一:线程
1.初始化线程的四种方式
1)、继承 Thread
public class ThreadTest {public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println("main...start...");Thread01 thread = new Thread01();//启动线程thread.start();System.out.println("main...end...");}public static class Thread01 extends Thread{@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println("当前线程:"+Thread.currentThread().getId());int i = 10/2;System.out.println("运行结果:"+i);}}
}
2)、实现 Runnable 接口
/*** 测试多线程的使用*/
public class ThreadTest {public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println("main...start...");Runable01 runable01 = new Runable01();new Thread(runable01).start();System.out.println("main...end...");}public static class Runable01 implements Runnable{@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println("当前线程:"+Thread.currentThread().getId());int i = 10/2;System.out.println("运行结果:"+i);}}
}
3)、实现 Callable 接口 + FutureTask (可以拿到返回结果,可以处理异常)
public class ThreadTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {System.out.println("main...start...");FutureTask<Integer> futureTask = new FutureTask<>(new Callable01());new Thread(futureTask).start();//等待整个异步方法执行完,获取返回结果Integer integer = futureTask.get();System.out.println("main...end..."+integer);}public static class Callable01 implements Callable<Integer> {@Overridepublic Integer call() throws Exception {System.out.println("当前线程:"+Thread.currentThread().getId());int i = 10/2;System.out.println("运行结果:"+i);return i;}}
}
- 阻塞等待,需要等所有异步执行完,获取到值,才会返回
4)、线程池(给线程池提交任务)
问:为什么要使用线程池?
答:高并发系统下,内存空间是有限的,会消耗系统资源,导致系统崩溃。应该将所有的异步任务都交给线程池执行,做到资源控制。
public class ThreadTest {//当前系统中池只有一两个,每个异步任务,直接提交给线程池public static ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {System.out.println("main...start...");executorService.execute(new Runable01());System.out.println("main...end...");}
}
总结:
- 方式 1 和方式 2:主进程无法获取线程的运算结果。无返回值。
- 方式 3:主进程可以获取线程的运算结果,但是不利于控制服务器中的线程资源。可以导致 服务器资源耗尽。
- 方式 1 ,方式 2和方式 3,都不可以控制资源
- 方式4:通过线程池性能稳定,也可以获取执行结果,并捕获异常。但是,在业务复杂情况下,一 个异步调用可能会依赖于另一个异步调用的执行结果。
- 一般情况下我们都使用线程池去管理线程。
2.线程池
1)开发中为什么使用线程池
