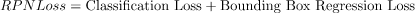文章目录
- Union
- 宏定义
- 数组和柔性数组
- 其它
Union
共用体中有int型和char[10]这两个成员,代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
union st {
int x;
char c[10];
}s;int main(void) {
s.x=50;
s.c="abcdef";
printf("%s",s.c);
return 0;
}
如果对s.c赋值一个字符串,VC 6.0编译器报错,error C2440: ‘=’ : cannot convert from ‘char [7]’ to ‘char [10]’,如何对共用体中的字符数组赋值?
字符串,或者说字符数组,除了初始化的时候可以用“=”,运行部分代码,必须使用strcpy等函数进行赋值
宏定义
这段代码运行后输出什么结果?
#define f(a,b) a##b
#define g(a) #a
#define h(a) g(a)
printf("h(f(1,2))-> %s, g(f(1,2))-> %s\n", h(f(1,2)), g(f(1,2)));
答案:
h(f(1,2))-> 12, g(f(1,2))-> f(1,2)
简言之:
#是将内容字符串化
##是连接字符串
#include <stdio.h>
#define message_for(a, b) \printf(#a " and " #b ": We love you!\n")
int main(void) {message_for(Carole, Debra);return 0;
}
答案:
Carole and Debra: We love you!
#include <stdio.h>
#define tokenpaster(n) printf ("token" #n " = %d", token##n)
int main(void) {int token34 = 40;tokenpaster(34);return 0;
}
答案:
token34 = 40
即 tokenpaster(34);这个通过预处理后就变成了printf ("token34 = %d", token34)
#define ABC(...) #__VA_ARGS__
printf(ABC(123, 456));
输出
123, 456
宏替换的规则
C99标准《ISO/IEC 9899:1999 (E)》
After the arguments for the invocation of a function-like macro have been identified, argument
substitution takes place. A parameter in the replacement list, unless preceded by a # or ##
preprocessing token or followed by a ## preprocessing token (see below), is replaced by the
corresponding argument after all macros contained there in have been expanded. Before being
substituted, each argument’s preprocessing tokens are completely macro replaced as if they formed
the rest of the preprocessing file; no other preprocessing tokens are available.
如何理解
1.首先要identify这个是function-like macro,即识别出这是一个函数式宏;
2.处理函数式宏里面的参数parameter,这里有个条件,在替换这些参数宏的时候,除非遇到#或##这样的东西,否则就将这些parameter替换到底;
3.待所有的parameter都替换完(或者#或 ##处理完),预处理器还会对整个宏剩下的继续处理,因为这个
function-like macro会替换出一些新东西,例如h( f(1,2) )--> g(12),g(12) --> "12"。于是,按以上规则把问题解析一遍:先看h(f(1,2)):
h(f(1,2))预处理先找到h这个function-like macro
然后处理其parameter,即将f(1,2)替换成12,即得到g(12)
继续往后走,得到12再看g(f(1,2)):
g(f(1,2))预处理先找到g这个function-like macro
然后替换parameter,发现替换后遇到#了,即得到#f(1,2)
再然后也没有然后了,将这个#f(1,2)变成了字符串f(1,2)了,因为预处理遇到#不会继续了。
例子
#define _STR(x) #x
#define STR(x) _STR(x)
char * pc1 = _STR(__FILE__);
char * pc2 = STR(__FILE__);
printf("%s %s %s\n", pc1, pc2, __FILE__);
输出结果
__FILE__ "c_test_c_file.c" c_test_c_file.c
提示
提示:宏中遇到#或##时就不会再展开宏中嵌套的宏了。typedef struct os_thread_def {os_pthread pthread; ///< start address of thread functionosPriority tpriority; ///< initial thread priorityuint32_t instances; ///< maximum number of instances of that thread functionuint32_t stacksize; ///< stack size requirements in bytes; 0 is default stack size
} osThreadDef_t;#define osThreadDef(name, priority, instances, stacksz) \
const osThreadDef_t os_thread_def_##name = \
{ (name), (priority), (instances), (stacksz) }osThreadDef会根据输入的参数创建一个结构体变量,包含部分参数当做结构体内容。
这样做不但简洁,而且还防止名字重复osThreadDef (Thread_Mutex, osPriorityNormal, 1, 0);
会变成
const osThreadDef_t os_thread_def_Thread_Mutex =
{ Thread_Mutex, osPriorityNormal, 1, 0
};
问题延伸
#define ABC "abc"#define _STR(x) #x#define STR(x) _STR(x)char * pc1 = _STR(ABC);char * pc2 = STR(ABC);char * pc3 = STR(_STR(ABC));char * pc4 = STR(STR(ABC));printf("pc1:%s\n",pc1);printf("pc2:%s\n",pc2);printf("pc3:%s\n",pc3);printf("pc4:%s\n",pc4);
输出结果:pc1:ABCpc2:"abc" //这个"abc"是把双引号""都打印出来pc3:"ABC"pc4:"\"abc\""
通过 gcc -E macro.c -o macro.i 来看看预编译后的结果:
int main() {char * pc1 = "ABC";char * pc2 = "\"abc\"";char * pc3 = "\"ABC\"";char * pc4 = "\"\\\"abc\\\"\"";printf("pc1:%s\n",pc1);printf("pc2:%s\n",pc2);printf("pc3:%s\n",pc3);printf("pc4:%s\n",pc4);return 0;
}
VA_ARGS 只能用于function-like macro
#define ABC __VA_ARGS__
#define ABC #__VA_ARGS__
#define ABC() __VA_ARGS__
以上3种都会编译报错,GCC会丢给你一个warning:
warning: __VA_ARGS__ can only appear in the expansion of a C99 variadic macro
正确形式
#define ABC(...) __VA_ARGS__
调试程序时,不想直接用printf打印log,想通过一个宏函数来输出log的时候,可以将其定义成空的东西。
#define DEBUG_PRINTF(format, ...) printf(format, ...)
