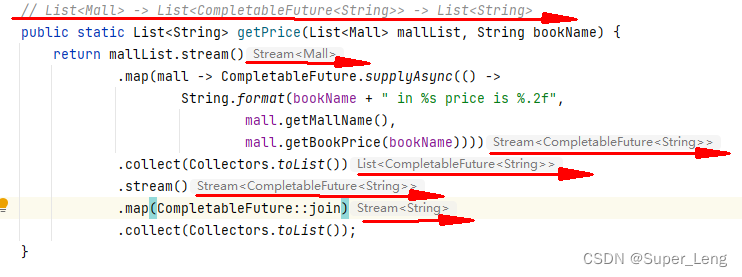
CompletableFuture 执行异步任务
参考:
(10条消息) Java 8 的异步编程利器 CompletableFuture 真香!_不才陈某的博客-CSDN博客
提供几十种方法,帮助异步任务执行调用;
主要包括:
- 创建异步任务
- 任务异步回调
- 多个任务组合处理
创建异步任务
创建异步任务一般有supplyAsync和runAsync两个方法
-
supplyAsync执行CompletableFuture任务,支持返回值
-
runAsync执行CompletableFuture任务,没有返回值。
supplyAsync
//使用默认内置线程池ForkJoinPool.commonPool(),根据supplier构建执行任务
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier)
//自定义线程,根据supplier构建执行任务
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier, Executor executor)
runAsync
//使用默认内置线程池ForkJoinPool.commonPool(),根据runnable构建执行任务
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable)
//自定义线程,根据runnable构建执行任务
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable, Executor executor)
使用:
@Testpublic void test1() {//可以自定义线程池ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);//runAsync的使用CompletableFuture<Void> runFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {System.out.println("执行runFuture的线程=" + Thread.currentThread().getName());System.out.println("run执行");}, executor);//supplyAsync的使用CompletableFuture<String> supplyFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("执行supplyFuture的线程=" + Thread.currentThread().getName());System.out.println("supply执行");return "捡田螺的小男孩";}, executor);
// CompletableFuture<String> supplyFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(
// () -> {
// System.out.println("执行supplyFuture的线程=" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
// System.out.println("supply执行");
// return "捡田螺的小男孩";
// });//不指定线程池,就使用默认的 ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1 线程//runAsync的future没有返回值,输出nullSystem.out.println("runFuture结果:" + runFuture.join());//supplyAsync的future,有返回值System.out.println("supplyFuture结果:" + supplyFuture.join());executor.shutdown(); // 线程池需要关闭}输出结果
执行runFuture的线程=pool-1-thread-1
run执行
runFuture结果:null
执行supplyFuture的线程=pool-1-thread-2
supply执行
supplyFuture结果:捡田螺的小男孩
任务异步回调
thenRun/thenRunAsync
不关心上一个任务的执行结果,无传参,无返回值
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRun(Runnable action);
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action);
两个方法的区别
thenRun 方法 会跟前一个任务共用同一个线程池,
thenRunAsync 方法,不指定线程池的话,会使用默认的ForkJoin线程池
使用:
@Testpublic void test2() {//可以自定义线程池ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);CompletableFuture<String> orgFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("执行supplyAsync的线程=" + Thread.currentThread().getName());System.out.println("先执行第一个CompletableFuture方法任务");return "捡田螺的小男孩";}, executor);// CompletableFuture thenRunFuture = orgFuture.thenRun(() -> {
