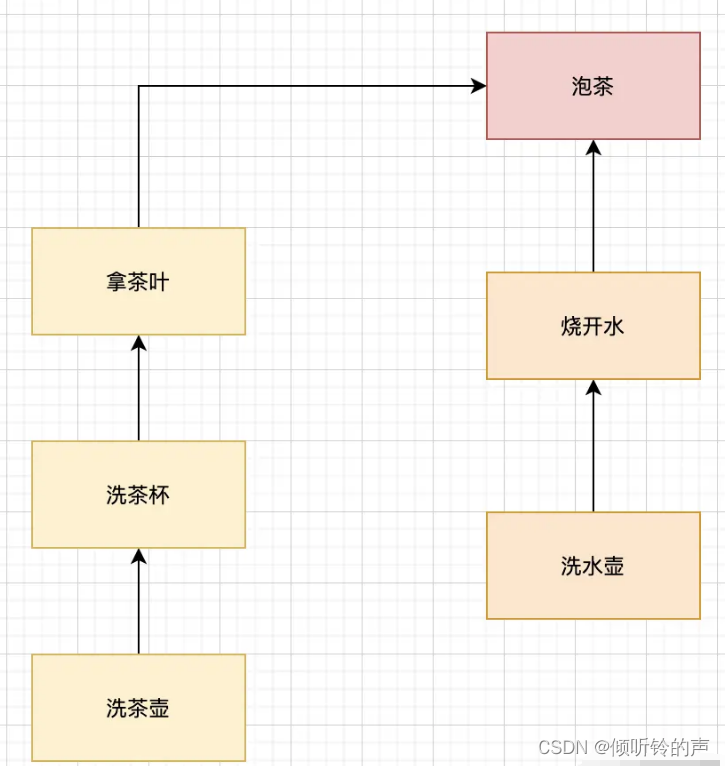
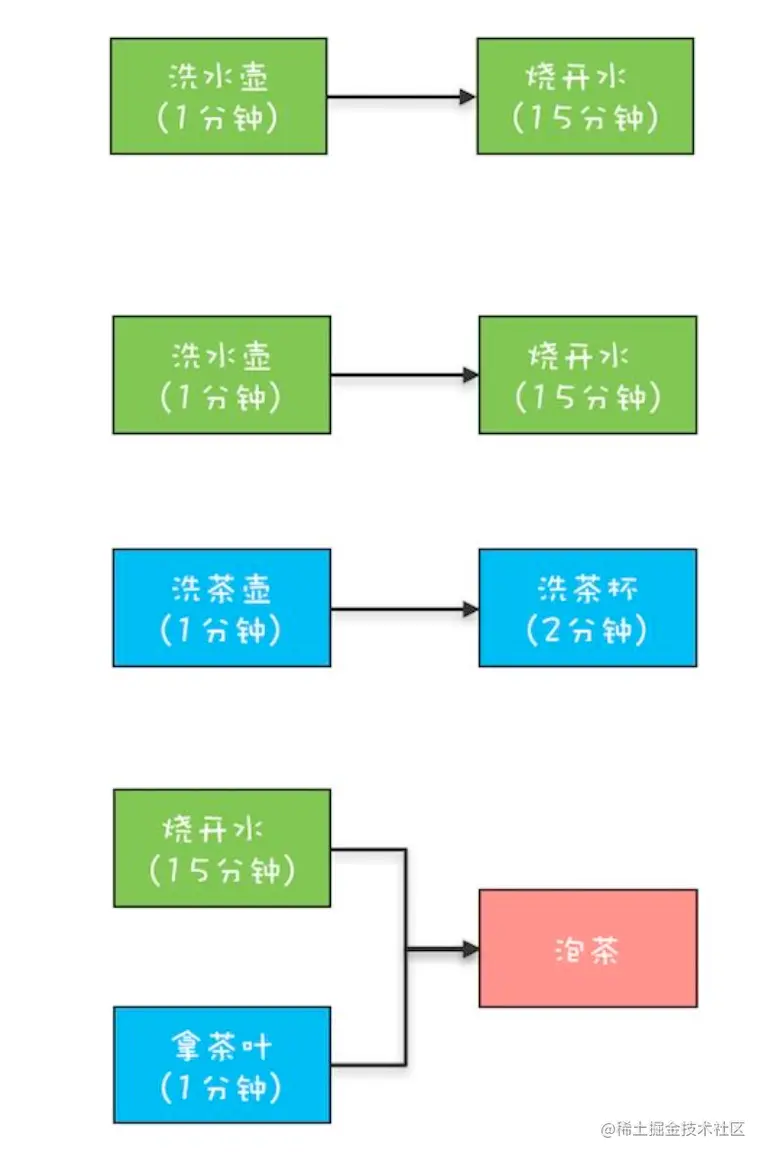
一般的 Executors 的 execute以及submit
并发包下 Executors 创建的线程存在 一个 execute(),以及三个 submit()
不同的是使用 execute() 执行的任务是没有返回值的,使用 submit() 则是存在返回值的,这与接下里要说的 CompletableFuture.runAsync 有些类似。

中测试代码如下:
@Testpublic void justFor(){ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();Future<Float> submit = executorService.submit(() -> {System.out.println("Thread.currentThread() = " + Thread.currentThread());return 1.03f;});Float aFloat = null;try {aFloat = submit.get();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (ExecutionException e) {e.printStackTrace();}// 根据自己需要决定是否需要调用关闭线程
// executorService.shutdown();System.out.println("aFloat = " + aFloat);}
结果:
Thread.currentThread() = Thread[pool-2-thread-1,5,main]
aFloat = 1.03
使用 submit 可以通过 get获取线程中任务的返回结果,可以通过对象获取当前状态 isDone 或者 isCancelled ;
子线程异步执行,主线程休眠等待子线程执行完成,子线程执行完成后唤醒主线程,主线程获取任务执行结果后退出
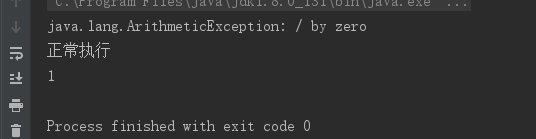
此时我加入一个异常代码,使其必定出错再来看看结果
@Testpublic void justFor(){ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();Future<Float> submit = executorService.submit(() -> {System.out.println("Thread.currentThread() = " + Thread.currentThread());int ii = 1/0;return 1.2f;});Float aFloat = null;try {aFloat = submit.get();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (ExecutionException e) {e.printStackTrace();}
// executorService.shutdown();System.out.println("aFloat = " + aFloat);}
执行结果:
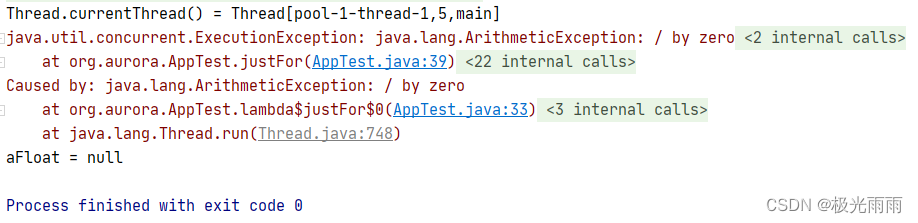
此时即使异常依旧终止了子线程以及主线程的执行。
CompletableFuture 的 supplyAsync() / runAsync()
supplyAsync 表示创建带返回值的异步任务,相当于ExecutorService submit(Callable< T> task)
runAsync 表示创建无返回值的异步任务,相当于ExecutorService submit(Runnable task)方法,这两个方法效果与 submit 一致
示例代码:
@Testpublic void justFor(){CompletableFuture<Float> floatCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("Thread.currentThread() = " + Thread.currentThread());return 1.03f;});try {Float aFloat = floatCompletableFuture.get();System.out.println("Thread.currentThread() = " + Thread.currentThread());System.out.println("aFloat = " + aFloat);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (ExecutionException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