DEBUG_PRINTF("Hello World!\n");
编译报错
error: expected expression before '...' token#define DEBUG_PRINTF(format, ...) printf(format, ...)^
note: in expansion of macro 'DEBUG_PRINTF'DEBUG_PRINTF("Hello World!\n");^需要__VA_ARGS__
#define DEBUG_PRINTF(format, ...) printf(format, __VA_ARGS__)
DEBUG_PRINTF("Hello World!\n");
结果
error: expected expression before ')' token#define DEBUG_PRINTF(format, ...) printf(format, __VA_ARGS__)^
note: in expansion of macro 'DEBUG_PRINTF'DEBUG_PRINTF("Hello World!\n");^#define DEBUG_PRINTF(format, ...) printf(format, __VA_ARGS__)
DEBUG_PRINTF("%s","Hello World!\n");
添加##,作用是将token(如format等)连接起来,如果token为空,那就不连接
#define DEBUG_PRINTF(format, ...) printf(format, ##__VA_ARGS__)
DEBUG_PRINTF("Hello World!\n");
DEBUG_PRINTF("Hello %s", "World!\n");宏的作用域
如果不知道一个宏是否已定义,可以用#ifdef来判断下,#undef取消宏定义
#ifdef ABC#undef ABC#define ABC 0
#else#define ABC 0
#endif
用宏实现行控制
# line digit-sequence "s-char-sequenceopt"
其中
digit-sequence是数值,范围为1~2147483647
"s-char-sequenceopt"是字符串,可以省略
对于
#line 12345 "abcdefg.xxxxx"
printf("%s line: %d\n", __FILE__, __LINE__);
printf("%s line: %d\n", __FILE__, __LINE__);
输出
abcdefg.xxxxx line: 12345
abcdefg.xxxxx line: 12346
用宏实现错误指示
# error pp-tokensopt
编译器遇到这个#error的时候就会停下来,然后输出其后面的信息
预定义宏名
| 预定义宏名 | Description |
|---|---|
__LINE__ | 当前源码的行号,是一个整数 |
__FILE__ | 当前源码的文件名,是一个字符串 |
__DATE__ | 源文件的翻译日期,是一个“Mmm dd yyyy”的字符串文字 |
__TIME__ | 源文件的翻译时间,是一个“hh:mm:ss”的字符串文字 |
| 特别注意,这些宏名,不可以被#define和#undef等修饰。 |
#define DEBUG_INFO() fprintf(stderr,"[DEBUG]%s:%d %s\n", __FILE__, __LINE__, __FUNCTION__);
Pragma命令
#pragma once
放在头文件里面,让其只参与一次编译,f防止在头文件重复包含,效果类似于
#ifndef _XXX_
#define _XXX_
···
#endif#pragma warning
#pragma warning(disable:4507)
#pragma warning(once:4385) 让4385这个警告只显示一次
#pragma warning(error:164) 把164号经过当error显示出来。
以上还可以合并起来写成
#pragma warning( disable : 4507; once : 4385; error : 164 )
#pragma pack
改变结构体内存对齐的方式。例如,以下结构体内存可按1字节对齐:
#pragma pack(1)
struct abc
{int a;char b;short c;int d;
};
#pragma pack() // cancel pack(1)
用宏取最小值
#define MIN(x, y) ((x) < (y)? (x) : (y))
double xx = 1.0;
double yy = MIN(xx++, 1.5);
printf("xx=%f, yy=%f\n",xx,yy);
结果
xx=3.000000, yy=2.000000GNU的改进方法:
#define MIN(A,B) ({ __typeof__(A) __a = (A); __typeof__(B) __b = (B); __a < __b ? __a : __b; })
double xx = 1.0;
double yy = MIN(xx++, 1.5);