- 降低资源的消耗 ——通过重复利用已经创建好的线程降低线程的创建和销毁带来的损耗
- 提高响应速度——因为线程池中的线程数没有超过线程池的最大上限时,有的线程处于等待分配任务 的状态,当任务来时无需创建新的线程就能执行
- 提高线程的可管理性 ——线程池会根据当前系统特点对池内的线程进行优化处理,减少创建和销毁线程带来 的系统开销。无限的创建和销毁线程不仅消耗系统资源,还降低系统的稳定性,使 用线程池进行统一分配
2)创建线程池
- 通过Executors工具类(Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10))
- new ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime,TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue workQueue, ThreadFactory threadFactory,RejectedExecutionHandler handler);
3)线程池的七大参数
- corePoolSize:【5】核心线程数;线程池中一直保持的线程的数量,即使线程空闲。除非设置了(allowCoreThreadTimeOut )
- maximumPoolSize: 池中允许的最大的线程数 ,控制资源
- keepAliveTime: 存活时间,当线程数大于核心线程数的时候,线程在最大多长时间没有接到新任务就会终止释放, 最终线程池维在 corePoolSize 大小
- unit: 时间单位
- workQueue 阻塞队列,用来存储等待执行的任务,如果当前对线程的需求超过了 corePoolSize 大小,就会放在这里等待空闲线程执行。
- threadFactory 创建线程的工厂,比如指定线程名等
- handler 拒绝策略,如果线程满了,线程池就会使用拒绝策略,拒绝执行任务。
4)运行流程
1、线程池创建,准备好 core 数量的核心线程,准备接受任务
2、新的任务进来,用 core 准备好的空闲线程执行。
(1) 、core 满了,就将再进来的任务放入阻塞队列中。空闲的 core 就会自己去阻塞队 列获取任务执行
(2) 、阻塞队列满了,就直接开新线程执行,最大只能开到 max 指定的数量
(3) 、max 都执行好了。Max-core 数量空闲的线程会在 keepAliveTime 指定的时间后自动销毁。最终保持到 core 大小
(4) 、如果线程数开到了 max 的数量,还有新任务进来,就会使用 reject 指定的拒绝策 略进行处理
3、所有的线程创建都是由指定的 factory 创建的。
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(5,200,10,TimeUnit.SECONDS,new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(100000),Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
5)常见的 4 种线程池
- newCachedThreadPool —— 创建一个可缓存线程池,如果线程池长度超过处理需要,可灵活回收空闲线程,若 无可回收,则新建线程。
- newFixedThreadPool——创建一个固定大小线程池,可控制线程最大并发数,超出的线程会在队列中等待。核心线程等于最大线程,都不可以回收。
- newScheduledThreadPool——创建一个定时任务线程池,支持定时及周期性任务执行。
- newSingleThreadExecutor——创建一个单线程化的线程池,它只会用唯一的工作线程来执行任务,保证所有任务 按照指定顺序(FIFO, LIFO, 优先级)执行。
6)一个线程池 core 7; max 20 ,queue:50,100 并发进来怎么分配的;
先有 7 个能直接得到执行,接下来 50 个进入队列排队,在多开 13 个继续执行。现在 70 个 被安排上了。剩下 30 个默认拒绝策略。
二:CompletableFuture 异步编排
1.业务场景:
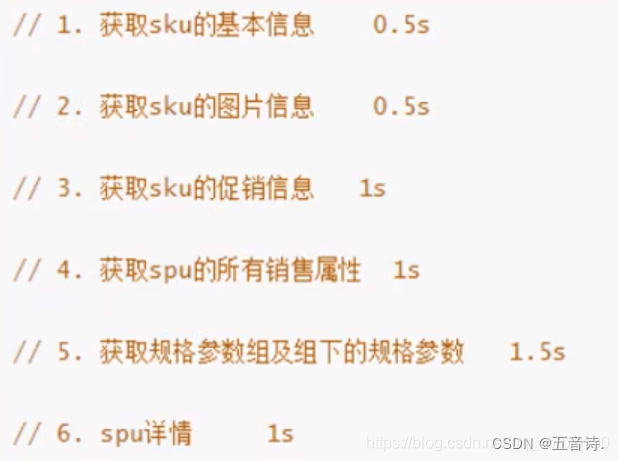
查询商品详情页的逻辑比较复杂,有些数据还需要远程调用,必然需要花费更多的时间。
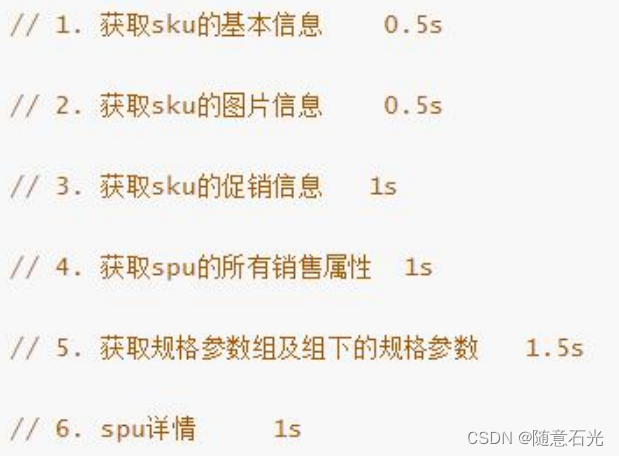
假如商品详情页的每个查询,需要如下标注的时间才能完成 那么,用户需要 5.5s 后才能看到商品详情页的内容。很显然是不能接受的。 如果有多个线程同时完成这 6 步操作,也许只需要 1.5s 即可完成响应。
2.创建异步对象