// //main
// System.out.println("执行thenRun的线程=" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
// System.out.println("接着执行第二个任务");
// });
// CompletableFuture thenRunFuture = orgFuture.thenRunAsync(() -> {
// //ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1 会使用默认的ForkJoin线程池
// System.out.println("执行thenRunAsync的线程=" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
// System.out.println("接着执行第二个任务");
// });CompletableFuture thenRunFuture = orgFuture.thenRunAsync(() -> {//pool-1-thread-2 指定使用自定义的线程池System.out.println("执行thenRunAsync的线程=" + Thread.currentThread().getName());System.out.println("接着执行第二个任务");}, executor);try {System.out.println(thenRunFuture.get());} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (ExecutionException e) {e.printStackTrace();}executor.shutdown(); // 线程池需要关闭}
thenAccept/thenAcceptAsync
依赖上一个任务的结果,有入参,无返回值
@Test
public void thenAccept() {//可以自定义线程池ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);CompletableFuture<String> orgFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("执行supplyAsync的线程=" + Thread.currentThread().getName());System.out.println("先执行第一个CompletableFuture方法任务");return "捡田螺的小男孩";}, executor);CompletableFuture thenAcceptAsync = orgFuture.thenAcceptAsync((r) -> {//pool-1-thread-2 指定使用自定义的线程池System.out.println("执行thenAcceptAsync的线程=" + Thread.currentThread().getName());System.out.println("接着执行第二个任务");System.out.println("上一个任务的结果=" + r);}, executor);try {System.out.println(thenAcceptAsync.get());} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (ExecutionException e) {e.printStackTrace();}executor.shutdown(); // 线程池需要关闭
}
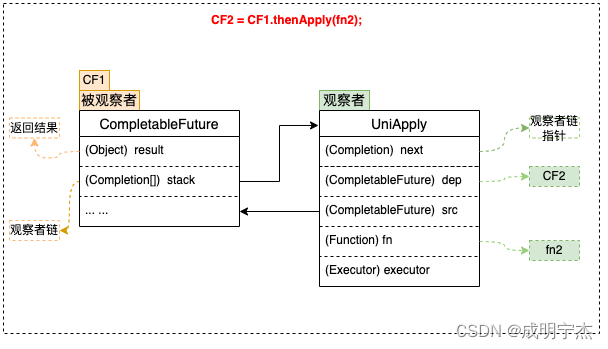
thenApply/thenApplyAsync
依赖上一个任务的结果,有入参,有返回值
@Test
public void thenApply() {//可以自定义线程池ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);CompletableFuture<String> orgFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("执行supplyAsync的线程=" + Thread.currentThread().getName());System.out.println("先执行第一个CompletableFuture方法任务");return "捡田螺的小男孩";}, executor);CompletableFuture thenApplyAsync = orgFuture.thenApplyAsync((r) -> {//pool-1-thread-2 指定使用自定义的线程池System.out.println("执行thenApplyAsync的线程=" + Thread.currentThread().getName());System.out.println("接着执行第二个任务");System.out.println("上一个任务的结果=" + r);return 666;}, executor);try {System.out.println(thenApplyAsync.get());} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (ExecutionException e) {e.printStackTrace();}executor.shutdown(); // 线程池需要关闭