printf("xx=%f, yy=%f\n",xx,yy);
结果
xx=2.000000, yy=1.000000
do{ } while(0)
#define set_on() set_on_func1(1); set_on_func2(1);
set_on();
如果遇到以下形式
#define set_on() set_on_func1(1); set_on_func2(1);
if(on)set_on();
会变成
#define set_on() set_on_func1(1); set_on_func2(1);
if(on)set_on_func1(1);
set_on_func2(1);
改进一下
#define set_on() {set_on_func1(1); set_on_func2(1);}
if(on)set_on();
编译还会出错,在于后面那个 ;
用do{ }while(0)试试,可以保证其内容在替换后不会被拆散,保持其一致性。
#define set_on() do{set_on_func1(1); set_on_func2(1);}while(0)
if(on)set_on();
要做一个接口给别人使用,就应当把接口做得万无一失
自动获取变量类型
#define var(left, right) __typeof__(right) left = (right)var(s, 1LL); // 相当于 long long s = 1LL;
补充:基于C99规范,最全C语言预处理知识总结
https://blog.csdn.net/lianyunyouyou/article/details/106315120
数组和柔性数组
C99中,结构体中的最后一个元素允许是未知大小的数组,叫做柔性数组,特点如下:
结构体中柔性数组成员前面必须至少有一个其他成员。
sizeof返回的这种结构大小不包括柔性数组的内存。
包含柔性数组成员的结构用malloc()函数进行内存的动态分配。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>typedef struct _data
{int len; char val[];
}data_t; int main(int arc, char *argv[])
{data_t test_data1 = {0}; printf("sizeof(data_t) = %ld\n", sizeof(data_t));char *src_data = "hello flexible arr";// 为结构体及其柔性数组成员申请一块连续的空间int len = strlen(src_data) + 1;data_t *p_test_data2 =(data_t*)malloc(sizeof(data_t) + sizeof(char) * len);if (NULL == p_test_data2) {printf("malloc p_test_data2 error\n");return EXIT_FAILURE;}// 填充结构体p_test_data2->len = len;strncpy(p_test_data2->val, src_data, p_test_data2->len); printf("p_test_data2->val = %s\n", p_test_data2->val); // 释放内存free(p_test_data2);p_test_data2 = NULL;return 0;
}
ITLV协议格式结构体可以如下两种进行创建
https://www.toutiao.com/article/7134725508952031748/?log_from=76e51044ec393_1667659796898
value字段以柔性数组的方式定义
typedef struct _protocol_format {uint16_t head; uint8_t id;uint8_t type;uint8_t length;uint8_t value[];
}protocol_format_t;
value字段以指针的方式定义
typedef struct _protocol_format {uint16_t head; uint8_t id;uint8_t type;uint8_t length;uint8_t *value;
}protocol_format_t;
柔性数组的方式相对与指针的方式更简洁,结构体所占内存更小,有利于内存对齐,柔性数组的方式只需申请一次空间,给结构体申请空间的同时也给柔性数组申请空间;而指针的方式,除了给结构体申请空间之外,还得给结构体里的指针成员申请空间。详见https://gcc.gnu.org/onlinedocs/gcc/Zero-Length.html

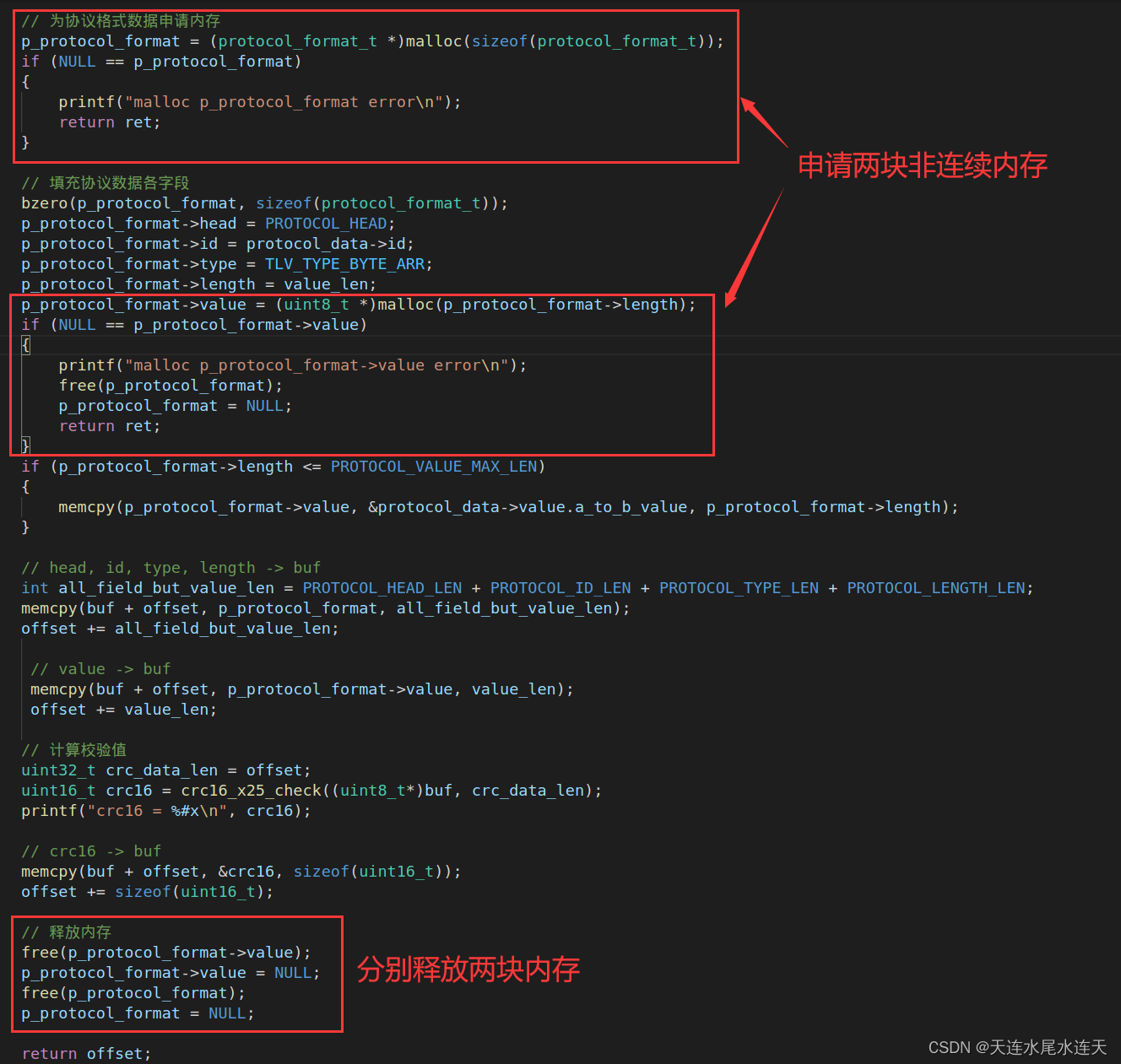
使用指针的方式会比柔性数组的方式更繁琐,特别地,如果在释放内存的时候把顺序弄反了,则结构体里的指针成员所指向的内存释放不掉,会造成内存泄露。
柔性数组的方式只需要申请一次空间,是一块连续的空间;而指针的方式,申请的两块空间不是连续的,连续的内存有益于提高访问速度。
数组的初始化
