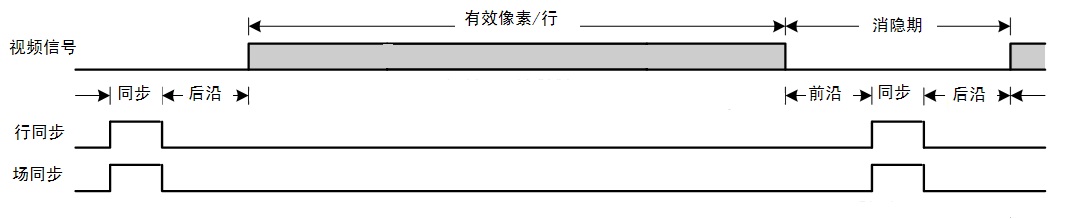
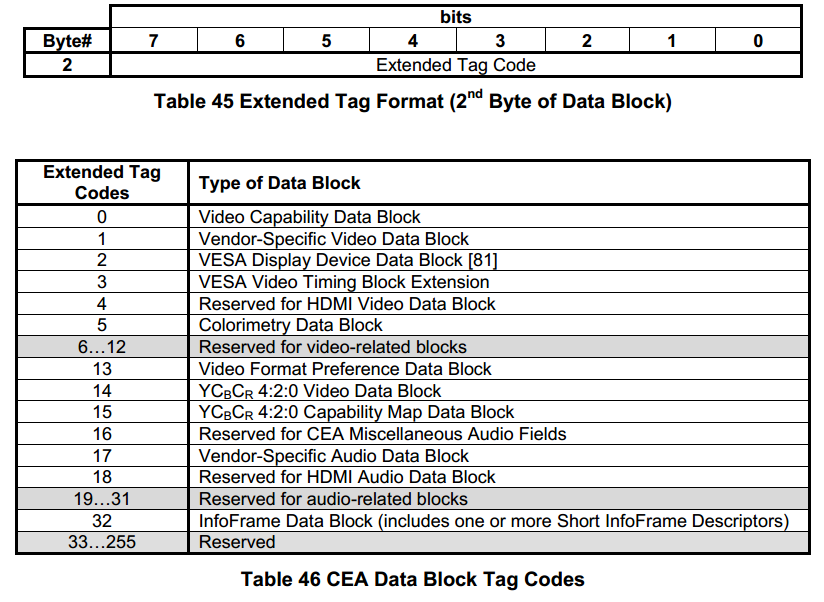
名词
- EDID Extended Display Identification Data (Legacy VESA structure, superseded by the DisplayID structure).
- E-EDID Enhanced Extended Display Identification Data (Legacy VESA structure, superseded by the DisplayID structure).
- DisplayID Display Identification Data (VESA).
-
DPCD DisplayPort Configuration Data
如上,单一的edid以及e-edid都是过时的标准
DPCD::1.4
都是link相关的配置信息,通过native读取
分别是:
DPCDAddress DPCD Field
00000h - 000FFh Receiver Capability
00100h - 001FFh Link Configuration
00200h - 002FFh Link/Sink Device Status
00300h - 003FFh Source Device-specific
00400h - 004FFh Sink Device-specific
00500h - 005FFh Branch Device-specific
00600h - 006FFh Link/Sink Device Power Control
00700h - 007FFh eDP-specific
00800h - 00FFFh RESERVED (usage to be defined)
01000h - 017FFh Sideband MSG Buffers
01800h - 01FFFh RESERVED (usage to be defined)
02000h - 021FFh DPRX Event Status Indicator
02200h - 022FFh Extended Receiver Capability
02300h - 02FFFh RESERVED (usage to be defined)
03000h - 030FFh Protocol Converter Extension
03100h - 5FFFFh RESERVED (usage to be defined)
60000h - 61CFFh Multi-touch (for eDP)
61D00h - 67FFFh RESERVED (usage to be defined)
68000h - 69FFFh HDCP 1.3 and HDCP2.2
6A000h - EFFFFh RESERVED (usage to be defined)
F0000h - F02FFh LT-tunable PHY Repeater
F0300h - FFEFFh RESERVED (usage to be defined)
FFF00h - FFFFFh MyDP-specific Table2-173 dpcd版本;每条lane的最大书传输速率1.62/2.7/5.4/8.1; lane的数量[1/2/4];下游屏幕接口[dp/vga/dvi/hdmi];是否有edid;i2c速率;等等,详细信息请参阅vesa:https://vesa.org/
关于edid变更历史
-
EDID Development History EDID Defines the data structures sent from a video display to a source over E-DDC lines to describe its capabilities
- EDID 1.0 Defined original 128-byte data structure (Deprecated)
- EDID 1.1 Defined some alternative uses for space in data structure (Deprecated)
- EDID 1.2 Defined some alternative uses for space in data structure (Deprecated)
- EDID 1.3 Current definitions for 128-byte EDID data fields
- EDID 2.0 Introduced new 256-byte data structure
- E-EDID Defined optional additional 128-byte extension blocks for EDID 1.3, incorporated EDID 2.0 as optional extensions
