目录
一、用两个队列实现一个栈
1.1 问题描述
1.2 问题分析
1.3 代码
二、用两个栈实现一个队列
2.1 问题描述
2.2 问题分析
2.3 代码
一、用两个队列实现一个栈
1.1 问题描述
oj链接:225. 用队列实现栈 - 力扣(LeetCode)

1.2 问题分析
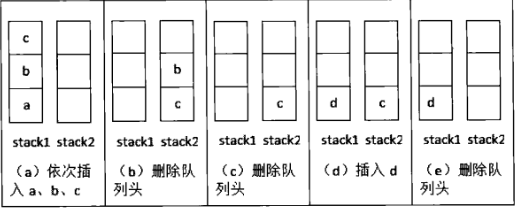
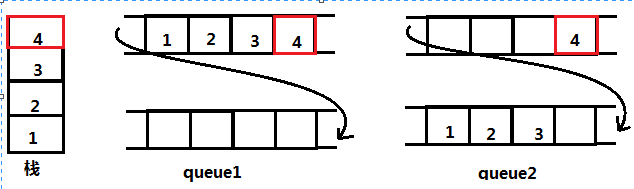
用两个队列来实现栈,首先我们需要了解栈和队列这两种结构各自的特点,栈要求先入后出,队列要求先进先出。
也就是说,用两个队列来模拟实现栈,主要是使用两个队列来完成先入后出的功能,而队列的特点是先入先出,在这里我们主要说明的是入栈和出栈操作:
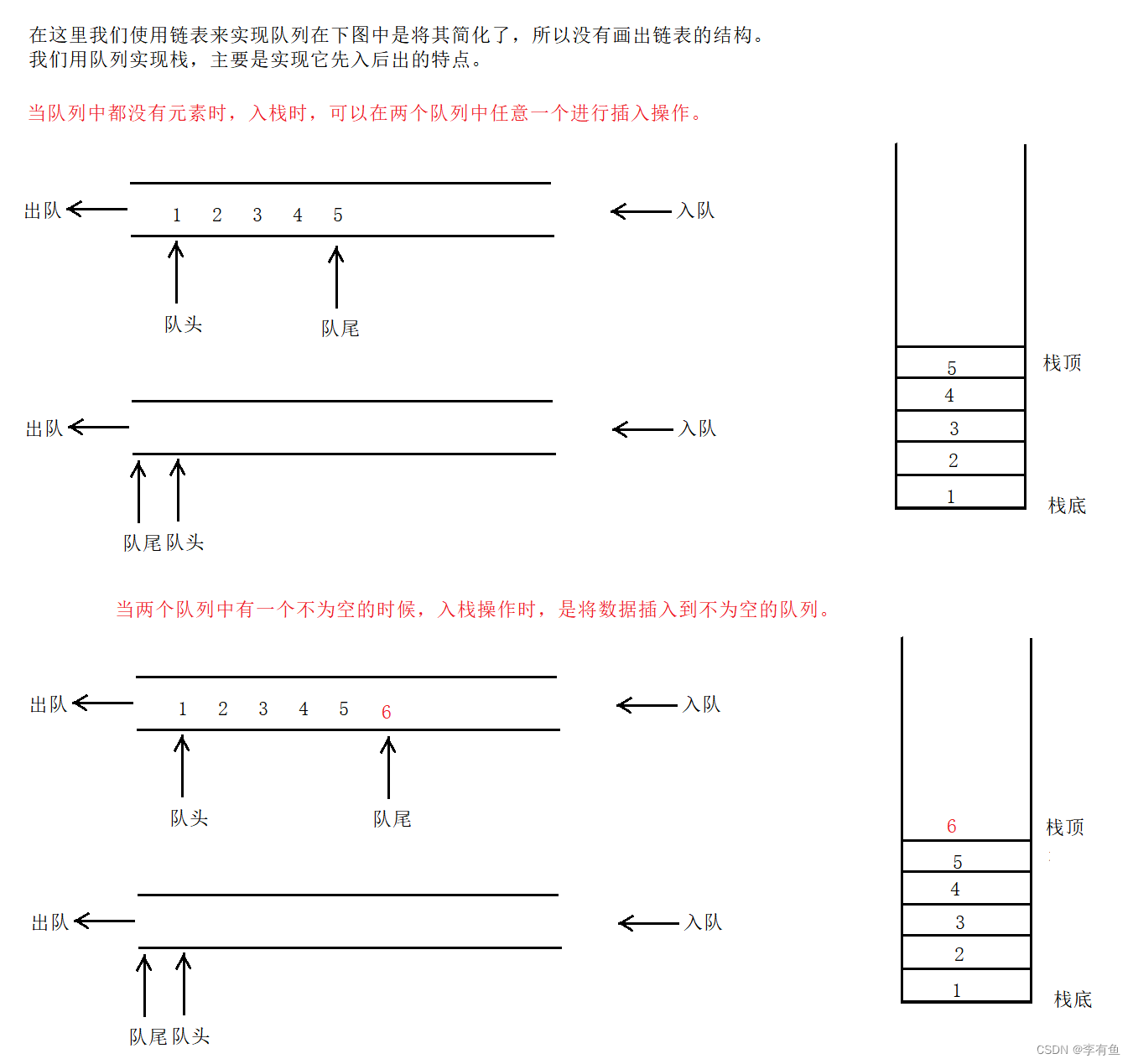
对于入栈:
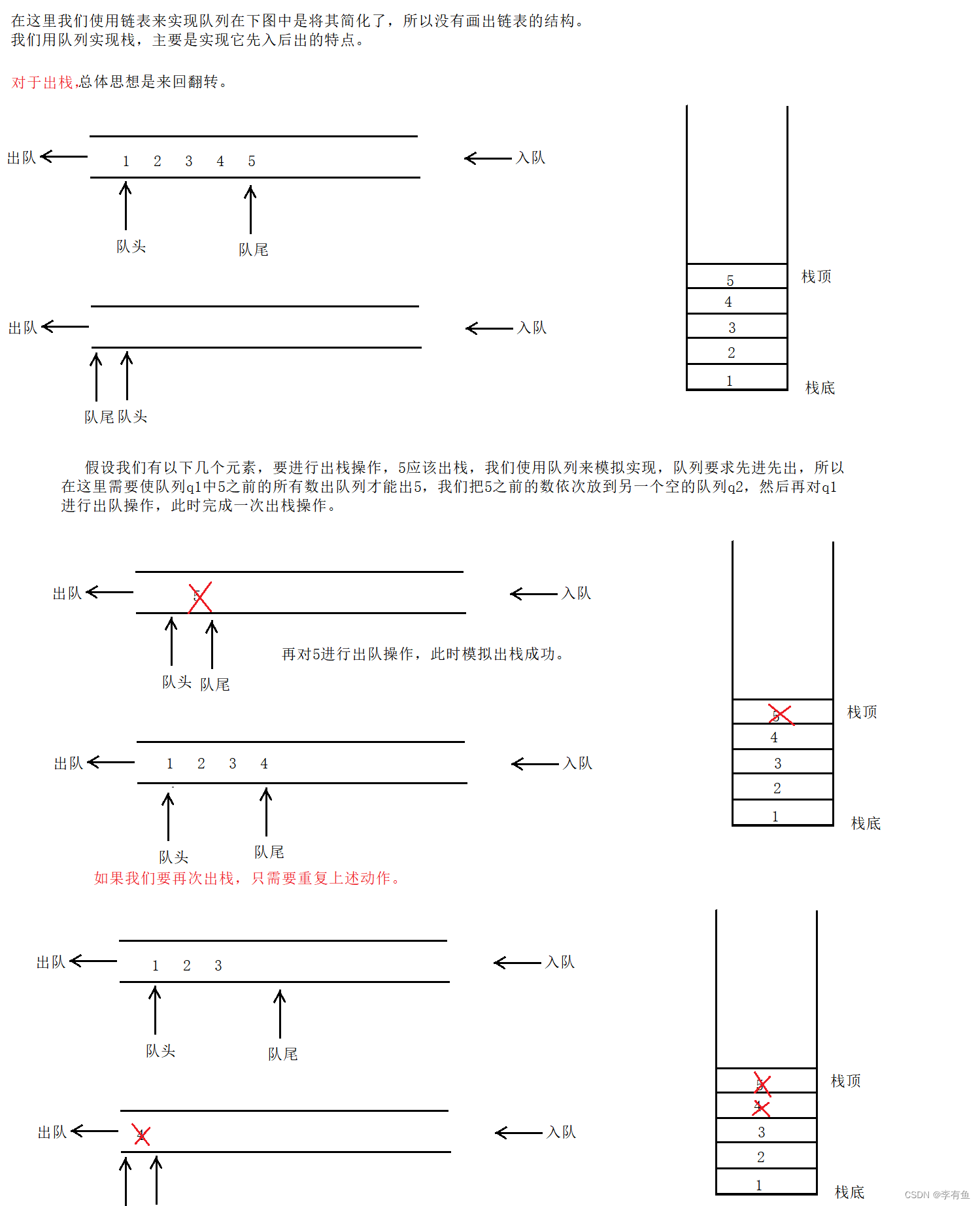
对于出栈:
总结起来即以下几点:
- 定义一个结构体Stack,包含两个队列q1和q2。
- 初始化栈时,分别初始化两个队列。
- 入栈操作时,将元素插入非空的队列中。
- 出栈操作时,将非空队列中的元素依次出队并插入另一个空队列中,直到只剩下一个元素,然后将该元素出队即可。
- 取栈顶元素时,将非空队列中的元素依次出队并插入另一个空队列中,直到只剩下一个元素,然后返回该元素即可。
- 判断栈是否为空时,判断两个队列是否都为空即可。
1.3 代码
typedef int QDatatype;
typedef struct QueueNode
{struct QueueNode* next;QDatatype data;
}QNode;typedef struct Queue
{QNode* head;QNode* tail;int size;
}Queue;//初始化函数
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;pq->size = 0;
}//销毁
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);QNode* cur = pq->head;while (cur){QNode* next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = next;}pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;pq->size = 0;
}//入队列
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDatatype x)
{assert(pq);QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));if (newnode == NULL){perror("malloc fail");return;}newnode->data = x;newnode->next = NULL;if (pq->head == NULL){assert(pq->tail == NULL);pq->head = pq->tail = newnode;}else{pq->tail->next = newnode;pq->tail = newnode;}pq->size++;