输出结果:
Thread.currentThread() = Thread[ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1,5,main]
Thread.currentThread() = Thread[main,5,main]
aFloat = 1.03
日志中 ForkJoinPool 为jdk1.7 提供的一个新的分而治之的性能更好的并发处理线程池,比一般的Executors 更好一点,适用于高密度计算的任务。
但也可以如此写
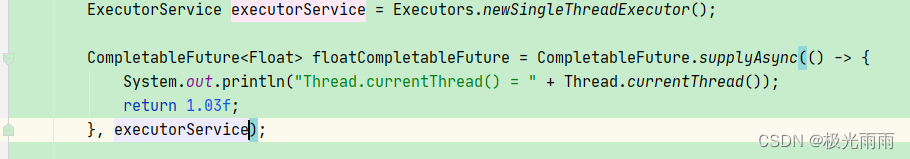
即将该任务提交到指定的线程池中执行该任务;
输出的线程池不一致
类似的 runAsync() 也可以这样,使用自己的异步线程或者提交到指定的线程池中执行
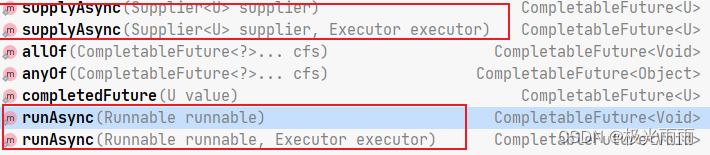
可以看得出使用第二个参数均提供了可以指定 Executor 没有指定时默认使用 ForkJoinPool.commonPool()
一般的
runAsync 如下:
CompletableFuture<Void> voidCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {System.out.println("Thread.currentThread() = " + Thread.currentThread());return;});
可以看得出 并没有任何返回值
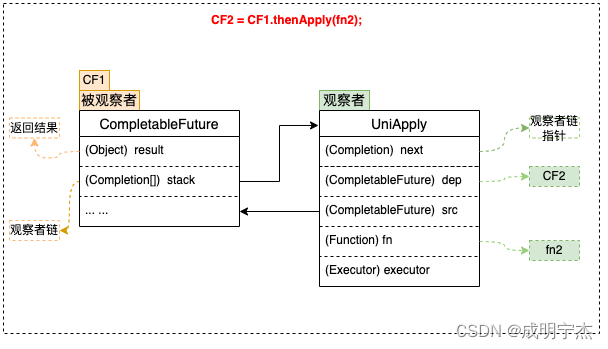
CompletableFuture 的 thenApply() / thenApplyAsync()
thenApply 表示某个任务执行完成后执行的动作即回调方法,会将该任务的执行结果即方法的返回值会作为作为入参传递到接下来的回调方法中
示例代码:
@Testpublic void justFor(){CompletableFuture<Float> floatCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("Thread.currentThread() = " + Thread.currentThread());return 1.03f;});CompletableFuture<Float> floatCompletableFuture1 = floatCompletableFuture.thenApply((resultFloat) -> {System.out.println("Thread.currentThread() = " + Thread.currentThread());System.out.println("接受上一个 resultFloat = " + resultFloat);return 2.01f;});CompletableFuture<Float> floatCompletableFuture2 = floatCompletableFuture1.thenApplyAsync((result2) -> {System.out.println("Thread.currentThread() = " + Thread.currentThread());System.out.println("result2 = " + result2);return 2.21f;});try {Float aFloat = floatCompletableFuture.get();System.out.println("Thread.currentThread() = " + Thread.currentThread());System.out.println("aFloat = " + aFloat);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (ExecutionException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
输出结果:
Thread.currentThread() = Thread[ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1,5,main]
Thread.currentThread() = Thread[main,5,main]
接受上一个 resultFloat = 1.03
Thread.currentThread() = Thread[main,5,main]
Thread.currentThread() = Thread[ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1,5,main]
aFloat = 1.03
result2 = 2.01
thenApplyAsync 与 thenApply 区别:
thenApplyAsync 将任务异步处理,可以选择提交到某一个线程池中执行,thenApply 则将会在上一个任务的同一个线程中执行。
上面代码也可以连着书写如下:
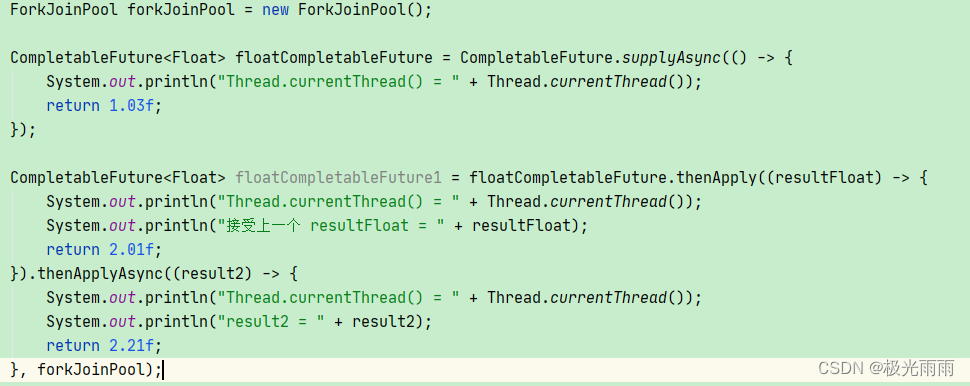
CompletableFuture 的 thenAccept() / thenRun()
thenAccept 同 thenApply 接收上一个任务的返回值作为参数但是没有返回值
thenAcceptAsync 同上但为异步线程,可以指定提交到某一个线程池中
thenRun 方法没有入参,也没有返回值
thenRunAsync 同上但为异步线程,可以指定提交到某一个线程池中
示例代码:
@Testpublic void justFor(){CompletableFuture<Float> floatCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("Thread.currentThread() = " + Thread.currentThread());return 1.03f;});CompletableFuture<Void> floatCompletableFuture1= floatCompletableFuture.thenApply((resultFloat) -> {System.out.println("Thread.currentThread() = " + Thread.currentThread());System.out.println("接受上一个 resultFloat = " + resultFloat);return 2.01f;}).thenAccept((result)->{System.out.println("Thread.currentThread() = " + Thread.currentThread());System.out.println("result = " + result);}).thenRun(()->{System.out.println("Thread.currentThread() = " + Thread.currentThread());System.out.println(" doNothing");});}
CompletableFuture exceptionally
指定某个任务执行异常时执行的回调方法,会将抛出异常作为参数传递到回调方法中,如果该任务正常执行则 exceptionally方法返回的CompletionStage的result就是该任务正常执行的结果
正常示例:
@Testpublic void justFor(){CompletableFuture<Float> floatCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("Thread.currentThread() = " + Thread.currentThread());
// float ii = 1/0;return 1.03f;});CompletableFuture<Float> exceptionally = floatCompletableFuture.exceptionally((exception) -> {System.out.println("catch exception");exception.printStackTrace();return 0.0f;});floatCompletableFuture.thenAccept((result)->{System.out.println("is OK");System.out.println("result = " + result);});}
输出结果:
