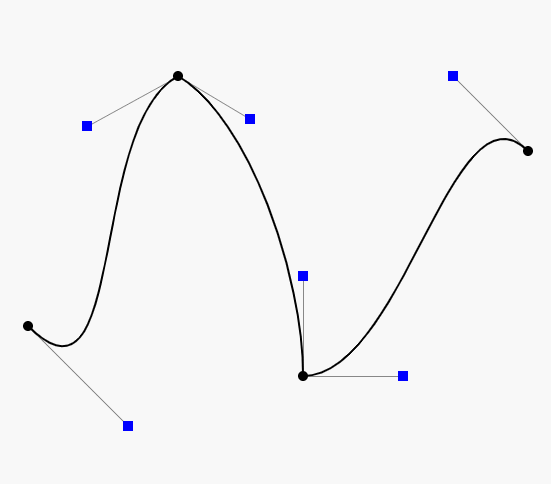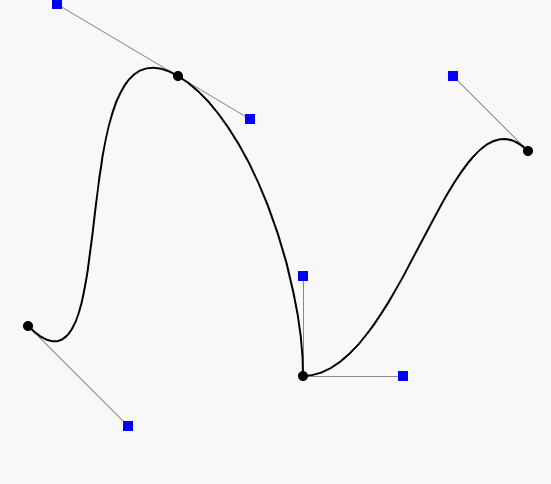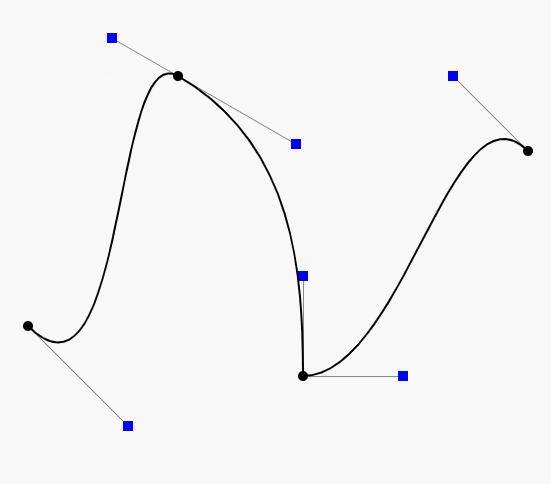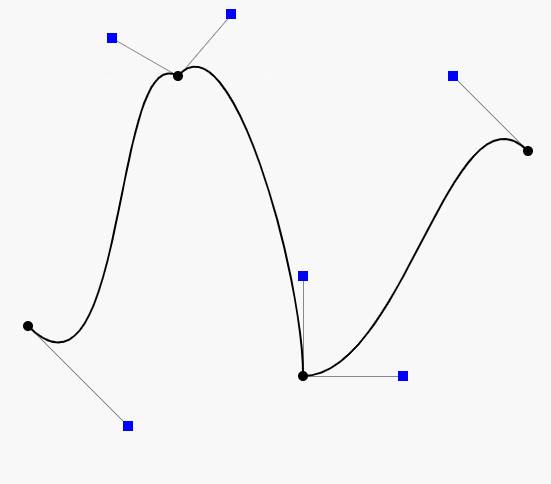
问题:如何将一个三阶贝塞尔曲线打断生成两个三阶贝塞尔曲线,生成的两条贝塞尔曲线与原来的贝塞尔曲线重合?
