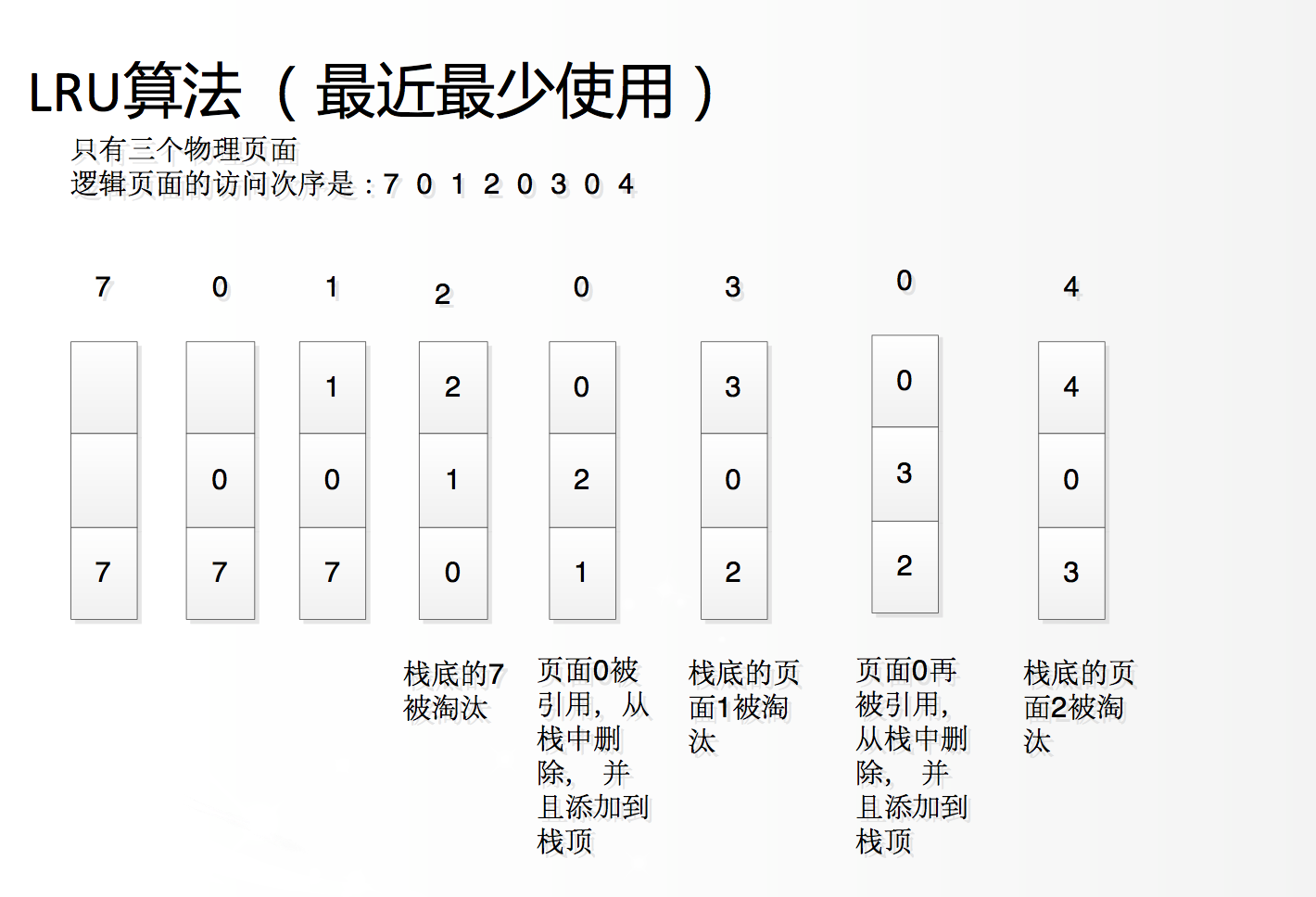
LRU 算法
LRU 是一种作为缓存的算法,像 CPU 缓存,数据库缓存,浏览器缓存。以及在移动端开发时的图片安缓存,采用 LRU 缓存策略的应用很广泛。在面试中也是常常考察的一个点。当然也有其他缓存方法,常见的策略有三种:先进先出策略 FIFO(First In,First Out)、最少使用策略 LFU(Least Frequently Used)、最近最少使用策略 LRU(Least Recently Used)。
下面就来一起实现一下 LRU 算法。
实现
主要思路:采用链式结构,越早加入到链中数据,顺序越靠近尾部,后来加入的数据添加到头部。
当开始需要访问数据时,先遍历链表,分两种情况:
(1)存在数据
- 数据在头部,则直接返回,不需要做操作
- 数据不在头部,将数据移动到头部(注意在尾部的情况)
(2)不存在数据
- 达到达到最大容量,删除尾部的一个元素,然后添加新元素到头部
- 未达到最大容量,直接添加到新元素到头部
public class LRUList<T> {private static final int DEFAULT_SIZE = 10;private int capacity;private Node<T> head;private Node<T> tail;private int size;public LRUList() {this(DEFAULT_SIZE);}public LRUList(int capacity) {this.capacity = capacity;}/*** 访问元素 t* -查询数据* --存在 - 在头部则返回 - 不在头部,移动到头部(是否是结尾)* --不存在 添加数据-添加到头部* ---是否达到capacity -是 移除尾部数据 -否 ¬不移除** @param t 元素*/public void access(T t) {int index = indexOfElement(t);if (index != -1) {if (index == 0) {return;} else {moveToHead(index);}} else {addElement(t);}}/*** 添加元素到头部** @param t 元素*/private void addElement(T t) {Node<T> node = new Node<>(t);if (size == capacity) {removeLast();}Node<T> f = head;node.prev = null;node.next = head;head = node;if (f == null) {tail = node;} else {f.prev = node;}size++;}/*** 移除最后一个节点*/private void removeLast() {if (isEmpty()) {return;}Node<T> l = tail;tail = tail.prev;if (tail == null) {head = null;} else {tail.next = null;}l.prev = null;l.item = null;size--;}/*** 将元素移动到头部** @param index 索引*/private void moveToHead(int index) {Node<T> node;if (index == size - 1) {node = tail;tail = tail.prev;tail.next = null;} else {node = getNodeByIndex(index);node.prev.next = node.next;node.next.prev = node.prev;}node.prev = null;node.next = head;head.prev = node;head = node;}/*** 