}
exceptionally
任务执行出现异常的回调方法
CompletableFuture的exceptionally方法表示,某个任务执行异常时,执行的回调方法;并且有抛出异常作为参数,传递到回调方法。
whenComplete方法
任务执行完后的回调方法,无返回值
CompletableFuture的whenComplete方法表示,某个任务执行完成后,执行的回调方法,无返回值;并且whenComplete方法返回的CompletableFuture的result是上个任务的结果。
handle方法
任务执行完后的回调方法,有返回值
handler既可以感知异常,也可以返回默认数据,是whenComplete和exceptionally的结合
CompletableFuture的handle方法表示,某个任务执行完成后,执行回调方法,并且是有返回值的;并且handle方法返回的CompletableFuture的result是回调方法执行的结果。
多个任务组合处理
AND组合关系
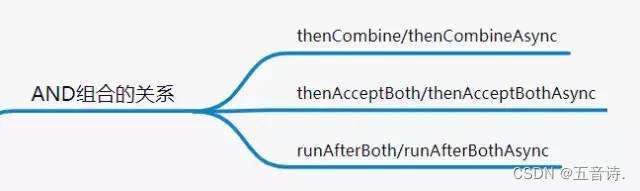
thenCombine / thenAcceptBoth / runAfterBoth都表示:将两个CompletableFuture组合起来,只有这两个都正常执行完了,才会执行某个任务。
区别在于:
- thenCombine:会将两个任务的执行结果作为方法入参,传递到指定方法中,且有返回值
- thenAcceptBoth: 会将两个任务的执行结果作为方法入参,传递到指定方法中,且无返回值
- runAfterBoth 不会把执行结果当做方法入参,且没有返回值。
OR 组合的关系
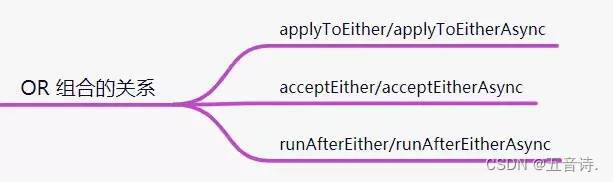
applyToEither / acceptEither / runAfterEither 都表示:将两个CompletableFuture组合起来,只要其中一个执行完了,就会执行某个任务。
区别在于:
- applyToEither:会将已经执行完成的任务,作为方法入参,传递到指定方法中,且有返回值
- acceptEither: 会将已经执行完成的任务,作为方法入参,传递到指定方法中,且无返回值
- runAfterEither:不会把执行结果当做方法入参,且没有返回值。
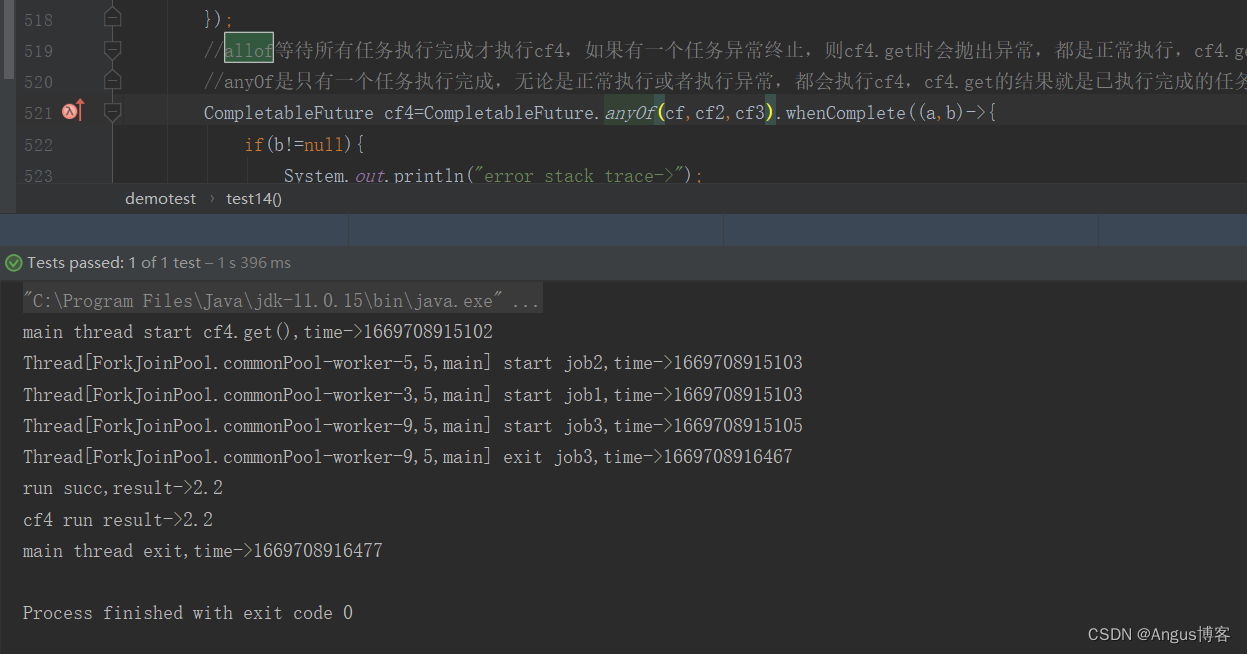
AllOf
所有任务都执行完成后,才执行 allOf返回的CompletableFuture。如果任意一个任务异常,allOf的CompletableFuture,执行get方法,会抛出异常
AnyOf
任意一个任务执行完,就执行anyOf返回的CompletableFuture。如果执行的任务异常,anyOf的CompletableFuture,执行get方法,会抛出异常
thenCompose
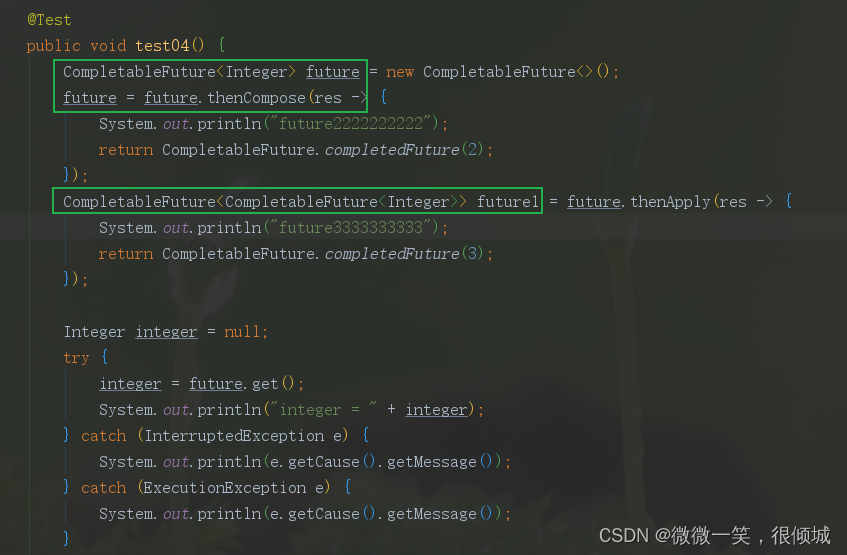
thenCompose方法会在某个任务执行完成后,将该任务的执行结果,作为方法入参,去执行指定的方法。该方法会返回一个新的CompletableFuture实例
- 如果该CompletableFuture实例的result不为null,则返回一个基于该result新的CompletableFuture实例;
- 如果该CompletableFuture实例为null,然后就执行这个新任务
@Test
public void thenCompose() {//可以自定义线程池ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);CompletableFuture<String> task1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("执行task1的线程=" + Thread.currentThread().getName());return "捡田螺的小男孩";}, executor);CompletableFuture<String> stringCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("执行task2的线程=" + Thread.currentThread().getName());return 666;}, executor).thenComposeAsync(data -> {System.out.println("执行thenComposeAsync的线程=" + Thread.currentThread().getName());System.out.println("task2的返回结果=" + data);//返回task1return task1;}, executor);System.out.println(stringCompletableFuture.join());executor.shutdown(); // 线程池需要关闭
}
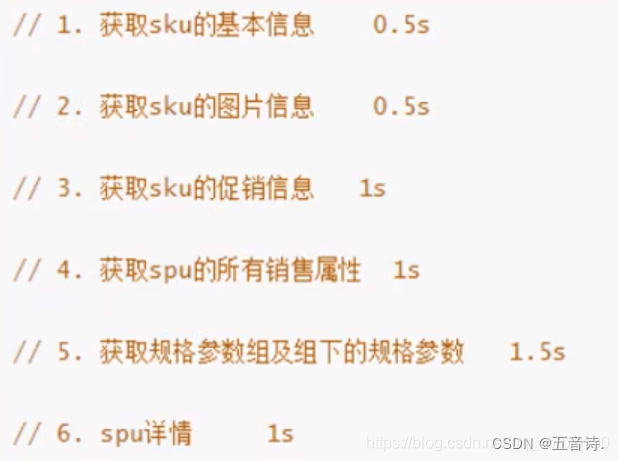
应用场景:
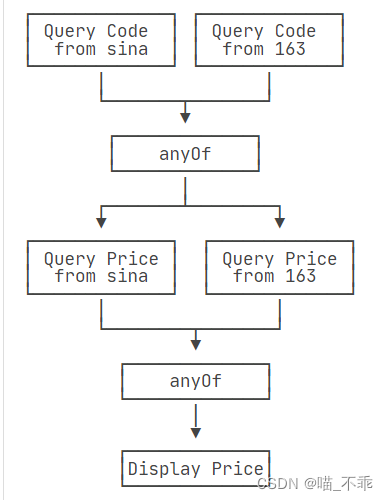
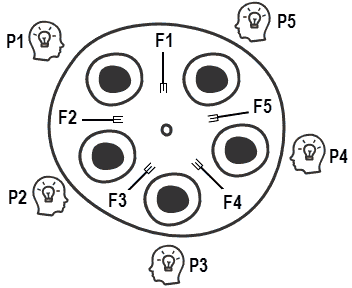
