目录
ACO简介
基本原理
算法步骤
流程图
参数意义
构建路径
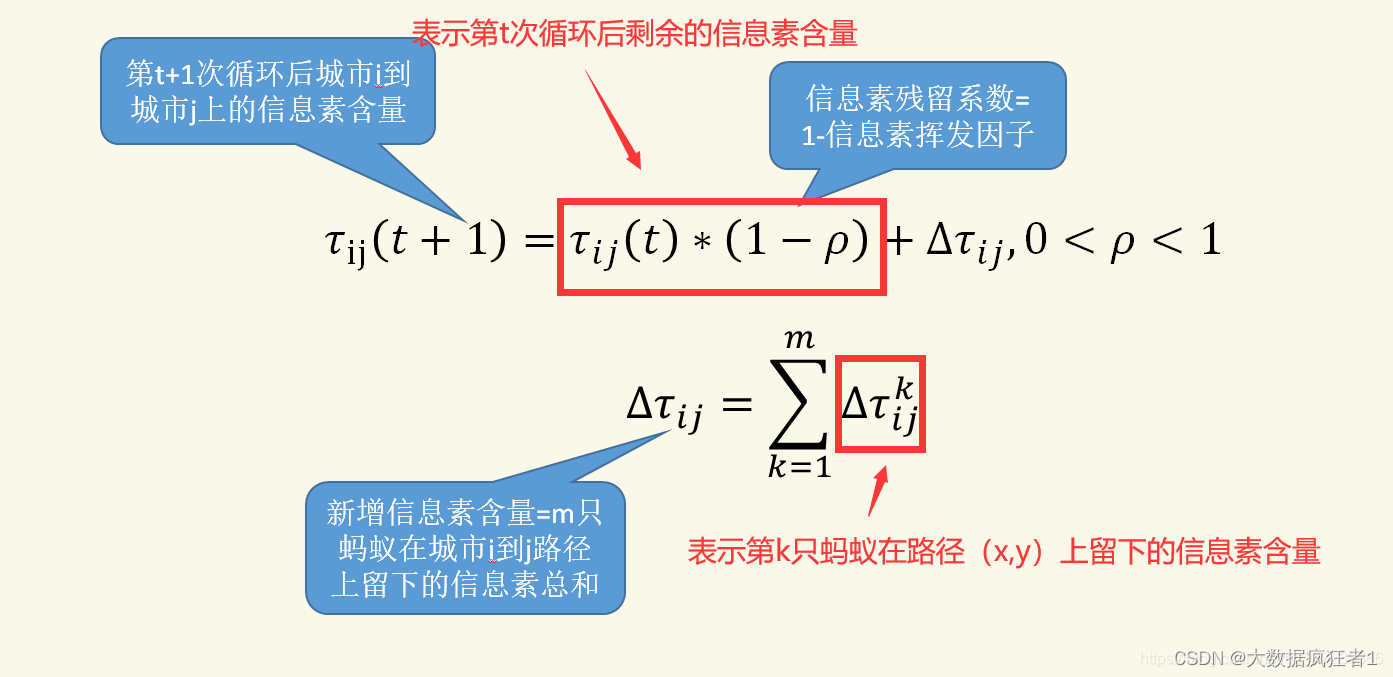
更新信息素
实例演示(TSP问题)
ACO简介
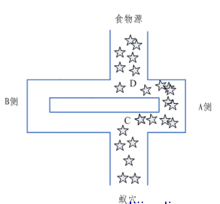
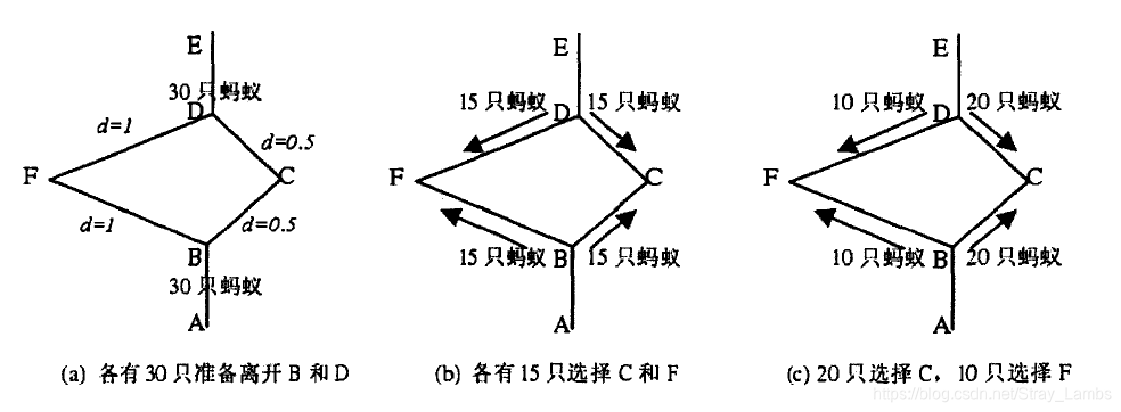
蚁群是自然界中常见的一种生物,人们对蚂蚁的关注大都是因为“蚁群搬家,天要下雨”之类的民谚。然而随着近代仿生学的发展,这种似乎微不足道的小东西越来越多地受到学者们地关注。1991年意大利学者M. Dorigo等人首先提出了蚁群算法,人们开始了对蚁群的研究:相对弱小,功能并不强大的个体是如何完成复杂的工作的(如寻找到食物的最佳路径并返回等)。在此基础上就诞生了蚁群算法(ant colony optimization, ACO),一种用来在图中寻找优化路径的机率型算法。该算法最初用来求解旅行商(Traveling Saleman Problem,TSP)问题。即求出某个商人从某一个点出发(原点),经过若干个给定的需求点,最终返回到原点所经过的最短路径。
基本原理
蚂蚁在行走过的路上留下一种挥发性的激素(信息素),蚂蚁就是通过这种激素进行信息交流。蚂蚁趋向于走激素积累较多的路径。找到最短路径的蚂蚁总是最早返回巢穴,从而在路上留下了较多的激素。由于最短路径上积累了较多的激素,选择这条路径的蚂蚁就会越来越多,到最后所有的蚂蚁都会趋向于选择这条最短路径,但信息素会随着时间的推移而逐渐挥发。基于蚂蚁这种行为而提出的蚁群算法具有群体合作,正反馈选择,并行计算等三大特点。
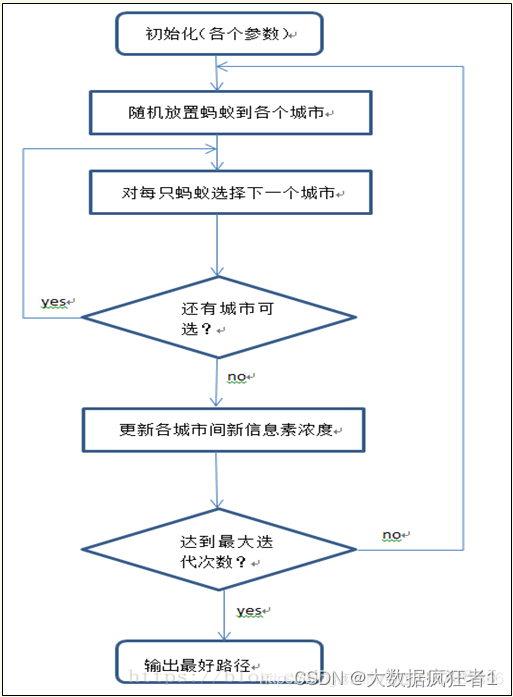
算法步骤
- 初始化(各个参数): 在计算之初需要对相关的参数进行初始化,如蚂蚁数量m、信息素因子α、启发函数因子β、信息素挥发因子ρ、信息素常数Q、最大迭代次数t等等。
- 构建解空间: 将各个蚂蚁随机地放置于不同的出发点,对每个蚂蚁k(k=1,2,……,m),计算其下一个待访问的城市,直到所有蚂蚁访问完所有的城市。
- 更新信息素: 计算各个蚂蚁经过的路径长度L,记录当前迭代次数中的最优解(最短路径)。同时,对各个城市连接路径上的信息素浓度进行更新。
- 判断是否终止: 若迭代次数小于最大迭代次数则迭代次数加一,清空蚂蚁经过路径的记录表,并返回步骤二;否则终止计算,输出最优解。
流程图
参数意义
| 参数名称 | 参数意义 | 参数设置过大 | 参数设置过小 |
| 蚂蚁数量m | 蚂蚁数量一般设置为目标数的1.5倍较为稳妥 | 每条路径上信息素趋于平均,正反馈作用减弱,从而导致收敛速度减慢 | 可能导致一些从未搜索过的路径信息素浓度减小为0,导致过早收敛,解的全局最优性降低 |
| 信息素常量Q | 信息素常量根据经验一般取值在[10,1000] | 会使蚁群的搜索范围减小容易过早的收敛,使种群陷入局部最优 | 每条路径上信息含量差别较小,容易陷入混沌状态 |