CompletableFuture 提供了四个静态方法来创建一个异步操作。
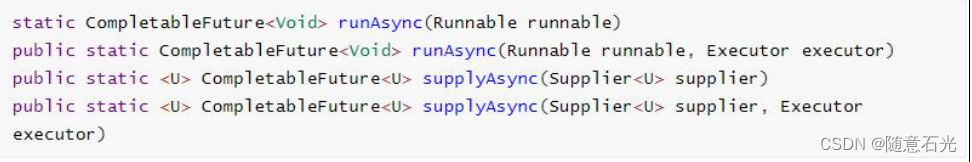
1)CompletableFuture无返回值——runAsync
public static void main(String[] args){System.out.println("main...start...");CompletableFuture<Void> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());int i = 10 / 2;System.out.println("运行结果:" + i);}, executorService);System.out.println("main...end...");}
2)CompletableFuture有返回值——supplyAsync
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {System.out.println("main...start...");CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());int i = 10 / 2;System.out.println("运行结果:" + i);return i;}, executorService);Integer integer = future.get();System.out.println("main...end..."+ integer);}
- runXxxx 都是没有返回结果的,supplyXxx 都是可以获取返回结果的
- 可以传入自定义的线程池,否则就用默认的线程池;
3.计算完成时回调方法
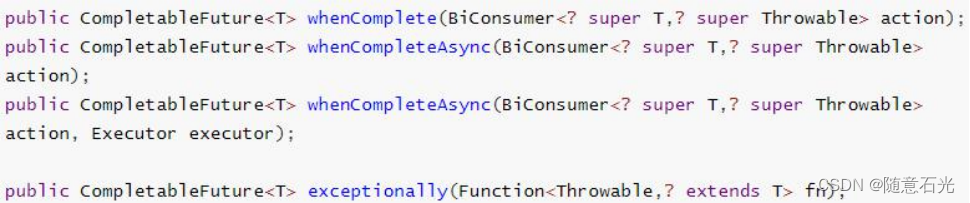
- whenComplete 可以处理正常和异常的计算结果,exceptionally 处理异常情况。
- whenComplete 和 whenCompleteAsync 的区别:
1)whenComplete:是执行当前任务的线程执行继续执行 whenComplete 的任务。
2)whenCompleteAsync:是执行把 whenCompleteAsync 这个任务继续提交给线程池 来进行执行。
1)测试whenComplete和exceptionally
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {System.out.println("main...start...");CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());int i = 10 / 2;System.out.println("运行结果:" + i);return i;}, executorService).whenComplete((res,exception)->{//whenComplete虽然可以得到异常信息,但是没办法修改返回值System.out.println("异步任务成功完成。结果是"+res+"异常是"+exception);}).exceptionally(throwable -> {//exceptionally可以感知,并且返回默认值return 10;});Integer integer = future.get();System.out.println("main...end..."+integer);}
- whenComplete虽然可以得到异常信息,但是没办法修改返回值
- exceptionally可以感知,并且返回默认值
4.handle 方法——方法完成后的处理
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {System.out.println("main...start...");/*** 方法完成后的处理*/CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());int i = 10 / 2;System.out.println("运行结果:" + i);return i;}, executorService).handle((res,thr)->{if( res != null ){return res*2;}if( thr!= null ){return 0;}return 0;});Integer integer = future.get();System.out.println("main...end..."+integer);}
5.线程串行化方法