Thread.currentThread() = Thread[ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1,5,main]
is OK
异常示例:
@Testpublic void justFor(){CompletableFuture<Float> floatCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("Thread.currentThread() = " + Thread.currentThread());int a = 121/0;return 1.03f;});CompletableFuture<Float> exceptionally = floatCompletableFuture.exceptionally((exception) -> {System.out.println("catch exception");exception.printStackTrace();return 0.0f;});floatCompletableFuture.thenAccept((result)->{System.out.println("is OK");System.out.println("result = " + result);});}
结果:
Thread.currentThread() = Thread[ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1,5,main]
catch exception
CompletableFuture whenComplete
当某个任务执行完成后执行的回调方法,会将执行结果或者执行期间抛出的异常传递给回调方法
正常执行则异常为null,回调方法对应的CompletableFuture的result和该任务一致
异常执行,则get方法抛出异常
同样提供 Async 异步相关方法
正常:
@Testpublic void justFor(){CompletableFuture<Float> floatCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("Thread.currentThread() = " + Thread.currentThread());return 1.03f;});floatCompletableFuture.whenComplete((result, exception) -> {System.out.println("result = " + result);System.out.println("exception = " + exception);});}
输出:
Thread.currentThread() = Thread[ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1,5,main]
result = 1.03
exception = null
异常时示例:
public static void main(String[] args) {CompletableFuture<Float> floatCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("Thread.currentThread() = " + Thread.currentThread());int ii = 12 / 0;return 1.03f;});floatCompletableFuture.whenComplete((result, exception) -> {System.out.println("result = " + result);System.out.println("exception = " + exception);});}
输出:
Thread.currentThread() = Thread[ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1,5,main]
result = null
exception = java.util.concurrent.CompletionException: java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
CompletableFuture handle
与 whenComplete 基本一致
区别在于handle的回调方法有返回值,且handle方法返回的CompletableFuture的result是回调方法的执行结果或者回调方法执行期间抛出的异常,与原始CompletableFuture的result无关