- DisplayID Introduced variable length data structure
EDID::1.4
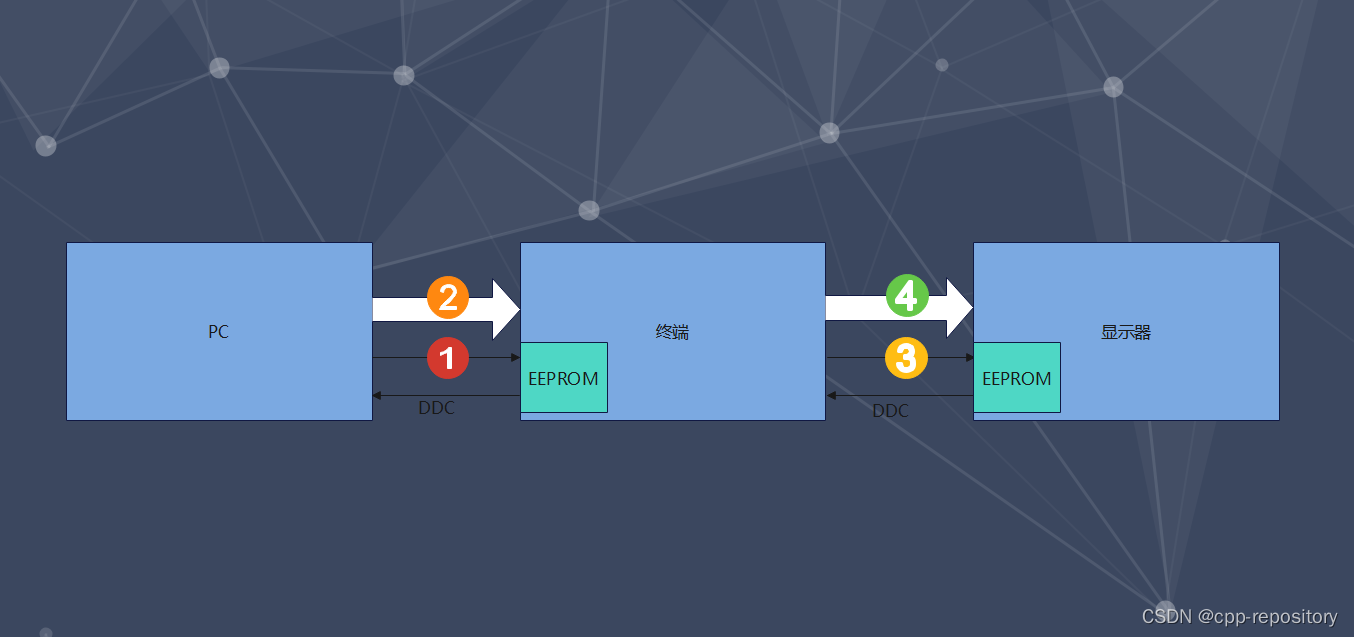
屏幕分辨率,功能等,通过i2c读取,首地址是50
分别是:
Address (Decimal) Data
0-7 Header
8-17 Vendor / Product Identification
18-19 EDID Version
20-24 Basic Display Parameters and Features 基本显示参数和特征定义为视频输入清晰度、最大水平图像尺寸,最大垂直图像尺寸,显示传输特性(Gamma),和功能支持。
25-34 Color Characteristics Color space definition
35-36 Established Supported Timings Timing information for all resolutions supported by the display are reported here
37 Manufacturer's Reserved Timing
38-53 EDID Standard Timing ID #1 – 8
54-71 Detailed Timing Descriptor Block 1
72-89 Detailed Timing Descriptor Block 2
90-107 Detailed Timing Descriptor Block 3
108-125 Detailed Timing Descriptor Block 4
126 Extension Flag Number of (optional) 128-byte extension blocks to follow
127 Checksum| Address (Decimal) 十进制地址 | Data-16进制 | General Description | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0-7 | "00h FFh FFh FFh FFh FFh FFh 00h" | 固定的header pattern 这些固定值是必须的正确标识EDID表数据的开始 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8-9 |
| 制造商ID。这是一个遗留的即插即用ID,由微软分配,它是一个16位的big-endian值,由三个5位字母组成: 00001, A; 00010, B; …; 11010, Z. E.g., 24 4d, 0 01001 00010 01101, "IBM". | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10-11 | 制造商的产品代码。16位数字,低位优先。 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 12–15 | 序列号。32位,低位优先。对序列号的数据或格式没有明确的要求。如果序列号包含在ASCII序列号描述符中,这个字段应该为零。如果块0中没有提供序列号,那么CEA-861-E实现应该使用0x00作为块0序列号的填充。 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 16-17 | 16 生产周数; 这个字段的指定值范围从1到53。大于53的值不被识别。当没有指定星期时,可以使用零。制造商决定周编号系统。制造商应该使用一种系统,在这种系统中,周数的整数值会随着年份的推移而增加。如果制造商选择只声明型号年份 (在17地址)那么0xFF应该放在地址10 (Week of Manufacture)。 17 生产年, 这个值由实际生产年份减去1990年确定。例如:2002 - 1990 = 12或0x0C | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 18-19 | 18 EDID version, usually 01 (for 1.3 and 1.4) 不允许使用其他数字。如果其他数字被放置在这个区域,源可能会忽略整个EDID表。 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 20 |
| 用于标识接收设备[显示器]所需的输出配置。对于数字显示,包括CE设备,建议设置为0x80。此值用于声明设备支持数字接口。 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 21-22 |
