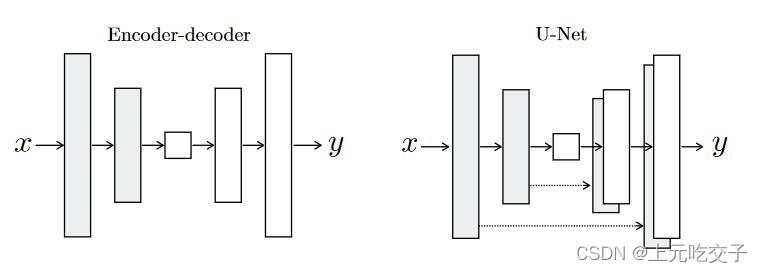
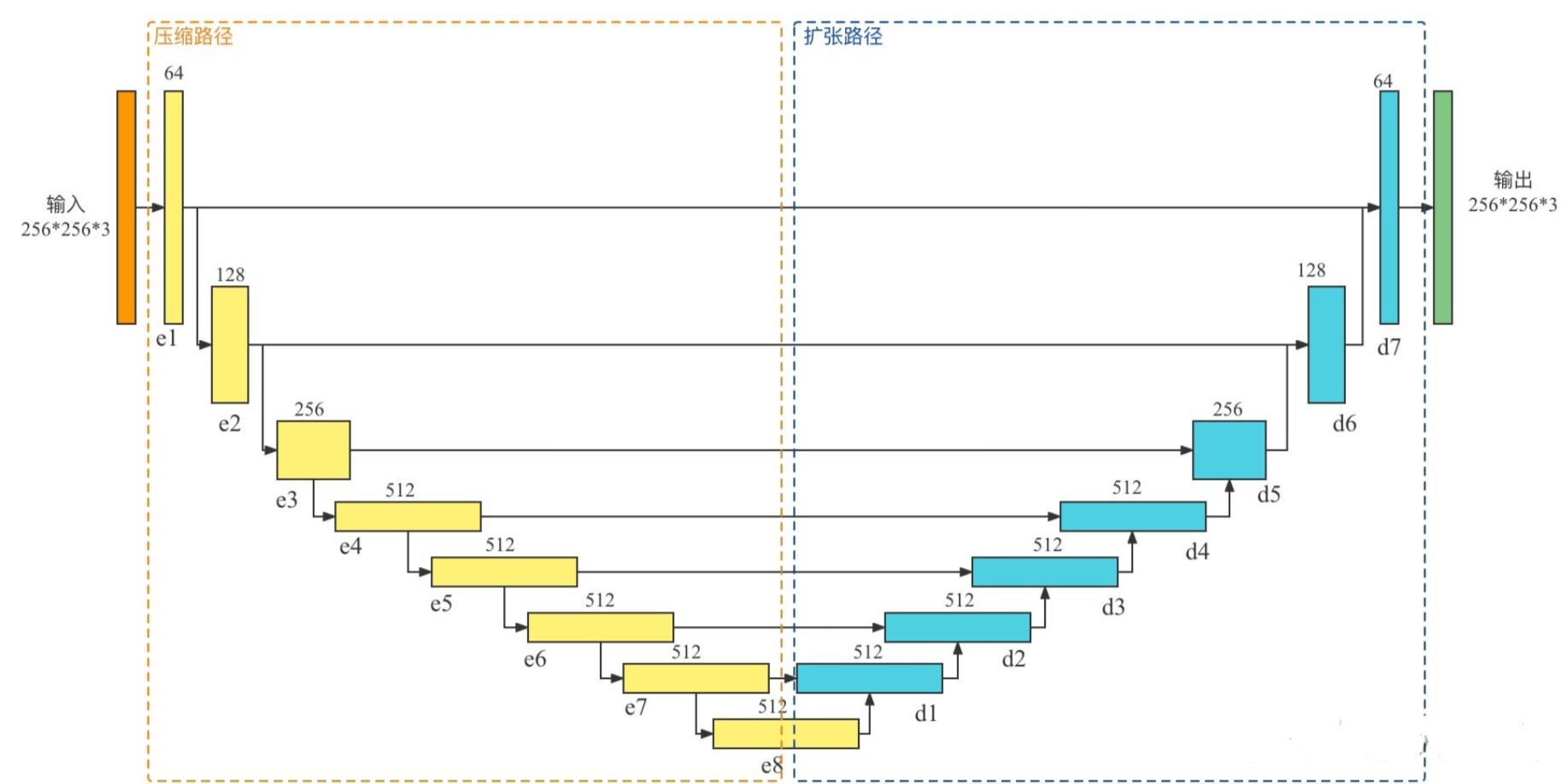
U-Net是一个用于医学图像分割的全卷积模型。它分为两个部分,其中左侧是由卷积和降采样操作组成的压缩路径,右侧是由卷积和上采样组成的扩张路径,扩张的每个网络块的输入由上一层上采样的特征和压缩路径部分的特征拼接而成。网络模型整体是一个U形的结构,因此被叫做U-Net。
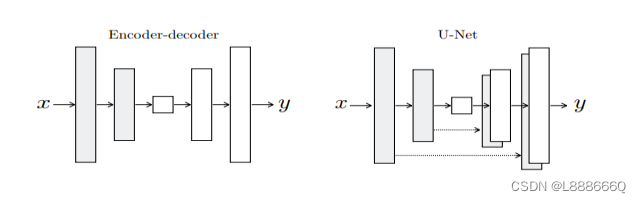
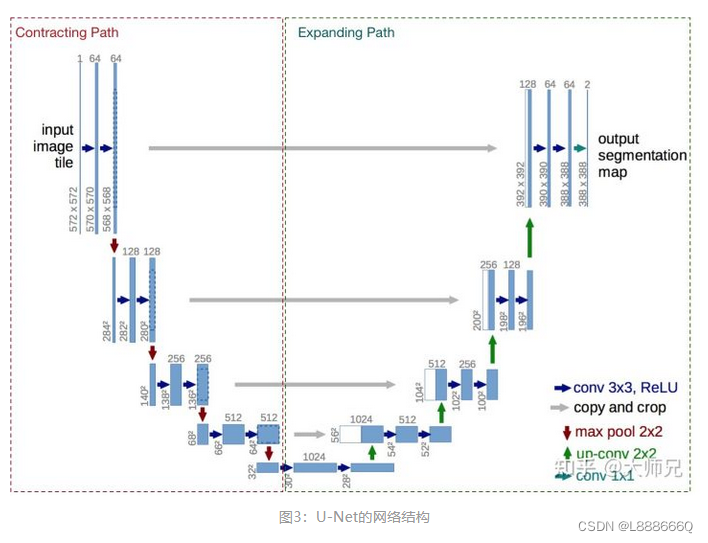
U-Net是德国Freiburg大学模式识别和图像处理组提出的一种全卷积结构。和常见的先降采样到低维度,再升采样到原始分辨率的编解码(Encoder-Decoder)结构的网络相比,U-Net的区别是加入skip-connection,对应的feature maps和decode之后的同样大小的feature maps按通道拼(concatenate)一起,用来保留不同分辨率下像素级的细节信息。U-Net对提升细节的效果非常明显。
判别器
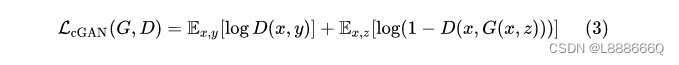
使用L1正则有助于使生成的图像更清楚
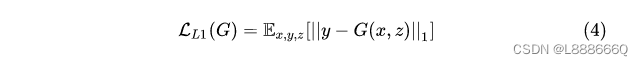
最终目标是在正则约束情况下的生成器和判别器的最大最小博弈
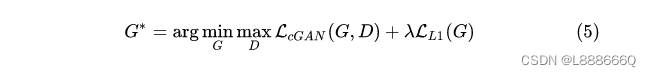
利用马尔科夫性的判别器(PatchGAN),pix2pix采用的策略是,用重建来解决低频成分,用GAN来解决高频成分。一方面,使用传统的L1 loss来让生成的图片跟训练的图片尽量相似,用GAN来构建高频部分的细节。
另一方面,使用PatchGAN来判别是否是生成的图片。PatchGAN的思想是,既然GAN只用于构建高频信息,那么就不需要将整张图片输入到判别器中,让判别器对图像的每个大小为N x N的patch做真假判别就可以了。因为不同的patch之间可以认为是相互独立的。pix2pix对一张图片切割成不同的N x N大小的patch,判别器对每一个patch做真假判别,将一张图片所有patch的结果取平均作为最终的判别器输出。具体实现的时候,使用的是一个NxN输入的全卷积小网络,最后一层每个像素过sigmoid输出为真的概率,然后用BCEloss计算得到最终loss。这样做的好处是因为输入的维度大大降低,所以参数量少,运算速度也比直接输入一张快,并且可以计算任意大小的图。
pix2pix_model.py
import torch
from .base_model import BaseModel
from . import networksclass Pix2PixModel(BaseModel):""" This class implements the pix2pix model, for learning a mapping from input images to output images given paired data.The model training requires '--dataset_mode aligned' dataset.By default, it uses a '--netG unet256' U-Net generator,a '--netD basic' discriminator (PatchGAN),and a '--gan_mode' vanilla GAN loss (the cross-entropy objective used in the orignal GAN paper).pix2pix paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1611.07004.pdf"""@staticmethoddef modify_commandline_options(parser, is_train=True):"""Add new dataset-specific options, and rewrite default values for existing options.Parameters:parser -- original option parseris_train (bool) -- whether training phase or test phase. You can use this flag to add training-specific or test-specific options.Returns:the modified parser.For pix2pix, we do not use image bufferThe training objective is: GAN Loss + lambda_L1 * ||G(A)-B||_1By default, we use vanilla GAN loss, UNet with batchnorm, and aligned datasets."""