示例代码:
@Testpublic void justFor(){CompletableFuture<Float> floatCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("Thread.currentThread() = " + Thread.currentThread());int ii = 12 / 0;return 1.03f;});floatCompletableFuture.handle((result, exception) -> {System.out.println("result = " + result);System.out.println("exception = " + exception);return "???";});}
CompletableFuture 组合处理 thenCombine / thenAcceptBoth / runAfterBoth
三个方法都是将两个 CompletableFuture 组合起来
只有这两个都正常执行完了才会执行某个任务区别在于
thenCombine 会将两个任务的执行结果作为方法入参传递到指定方法中,且该方法有返回值;thenAcceptBoth 同样将两个任务的执行结果作为方法入参,但是无返回值;
runAfterBoth 没有入参,也没有返回值。注意两个任务中只要有一个执行异常,则将该异常信息作为指定任务的执行结果
同时这些也提供了Async 异步方法
示例代码:
@Testpublic void justFor(){CompletableFuture<Float> a1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("Thread.currentThread() = " + Thread.currentThread());return 1.03f;});CompletableFuture<Float> a2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("Thread.currentThread() = " + Thread.currentThread());return 2.03f;});// 传递结果 有返回值CompletableFuture<String> objectCompletableFuture = a1.thenCombine(a2, (a, b) -> {return "12";});// 传递结果 无返回值CompletableFuture<Void> voidCompletableFuture = a1.thenAcceptBoth(a2, (a, b) -> {});// 无入参 无返回值a1.runAfterBoth(a2, ()->{//});}
CompletableFuture applyToEither / acceptEither / runAfterEither
三个方法都是将两个CompletableFuture组合起来
但与上面不同的是只要其中一个执行完了就会执行某个任务,区别
applyToEither 会将已经执行完成的任务的执行结果作为方法入参,并有返回值;
acceptEither 同样将已经执行完成的任务的执行结果作为方法入参,但是没有返回值;runAfterEither 没有方法入参,也没有返回值。
注意 两个任务中只要有一个执行异常,则将该异常信息作为指定任务的执行结果
同时这些也提供了Async 异步方法
示例代码:
@Testpublic void justFor(){CompletableFuture<Float> a1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("Thread.currentThread() = " + Thread.currentThread());return 1.03f;});CompletableFuture<Float> a2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("Thread.currentThread() = " + Thread.currentThread());return 2.03f;});// 传递结果 有返回值CompletableFuture<String> objectCompletableFuture = a1.applyToEither(a2, (b) -> {return "12";});// 传递结果 无返回值CompletableFuture<Void> voidCompletableFuture = a1.acceptEither(a2, (b) -> {});// 无入参 无返回值a1.runAfterEither(a2, ()->{//});}