电商项目中,获取商品详情通常业务比较复杂,还需要调用别的服务的接口,比较耗时。假如每个数据的获取时间如下图所示,如果不使用异步,用户需要5.5s后才能看到页面内容,显然是不合理的。如果使用异步,同时有6个线程同时获取这些数据,用户只需要1.5s即可看到!
CompletableFuture实现了Future接口,FutureTask也实现了Future接口
package com.ung.test;import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;import java.util.concurrent.*;/*** @author: wenyi* @create: 2022/10/11* @Description: CompletableFuture异步编排*/
public class ThreadTest {@Testpublic void testCompletableFuture() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {//定义线程池 核心线程数和最大线程数都是10ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);/*** 1.无返回值的异步任务* Void runAsync(Runnable runnable,Executor executor)*/
// CompletableFuture<Void> voidCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
// System.out.println("线程号******" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
// int i = 5;
// System.out.println("无返回值的 runAsync ,i=" + i);
// }, threadPool);/*** 2.有返回值的 supplyAsync* whenComplete, handle,外面的结果打印执行的都是主线程main* supplyAsync 执行的是线程池里的线程 pool-1-thread-1*/
// CompletableFuture<Integer> integerCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// System.out.println("supplyAsync 线程号******" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
// int i = 5;
// System.out.println("有返回值的 supplyAsync ,i=" + i);
// return i;
// }, threadPool).whenComplete((r, e) -> {
// /**
// * CompletableFuture<T> whenComplete(@NotNull java.util.function.BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> action)
// * whenComplete 的参数 BiConsumer对象的构造第一个参数是结果,第二个参数是异常,他可以感知异常,无法返回默认数据
// */
// System.out.println("whenComplete 线程号******" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
// System.out.println("执行后结果 " + r);
// System.out.println("whenComplete 里的异常:" + e);
// }).exceptionally(u -> {
// /**
// * CompletableFuture<T> exceptionally(Function<Throwable, ? extends T> fn)
// * 方法的参数 fn 的构造是 异常
// * 可以感知异常,然后返回默认数据10
// */
// System.out.println("exceptionally 线程号******" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
// System.out.println("exceptionally 里的异常:" + u);
// return 10;
// }).handle((r, e) -> {
// /**
// * CompletableFuture<U> handle(BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn)
// * handler既可以感知异常,也可以返回默认数据,是whenComplete和exceptionally的结合
// */
// System.out.println("handle 线程号******" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
// if (r != null) {
// System.out.println("handle:结果:" + r);
// return r;
// }
// if (e != null) {
// System.out.println("handle:异常:" + e);
// System.out.println("handle:结果为null,异常不null,返回出现异常的默认值");
