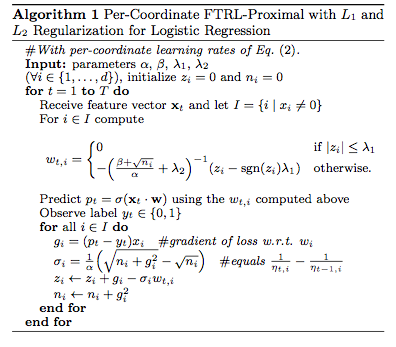
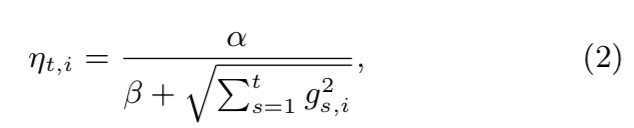理解要点:主要是梯度更新的方法使用了FTRL。即更改了梯度的update函数。
相关参考:https://github.com/wan501278191/OnlineLearning_BasicAlgorithm/blob/master/FTRL.py
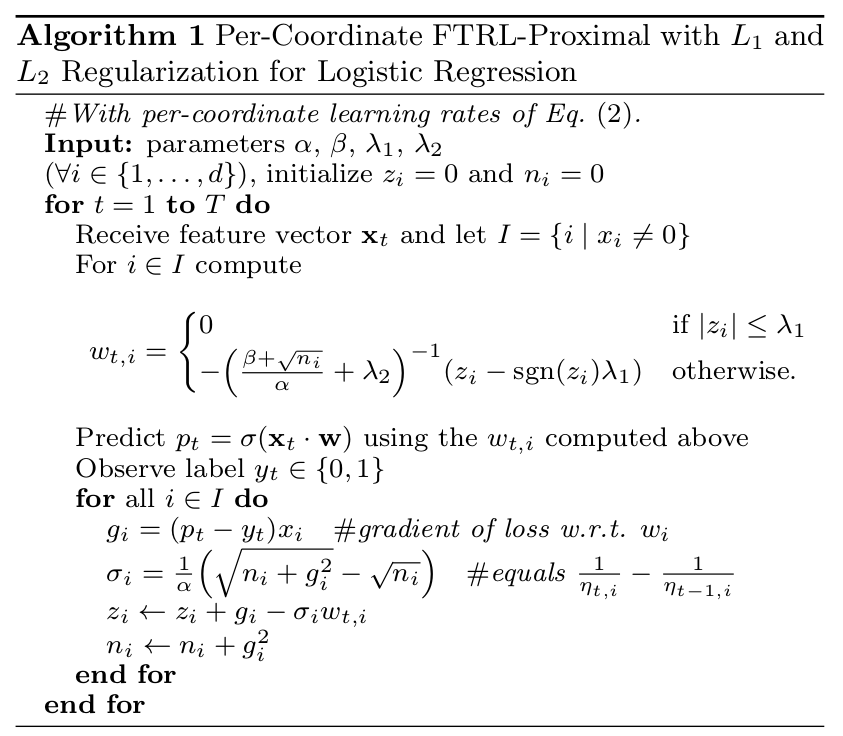
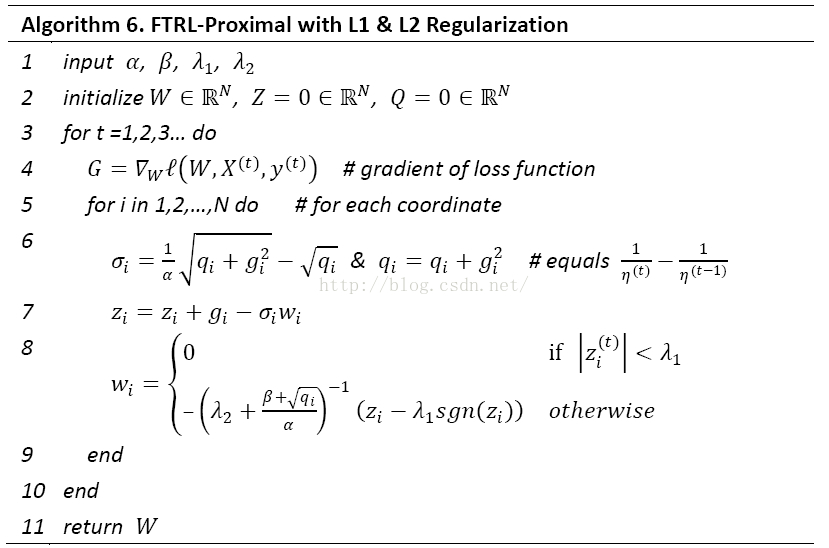
FTRL(Follow The Regularized Leader)是一种优化方法,就如同SGD(Stochastic Gradient Descent)一样。这里直接给出用FTRL优化LR(Logistic Regression)的步骤:
其中pt=σ(Xt⋅w)是LR的预测函数,求出pt的唯一目的是为了求出目标函数(在LR中采用交叉熵损失函数作为目标函数)对参数w的一阶导数g,gi=(pt−yt)xi。上面的步骤同样适用于FTRL优化其他目标函数,唯一的不同就是求次梯度g(次梯度是左导和右导之间的集合,函数可导--左导等于右导时,次梯度就等于一阶梯度)的方法不同。
一、先查看一下数据

二、构建FTRL模型
# %load FTRL.py
# Date: 2018-08-17 9:47
# Author: Enneng Yang
# Abstract:ftrl ref:http://www.cnblogs.com/zhangchaoyang/articles/6854175.htmlimport sys
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
import random
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf# logistic regression
class LR(object):@staticmethoddef fn(w, x):''' sigmod function '''return 1.0 / (1.0 + np.exp(-w.dot(x)))@staticmethoddef loss(y, y_hat):'''cross-entropy loss function'''return np.sum(np.nan_to_num(-y * np.log(y_hat) - (1-y)*np.log(1-y_hat)))@staticmethoddef grad(y, y_hat, x):'''gradient function'''return (y_hat - y) * xclass FTRL(object):def __init__(self, dim, l1, l2, alpha, beta, decisionFunc=LR):self.dim = dimself.l1 = l1self.l2 = l2self.alpha = alphaself.beta = betaself.decisionFunc = decisionFuncself.z = np.zeros(dim)self.q = np.zeros(dim)self.w = np.zeros(dim)def predict(self, x):return self.decisionFunc.fn(self.w, x)def update(self, x, y):self.w = np.array([0 if np.abs(self.z[i]) <= self.l1else (np.sign(self.z[i]) * self.l1 - self.z[i]) / (self.l2 + (self.beta + np.sqrt(self.q[i]))/self.alpha)for i in range(self.dim)])y_hat = self.predict(x)g = self.decisionFunc.grad(y, y_hat, x)sigma = (np.sqrt(self.q + g*g) - np.sqrt(self.q)) / self.alphaself.z += g - sigma * self.wself.q += g*greturn self.decisionFunc.loss(y,y_hat)def training(self, trainSet, max_itr):n = 0all_loss = []all_step = []while True:for var in trainSet:x= var[:4]y= var[4:5]loss = self.update(x, y)all_loss.append(loss)all_step.append(n)print("itr=" + str(n) + "\tloss=" + str(loss))n += 1if n > max_itr:print("reach max iteration", max_itr)return all_loss, all_step