}//判断是否为空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);return pq->size == 0;
}//出队列
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(!(QueueEmpty(pq)));if (pq->head == pq->tail){free(pq->head);pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;}else{QNode* next = pq->head->next;free(pq->head);pq->head = next;}pq->size--;
}//求队列的元素个数
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);return pq->size;
}//返回队首元素
QDatatype QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(!(QueueEmpty(pq)));return pq->head->data;
}//返回队尾元素
QDatatype QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(!(QueueEmpty(pq)));return pq->tail->data;
}void QueueInit(Queue* pq);
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq);
void QueuePush(Queue* pq,QDatatype x);
void QueuePop(Queue* pq);
int QueueSize(Queue* pq);
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);
QDatatype QueueFront(Queue* pq);
QDatatype QueueBack(Queue* pq);typedef struct {Queue q1;Queue q2;
} MyStack;MyStack* myStackCreate() {MyStack* pst = (MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));if(pst==NULL){perror("malloc fail");return NULL;}QueueInit(&pst->q1);QueueInit(&pst->q2);return pst;
}void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) {if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)){QueuePush(&obj->q1, x);}else{QueuePush(&obj->q2, x);}
}bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) {return QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)&&QueueEmpty(&obj->q2);
}int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) {assert(!myStackEmpty(obj));Queue* nonemptyque = &obj->q1;Queue* emptyque = &obj->q2;if(QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)){nonemptyque = &obj->q2;emptyque = &obj->q1;}while(QueueSize(nonemptyque)>1){QueuePush(emptyque,QueueFront(nonemptyque));QueuePop(nonemptyque);}int x = QueueFront(nonemptyque);QueuePop(nonemptyque);return x;
}int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) {assert(!myStackEmpty(obj));Queue* nonemptyque = &obj->q1;Queue* emptyque = &obj->q2;if(QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)){nonemptyque = &obj->q2;emptyque = &obj->q1;}return QueueBack(nonemptyque);
}void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) {QueueDestroy(&obj->q1);QueueDestroy(&obj->q2);free(obj);
}二、用两个栈实现一个队列
2.1 问题描述
oj链接:232. 用栈实现队列 - 力扣(LeetCode)

2.2 问题分析
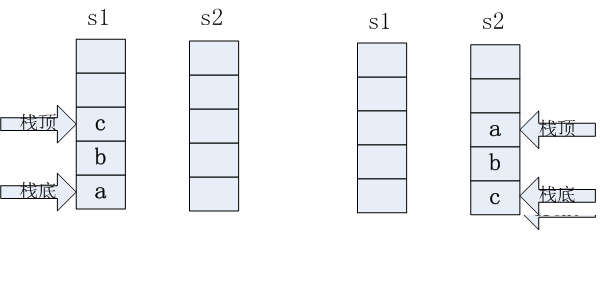
我们要用两个栈来实现一个队列,栈的特点是先入后出,队列的特点是先入先出,我们这里的目的是使用两个栈达到先入先出的目的。
与之前的用两个队列来实现栈,用两个栈来实现队列相对简单,在之前的用两个队列来实现栈,我们在出栈时需要把两个队列中的数据来回翻转,但在本题中,我们只需要定义一个栈来进行插入操作,一个用来删除。
我们固定使用栈q1来进行入队操作,使用栈q2来进行出队操作。
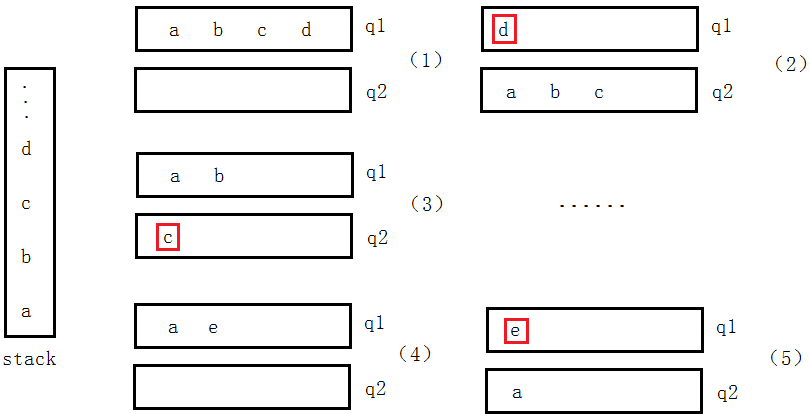
入队时:
直接将数据插入到q1中。
出队时:
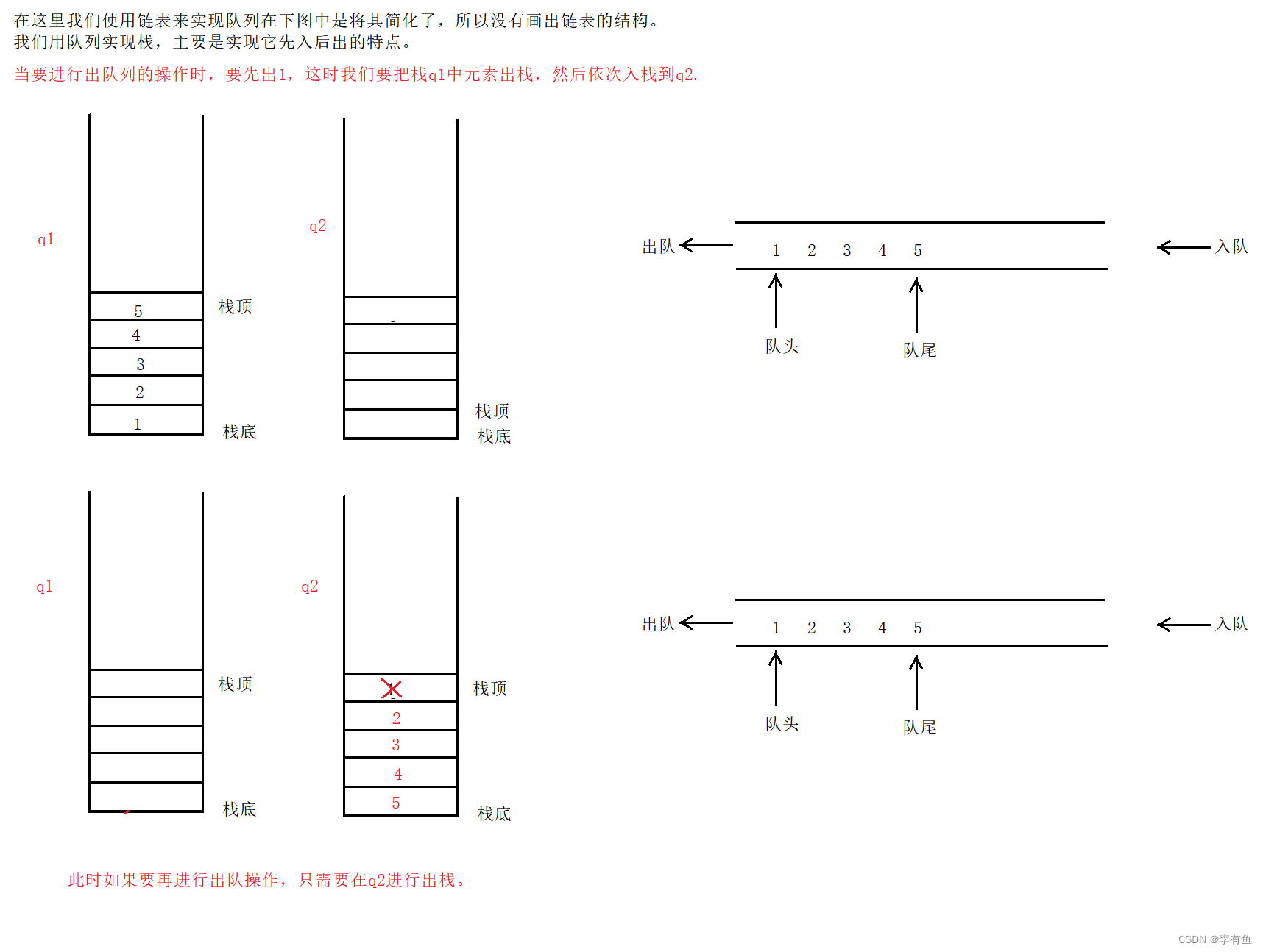
当q2为空时,再次将q1中数据依次出栈,然后依次插入到栈q2中。