// return 0;
// }
// System.out.println("handle:结果为null,异常也为null,最后返回默认 15");
// return 15;
// });
// try {
// System.out.println("外面 线程号******" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
// Integer result = integerCompletableFuture.get();
// System.out.println("最后的结果:" + result);
// } catch (InterruptedException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// } catch (ExecutionException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }/*** 3.线程串行化* 就是将前面和后面的任务串起来执行*//*** thenRunAsync 不能接收返回值处理,最后无返回值返回* CompletableFuture使用了默认线程池是ForkJoinPool.commonPool。* 执行的是 ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1*/CompletableFuture<Void> voidCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {//线程号:pool-1-thread-1System.out.println("supplyAsync 线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());int i = 5;System.out.println("i ***** " + i);return i;}, threadPool).thenRunAsync(() -> {//线程号:ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1System.out.println("thenRunAsync 线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());System.out.println("thenRunAsync , 不可接收传来的值,自己无返回值的串行化");},threadPool);
// Void aVoid = voidCompletableFuture.get();/*** thenAccept(x) 可以接收返回值处理,最后无返回值返回* 执行的是main线程*/
// CompletableFuture<Void> voidCompletableFuture1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// //supplyAsync 线程号:pool-1-thread-1
// System.out.println("supplyAsync 线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
// int i = 5;
// System.out.println("i ***** " + i);
// return i;
// }, threadPool).thenAccept((r) -> {
// //thenAccept 线程号:main
// System.out.println("thenAccept 线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
// System.out.println("thenAccept接收的结果:" + r);
// System.out.println("thenAccept可接受传来的值,自己无返回值的串行化---");
// });
// Void aVoid = voidCompletableFuture1.get();/*** thenApply 可以接收返回值,也返回自己的返回值* 执行的是main线程*/
// CompletableFuture<Integer> integerCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// //supplyAsync 线程号:pool-1-thread-1
// System.out.println("supplyAsync 线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
// int i = 5;
// System.out.println("i ***** " + i);
// return i;
// }, threadPool).thenApply((r) -> {
// //thenApply 线程号:main
// System.out.println("thenApply 线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
// System.out.println("thenApply 接收的结果:" + r);
// System.out.println("thenApply可接受传来的值,自己有返回值的串行化---");
// return 15;
// });