# changing the default values to match the pix2pix paper (https://phillipi.github.io/pix2pix/)parser.set_defaults(norm='batch', netG='unet_256', dataset_mode='aligned')if is_train:parser.set_defaults(pool_size=0, gan_mode='vanilla')parser.add_argument('--lambda_L1', type=float, default=100.0, help='weight for L1 loss')return parserdef __init__(self, opt):"""Initialize the pix2pix class.Parameters:opt (Option class)-- stores all the experiment flags; needs to be a subclass of BaseOptions"""BaseModel.__init__(self, opt)# specify the training losses you want to print out. The training/test scripts will call <BaseModel.get_current_losses>self.loss_names = ['G_GAN', 'G_L1', 'D_real', 'D_fake']# specify the images you want to save/display. The training/test scripts will call <BaseModel.get_current_visuals>self.visual_names = ['real_A', 'fake_B', 'real_B']# specify the models you want to save to the disk. The training/test scripts will call <BaseModel.save_networks> and <BaseModel.load_networks>if self.isTrain:self.model_names = ['G', 'D']else: # during test time, only load Gself.model_names = ['G']# define networks (both generator and discriminator)self.netG = networks.define_G(opt.input_nc, opt.output_nc, opt.ngf, opt.netG, opt.norm,not opt.no_dropout, opt.init_type, opt.init_gain, self.gpu_ids, opt.block_nums)if self.isTrain: # define a discriminator; conditional GANs need to take both input and output images; Therefore, #channels for D is input_nc + output_ncself.netD = networks.define_D(opt.input_nc + opt.output_nc, opt.ndf, opt.netD,opt.n_layers_D, opt.norm, opt.init_type, opt.init_gain, self.gpu_ids)if self.isTrain:# define loss functionsself.criterionGAN = networks.GANLoss(opt.gan_mode).to(self.device)self.criterionL1 = torch.nn.L1Loss()# initialize optimizers; schedulers will be automatically created by function <BaseModel.setup>.self.optimizer_G = torch.optim.Adam(self.netG.parameters(), lr=opt.lr, betas=(opt.beta1, 0.999))self.optimizer_D = torch.optim.Adam(self.netD.parameters(), lr=opt.lr, betas=(opt.beta1, 0.999))self.optimizers.append(self.optimizer_G)self.optimizers.append(self.optimizer_D)def