三、训练
if __name__ == '__main__':d = 4trainSet = np.loadtxt('Data/FTRLtrain.txt')ftrl = FTRL(dim=d, l1=0.001, l2=0.1, alpha=0.1, beta=1e-8)all_loss, all_step = ftrl.training(trainSet, max_itr=100000)w = ftrl.wprint(w)testSet = np.loadtxt('Data/FTRLtest.txt')correct = 0wrong = 0for var in testSet:x = var[:4]y = var[4:5]y_hat = 1.0 if ftrl.predict(x) > 0.5 else 0.0if y == y_hat:correct += 1else:wrong += 1print("correct ratio:", 1.0 * correct / (correct + wrong), "\t correct:", correct, "\t wrong:", wrong)plt.title('FTRL')plt.xlabel('training_epochs')plt.ylabel('loss')plt.plot(all_step, all_loss)plt.show()打印如下:
itr=99996 loss=6.573507715996819e-05
itr=99997 loss=0.004460476965465843
itr=99998 loss=0.27559826174822016
itr=99999 loss=0.49269693073256776
itr=100000 loss=0.00031078609741847434
reach max iteration 100000
[ 4.40236724 1.98715805 11.66128074 3.37851271]
correct ratio: 0.994 correct: 994 wrong: 6
其他参考:
# coding=utf-8
__author__ = "orisun"import numpy as npclass LR(object):@staticmethoddef fn(w, x):'''决策函数为sigmoid函数'''return 1.0 / (1.0 + np.exp(-w.dot(x)))@staticmethoddef loss(y, y_hat):'''交叉熵损失函数'''return np.sum(np.nan_to_num(-y * np.log(y_hat) - (1 - y) * np.log(1 - y_hat)))@staticmethoddef grad(y, y_hat, x):'''交叉熵损失函数对权重w的一阶导数'''return (y_hat - y) * xclass FTRL(object):def __init__(self, dim, l1, l2, alpha, beta, decisionFunc=LR):self.dim = dimself.decisionFunc = decisionFuncself.z = np.zeros(dim)self.n = np.zeros(dim)self.w = np.zeros(dim)self.l1 = l1self.l2 = l2self.alpha = alphaself.beta = betadef predict(self, x):return self.decisionFunc.fn(self.w, x)def update(self, x, y):self.w = np.array([0 if np.abs(self.z[i]) <= self.l1 else (np.sign(self.z[i]) * self.l1 - self.z[i]) / (self.l2 + (self.beta + np.sqrt(self.n[i])) / self.alpha) for i in range(self.dim)])y_hat = self.predict(x)g = self.decisionFunc.grad(y, y_hat, x)sigma = (np.sqrt(self.n + g * g) - np.sqrt(self.n)) / self.alphaself.z += g - sigma * self.wself.n += g * greturn self.decisionFunc.loss(y, y_hat)def train(self, trainSet, verbos=False, max_itr=100000000, eta=0.01, epochs=100):itr = 0n = 0while True:for x, y in trainSet:loss = self.update(x, y)if verbos:print ("itr=" + str(n) + "\tloss=" + str(loss))if loss < eta:itr += 1else:itr = 0if itr >= epochs: # 损失函数已连续epochs次迭代小于etaprint ("loss have less than", eta, " continuously for ", itr, "iterations")returnn += 1if n >= max_itr:print ("reach max iteration", max_itr)returnclass Corpus(object):def __init__(self, file, d):self.d = dself.file = filedef __iter__(self):with open(self.file, 'r') as f_in:for line in f_in:arr = line.strip().split()if len(arr) >= (self.d + 1):yield (np.array([float(x) for x in arr[0:self.d]]), float(arr[self.d]))if __name__ == '__main__':d = 4#corpus = Corpus("train.txt", d)corpus = Corpus("./Data/FTRLtrain.txt", d)ftrl = FTRL(dim=d, l1=1.0, l2=1.0, alpha=0.1, beta=1.0)ftrl.train(corpus, verbos=False, max_itr=100000, eta=0.01, epochs=100)w = ftrl.wprint (w)correct = 0wrong = 0for x, y in corpus:y_hat = 1.0 if ftrl.predict(x) > 0.5 else 0.0if y == y_hat:correct += 1else:wrong += 1print ("correct ratio", 1.0 * correct / (correct + wrong))打印如下:
reach max iteration 100000
[ 4.0726218 1.8432749 10.83822051 3.11898096]
correct ratio 0.9944444444444445当把参数调为λ1=0,λ2=0,α=0.5,β=1λ1=0,λ2=0,α=0.5,β=1时,准确率能达到0.9976。
train.txt文件前4列是特征,第5列是标签。内容形如:
-0.567811945258 0.899305436215 0.501926599477 -0.222973905568 1.0
-0.993964260114 0.261988294216 -0.349167046026 -0.923759536056 0.0
0.300707261785 -0.90855090557 -0.248270600228 0.879134142054 0.0
-0.311566995194 -0.698903141283 0.369841040784 0.175901270771 1.0
0.0245841670644 0.782128080056 0.542680482068 0.44897929707 1.0
0.344387543846 0.297686731698 0.338210312887 0.175049733038 1.0相关参考:
FTRL代码实 https://www.cnblogs.com/zhangchaoyang/articles/6854175.html
在线学习算法:https://blog.csdn.net/kyq156518/article/details/83860804?depth_1-utm_source=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task&utm_source=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task