| 信息素因子ɑ | 反映了蚂蚁运动过程中路径上积累的信息素的量在指导蚁群搜索中的相对重要程度。取值范围通常在[1, 4]之间。 | 蚂蚁选择以前已经走过的路可能性较大,容易使随机搜索性减弱 | 蚁群易陷入纯粹的随机搜索,使种群陷入局部最优 |
| 启发函数因子𝛽 | 反映了启发式信息在指导蚁群搜索中的相对重要程度,蚁群寻优过程中先验性、确定性因素作用的强度取值范围在[0, 5]之间 | 虽然收敛速度加快,但是易陷入局部最优 | 蚁群易陷入纯粹的随机搜索,很难找到最优解 |
| 信息素挥发因子𝜌 | 反映了信息素的消失水平,相反的1-𝜌反映了信息素的保持水平。取值范围通常在[0.2, 0.5]之间 | 信息素挥发较快,容易导致较优路径被排除 | 各路径上信息素含量差别较小,收敛速度降低 |
| 最大迭代次数t | 最大迭代次数一般取[100,500],建议取200 | 运算时间过长 | 可选路径较少,使种群陷入局部最优。 |
构建路径
我们知道蚂蚁是根据信息素的浓度来判断所走的路线的,但是事实上,不是说哪条路的信息素浓度高蚂蚁就一定走哪条路,而是走信息素浓度高的路线的概率比较高。那么首先我们就需要知道蚂蚁选择走每个城市的概率,然后通过轮盘赌法(相当于转盘)确定蚂蚁所选择的城市。
概率公式 :
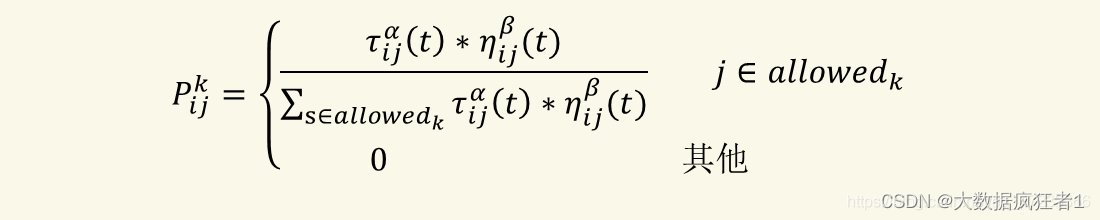
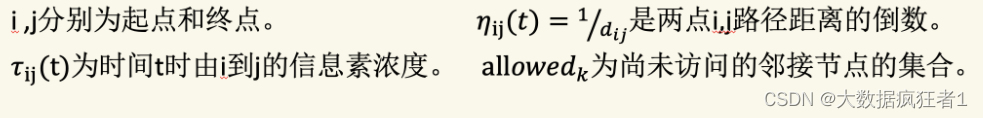
更新信息素
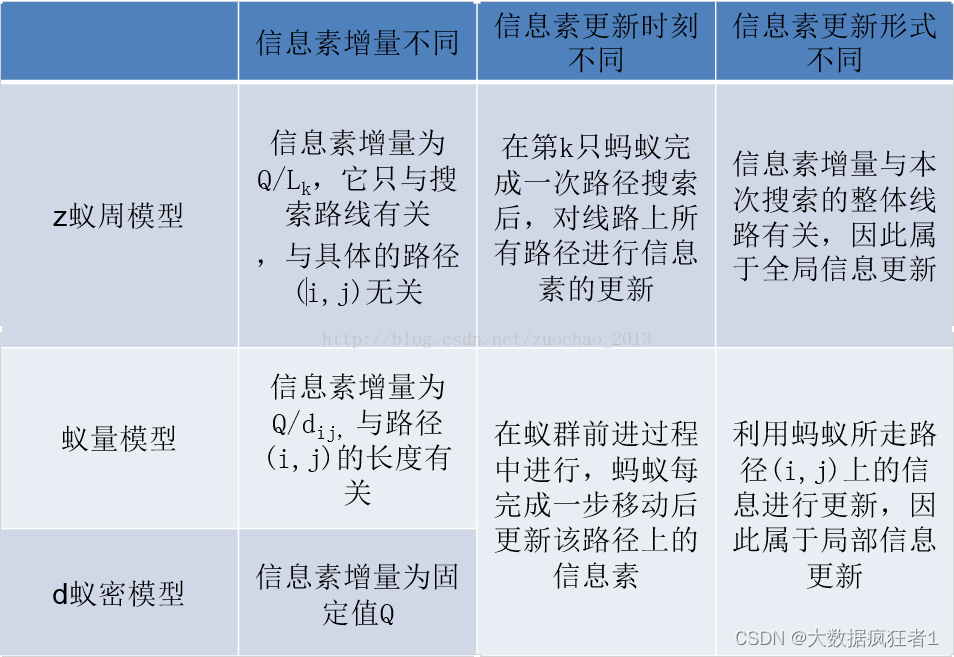
根据不同的规则我们可以将蚁群算法分为三种模型——蚁周模型(Ant-Cycle)、蚁量模型(Ant-Quantity)和蚁密模型(Ant-Density)。蚁周模型是完成一次路径循环后,蚂蚁才释放信息素,其利用的是全局信息。蚁量模型和蚁密模型蚂蚁完成一步后就更新路径上的信息素,其利用的是局部信息。本文章使用的是最常见的蚁周模型。
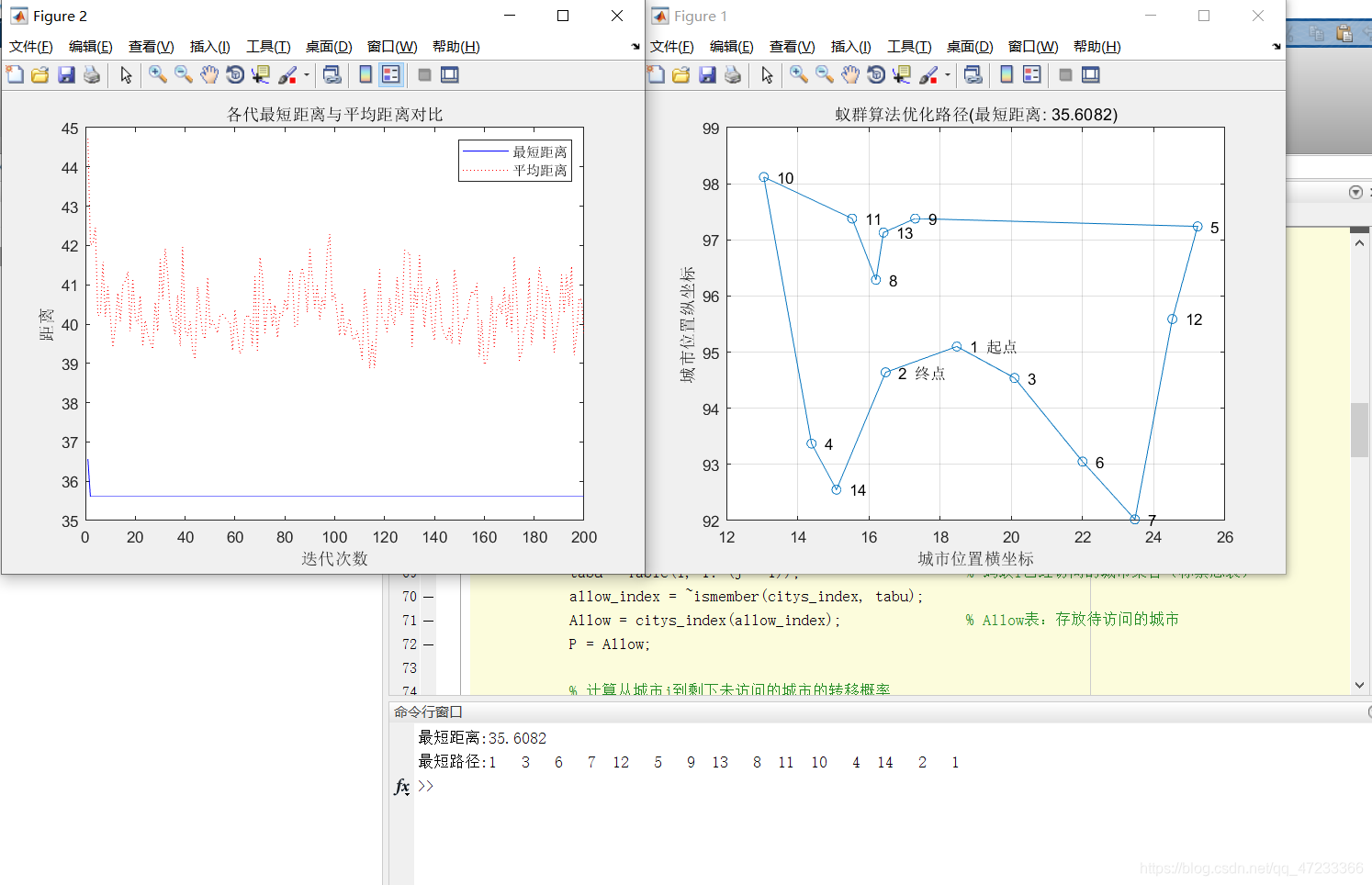
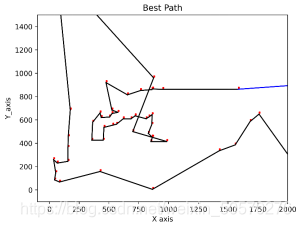
实例演示(TSP问题)
旅行商问题(TSP问题)。假设有一个旅行商人要拜访全国31个省会城市,他需要选择所要走的路径,路径的限制是每个城市只能拜访一次,而且最后要回到原来出发的城市。路径的选择要求是:所选路径的路程为所有路径之中的最小值。全国31个省会城市的坐标为[1304 2312;3639 1315;4177 2244;3712 1399;3488 1535;3326 1556;3238 1229;4196 1044;4312 790;4386 570;3007 1970;2562 1756;2788 1491;2381 1676;1332 695;3715 1678;3918 2179;4061 2370;3780 2212;3676 2578;4029 2838;4263 2931;3429 1908;3507 2376;3394 2643;3439 3201;2935 3240;3140 3550;2545 2357;2778 2826;2370 2975]。