根据索引获取节点** @param index 索引* @return 节点*/private Node<T> getNodeByIndex(int index) {if (index < 0 || index >= size) {throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("index out of bounds");}Node<T> node = head;for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {node = node.next;}return node;}/*** 查找节点索引** @param t 元素* @return 不考虑为空的元素*/private int indexOfElement(T t) {if (isEmpty()) {return -1;}int index = 0;for (Node node = head; node != null; node = node.next) {if (node.item.equals(t)) {return index;}index++;}return -1;}public boolean isEmpty() {return size == 0;}@Overridepublic String toString() {if (isEmpty()) {return "[]";}StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();for (Node<T> node = head; node != null; node = node.next) {builder.append(node.item.toString()).append(",");}String result = builder.toString();return result.substring(0, result.length() - 1);}private static class Node<T> {private Node<T> prev;private Node<T> next;private T item;public Node(T item) {this.item = item;}}
}
测试
public class LRUListTest {@Testpublic void test() {LRUList<Integer> frame = new LRUList<>(3);frame.access(7);frame.access(0);frame.access(1);Assert.assertEquals("1,0,7", frame.toString());frame.access(2);Assert.assertEquals("2,1,0", frame.toString());frame.access(0);Assert.assertEquals("0,2,1", frame.toString());frame.access(0);Assert.assertEquals("0,2,1", frame.toString());frame.access(3);Assert.assertEquals("3,0,2", frame.toString());frame.access(0);Assert.assertEquals("0,3,2", frame.toString());frame.access(4);Assert.assertEquals("4,0,3", frame.toString());}
}




![[数据分析] RFM分析方法](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/4afccd29631649ee96f6f08818292452.png)