| 最大水平图像大小和垂直图像大小字段(字节0x15、0x16)用于指示接收的屏幕大小和长宽比。当已知时,应该提供有效显示区域的最大物理尺寸(在这些字段中,cm)。这些字段的一个重要用途是指示实际屏幕的高宽比。如果已知最大图像大小的高宽比,那么最大大小字段的比率应该等于该高宽比,即使最大图像大小是未知的,或者在不同的设备配置中是可变的(比如在投影中) 在填写最大图像大小字段时,应使用以下规则: a)如果已知高宽比和显示大小,则应显示实际大小,以最接近的cm为准。 如果字段被设置为零,source不应该对屏幕大小或高宽比做任何假设。 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 23 | Display gamma, factory default (range 1.00–3.54), datavalue = (gamma×100) − 100 = (gamma − 1)×100. If 225, gamma is defined by DI-EXT block. | 显示传输特性(Gamma):可以由source根据显示设备的Gamma来定制视频输出。宣告伽玛的概念与个人计算机CRT显示器,接受非伽玛校正信号有关。数字和模拟电视视频信号是伽玛纠正根据建立的行业惯例,因此需要声明,CRT伽马射线并不总是必要的。然而,这是需要的个人计算机CRT应用。虽然信号源可能不需要使用显示器的伽马值,但显示器设备的正确伽马值应该是存在的。由于一些电视阴极射线管通常具有相似的伽马值,因此在本例中使用2.2。伽马值本身没有插入到表中。相反,插入一个等于(gamma x 100) - 100的值。 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 24 |
| 特性支持由识别各种显示或接收参数的8位组成。这些包括基于VESA显示电源管理信令标准(DPMS)的节能模式,显示类型、标准默认颜色空间、首选定时模式和默认通用定时公式(GTF)。在大多数情况下,这些信息都与CE设备和个人计算机显示无关,因为GTF不常用。 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 25-34 |
| 颜色特性提供了显示设备的色度和色温参数(白色温度开氏度)的信息。 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 35-37 |
| 用于声明已建立的timing。建立的timing是由VESA识别的计算机显示时间。此表还用于指示在工厂调整和验证了所建立的timing,这意味着这些timing被支持并正确地呈现在显示器上。 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 38-53 |
| 标准时间是那些通过VESA离散显示屏幕timing或由VESA识别的 通用定时公式标准。显示设备应该列出支持的timing。数据长度是两个字节。CE设备可能不支持任何VESA计时或GTF,当没有声明timing时,就需要用0x01填充字节对中每个未使用的字节。 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 54-125 |
| 详细的计时部分长度为72字节,可分为四个描述符块,每个描述符块为18字节。在下面的示例中,这四个块的地址范围是0x36-0x47, 0x48- First Detailed Timing Descriptor, Second Detailed Timing Descriptor, First Monitor Descriptor (Monitor Name), and Second Monitor Descriptor (Monitor Range). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 54-71 |
When used for another descriptor, the pixel clock and some other bytes are set to 0: | 注意描述h-active和h-blanking,0x3A的高四位和第四位分别描述的不同timing: 1920 ==》0111 1000 0000 280 ==》0001 0001 1000 0x38 ==》 1000 0000 //1920的后八位 0x39 ==》 0001 1000 0x3A ==》 0111 0001 //1920的前四位:280的前四位
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 72–89 | Second Detailed Timing Descriptor, | Second Detailed Timing Descriptor, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 90–107 |