import numpy as np
import math
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltclass TSP():def __init__(self):# 初始化参数self.antcount = 50 # 蚂蚁数量self.alpha = 1 # 信息素重要程度因子self.beta = 5 # 启发函数重要程度因子self.rho = 0.1 # 信息素挥发因子self.Q = 100 # 信息素常量self.max_iter = 200 # 最大迭代次数self.iter = 1 # 迭代计数器self.city_location = np.array([[1304, 2312], [3639, 1315], [4177, 2244], [3712, 1399], [3488, 1535],[3326, 1556], [3238, 1229], [4196, 1044], [4312, 790], [4386, 570],[3007, 1970], [2562, 1756], [2788, 1491], [2381, 1676], [1332, 695],[3715, 1678], [3918, 2179], [4061, 2370], [3780, 2212], [3676, 2578],[4029, 2838], [4263, 2931], [3429, 1908], [3507, 2376], [3394, 2643],[3439, 3201], [2935, 3240], [3140, 3550], [2545, 2357], [2778, 2826],[2370, 2975]])self.city_num = len(self.city_location) # 城市数量self.distance = np.zeros((self.city_num, self.city_num)) # 城市距离矩阵self.eta = np.zeros((self.city_num, self.city_num)) # 启发因子(距离的倒数)self.information = np.ones((self.city_num, self.city_num)) # 信息素矩阵self.path = np.zeros((self.antcount, self.city_num)).astype(int) # 路径矩阵self.r_best = np.zeros((self.max_iter, self.city_num)).astype(int) # 