// try {
// //外面获取值 线程号:main
// System.out.println("外面获取值 线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
// Integer integer = integerCompletableFuture.get();
// System.out.println("rusult=" + integer);
// } catch (InterruptedException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// } catch (ExecutionException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }/*** 异步任务组合* 两个任务都完成,第三个任务才开始*///任务1CompletableFuture<Integer> task1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("task1 线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());int i = 5;System.out.println("任务1开始执行" + i);return i;}, threadPool);//任务2CompletableFuture<Integer> task2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("task2 线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());try {Thread.sleep(5000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}int i = 10;System.out.println("任务2开始执行" + i);return i;}, threadPool);//要求任务1和任务2都完成后再执行任务3//runAfterBothAsync 无传入值,无返回值,
// task1.runAfterBothAsync(task2, () -> {
// //task3 线程号:pool-1-thread-3 执行的是线程池的线程
// System.out.println("task3 线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
// System.out.println("任务3开始执行:runAfterBothAsync 无传入值,无返回值");
// }, threadPool);//thenAcceptBothAsync 有传入值,无返回值,
// CompletableFuture<Void> voidCompletableFuture = task1.thenAcceptBothAsync(task2, (x, y) -> {
// //pool-1-thread-3
// System.out.println("task3 线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
// System.out.println("任务3开始执行:thenAcceptBothAsync 有传入值,无返回值,task1的结果=" + x + "task2的结果=" + y);
// }, threadPool);//thenCombineAsync 有传入值,有返回值
// CompletableFuture<Integer> integerCompletableFuture = task1.thenCombineAsync(task2, (x, y) -> {
// //pool-1-thread-3
// System.out.println("task3 线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
// System.out.println("任务3开始执行:thenCombineAsync 有传入值,有返回值,task1的结果=" + x + "task2的结果=" + y);
// return 20;
// }, threadPool);
// try {
// Integer integer = integerCompletableFuture.get();
// System.out.println(integer);
// } catch (InterruptedException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// } catch (ExecutionException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }/*** 两个任务完成其中一个,第三个任务才开始* * runAfterEither 无传入值、无返回值* * acceptEither 有传入值、无返回值* * applyToEither 有传入值、有返回值*//*** 又见一个新的异步任务,里面任务1执行比较快,任务2执行慢,最后打印结果是线程1执行完毕后,线程2还没执行完,就会执行线程3* 最后线程2再执行完*/
// CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// //runAfterEitherAsync 无传入值,无返回值,