具体总结如下:
- 定义一个结构体Queue,包含两个栈s1和s2。
- 初始化队列时,分别初始化两个栈。
- 入队操作时,将元素插入非空的栈s1中。
- 出队操作时,如果栈s2为空,则将栈s1中的元素依次出栈并插入栈s2中,然后将栈s2的栈顶元素出栈即可。
- 取队首元素时,如果栈s2为空,则将栈s1中的元素依次出栈并插入栈s2中,然后返回栈s2的栈顶元素即可。
- 判断队列是否为空时,判断两个栈是否都为空即可。
2.3 代码
typedef int STDataType;
#define N 4
typedef struct Stack
{STDataType* a;int top;int capacity;
}ST;void STInit(ST* ps);
void STDestroy(ST* ps);
void STPush(ST* ps, STDataType x);
void STPop(ST* ps);
int STsize(ST* ps);
bool STEmpty(ST* ps);
STDataType STTop(ST* ps);//初始化函数
void STInit(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);ps->a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType)*N);if (ps->a == NULL){perror("malloc fail");return;}ps->top = 0;ps->capacity = N;
}//销毁
void STDestroy(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);free(ps->a);ps->a = NULL;ps->top = 0;ps->capacity = 0;
}//求栈中的元素
int STsize(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);return ps->top;
}//入栈
void STPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
{assert(ps);if (STsize(ps) == ps->capacity){STDataType* p = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a, sizeof(STDataType) * ps->capacity * 2);if (p == NULL){perror("realloc fail");return;}ps->a = p;ps->capacity *= 2;}ps->a[ps->top] = x;ps->top++;
}//判断栈是否为空
bool STEmpty(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);return ps->top == 0;
}//出栈