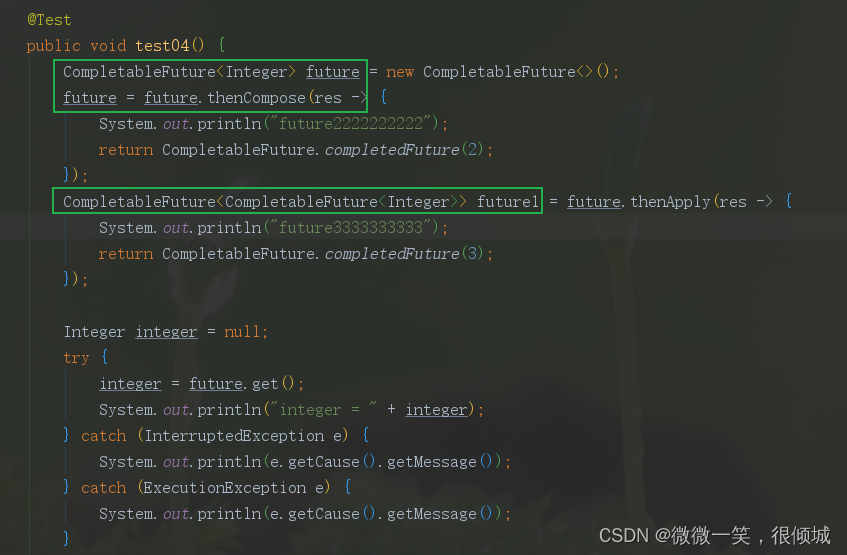
CompletableFuture thenCompose
thenCompose
在某个任务执行完成后,将该任务的执行结果作为方法入参然后执行指定方法,该方法会返回一个新的CompletableFuture实例
如果该CompletableFuture实例的result不为null,则返回一个基于该result的新的CompletableFuture实例;
如果该CompletableFuture实例为null,则执行这个新任务
同样的提供Async方式
@Testpublic void justFor(){CompletableFuture<Float> a1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("Thread.currentThread() = " + Thread.currentThread());return 1.03f;});CompletableFuture<String> stringCompletableFuture = a1.thenCompose((result) -> {System.out.println("result = " + result);try {Thread.sleep(100);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {return "154";});});}
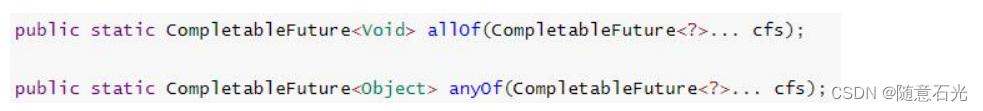
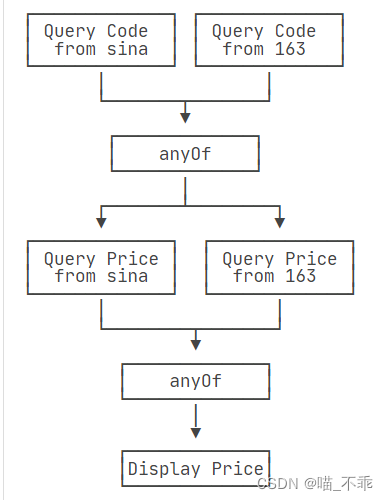
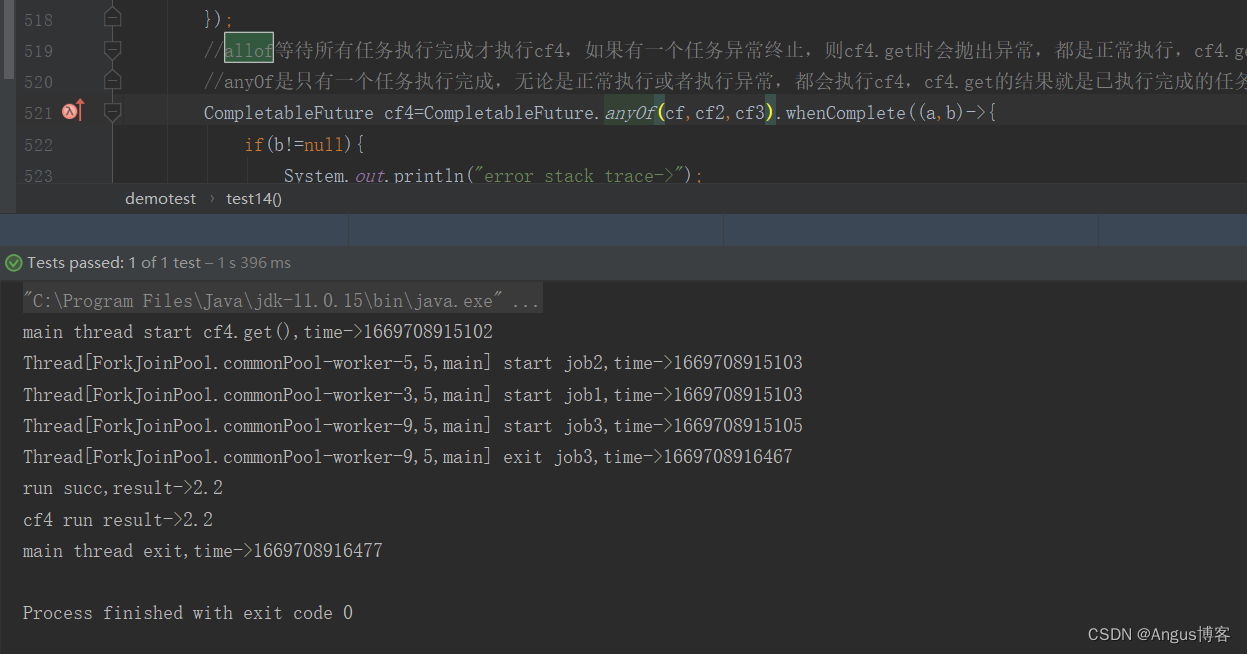
CompletableFuture 的 allOf() anyOf()
allOf 返回的CompletableFuture是多个任务都执行完成后才会执行,只要有一个任务执行异常,则返回的 CompletableFuture 执行get方法时会抛出异常,如果都正常执行,则get返回null
anyOf 只要有一个任务执行完成,无论是正常执行或者执行异常,都会执行向下执行
示例代码:
@Testpublic void justFor(){CompletableFuture<Float> a1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("Thread.currentThread() = " + Thread.currentThread());return 1.03f;});CompletableFuture<Float> a2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("Thread.currentThread() = " + Thread.currentThread());return 2.03f;});CompletableFuture<Float> a3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("Thread.currentThread() = " + Thread.currentThread());return 23.03f;});CompletableFuture.allOf(a1, a2, a3).whenComplete((a, b)->{System.out.println("a = " + a);System.out.println("b = " + b);});CompletableFuture<Object> objectCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.anyOf(a1, a2, a3);try {Object o = objectCompletableFuture.get();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (ExecutionException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}