以前
int arr[10] = {0, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 0, 0, 0, 0};
现在
int arr[10] = {[1... 5] = 5};
数组的访问
取数组的第6个元素(下标为5),教科书教你这样做:
int arr[10] = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9};
int n1 = arr[5];
int n2 = *(arr+5);
其实你可以:
int arr[10] = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9};
int n = 5[arr];
实际上
arr[5]对应*(arr+5),而5[arr]对应*(5+arr),没多大区别。
结构体的初始化
传统做法
typedef struct
{int a;int x;int y;int z;char b;short c;
}S;
S s = {100, 0, 0, 0, 'A', 0x12);
对于C99
typedef struct
{int a;int x;int y;int z;char b;short c;
}S;
S s = {.a = 100, .b = 'A', .c = 0x12};
用include的方式初始化大数组
double array[SIZE][SIZE] = {#include "float_values.txt"
}
其它
int main(void) {int n = 10; while(n --> 0 ) // n goes to 0 是--和>的组合{ printf("%d ", n);}printf("\n");
}
获得任意类型数组的元素数目
#define NUM_OF(arr) (sizeof (arr) / sizeof (*arr))
判断运行环境的大小端
static union { char c[4]; unsigned long l; } endian_test = { { 'l', '?', '?', 'b' } };#define ENDIANNESS ((char)endian_test.l)printf("ENDIANNESS: %c\n", ENDIANNESS);
用异或运算实现数据交换
// 方法1,需要第三个变量
temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
// 方法2,存在数据溢出可能
a=a+b;
b=a-b;
a=a-b;
//
a = a ^ b;
b = a ^ b;
a = a ^ b;
用冒号表达式替代if…else…语句
if(y < 0) {x = 10;
}
else {x = 20;
}
替换为
x = (y < 0) ? 10 : 20;
判断一个整数是否为2的幂
#define is_power_of_2(n) ((n) != 0 && ((n) & ((n) - 1)) == 0)
静态链表
struct mylist {int a;struct mylist* next;};#define cons(x, y) (struct mylist[]){{x, y}}struct mylist *list = cons(1, cons(2, cons(3, NULL)));struct mylist *p = list;while(p != 0) {printf("%d\n", p->a);p = p -> next;};
数组之间直接赋值
int a[10] = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
int b[10] = {0};
b = a;
非法,可以让数组穿个马甲
typedef struct {int n[10];
}S;
S a = {{0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9}};
S b = {0};
b = a;
C和C++代码混合编译
在C的头文件上面
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif
然后再头文件下面
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
用查表法实现hex2str
void hex2str(const unsigned char* hex, int size, char* str)
{char char_arr[17] = "0123456789ABCDEF";for(int i = 0; i < size; i++) {str[3*i] = char_arr[hex[i]>>4];str[3*i+1] = char_arr[hex[i]&0x0F];str[3*i+2] = ' ';}
}
用 sprintf 实现hex2str
void hex2str(const unsigned char* hex, int size, char* str)
{for(int i = 0; i < size; i++) {sprintf(&str[3*i], "%02X ", hex[i]);}