void STPop(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);assert(!STEmpty(ps));ps->top--;
}//取出栈顶元素
STDataType STTop(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);assert(!STEmpty(ps));return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}typedef struct {ST q1;ST q2;
} MyQueue;MyQueue* myQueueCreate() {MyQueue* pst = (MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));if(pst==NULL){perror("malloc fail");return NULL;}STInit(&pst->q1);STInit(&pst->q2);return pst;
}void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x) {STPush(&obj->q1, x);
}bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj) {return STEmpty(&obj->q1)&&STEmpty(&obj->q2);
}int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj) {assert(!myQueueEmpty(obj));if(STEmpty(&obj->q2)){while(STsize(&obj->q1)>0){STPush(&obj->q2, STTop(&obj->q1));STPop(&obj->q1);}int x= STTop(&obj->q2);STPop(&obj->q2);return x; }else{int x= STTop(&obj->q2);STPop(&obj->q2);return x;}
}int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj) {assert(!myQueueEmpty(obj));if(STEmpty(&obj->q2)){while(STsize(&obj->q1)>0){STPush(&obj->q2, STTop(&obj->q1));STPop(&obj->q1);}int x= STTop(&obj->q2);return x; }else{int x= STTop(&obj->q2);return x;}
}void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj) {STDestroy(&obj->q1);STDestroy(&obj->q2);free(obj);
}









![[Prescan]Prescan中Sensor学习](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/2019100909585445.png)