每次迭代的最优路径self.d_best = np.zeros(self.max_iter) # 每次迭代的最短距离def get_dictance(self):for i in range(self.city_num):for j in range(self.city_num):if i != j:self.distance[i][j] = math.sqrt(np.power((self.city_location[i][0] - self.city_location[j][0]), 2) + \np.power((self.city_location[i][1] - self.city_location[j][1]), 2))else:self.distance[i][j] = 100000self.eta = 1.0 / self.distance # 启发因子(距离的倒数)def get_firstplace(self): # 将antcount只蚂蚁放到city_num个城市上if self.antcount <= self.city_num:self.path[:, 0] = np.random.permutation(range(self.city_num))[:self.antcount]else:leave = self.antcount - self.city_num # 剩下几个蚂蚁n = 1self.path[:self.city_num, 0] = np.random.permutation(range(self.city_num))while leave > self.city_num:self.path[self.city_num * n:self.city_num * (n + 1), 0] = np.random.permutation(range(self.city_num))leave = leave - self.city_numn += 1self.path[self.city_num * n:self.antcount, 0] = np.random.permutation(range(self.city_num))[:leave]def get_nextplace(self): # 选择下一步走哪个城市self.length = np.zeros(self.antcount) # 每次迭代每只蚂蚁走过的总路程for i in range(self.antcount):unvisit = list(range(self.city_num)) # 创建每只蚂蚁未走过的城市列表visit = self.path[i, 0] # 每只蚂蚁走过的城市unvisit.remove(visit) # 删除走过的城市for j in range(1, self.city_num):probability = np.zeros(len(unvisit))for k in range(len(unvisit)): # 下一个城市的概率probability[k] = np.power(self.information[visit][unvisit[k]], self.alpha) * \np.power(self.eta[visit][unvisit[k]], self.beta)# 累积概率 轮盘赌选择cousumprobability = (probability / sum(probability)).cumsum()cousumprobability -= np.random.rand()# 下一步该走的城市next = unvisit[list(cousumprobability > 0).index(True)]self.path[i, j] = nextunvisit.remove(next)self.length[i] += self.distance[visit][next] # 第i只蚂蚁走过的路程visit = nextself.length[i] += self.distance[visit][self.path[i, 0]] # 回到开始的城市def get_best(self): # 得到最优路径和最短距离if self.iter == 1:self.r_best[self.iter - 1] = self.path[self.length.argmin()].copy()self.d_best[self.iter - 1] = self.length.min()else:if self.length.min() > self.d_best[self.iter- 2]:self.r_best[self.iter - 1] = self.r_best[self.iter - 2]self.d_best[self.iter - 1] = self.d_best[self.iter - 2]else:self.r_best[self.iter - 1] = self.path[self.length.argmin()].copy()self.d_best[self.iter - 1] = self.length.min()def update_infor(self): # 更新信息素j=0information_increase = np.zeros((self.city_num, self.city_num)) # 信息素增加矩阵for i in range(self.antcount):for j in range(self.city_num - 1):information_increase[self.path[i, j]][self.path[i][j + 1]] += self.Q / self.length[i]information_increase[self.path[i][j+1]][self.path[i,0]]+= self.Q / self.length[i]# 信息素矩阵更新self.information = (1 - self.rho) * self.information + information_increaseself.iter += 1def paint(self):# 绘图x = []y = []road = []for i in range(len(self.r_best[-1])):x.append(self.city_location[self.r_best[-1][i]][0])y.append(self.city_location[self.r_best[-1][i]][1])road.append(self.r_best[-1][i])x.append(x[0]) #回到开始城市y.append(y[0])road.append(road[0])plt.figure(figsize=(30, 30))plt.rcParams['font.family'] = ['Fangsong'] #设置字体for i in range(len(x)):#注释plt.annotate(str(road[i]) + ':' + '(' + str(x[i]) + ',' + str(x[i]) + ')',xy=(x[i], y[i]), xytext=(x[i] + 0.5, y[i] + 0.5), color='r')plt.plot(x, y, 'g-o')plt.title('最短距离:' + str(self.d_best[-1]), fontsize=40)plt.xlabel('x', fontsize=40)plt.ylabel('y', fontsize=40, rotation='horizontal')plt.show()plt.figure()plt.title("迭代距离变化") # 距离迭代图plt.plot([i for i in range(1, len(self.d_best) + 1)], self.d_best)plt.xlabel("迭代次数") # 迭代次数plt.ylabel("距离") # 距离值plt.show()def run(self):self.get_dictance()while self.iter<=self.max_iter:self.get_firstplace()self.get_nextplace()self.get_best()self.update_infor()print('蚁群最优路径', self.r_best[-1])print('最优解', self.d_best[-1])self.paint()if __name__ == '__main__':tsp=TSP()tsp.run()