- thenApply 方法:当一个线程依赖另一个线程时,获取上一个任务返回的结果,并返回当前 任务的返回值。
- thenAccept 方法:消费处理结果。接收任务的处理结果,并消费处理,无返回结果。
- thenRun 方法:只要上面的任务执行完成,就开始执行 thenRun,只是处理完任务后,执行 thenRun 的后续操作 带有 Async 默认是异步执行的。同之前。
以上都要前置任务成功完成。 - Function<? super T,? extends U>
T:上一个任务返回结果的类型
U:当前任务的返回值类型
1)thenRun:不能获取到上一步执行结果,无返回值
CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());int i = 10 / 2;System.out.println("运行结果:" + i);return i;}, executorService).thenRunAsync(() -> {System.out.println("任务2启动了");});System.out.println("main...end...");
2)thenAcceptAsync:可以获取到上一步的返回结果,无返回值
CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());int i = 10 / 2;System.out.println("运行结果:" + i);return i;}, executorService).thenAcceptAsync((res) -> {System.out.println("任务2启动了"+res);},executorService);System.out.println("main...end...");
3)thenApplyAsync:可以获取到上一步的返回结果,有返回值
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());int i = 10 / 2;System.out.println("运行结果:" + i);return i;}, executor).thenApplyAsync((res) -> {System.out.println("任务2启动了" + res);return "hello" + res;}, executor);System.out.println("main...end..."+future.get());
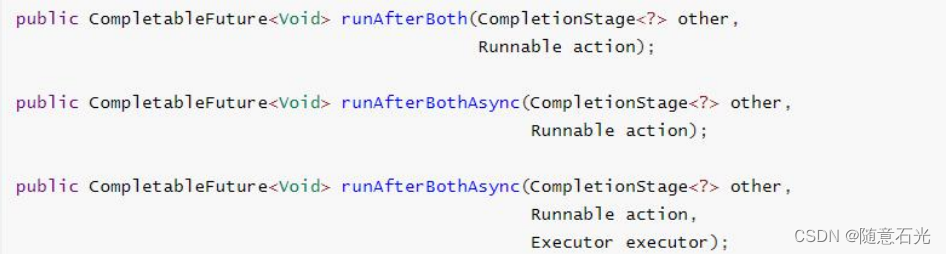
6.两任务组合 - 都要完成

/*** 两个都完成*/CompletableFuture<Integer> future01 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("任务一线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());int i = 10 / 2;System.out.println("任务一结束:" + i);return i;}, executor);CompletableFuture<String> future02 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("任务二线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());System.out.println("任务二结束");return "hello";});//方式一future01.runAfterBothAsync(future02,()->{System.out.println("任务三开始");},executor);//方式二future01.thenAcceptBothAsync(future02,(f1,f2)->{System.out.println("任务三开始"+f1+"---"+f2);},executor);//方式三CompletableFuture<String> future = future01.thenCombineAsync(future02, (f1, f2) -> {return f1 + ":" + f2 + "hahah";}, executor);System.out.println("main...end..."+future.get());
- 两个任务必须都完成,触发该任务。
- thenCombine:组合两个 future,获取两个 future 的返回结果,并返回当前任务的返回值