Currently defined descriptor types are:
| VESA标准[10]要求四个18字节描述符中的一个是监视器名称描述符。
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 108–125 | Second Monitor Descriptor (Monitor Range Limits) | 块0中的下一个和最后一个18字节描述符应该用作第二个监视器描述符。在本例中,它是监视器范围限制,用于指定水平和垂直频率的最小和最大参数以及最大像素时钟率。在下面的示例中,数据块的范围从0x6C到0x7D。数据格式是二进制编码的整数。 位置0x71到0x75用于指定水平和垂直频率的最小和最大参数,以及最大像素时钟。表72包含一个支持60hz垂直刷新率、15khz到46khz水平率的DTV示例,它覆盖了720x480i和1280x720p格式所需的频率,包括480x720p和1920x1080i,以及最大像素时钟80 MHz。 地址0x76用作辅助通用定时公式(GTF)的标记,通常不用于CE设备。在本例中,标志被设置为零。地址0x77到0x7D与这个标记相关。
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 126-127 | Extension Flag and Checksum | 扩展标志用于声明EDID表中存在的扩展数量。实际提供的扩展总数应该等于在基本EDID中声明的扩展数。在基本EDID中声明的扩展数量不应包括基本EDID,而应包括块映射。例如,如果EDID数据中不存在扩展,那么扩展标志应该设置为零。如果有一个扩展名(例如CEA),那么该标志应该设置为1。如果两个(例如CEA)扩展被使用,那么VESA EDID标准也需要一个块映射扩展—将扩展的总数增加到三个。 表73包含了基于本文档中给出的表的示例数据。0x7E位置上的扩展标志被设置为1,表明存在块1。由于本例中的扩展标志等于1,因此不存在其他块。校验和的设置使整个128字节块的模256的和等于0x00
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
相关链接:
https://media.extron.com/public/download/files/articles/understandingedid.pdf
http://read.pudn.com/downloads178/ebook/828201/EIA-CEA-861E.pdf
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DisplayPort
https://zh.wikipedia.org/zh-tw/EDID
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Extended_Display_Identification_Data
E-EDID
E-EDID作为edid的拓展。
块0是惟一的强制块[0-127]。该表显示了E-EDID块的必要用法。所有块的长度都是128字节。所有扩展块必须是连续的。

相关链接:
http://read.pudn.com/downloads110/ebook/456020/E-EDID%20Standard.pdf
DisplayID
DisplayID v2.0是真正的第二代EDID,它是一种更灵活和可扩展的显示标识数据格式,旨在满足各种显示类型、技术和应用程序的需要。DisplayID v2.0和EDID之间最明显的区别,使用了基于“数据块”概念的模块化结构,这些数据块是单独定义的、自包含的数据格式,每个数据块提供一组特定的相关显示信息。
下面这幅图讲述的是displayid的数据块
NOTE
一般来说,edid第一个128是标准的edid块,接下来可能是其他的块;关于block,displayid是以70开头的块,如果是以02开头的块,则是cea的audio以及speaker的块
一份详细的关于edid+cea+diplayid的raw和解释
https://download.csdn.net/download/u012839187/12792110
一份关于displayid 1.3的public版本spec,非常给力
https://download.csdn.net/download/u012839187/12793610
hw-edid的值,涵盖非常多的常用显示器,值得收藏 https://github.com/linuxhw/EDID
linux代码里也有类似结构体,可以拿来用https://lxr.missinglinkelectronics.com/linux/drivers/gpu/drm/drm_edid.c
edid https://www.quantumdata.com/downloads.html