set_input(self, input):"""Unpack input data from the dataloader and perform necessary pre-processing steps.Parameters:input (dict): include the data itself and its metadata information.The option 'direction' can be used to swap images in domain A and domain B."""AtoB = self.opt.direction == 'AtoB'self.real_A = input['A' if AtoB else 'B'].to(self.device)self.real_B = input['B' if AtoB else 'A'].to(self.device)self.image_paths = input['A_paths' if AtoB else 'B_paths']def forward(self):"""Run forward pass; called by both functions <optimize_parameters> and <test>."""self.fake_B = self.netG(self.real_A) # G(A)def backward_D(self):"""Calculate GAN loss for the discriminator"""# Fake; stop backprop to the generator by detaching fake_Bfake_AB = torch.cat((self.real_A, self.fake_B),1) # we use conditional GANs; we need to feed both input and output to the discriminatorpred_fake = self.netD(fake_AB.detach())self.loss_D_fake = self.criterionGAN(pred_fake, False)# Realreal_AB = torch.cat((self.real_A, self.real_B), 1)pred_real = self.netD(real_AB)self.loss_D_real = self.criterionGAN(pred_real, True)# combine loss and calculate gradientsself.loss_D = (self.loss_D_fake + self.loss_D_real) * 0.5self.loss_D.backward()def backward_G(self):"""Calculate GAN and L1 loss for the generator"""# First, G(A) should fake the discriminatorfake_AB = torch.cat((self.real_A, self.fake_B), 1)pred_fake = self.netD(fake_AB)self.loss_G_GAN = self.criterionGAN(pred_fake, True)# Second, G(A) = Bself.loss_G_L1 = self.criterionL1(self.fake_B, self.real_B) * self.opt.lambda_L1# combine loss and calculate gradientsself.loss_G = self.loss_G_GAN + self.loss_G_L1self.loss_G.backward()def optimize_parameters(self):self.forward() # compute fake images: G(A)# update Dself.set_requires_grad(self.netD, True) # enable backprop for Dself.optimizer_D.zero_grad() # set D's gradients to zeroself.backward_D() # calculate gradients for Dself.optimizer_D.step() # update D's weights# update Gself.set_requires_grad(self.netD, False) # D requires no gradients when optimizing Gself.optimizer_G.zero_grad() # set G's gradients to zeroself.backward_G() # calculate graidents for Gself.optimizer_G.step() # udpate G's weights