- thenAcceptBoth:组合两个 future,获取两个 future 任务的返回结果,然后处理任务,没有 返回值。
- runAfterBoth:组合两个 future,不需要获取 future 的结果,只需两个 future 处理完任务后, 处理该任务。
7.两任务组合 - 一个完成

CompletableFuture<Object> future01 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("任务一线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());int i = 10 / 2;System.out.println("任务一结束:" + i);return i;}, executor);CompletableFuture<Object> future02 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("任务二线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());try {Thread.sleep(3000);System.out.println("任务二结束");} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "hello";});future01.runAfterEitherAsync(future02,()->{System.out.println("任务三开始");},executor);future01.acceptEitherAsync(future02,(res)->{System.out.println("任务三开始");},executor);CompletableFuture<String> future = future01.applyToEitherAsync(future02, (res) -> {return res.toString();}, executor);System.out.println("main...end..."+future.get());
- 当两个任务中,任意一个 future 任务完成的时候,执行任务。
- applyToEither:两个任务有一个执行完成,获取它的返回值,处理任务并有新的返回值。
- acceptEither:两个任务有一个执行完成,获取它的返回值,处理任务,没有新的返回值。
- runAfterEither:两个任务有一个执行完成,不需要获取 future 的结果,处理任务,也没有返 回值。
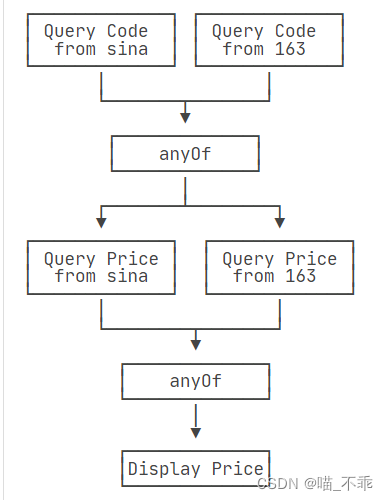
8.多任务组合
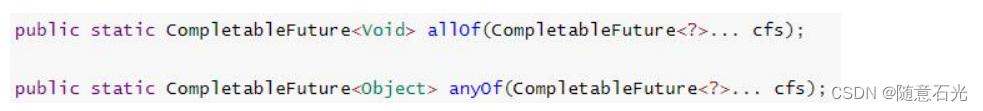
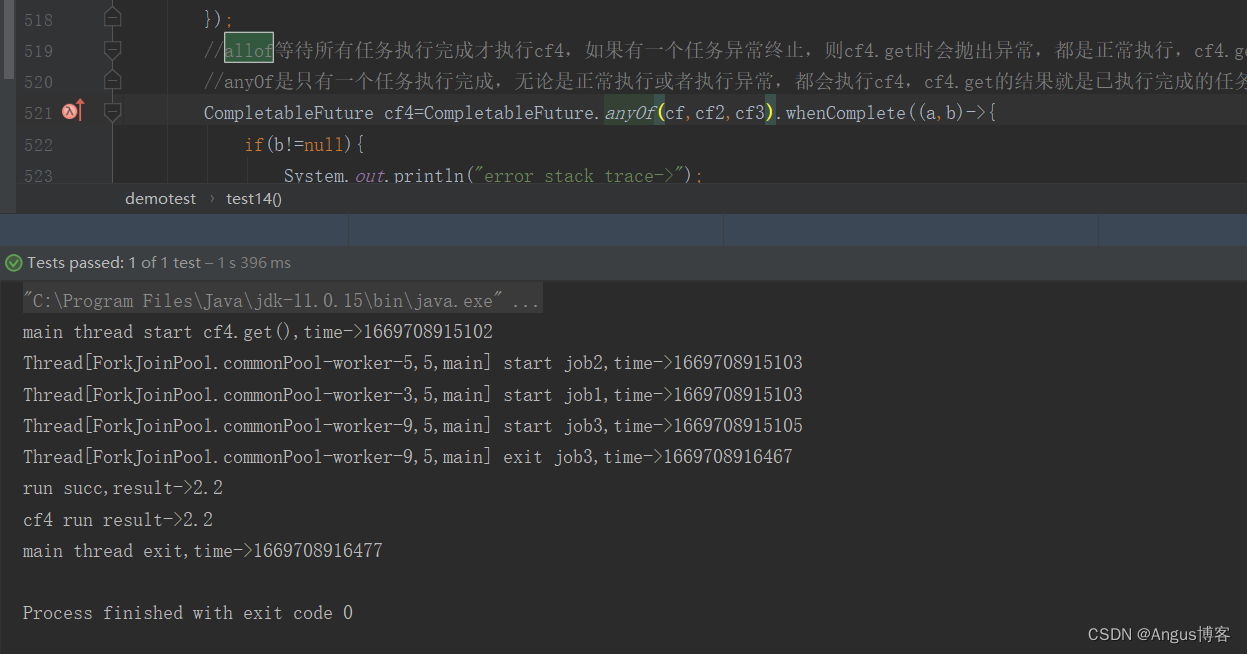
CompletableFuture<String> futureImg = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("查询商品的图片信息");return "hello.jpg";},executor);CompletableFuture<String> futureAttr = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("查询商品的属性信息");return "黑色256g";},executor);CompletableFuture<String> futureDesc = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {Thread.sleep(3000);System.out.println("查询商品的介绍");} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "华为";},executor);//allOfCompletableFuture<Void> allOf = CompletableFuture.allOf(futureImg, futureAttr, futureDesc);//anyOfCompletableFuture<Object> anyOf = CompletableFuture.anyOf(futureImg, futureAttr, futureDesc);//allOf.get();//等待所有结果完成anyOf.get();System.out.println("main...end...");
- allOf:等待所有任务完成
- anyOf:只要有一个任务完成