// task2.runAfterEither(task1, () -> {
// //task3 线程号:pool-1-thread-3 执行的是线程池的线程
// System.out.println("task3 线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
// System.out.println("任务3开始执行:runAfterEitherAsync 无传入值,无返回值");
// });
// int i = 10;
// return i;
// }, threadPool);/*** 异步,多任务组合 :多个任务都完成,才进行下一步操作* allOf() 等待所有任务完成* anyOf() 只要有一个任务完成即可* 注意:最后使用get()方法:阻塞式等待所有任务都做完,再进行下一步*///allOf 任务1和任务2都要执行完才可以执行任务3
// CompletableFuture<Void> voidCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.allOf(task1, task2).thenRunAsync(() -> {
// //pool-1-thread-3
// System.out.println("task3 线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
// System.out.println("第三个任务开始执行");
// }, threadPool);//anyOf 任务1执行完后就会执行任务3CompletableFuture.anyOf(task1, task2).thenRunAsync(() -> {//pool-1-thread-3System.out.println("task3 线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());System.out.println("第三个任务开始执行");}, threadPool);Thread.sleep(10000);}
}
CompletableFuture使用有哪些注意点
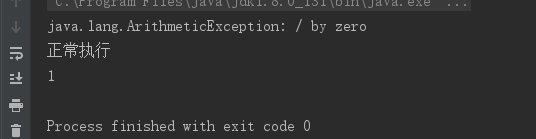
1. Future需要获取返回值,才能获取异常信息
如果不加 get()/join()方法,看不到异常信息。
注意 考虑是否加try…catch…或者使用exceptionally方法。
@Testpublic void test3() {ExecutorService executorService = new ThreadPoolExecutor(5, 10, 5L,TimeUnit.SECONDS, new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(10));CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {int a = 0;int b = 666;int c = b / a;return true;}, executorService).thenAccept(System.out::println);//如果不加 get()方法这一行,看不到异常信息
// try {
// future.get();
// } catch (InterruptedException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// } catch (ExecutionException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }}
2. CompletableFuture的get()方法是阻塞的。
如果使用它来获取异步调用的返回值,需要添加超时时间
//反例CompletableFuture.get();
//正例
CompletableFuture.get(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
future.get方法会阻塞当前主流程,在超时时间内等待子线程返回结果,如果超时还没结果则结束等待继续执行后续的代码
3.默认线程池的注意点
CompletableFuture代码中又使用了默认的线程池,处理的线程个数是电脑CPU核数-1。
在大量请求过来的时候,处理逻辑复杂的话,响应会很慢。一般建议使用自定义线程池,优化线程池配置参数。
4.自定义线程池时,注意饱和策略
CompletableFuture的get()方法是阻塞的,我们一般建议使用future.get(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS)。并且一般建议使用自定义线程池。
但是如果线程池拒绝策略是DiscardPolicy或者DiscardOldestPolicy,当线程池饱和时,会直接丢弃任务,不会抛弃异常。拒绝策略不能使用DiscardPolicy,这种丢弃策略虽然不执行子线程的任务,但是还是会返回future对象,后续代码即使判断了future!=null也没用,这样的话还是会走到future.get()方法,如果get方法没有设置超时时间会导致一直阻塞下去!
因此建议,CompletableFuture线程池策略最好使用AbortPolicy,然后耗时的异步线程,做好线程池隔离哈。
[Java踩坑记系列之线程池 - 老K的Java博客 (javakk.com)](