}
将变量名变字符串
如果想打印一个变量名和它的值,可以这样:
unsigned int program_flag = 0xAABBCCDD;
printf("program_flag: 0x%08X\n", program_flag);
如果有很多这样的变量要打印,建议做个宏函数:
#define PRINT_HEX_VAR(var) printf("%s: 0x%08X\n", #var, var);
unsigned int program_flag = 0xAABBCCDD;
PRINT_HEX_VAR(program_flag);
获取结构体元素的偏移
#define offsetof(type, member) ( (size_t)&((type*)0->menber) )typedef struct {char a;int b;}S;offsetof(S, b);
根据结构体成员获取结构体变量指针
#define offsetof(TYPE, MEMBER) ((size_t) &((TYPE *)0)->MEMBER)
/*** container_of - cast a member of a structure out to the containing structure* @ptr: the pointer to the member.* @type: the type of the container struct this is embedded in.* @member: the name of the member within the struct.**/
#define container_of(ptr, type, member) ({ \const typeof( ((type *)0)->member ) *__mptr = (ptr); \ (type *)( (char *)__mptr - offsetof(type,member) );}) 这个怎么玩?看看链表struct list_head {struct list_head *next;struct list_head *prev;
};struct ipstore{unsigned long time;__u32 addr[4];struct list_head list;
};container_of(ist1->list, struct ipstore, list)
scanf 高级玩法
scanf(“%[^,]”, a); // This doesn’t scrap the comma
scanf(“%[^,],”,a); // This one scraps the comma
scanf(“%[^\n]\n”, a); // It will read until you meet '\n', then trashes the '\n'
scanf(“%*s %s”, last_name); // last_name is a variable
两个数相加可以不用+号
int Add(int x, int y)
{if (y == 0)return x;elsereturn Add( x ^ y, (x & y) << 1);
}
调试的时候打印数组
#define ARR_SIZE(arr) (sizeof(arr)/sizeof(*arr))
#define PRINT_DIGIT_ARR(arr) do{\printf("%s: ", #arr); \for(int i=0; i < ARR_SIZE(arr); i++) \printf("%d ", arr[i]);\printf("\n");\}while(0)int arr[10] = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9};
PRINT_DIGIT_ARR(arr);
switch-case的特殊玩法
void send(uint8* to, uint8 from, uint16 count)
{uint16 n = (count + 7) / 8; switch (count % 8) { case 0: do { *to = *from++; case 7: *to = *from++; case 6: *to = *from++; case 5: *to = *from++; case 4: *to = *from++; case 3: *to = *from++; case 2: *to = *from++; case 1: *to = *from++; } while (--n > 0);
}
实际上它是,网上自行搜索“Duff’s Device”
void send(uint8* to, uint8 from, uint16 count)
{do { *to = *from++; } while (--count > 0);
}
https://blog.csdn.net/lianyunyouyou/article/details/117534039?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502