输入:一条贝塞尔曲线的四个控制点P1,C1,C2,P2,和一个打断点E(E在曲线上)
输出:两条贝塞尔曲线:
P1,F,I,E
E,J,H,P2
解决大致分为两步
第一步:求出E点对应的贝塞尔曲线的参数e
第二步:根据e计算出四个控制点F,I,J,H
依次多个点打断,红色线表示原始贝塞尔,蓝色线是打断的两个贝塞尔曲线,效果如下:蓝色线和红色线基本重合。

源码
原理解析:
如图的红色曲线就是原始贝塞尔曲线,加入打断点就是E点,因为E在曲线上,所以必存在一个时刻e。
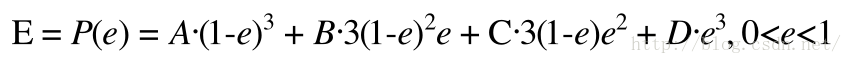

根据贝塞尔曲线的特征我们可以得到以下结论
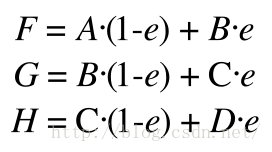
根据上式可以得到以下式子
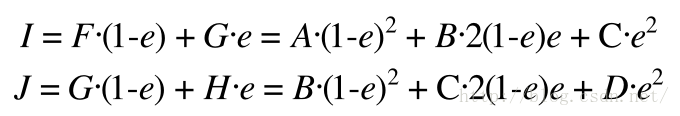
E也可以通过I和J来定义
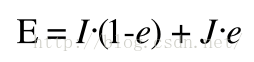
所以,如果知道断点E对应的时刻e,计算F,I,J,H相对比较简单。
下面介绍如何计算e
方法1 解方程
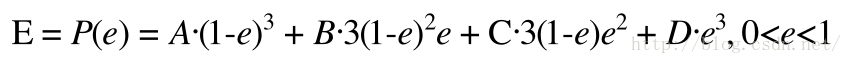
可以看到求解e就是解关于e的一元三次方程,数学相对简单,但是工程上实现较为复杂。
方法2 迭代
从0开始迭代t,设置一个步长d,计算Pi = P(ti) ti = ti+d,每次迭代时计算Pi和E的欧式距离,并记录距离最小时的时刻e = ti,就可以粗略计算出e。经测试,步长设置为0.01,效果良好。
下面给出QML代码示例:
import QtQuick 2.15
import QtQuick.Window 2.15Window {visible: truewidth: 1920height: 1080title: qsTr("Hello World")//测试点property var testP1: Qt.vector2d(1909, 12)property var testC1: Qt.vector2d(1910, 998)property var testC2: Qt.vector2d(31, 15.233737999999903)property var testP2: Qt.vector2d(11, 4)//三次贝塞尔曲线//a1 * (1 - t) * (1 - t) * (1 - t) + 3 * a2 * t * (1 - t) * (1 - t) + 3 * a3 * t * t * (1 - t) + a4 * t * t * t;/*t:时间变量 [0-1]p1:首端点p2:末端点c1:首端点控制点c2:末端点控制点返回值:t时刻贝塞尔曲线上的点控制点、端点和返回值的数据类型为:vector2d*/function thirdOrderBeziercurve(t, p1, c1, c2, p2) {if(t<0 || t>1)return;var p = p1.times(Math.pow(1 - t,3))p = p.plus(c1.times(3 * t * Math.pow(1-t,2)))p = p.plus(c2.times(3 * (1-t) * Math.pow(t,2)))p = p.plus(p2.times(Math.pow(t,3)))return p//return}// 计算两个点指点的距离,点的数据类型可以是vector2d或者Qt.pointfunction distance(p1,p2){return Math.sqrt(Math.pow(p1.x-p2.x,2)+Math.pow(p1.y-p2.y,2))}//根据时间t获取打断后的两条贝塞尔曲线的控制点/*return [c11,c21,c22,c31]*/function getControlPointByT(p1, c1, c2, p2,t){//辅助点gvar g = c1.times(1-t).plus(c2.times(t))var c11 = p1.times(1-t).plus(c1.times(t))var c21 = c11.times(1-t).plus(g.times(t))var c31 = c2.times(1-t).plus(p2.times(t))var c22 = g.times(1-t).plus(c31.times(t))return [c11,c21,c22,c31]}//判断点是否在贝塞尔曲线上,如果在(误差范围内),返回时间t和逼近点/*输入:p1,c1,c2,p2:是贝塞尔曲线的参数p:特定点坐标errorValue:误差值输出:1.如果p点在贝塞尔曲线上,返回打断后的两条贝塞尔曲线的控制点和纠正点[c11,c21,c22,c31,rightPoint]2.否则,返回[]*/function getControlPointByPoint(p1, c1, c2, p2, p, errorValue){var m = 1000000;var t = 0var pt = Qt.vector2d(-1,-1)for(var i = 0;i<=1;i=i+0.01){var pi = thirdOrderBeziercurve(i,p1, c1, c2, p2)var d = distance(pi,p)if(d< m){m =dt = ipt = pi}}if(m < errorValue){console.log(t)var ctrlsPoints = getControlPointByT(p1, c1, c2, p2,t)//ctrlsPoints.push(pt)return ctrlsPoints}return []}Canvas{id:cvsanchors.fill: parentproperty var c: testP1property var ctrs:[]onPaint:{var ctx = cvs.getContext('2d')ctx.reset()ctx.save()ctx.clearRect(0,0,width,height)ctx.beginPath()ctx.moveTo(testP1.x,testP1.y)ctx.lineWidth="4"ctx.strokeStyle="red"ctx.bezierCurveTo(testC1.x,testC1.y,testC2.x,testC2.y,testP2.x,testP2.y)ctx.stroke()//ctx.closepath()//ctx.save()ctx.beginPath()ctx.arc(c.x,c.y,10,0,360,true)ctx.stroke()if(ctrs.length != 0){ctx.lineWidth="1"ctx.strokeStyle="blue"ctx.beginPath()ctx.moveTo(testP1.x,testP1.y)ctx.bezierCurveTo(ctrs[0].x,ctrs[0].y,ctrs[1].x,ctrs[1].y,cvs.c.x,cvs.c.y)ctx.bezierCurveTo(ctrs[2].x,ctrs[2].y,ctrs[3].x,ctrs[3].y,testP2.x,testP2.y)ctx.stroke()}}}Timer{interval: 100;running: true;repeat: trueproperty var t: 0.0onTriggered: {cvs.c = thirdOrderBeziercurve(t,testP1,testC1,testC2,testP2)cvs.ctrs = getControlPointByPoint(testP1,testC1,testC2,testP2,cvs.c,100)cvs.requestPaint()t = t+0.01if(t >1)t = 0}}
}